Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Convergence and The Imaginary Number
Hochgeladen von
cimpocteOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Convergence and The Imaginary Number
Hochgeladen von
cimpocteCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Open Access Journal of Mathematical and Theoretical Physics
Mini Review Open Access
Convergence and the imaginary number
Abstract Volume 1 Issue 2 - 2018
The aim of this paper is to show that mathematics converges on one solution. At the heart
Paul TE Cusack
of the issue is determining a value for “i” the imaginary number. We provide here a brief
Park Ave, Saint John, Canada
explanation of the derivation of the imaginary number. Our results relate 0, 1, π , base e
, 2, 3, i , and the golden mean 1.618 -the key parameters of Applied Mathematics. Correspondence: Paul TE Cusack, Dule 23 Park Ave, Saint
John, NB E2J 1R2, Canada, Email st-michael@hotmail.com
We see that mathematics converges upon one solution which manifested in the physical
universe. Received: February 27, 2018 | Published: April 17, 2018
Keywords: imaginary number, fibonacci sequence, astro-theology math, physics,
mathematical constant
Introduction Refer to AT math for more on the physics this creates (Figure 1).
Everything in the universe is in motion. A static point is a special Since the fraction converges at 15 decimals
case that really doesn’t exist. It is just a frame of reference convenient 1 / (15−1)
2
for analysis. The laws of Physics work for an observer in motion; or
also for a point in motion observing the same thing. As Einstein had it, =1/142
the laws are all relative depending upon the observer.
1/196, 196 is a convergent number. 1 / 196 = 0= 1 / infinity
We have two points A and B separated by a distance of 1km, if we
Now for some AT Math
move from point A toward point B by half the distance, we still have
½ a Km to go. Take half again; we have of course ¼ of a km. If we 1/ π
3− 2 =
keep taking half the distance, how do we ever get to point B?
1 / π =frequency of the human mind
The answer lies in that as we move toward point A, point A moves
toward us. So half the distance from A to B =1/2 where they meet. If But, we know from AT Math
the distance is x, instead of half, we get the following series: 3 =time=t=eigenvector
x ) 1 / [1+ x ]
f (= and
(
f f ( x) ) =1 / [1+[ 1 / (1+ x )] = /v t/d
2 1=
=etc.... But v = d / t
=0.618034=i /v t/d
2 1=
so, =
i =
9.8066/0.15585 =g /[1− sin 1]=0.618=g / Moment so,
The numerator is a Fibonacci sequence. Where they converge is 1/ π 1/ 3 −
= ( 2)
at the imaginary number, “I” which is the conjugate of the Golden
Mean. “i” is the fraction of a decimal. It is where infinite mathematics = 1 / ( t −t / d )
meets finite mathematics. Or, y= y ′= e x Note that the Mathematical = 1 / ( td −t ) / d
Constant, base e , can be expressed as a nested fraction also. So can
Pi. Take the derivative of that function = d / ( td −t )
Let t = 1
Result
= d / ( d −1)
1/( x−1)2 Centres around “1”; the essence of mathematics.
Everything is defined in terms of one. Ln = ( 0t ) Ln
= ( 0 ) 1 = x / ( x −1)
Mathematics is the study of the number “1” and its relations (which is
defined as something as opposed to nothing) and the tension created = 1 = / π 1= /t E
by the constants. One salt shaker contains thousands of grains of So, =1 / t x / ( x −1)
salt. One grain of salt contains millions of atoms of NaCl. “One” is a
definition: a mental construct.1,2 ( x −1) (1) = tx
When t = 0 , we are outside the physical universe. Mathematics is −tx − x + 1 =0
the only thing that survives out the universe where there is no time. Let t=x
Submit Manuscript | http://medcraveonline.com Open Acc J Math Theor Phy. 2018;1(2):70‒71 70
© 2018 Cusack. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and build upon your work non-commercially.
Copyright:
Convergence and the imaginary number ©2018 Cusack 71
Conclusion
x 2 − x +1=0 Golden Mean Parabola and we know
When you have motion, you necessarily have velocity, of d =v / t .
π
3+ 2 = Therefore, you have time. Time is K.E.; everything inside the universe
This simply changes the minus sign to a positive is subject to time and motion. Outside the universe, the static condition
is timeless or eternal, or also named God. God is outside of time.
x + 1 − x =0 He is eternal. The best way to express God is through mathematics.
x + 1 − x =0 There is a limit to amount of math ones need to know up till we see
convergence. There is only one solution sand it’s really the only one
x= t= 1; 0 we need to know. The frequency of the human mind, the golden mean,
and irrational roots all converge in this solution. This convergence of
Discrete meets the continuous. Ln ( 0 )=1
mathematics is important in helping us understand how and why the
universe came to be. There was no choice.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
References
1. Paul TE Cusack. Convergence of Physical Mathematics and the Universal
Torus. AJMS. 2017;1(3).
2. Eugene Don. Schaum’s Outline of Mathematica 2nd ed. USA: McGraw
Hill; 2009. p. 384.
2
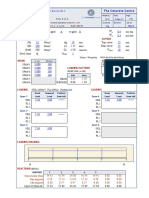
Figure 1 Plot of the derivative 1 / ( x − 1) .
Citation: Cusack PTE. Convergence and the imaginary number. Open Acc J Math Theor Phy. 2018;1(2):70‒71. DOI: 10.15406/oajmtp.2018.01.00011
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- How To Make Bom Camparison in AGILEDokument3 SeitenHow To Make Bom Camparison in AGILEcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paulymath Book2 PDFDokument741 SeitenPaulymath Book2 PDFcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Coils Equispaced Around Core and Series Connected So As To Buck Each NeighbourDokument10 Seiten4 Coils Equispaced Around Core and Series Connected So As To Buck Each NeighbourcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreviewDokument31 SeitenPreviewcimpocte100% (1)
- FURNIZ - AMBULAT.CLINIC La 01.07.2018Dokument9 SeitenFURNIZ - AMBULAT.CLINIC La 01.07.2018cimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translated AvionDokument3 SeitenTranslated AvioncimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cusack5239 The Collected Works Book 4 PDFDokument952 SeitenCusack5239 The Collected Works Book 4 PDFcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gnostic Myth of Sophia in Dark CityDokument35 SeitenThe Gnostic Myth of Sophia in Dark Citycimpocte100% (1)
- The Ether The Universal MaterialDokument3 SeitenThe Ether The Universal MaterialcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Value of SQRT (1)Dokument8 SeitenWhat Is The Value of SQRT (1)cimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serrano Miguel - The Golden CordDokument28 SeitenSerrano Miguel - The Golden CordcimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- LucidDream ExpansionDokument40 SeitenLucidDream Expansioncimpocte100% (1)
- LucidDream ExpansionDokument189 SeitenLucidDream ExpansioncimpocteNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Complexity: A Guided TourDokument12 SeitenComplexity: A Guided TourAnikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3M Scotchkote - Custom Coating GuideDokument16 Seiten3M Scotchkote - Custom Coating GuideUgoRibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 - Derivation of The Diffusivity EquationDokument4 SeitenModule 2 - Derivation of The Diffusivity EquationMuhammad Umair AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- (DOC) EXACTLY HOW THE UNIVERSE IS CONSTRUCTED - Docx - MIKE EMERY - Academia - EduDokument3 Seiten(DOC) EXACTLY HOW THE UNIVERSE IS CONSTRUCTED - Docx - MIKE EMERY - Academia - EduStellaEstelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Outrigger and Belt Wall SystemDokument24 Seiten1 Outrigger and Belt Wall SystemBurhan NasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Katalog AC (Floor Standing R410a)Dokument2 SeitenKatalog AC (Floor Standing R410a)AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On Application of Fuzzy Logic in Electrical Discharge Machining (Edm)Dokument37 SeitenA Case Study On Application of Fuzzy Logic in Electrical Discharge Machining (Edm)TanviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test BanksDokument21 SeitenTest Banksalex_flutistNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCC31 One-Way SlabsDokument43 SeitenTCC31 One-Way SlabsMuscadin MakensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Ductile-To-Brittle Transition Temperature in Steel Low CarbonDokument12 SeitenEvaluation of The Ductile-To-Brittle Transition Temperature in Steel Low CarbonBurag HamparyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air-Cooled Liquid Chillers High Outdoor Temperature Version: Nominal Cooling Capacity 270-1700 KWDokument36 SeitenAir-Cooled Liquid Chillers High Outdoor Temperature Version: Nominal Cooling Capacity 270-1700 KWAsad IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Energy and Propulsion Systems Based On Chronal Reaction Method - Alexander V. Frolov PDFDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Energy and Propulsion Systems Based On Chronal Reaction Method - Alexander V. Frolov PDFGherghe BogdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functionally Graded Materials 2017Dokument118 SeitenFunctionally Graded Materials 2017alfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Analysis of Ice Throw - Seifert - 2003 and 1998 PapersDokument18 SeitenRisk Analysis of Ice Throw - Seifert - 2003 and 1998 PapersKashif MannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Control Systems Engineering 2005Dokument79 SeitenBoiler Control Systems Engineering 2005Jorge EcheverriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Riemann-Stieltjes Integral and Some PDFDokument49 SeitenThe Riemann-Stieltjes Integral and Some PDFAlexis Garcia DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- K FactorDokument3 SeitenK FactorAnonymous hISvHbfiB1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 658 VLSI Design - I Homework-III Due Date: September 29, 2016 Prof. D. MisraDokument2 SeitenECE 658 VLSI Design - I Homework-III Due Date: September 29, 2016 Prof. D. MisraAnuj DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowizard 3.1Dokument4 SeitenFlowizard 3.1Antonio MezzopreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolerance AnalysisDokument10 SeitenTolerance Analysisdineshnexus100% (1)
- 1.7 Periodic Trends in Atomic PropertiesDokument5 Seiten1.7 Periodic Trends in Atomic PropertiesSilver AbdulahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetalDokument9 SeitenMetaldjtomcraftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of Materials For Roller Chains From The Perspective of Manufacturing ProcessDokument7 SeitenSelection of Materials For Roller Chains From The Perspective of Manufacturing Processhijzain0% (1)
- PDF WH1604A TMI CT WinstarDokument26 SeitenPDF WH1604A TMI CT WinstarСергейNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abaqus Tutorial 1Dokument11 SeitenAbaqus Tutorial 1Dg IRfan100% (1)
- Completed Guide To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns PDFDokument14 SeitenCompleted Guide To Elliott Wave Correction Patterns PDFQasim AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reducerea FrecariiDokument82 SeitenReducerea FrecariiDragomir IsabellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted Lead PollutionDokument4 SeitenSubmitted Lead PollutionRakesh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic TX L32C10P 10PS Chassis GLP24Dokument38 SeitenPanasonic TX L32C10P 10PS Chassis GLP24yacosNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Science in The Modern Age: ReadingDokument4 SeitenHistory of Science in The Modern Age: ReadingDebashis ChakrabrtyNoch keine Bewertungen