Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Accounting Ratios
Hochgeladen von
atifCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Accounting Ratios
Hochgeladen von
atifCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
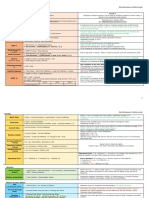
Ratios
1-PROFITABILITY RATIOS
1.1 Gross Profit ratio
Formula GP ratio = Gross profit x 100 %
Net Sales
Here:
Net Sales = Sales – Sales returns
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It shows the relationship between gross profit and sales and
the efficiency with which a business produces its product.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Increase in selling price Decrease in selling price
Reduction in cost Increase in cost
Undervaluation of opening Overvaluation of opening
stock or overvaluation of stock or undervaluation of
closing stock closing stock
1.2 Net Profit Ratio
Formula NP ratio = Net profit x 100 %
Net Sales
Here:
Net profit = Profit after tax
Net Sales = Sales – Sales returns
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It shows the overall profitability of business. It shows how
efficiently the business is conducting its operations to ensure
higher profits.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Efficient operating expenses Uncontrolled expenses
Low finance cost High finance cost
By Nasir Abbas FCA 1
Ratios
1.3 Return on capital employed (ROCE)
Formula ROCE = PBIT x 100%
Avg. Capital Employed
Here:
PBIT = Operating Profit = Profit before interest (after
interest of overdraft) & tax
Capital employed = Non-current assets + Current assets –
Current liabilities (excluding current portion of NCL)
OR
Capital employed = Equity + Non- current liabilities
(including current portion of NCL)
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It is considered the best measure of overall profitability of
business and indicates how well the management has used the
investment made by owners and creditors into the business.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Efficient funds management Inefficient funds
management
1.4 Return on equity (ROE)
Formula ROE = Net Profit x 100%
Avg. Equity
Here:
Net Profit = Profit after tax
Equity = Capital and all reserves
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It measures the overall efficiency of a company. This ratio is of
great importance to present and prospective shareholders as
well as management.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Efficient funds management Inefficient funds
management
By Nasir Abbas FCA 2
Ratios
2- INVESTORS RATIOS
2.1 Earnings per share (EPS)
Formula EPS = Net Profit
No. of ordinary shares
Here:
Net Profit =Profit after tax
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It shows the earnings of the company per ordinary share basis.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Efficient funds management Inefficient funds
management
2.2 Price to Earnings ratio (P/E ratio)
Formula P/E Ratio = MPS times
EPS
Here:
MPS = Market price per share
EPS = Earnings per share
Comments
Ratio result- Generally “higher” is better
Meaning- It helps the investor in deciding whether to buy or not to buy
the shares. It also helps in knowing whether the shares of a
company are under or overvalued.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Growth prospects No growth prospects
Overvalued share Undervalued share
By Nasir Abbas FCA 3
Ratios
2.3 Dividend per share (DPS)
Formula DPS = Dividend
No. of ordinary shares
Here:
Dividend = Total ordinary dividend
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It shows the dividend a prospective investor may expect to get
on per share basis.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
High dividend payout Low dividend payout
Higher profitability Lower profitability
High required return Low required return
2.4 Dividend Cover
Formula Dividend cover = PAT times
Dividend
Here:
PAT = Net Profit after tax for the year
Dividend = Total ordinary dividend
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It indicates whether the business earned sufficient profits to
pay periodically the ordinary dividend.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Low dividend payout High dividend payout
Ability to pay dividends Difficulty in paying
dividend
By Nasir Abbas FCA 4
Ratios
2.5 Earning yield
Formula Earning yield = EPS x 100 %
MPS
Here:
MPS = Market price per share
EPS = Earnings per share
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It measures the return which will be earned on investment in
share.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Undervalued share Overvalued share
2.6 Dividend yield
Formula Dividend yield = DPS x 100%
MPS
Here:
DPS = Dividend per share
MPS = Market price per share
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It helps the prospective investor in knowing the effective
return he will receive on proposed investment.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
High required return Low required return
Undervalued share Overvalued share
By Nasir Abbas FCA 5
Ratios
3-LIQUIDITY/SHORT TERM SOLVENCY RATIOS
3.1 Current ratio
Formula Current ratio = Current assets [x : 1]
Current Liabilities
Here:
Current assets = All current assets including prepayments.
Current Liabilities = All current liabilities including Bank
Overdraft
Comment
Ratio result- “near 2:1” is normal / standard
Meaning- It represents the margin of safety or cushion available to the
creditors. It is an index of the business financial stability.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Better liquidity position Financial difficulty
Larger inventories Lower inventories
Less credit purchases Longer creditor’s credit
periods
3.2 Liquid ratio/acid test ratio/quick ratio
Formula Quick ratio = Current asset –Inventory-prepayments [x : 1]
Current liabilities
Here:
Current liabilities = All current liabilities including Bank
Overdraft.
Comment
Ratio result- “near 1:1” is normal / standard
Meaning- It measures the business’s capacity to pay off current
obligations immediately and is more accurate test of liquidity
than the current ratio.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Better liquidity position Financial difficulty
Longer debtors’ credit period Lower inventories
Shorter debtors’ credit
period
By Nasir Abbas FCA 6
Ratios
4-ACTIVITY/ WORKING CAPITAL RATIOS
4.1 Inventory turnover ratio
Formula Inventory turnover = Cost of sales times
Avg. Inventory
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It measures the velocity of conversion of stock into sales.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Efficient inventory Inefficient inventory
management management
Higher sales Lower sales
4.2 Inventory period
Formula Inventory period = Avg. Inventory x 365 days
Cost of sales
Comment
Ratio result- “lower” is better
Meaning- It measures the period for which goods remain in stock before
getting sold.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Inefficient inventory Efficient inventory
management management
Lower sales Higher sales
4.3 Debtors turnover ratio
Formula Debtors turnover = Credit sales times
Avg. Debtors
Note:
If Credit sales are not given in question then use
“Total sales”
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It measures the velocity of debt collection of the business.
By Nasir Abbas FCA 7
Ratios
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Better control over debtors Poor control over debtors
Shorter credit periods Longer credit periods
More discounts offered Less discounts offered
4.4 Debtors collection period
Formula Debtors collection period = Average debtors x 365 days
Credit sales
Note:
If Credit sales are not given in question then use “Total
sales”
Comment
Ratio result- “Lower” is better
Meaning- It indicates the number of days for which a business has to
wait before its debtors are converted into cash.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Poor control over debtors Better control over debtors
Longer credit periods Shorter credit periods
Less discounts offered More discounts offered
4.5 Creditors turnover ratio
Formula Creditors turnover ratio = Credit purchases times
Avg. Creditors
Note:
If Credit purchases are not given in the question then use
“Total Purchases”
If Purchases are not given then use “Cost of sales”
Comment
Ratio result- Generally “higher” is better as it shows credit worthiness,
however higher ratio may indicate that credit period is not
fully availed.
Meaning- It measures the velocity of paying to creditors of the business.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Timely payment to suppliers Late payment to suppliers
Credit worthiness Less credit worthiness
More discounts availed Less discounts availed
By Nasir Abbas FCA 8
Ratios
4.6 Creditors payment period
Formula Payment period = Average creditors x 365 days
Credit purchases
Note:
If credit purchases is not given in question then use “Total
Purchases” or “Cost of sales”
Comment
Ratio result- Generally “lower” is better as it shows credit worthiness,
however lower ratio may indicate that credit period is not fully
availed.
Meaning- It indicates the number of days of credit period enjoyed by the
business in paying creditors.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Late payment to Timely payment to suppliers
suppliers Credit worthiness
Less credit worthiness More discounts availed
Less discounts availed
4.7 Assets turnover ratio
Formula Assets turnover = Sales times
Assets
Here:
Sales = Sales – sales return
Assets = Non-current assets + Current assets – Current liabilities
OR alternatively
Assets = Non-current assets
Comments
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It measures the efficiency and profit earning capacity of
business assets. It indicates how well the assets are utilized to
generate revenue.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Efficient utilization of assets Inefficient use of assets
High productivity of assets Low productivity
By Nasir Abbas FCA 9
Ratios
4.8 Working capital cycle
Formula
Working capital cycle= [Inventory period + debtors
collection period – creditors period] days
Comments
Ratio result- “Lower” is better
Meaning- It reflects the period for which a firm’s investment is
maintained in working capital as it moves through the
production process towards sales.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Low inventory turnover High inventory turnover
Poor control over debtors Better control over debtors
Timely payment to suppliers Late payment to suppliers
5- LONG TERM SOLVENCY / LEVERAGE RATIOS
5.1 Debt to assets ratio
Formula Debt to asset ratio = Debt x 100 %
Total assets
Here:
Debt = Non current liabilities (including current portion)
Total assets = Equity + Non current liabilities
(including current portion)
Comments
Ratio result- It depends upon nature of business that which ratio is better
Meaning- It measures the portion of total finance of a business, relating
to outsiders.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
High amount of debts Lower debt
Less ability to pay off debts Better solvency position
By Nasir Abbas FCA 10
Ratios
5.2 Debt Equity Ratio / Gearing ratio
Formula Debt Equity ratio = Debt [x : y or in %]
Equity
Here:
Debt = Non current liabilities
Equity = Capital and all reserves
Comment
Ratio result- Generally “1:1” is standard, however, it largely varies from
business to business.
Meaning- It indicates the relationship between external finance and
internal finance.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher debts Lower debts
Less risk shared by owners More risk shared by owners
Less solvent business Better solvency position
5.3 Interest cover / Debt service ratio
Formula Interest cover = PBIT times
Interest
Here:
PBIT= Operating Profit = Profit before interest and tax
Interest = finance cost for the year
Comment
Ratio result- “higher” is better
Meaning- It indicates whether the business earned sufficient profits to
pay periodically the interest charges.
Reasons for- High ratio Low ratio
Higher profitability Lower profitability
Less use of debts More use of debts
Ability to take further debts Less credit worthiness
By Nasir Abbas FCA 11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TCS Financial ModelDokument47 SeitenTCS Financial ModelPrince PriyadarshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Ratios FormulaDokument4 SeitenFinancial Ratios FormulaKamlesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Reference To Managerial AccountingDokument2 SeitenQuick Reference To Managerial AccountingAmilius San Gregorio100% (1)
- Wiley Notes Part 2 PDFDokument183 SeitenWiley Notes Part 2 PDFEdward Joseph Mabborang CaronanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3b. (NEW) Financing Enterprises 200910 TEXTBOOK 2nd Edn NewDokument355 Seiten3b. (NEW) Financing Enterprises 200910 TEXTBOOK 2nd Edn NewTrần Linh100% (2)
- Ratio Analysis: It Is Concerned With The Calculation ofDokument19 SeitenRatio Analysis: It Is Concerned With The Calculation ofsajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Investment FrameworkDokument10 SeitenMy Investment Frameworkkaya nathNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProfitabilityDokument30 SeitenProfitabilitySumit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Ratio AnalysisDokument12 SeitenNotes On Ratio AnalysisVaishal90% (21)
- Fundamental AnalysisDokument15 SeitenFundamental AnalysisGagan VibhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Capital Practice SetDokument12 SeitenWorking Capital Practice SetRyan Malanum AbrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance CH 2Dokument32 SeitenFinance CH 2ValeriaRios67% (3)
- Working Capital Management - IVth Semester MBA Project-M.G.University - Kottayam - KeralaDokument149 SeitenWorking Capital Management - IVth Semester MBA Project-M.G.University - Kottayam - KeralaSasikumar R Nair77% (31)
- Practice Quiz - Review of Working CapitalDokument9 SeitenPractice Quiz - Review of Working Capitalcharisse nuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ron Weber SummariesDokument47 SeitenRon Weber SummariesromeorabNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Balance Sheet: Assets Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity 2012 2011 2012 2011Dokument23 SeitenThe Balance Sheet: Assets Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity 2012 2011 2012 2011Phạm Ngô Diễm QuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis and Reporting 1Dokument4 SeitenFinancial Analysis and Reporting 1Anonymous ryxSr2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Failure (Assignment)Dokument9 SeitenCorporate Failure (Assignment)Talha MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Ratios - Class NotesDokument8 SeitenAccounting Ratios - Class NotesAbdullahSaqibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Ratios Type Standard Norm For Investors For Company Profitability RATIOS: (Expressed in %)Dokument12 SeitenClassification of Ratios Type Standard Norm For Investors For Company Profitability RATIOS: (Expressed in %)parivesh16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Cheat Sheet FA ML X MM UpdatedDokument8 SeitenFinal Cheat Sheet FA ML X MM UpdatedIrina StrizhkovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LearnXtra Accounting g12Dokument8 SeitenLearnXtra Accounting g12Nezer Byl P. VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0.3-Financial Statement AnalysisDokument26 Seiten0.3-Financial Statement AnalysisMatsuno ChifuyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 5 Profitability and Ratio AnalysisDokument2 Seiten3 5 Profitability and Ratio AnalysisKANAK KOKARENoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis: 1. Gross Profit PercentageDokument4 SeitenRatio Analysis: 1. Gross Profit PercentageannabellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Fin StatementsDokument22 SeitenInterpretation of Fin StatementstinashekuzangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Financial Statements: Ratio Analysis and ReportingDokument9 SeitenInterpretation of Financial Statements: Ratio Analysis and ReportingSania SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms & Oracle Project Ex DDokument53 SeitenMs & Oracle Project Ex DA.D. Home TutorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leverage My PptsDokument34 SeitenLeverage My PptsMadhuram SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Outcomes: Subject: Accounting Grade 12 Chapter: Companies Lesson: Analysis and Interpretation-RatiosDokument8 SeitenUnit Outcomes: Subject: Accounting Grade 12 Chapter: Companies Lesson: Analysis and Interpretation-Ratios903712594Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Final Account RatiosDokument14 SeitenBasic Final Account RatiosJahanzaib ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIFA CheatSheet MM X MLDokument10 SeitenTIFA CheatSheet MM X MLCorina Ioana BurceaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio AnalysisDokument10 SeitenRatio AnalysisUdayan KarnatakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDokument5 SeitenFinancial Ratio AnalysisPhuoc TruongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of Financial StatementsDokument26 SeitenInterpretation of Financial StatementsPresident Musuki100% (1)
- 15 FINANCIAL Performance MeasurementDokument8 Seiten15 FINANCIAL Performance MeasurementJack PayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- RATIO ANALYSIS BREAKDOWNDokument7 SeitenRATIO ANALYSIS BREAKDOWNvarun325Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manajemen Strategis - Pertemuan 4Dokument18 SeitenManajemen Strategis - Pertemuan 4Ferdian PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM Ass 1 3 Prob 1Dokument2 SeitenFM Ass 1 3 Prob 1rhea ann servandilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis: A Guide to Financial Statement RatiosDokument13 SeitenRatio Analysis: A Guide to Financial Statement Ratiosmuralib4u5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial RatiosDokument3 SeitenFinancial RatiosluudieulinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 27 Interpretaion and Analysis (A1 Ratios)Dokument14 SeitenChapter 27 Interpretaion and Analysis (A1 Ratios)Burhan AzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa Cheat Sheet MM MLDokument8 SeitenFa Cheat Sheet MM MLIrina StrizhkovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORKDokument19 SeitenSTRATEGIC MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORKCharles CagaananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Accounting - Chapter6Dokument20 SeitenManagerial Accounting - Chapter6Nazia AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 Q1 LAS5 W5 For-LectureDokument19 SeitenG10 Q1 LAS5 W5 For-Lecturekaorinim28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Financial Ratios AnalysisDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding Financial Ratios AnalysismanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Investor Section 2: Understanding Profits MarginsDokument38 SeitenSmart Investor Section 2: Understanding Profits MarginsLyfe SpanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Ratios: Higgin Lecture TheatreDokument17 SeitenFinancial Ratios: Higgin Lecture Theatresidharth90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDokument19 SeitenAnalysis of Financial StatementsGautam MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 21 22 23 Ratio Analysis Formula 2023Dokument2 SeitenSession 21 22 23 Ratio Analysis Formula 2023Chanukya GvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profitability Ratios (Teoría)Dokument14 SeitenProfitability Ratios (Teoría)leonardo ramirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Ratios AnalysisDokument30 SeitenFinancial Statement Ratios AnalysisA.m. selvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breaking Down Roe Using The Dupont Formula PPT K LeyeahDokument5 SeitenBreaking Down Roe Using The Dupont Formula PPT K LeyeahUmar NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statement Analysis: 17-5 The Dividend Yield Is TheDokument51 SeitenFinancial Statement Analysis: 17-5 The Dividend Yield Is TheMafi De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANFIN 0 Break ROE Dec 12 5p CopieDokument5 SeitenANFIN 0 Break ROE Dec 12 5p Copiestephyl0722Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ellie Tatters - Ratio Summary TableDokument4 SeitenEllie Tatters - Ratio Summary TableElllie TattersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin420-Chapter 3 Financial Ratio and AnalysisDokument29 SeitenFin420-Chapter 3 Financial Ratio and AnalysisEmmy AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management FormulasDokument5 SeitenFinancial Management FormulasDaniel Kahn GillamacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Ratio AnalysisDokument33 SeitenIntroduction To Ratio AnalysisSayantan KhamruiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMS-2 Semester Batch 2010 - 2011 VesimsrDokument11 SeitenMMS-2 Semester Batch 2010 - 2011 VesimsrVishal ShanbhagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valution IndicatorsDokument5 SeitenValution Indicatorsramjidixitv987Noch keine Bewertungen
- The City School: Ratio Analysis and InterpretationDokument9 SeitenThe City School: Ratio Analysis and InterpretationHasan ShoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio Analysis:: Liquidity Measurement RatiosDokument8 SeitenRatio Analysis:: Liquidity Measurement RatiossammitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Finance CH 3Dokument5 SeitenManagerial Finance CH 3MPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk & Ratio Analysis of Emami and NestleDokument9 SeitenRisk & Ratio Analysis of Emami and NestleKeshav GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- FA M8 NotesDokument22 SeitenFA M8 Noteslim hwee lingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Management RatiosDokument6 SeitenBusiness Management RatiosBrittney KotzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 13 Financial Statement AnalysisDokument32 SeitenTopic 13 Financial Statement AnalysisAbd AL Rahman Shah Bin Azlan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutual Fund QADokument5 SeitenMutual Fund QAatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alteration of MOADokument3 SeitenAlteration of MOAatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ifrs For SmesDokument6 SeitenIfrs For SmesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Guide SecpDokument16 SeitenAccounting Guide SecpadeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8Dokument64 SeitenOperating Segments: International Financial Reporting Standard 8atifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Management Past Papers Along With Icap Suggested AnswersDokument81 SeitenBusiness Management Past Papers Along With Icap Suggested AnswersatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business ManagementDokument36 SeitenBusiness Managementalishayan123Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITMAC Notes by Nowsherwan Adil Niazi PDFDokument189 SeitenITMAC Notes by Nowsherwan Adil Niazi PDFmiqbaaalllNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAS 02 InventoriesDokument20 SeitenIAS 02 InventoriesVijay PeesapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT SummariesDokument84 SeitenIT SummariesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acquisition of Information Technology: July 2000Dokument13 SeitenAcquisition of Information Technology: July 2000api-26916217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Money Laundering Act 2010Dokument39 SeitenAnti Money Laundering Act 2010atifNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA Topic Wise ECDokument233 SeitenQA Topic Wise ECatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITC-Guideline 2Dokument18 SeitenITC-Guideline 2api-26916217Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT SummariesDokument84 SeitenIT SummariesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT ServicesDokument42 SeitenIT ServicesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITC-Guideline 1Dokument21 SeitenITC-Guideline 1api-26916217Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT ServicesDokument28 SeitenIT ServicesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT ServicesDokument28 SeitenIT ServicesatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Capital Management of Nepal Doorsanchar Company LimitedDokument48 SeitenWorking Capital Management of Nepal Doorsanchar Company LimitedSovit Subedi100% (2)
- Principles of Bank LendingDokument66 SeitenPrinciples of Bank LendingKetki TeloreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing Your Franchised BusinessDokument17 SeitenFinancing Your Franchised BusinessDanna Marie BanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument65 Seiten4Pappu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Administration Paper 2000 SEC-optimized titleDokument37 SeitenBusiness Administration Paper 2000 SEC-optimized titleKeera KilerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working CapitalDokument62 SeitenWorking CapitalSahil SethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Accounting Chapter 15 AnalysisDokument175 SeitenManagerial Accounting Chapter 15 AnalysismostfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profitability & Liquidity Ratio AnalysisDokument19 SeitenProfitability & Liquidity Ratio AnalysisananditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statements Analysis On Renata LimitedDokument43 SeitenFinancial Statements Analysis On Renata LimitedZafour80% (5)
- A Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Sail and Tata Steel LTDDokument22 SeitenA Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Sail and Tata Steel LTDpreetiaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Century Properties Group, Inc ReportDokument38 SeitenCentury Properties Group, Inc Reportカイ みゆきNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS Business Administration MCQsDokument9 SeitenCSS Business Administration MCQsMuhammad YouneebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Capital ManagementDokument13 SeitenWorking Capital ManagementDr. Prasad JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working CapitalDokument44 SeitenWorking CapitalBharath GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMR Constructions LTD PDFDokument290 SeitenAMR Constructions LTD PDFVikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Planning: WK04-LAS1-BF-II-12Dokument19 SeitenFinancial Planning: WK04-LAS1-BF-II-12Benj Jamieson DuagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Millat Tractors... (Inventories)Dokument11 SeitenMillat Tractors... (Inventories)juni6100% (1)
- Apollo Tyres LTD Project Report On Working Capital ManagementDokument83 SeitenApollo Tyres LTD Project Report On Working Capital Managementprateeksri1033% (3)
- Practice-Assignment - Afs - 31-Augsut-2019Dokument10 SeitenPractice-Assignment - Afs - 31-Augsut-2019Waqar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wipro Balance Sheet and Financial Statements from 2006-2010Dokument17 SeitenWipro Balance Sheet and Financial Statements from 2006-2010Rekha RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex Ante Project AnalysisDokument85 SeitenEx Ante Project AnalysisVernon BacangNoch keine Bewertungen