Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ANSYS
Hochgeladen von
marcosandia1974Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ANSYS
Hochgeladen von
marcosandia1974Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
17.
0 Release
Module 01: Core Skills
Introduction to ANSYS SpaceClaim Direct Modeler
1 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Overview
In this module we will learn about:
• Pre-processing Workflow using ANSYS WB tools
• What is SpaceClaim Direct Modeler (SCDM)?
• Launching SCDM
• Interface
• File Operations
• Working with Assemblies
• Shared Topology
• Working with Layers
• Display and managing views
• SpaceClaim Main Tools
2 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Overall Process
FEA Modeling
Module 4
Creating
Geometry
Module 2
Core
Skills CFD Modeling
Module 1 Repairing Module 5
Geometry
Module 3
SCDM to
Workbench
Module 6
3 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
What is SpaceClaim Direct Modeler? Sketching Modeling
• Industry leading direct modeling tool for rapid
concept design and geometry manipulation
• Analysis-focused tools to repair, prepare, and
optimize models
• Computer-Aided Design (CAD) – like approach to
create new models OR Import CAD models
without CAD connection
CAD Import
• Dead model parameterization & Clean-up
– No need of native CAD data for parameterization
• Freedom to explore solutions without relying on CAD team
– More flexibility to make unplanned and local changes
• No features + No constraints = No regeneration failures
• Short learning curve for engineers without CAD
background
4 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Launching SpaceClaim Direct Modeler
Standalone Session From Geometry cell of any System
ANSYS SpaceClaim
Direct Modeler is
supported only on the
‘Windows’ platform
• ANSYS SCDM is launched within Workbench
• Right click on “Geometry” and select “New SpaceClaim
Geometry”
5 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
SpaceClaim Interface
Quick Access Toolbar
Ribbon Toolbar
Structure Panel
Options Panel
Properties Panel
Graphics
Window
Status Bar
6 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Quick Access Toolbar (QAT)
• Open, Save, Undo, Redo options available by
default on the QAT
• Undo (CTRL-Z) can be used to undo your last
action. Redo (CTRL-Y) can be used to repeat it.
• Frequently used tools can be added to the QAT
– Select the down arrow to the right of the Quick
Access Toolbar (QAT)
– Choose “Customize Quick Access Toolbar” from the
drop down list
7 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Ribbon Toolbar
• Familiar ribbon UI design
Display Tab
• Tools categorized in a series of Tabs
– File handling
– Designing
– Displaying Repair Tab
– Repairing
– Etc.
Prepare Tab
• Each Tab displays relevant tools in
organized sections
8 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Structure Panel
SpaceClaim Direct Modeler is not a feature-based modeler
• Operations are not stored under Structure Tree
– This is characteristic of history-based or feature-based modelers
• Structure Tree shows the objects/entities
– Bodies (solid, surface)
– Curves (sketch curves, 3D curves)
– Assembly constraints
– Origin
– Plane
9 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Options Panel and Properties Panel
Options Panel
• Displays options for modifying functions of active SpaceClaim
tool
– E.g., Pull tool contains option for add material, subtract
material, create fillet, chamfer, etc.
Properties Panel
• Displays properties of selected entity in Graphics window or
Structure panel
• Modify property values
– Color
10 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Tool Guide and Mini Toolbar Mini Toolbar
Mini Toolbar
• Contains frequently used options of active tool
Tool Guide
• Contains different options to change behavior of active tool
– E.g., Tool guide of “Pull” tool contains option for Revolve,
Sweep, Scale, etc.
Tool Guide
11 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Status Bar
Quick Selection Selection
Measurement List options
Status Error/Warning View
Message Message controls
Status Message: Displays message and progress information about current tool
Quick Measurement: Displays simple measurement of selected entities (distance, angle)
Error/Warning Message: Displays error and warning messages
Selection List: Displays list of currently selected objects to the right and being hovered over at the left
Selection Options: Hosts various options for selection
View Controls: Controls for spin, pan, zoom, and switch to previous or next views
12 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Selection
• You can select vertices (including centers of circles and ellipses, midpoints of lines, and points on splines),
edges, planes, axes, faces, surfaces, rounds, solids, and components.
• Most commonly used selection methods are:
– Click to select an object.
– Double-click to select an edge loop. (Double-click again to cycle through alternate loops.)
– Triple-click to select a solid.
– Drag to create a selection Box (can also use Lasso, Polygon, and Paint). If you draw the box from left to right,
all objects fully enclosed within the box will be selected. If you draw the box from right to left, all objects
touching the box will be selected.
– Press CTRL+A to select all similar objects, such as faces, edges, or points on the same solid or surface part.
– Hold CTRL and select to add or remove items from the selection. Ctrl with box-selection toggles the selection;
Shift with box-selection adds to the selection.
Selection Selection
List options
13 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Selection
Selecting entities
• Select vertices (including centers of circles and
ellipses, midpoints of lines, and points on
splines), edges, planes, axes, faces, surfaces,
rounds, solids, and components.
14 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Power Selection
• Selection Panel: Use the Selection panel to select objects in the same part that are similar or related to
the object currently selected. The results list is based on the geometry you select for the search.
• The relations available are displayed in the Selection window as per the item selected and items
15 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Power Selection
Category Description Example Selection types
• Coaxial Hole, Protrusion, Cylinder
• Coaxial protrusion
Coaxial Faces Objects with the same axis
• Coaxial cylinder
• Coaxial surfaces
• Edges with same length
• Edges with same length and same
Edges that are like the currently orientation
Edges
selected edge • Edges with same length in same face
• Surface edge loop
• Hard sheet metal edges
• Protrusion
Groups of faces that form protrusions,
• Depression
Features depressions, inner faces, or that enclose
• Inner faces
other faces
• Enclosed by
• All offset baseline faces
Faces that have an offset relationship • All offset faces
Offset faces
defined • Faces with same offset
• All coincident faces
16 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Power Selection
Category Description Example Selection types
Pattern members, entire
patterns, or recognized • Pattern member
patterns • Recognized pattern
Patterns • All pattern members
• Equal radius rounds
• Equal or smaller radius rounds
• Equal or smaller-sized chamfers
Rounds Rounds and chamfers • Variable radius round
• Faces and chains of faces even if they are
composed of a mix of constant and
variable faces
Same curve Curves of the same color, • Faces with the same color as the
type type, and length originally selected face
Beams based on the This category is useful when the display is set to
Beams profile of the currently Wire Beams, or when you have several profiles Beams
selected beam that are only slightly different
17 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Power Selection
Category Description Example Selection types
Faces of the same
Same color • Faces
color
Standard Holes with
Same hole
the same Hole • Standard holes
dimensions
Dimensions
• Miter corners
Sheet metal Sheet metal objects • Same Junction type and parameters
• Beads and forms with the same parameters
• Equal radius cylinder
• Equal radius hole
Faces that have the
Same size • Equal radius protrusion
same radius or area
• Faces with the same area
• Holes equal to or smaller than
Finding zero thickness faces and surface bodies
Midsurface faces with
Midsurface allows you to verify that thickness has been
the same thickness • Faces and Bodies
Face Thickness assigned to all faces and surface bodies in the
(including zero)
model.
18 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Mouse and View Controls
• Easy-to-use Mouse and View controls to speed up operations
and manipulate graphics
• Controls listed in “Quick Reference Card”
• “Quick Reference Card” can be accessed during SCDM launch
Notice: The controls shown here are true after doing a ‘Reset
All’ in File/SpaceClaim Options/Navigation. They can be
changed to match those of your CAD Software by changing the
Theme or can be customized.
19 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
File Handling File Formats
SpaceClaim Options
• Supports import from major CAD
packages (CATIA, Pro/E, NX, Solid
Works, etc.)
- Separate license not required
except for CATIA V5 and V6, JT, and
PDF3D
• Neutral file formats like STEP and
Parasolid are also supported
• Additional options for controlling
import/export of file formats
available in SpaceClaim Options panel
20 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Working with Assemblies (1)
• Components are shown on the structure tree and are created automatically
• Components can be created manually by:
– Right-click any component and select New Component
– Right-click an object and select Move to New Component, it will create a
component within the Active Component
– Ctrl+click multiple objects, then right-click and select Move Each to New
Components to create a new component for each object
• Activating a component (right-click Activate Component) allows to work with the
objects within that component
• Components can be copied, cut, pasted, mirrored, renamed and deleted
21 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Working with Assemblies (2)
Components
• Reorder bodies/components using
drag and drop
Active Component
• Allows to work with objects
within that component
• Other components get greyed out
• To activate, right click on the
component and select “Activate
Component”
22 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Working with Assemblies (3)
Open Component
• Ability to work on a specific
component by opening it in a
new session
– Right click and select “Open
Component”
• Changes made to the component
objects get reflected in the Component Changes made Changes reflected
original model opened in new to component in original model
session (added fillet)
23 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Working with Assemblies (4)
Replace Component
• Replace an existing component with
another saved component
– Reuse existing models
24 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Shared Topology (1)
• Shared Topology
– SpaceClaim can share topology (face, edge, and vertex
connections) between bodies and surfaces in contact
that are transferred to Workbench
– Shared topology is the only way to achieve a
conformal mesh where bodies meet
– Shared topology also applies to volume and surface
bodies that are enclosed within other volume or
surface bodies. This situation is common in analyses
involving fluid flow
– Shared Topology is passed from SpaceClaim to
Workbench when the shared topology property for
the parent Component is set to ‘Share’
– Solids or Surfaces under the same component will be
treated as a multi-body part and will share topology
when the property is set
25 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Shared Topology (2)
• Shared Topology Settings
– None (default): does nothing to geometry during
transfer to ANSYS/Workbench
– Merge is used for Baffles:
• It merges surfaces with solids and trims away any
parts of the surfaces outside of the solid
• Faces do not need to intersect
• Surfaces that are completely inside a solid are
merged with that body
– Share: imprints and merges all bodies in the
components the result to ANSYS as multi-body part
– Group: groups all bodies in the components into a
multi-body part but does not merge or share faces and
edges of the bodies with each other
26 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Shared Topology (3)
• Shared Topology Examples
– Mesher meshes two blocks with shared topology.
The blue block will gain a new imprinted face
which will be shared between the green and blue
blocks.
– Mesher creates separate meshes for two parts
because they are in different components and the
root part has Shared Topology set to None.
– The mesh for shared topology is not the same as
merged geometry. Here the boxes are merged,
and you can see that the mesh is different than it
is for two bodies with shared topology.
– Note: If a solid body is taken out of parent
component which is set to shared topology, it will
have no imprints and no shared faces/edges with
the previous parent part
27 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Beams and Shared Topology
Beams can share topology with surfaces when:
• The end point of the beam lies on the surface:
• The path of the beam lies in the surface
• The beam intersects a surface at a point
• The beams and surfaces must be in the same component which must be set to share
28 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Show Contact
• Show contact
– This tool in the CAE group on the Prepare tab displays a preview of topology sharing. ‘Show
Contact’ lets you see – before sending to Workbench – exactly what topology would be shared.
– Allows you to modify/correct the geometry so that it is transferred to Workbench as intended
29 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Show Contact
• Show Contact - Options
Show Contact settings Display
Description
in the Options Panel color
Edge options control the display of
Edge Options connected and disconnected paths
(i.e. edges, sketch curves, Beam paths.
Shared edges of solids or surfaces and
Show Edge Junctions Blue
Beams
Edges of surface bodies that are not
Show Laminar Edges Red
connected to anything
Beams that are not entirely connected
Show Free Beams Orange (i.e. coincident to an edge or
embedded within a face.
Vertex options control the display of
Vertex Options connected endpoints (Beam
endpoints and intersections).
Shared points on Beams (i.e. shared
Show Beam Junctions Blue
endpoints or interior intersections).
Show Beam Ends Red Non-shared endpoints of Beams.
30 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Working with Layers
Layers
• Useful for grouping objects based on visual characteristics
– Visibility
• Click bulb icon to change visibility
Objects are hidden
Objects are visible
– Color
– Linestyle, not for 3D objects
• Right click in Layers panel and select “New” to create a new
layer
– Set appropriate layer color
– All new objects created in this layer will have the same layer
color
• To add selected objects to a layer, right click on the desired
layer and select “Assign To Layer”
31 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Managing Views
Views
• Change shortcuts for standard views Create View Panel
• Create custom views to save object
orientation and visibility
• Control visibility behavior for custom
views
– Leave Unchanged: New objects retain
their visibility
– Visible: New objects become visible
– Hidden: New Objects get hidden
32 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Display (1)
Display tab
• Hosts several features for managing Change Transparency
display of geometry
– Cut, Copy, Paste objects
– Standard and custom view
– Change object color
– Manage layers
– Change graphics mode
• Wireframe, shaded etc.
– Rendering options
– Change transparency
– Arrange graphics windows
– Etc.
Opaque Transparent
33 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Display (2)
Display tab
• Change face color
– Select face
– Right click and open Color panel
– Select “Face” target
– Select desired color
34 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Display: Clip with volume
• Enables you to create a clip volume around an object so that you can selectively isolate a
specific region of a design:
– Right click on the area you want to view and click Clip with Volume > Set using selection then release the
mouse
– Right click and select Clip with Volume > Select. In the Properties panel, you can choose between a
sphere and a cube and change the center and the radius.
– Right click and select Clip with Volume > Resize to change the dimensions
35 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
SpaceClaim Main Tools
There are 4 main Tools in SpaceClaim that must be known by all the users:
• Pull Tool
• Move Tool
• Fill Tool
• Combine Tool
Notice: In this Module we will just give a brief description of these tools
For more information, please consult the Module 2: Creating Geometry
36 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Pull Tool
• Used to convert sketches to 3D
– Pulling a line creates a surface
– Pulling a surface creates a solid
• Distort or deform existing geometry
• Drag the selected object in a chosen direction when
Pull tool is active
• Multi-functional tool
– Extrude, Revolve, Sweep, Offset and Draft faces
– Create Rounds (Fillets), Chamfers or Extrude edges
– Pull a point to create Line
• Several tool guides available to alter its behaviour
37 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Move Tool
• Multi functional tool
– Translate Translation movement
– Rotate
Move Handle
– Pattern
• Move handle guides the direction of
movement
– Translational movement along 3
“linear” axes
– Rotational movement along 3
“curved” axis Rotational movement
• Drag the selected object along the
Move handle axis (linear, curved) to
facilitate Move
• Distort or deform existing geometry
• Several tool guides available to alter
tool behaviour
38 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Fill Tool
• Fill selected region with surrounding
surface or solid
• Acts as a “healing” tool to remove:
– Fillets
– Chamfers
– Holes
– Protrusions
– Depressions
Notice: Sometimes a simple delete after
selecting the entities can replace the Fill Tool
39 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Combine Tool
• Perform Boolean operations Merge multiple objects
– Add
– Subtract
• By default, second selected
object acts as a cutter to
perform subtract operation
– Cutter tool guide gets activated once
a body is selected
• Select multiple objects using
“Ctrl” key to add them
– “Merge” tool guide gets activated
automatically Select cylinder Select region
• Option to delete or retain left as cutter to remove
over region after subtract
operation
– “Regions to Remove” tool guide
automatically gets activated after
subtract operation
40 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Summary
What have we learnt in this session?
• What is the normal Pre-processing Workflow within ANSYS WB tools?
• What is SpaceClaim Direct Modeler (SCDM)?
• Launching SCDM
• SpaceClaim Interface
• File Operations
• Working with Assemblies
• Shared Topology options
• How to work with layers?
• How to manage views?
• SpaceClaim Main Tools: pull, move, fill and combine
41 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Workshop 1.1 Basics
42 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Workshop 1.2 Sketching in SpaceClaim
43 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Videos available (look for separate directory)
Module1_Basic_UI.mp4 Module1_Basic_Select.mp4
Module1_Partitioning.mp4
Demo of Basic UI Demo of Selection Demo of Partitioning
(10:38) (10:38) (07:52)
44 © 2016 ANSYS, Inc. March 16, 2016
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SCDM-Intro 17.0 Module02 Creating GeometryDokument47 SeitenSCDM-Intro 17.0 Module02 Creating Geometrymarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringVon EverandGuide to Load Analysis for Durability in Vehicle EngineeringP. JohannessonBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- NX Assign Material PropertiesDokument54 SeitenNX Assign Material PropertiesbiondavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ANSYS Mechanical (2D)Dokument19 SeitenIntroduction To ANSYS Mechanical (2D)Mi BoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Buckling Analysis: Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0Dokument18 SeitenLinear Buckling Analysis: Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0Aghil BuddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explicit Dynamics Chapter 2 Intro To WBDokument29 SeitenExplicit Dynamics Chapter 2 Intro To WBalexandrusssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ANSYS Mechanical 2D Structural AnalysisDokument19 SeitenIntroduction To ANSYS Mechanical 2D Structural AnalysisFabián Stark CatongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 1Von EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- Explicit Dynamics Explicit MeshingDokument51 SeitenExplicit Dynamics Explicit MeshingShivu Patil100% (1)
- 3D FEA Simulations in MachiningDokument95 Seiten3D FEA Simulations in MachiningAyman TamimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Spaceclaim Direct Modeler Brochure 16Dokument2 SeitenAnsys Spaceclaim Direct Modeler Brochure 16Tuğrulhan ÖzdemirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis and Adina: Proceedings of the 4th ADINA ConferenceVon EverandNonlinear Finite Element Analysis and Adina: Proceedings of the 4th ADINA ConferenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- L&T Random Vibration Analysis and Fatigue Life Evaluation of Auxiliary Heater BracketDokument12 SeitenL&T Random Vibration Analysis and Fatigue Life Evaluation of Auxiliary Heater BracketalfonxxlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic To Advanced CAD Using NX 12 Sample PDFDokument29 SeitenBasic To Advanced CAD Using NX 12 Sample PDFYaseen JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys 18.2: Transient Analysis On The BridgeDokument7 SeitenAnsys 18.2: Transient Analysis On The BridgeUsman Khalil50% (2)
- Solidworks Hardware Guide - 2018Dokument16 SeitenSolidworks Hardware Guide - 2018MANJUNATH SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Analysis TechniquesDokument40 SeitenContact Analysis TechniquesRaj DevarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Meshing Application IntroductionDokument11 SeitenANSYS Meshing Application IntroductionMudassir FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys Explicit DynamicsDokument8 SeitenAnsys Explicit DynamicsMulugeta Kiros GebeyehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro-e/Sheet Metal DesignDokument214 SeitenPro-e/Sheet Metal DesignStephen Thathampilly AnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractureDokument57 SeitenFractureAdool FighterNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks OptimisationDokument9 SeitenSolidWorks OptimisationBobi PitropNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optislang Inside AnsysDokument32 SeitenOptislang Inside AnsysRaees SwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skill Builder-Derived Parts3Dokument3 SeitenSkill Builder-Derived Parts3Ndianabasi UdonkangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 387 PDFDokument258 Seiten387 PDFmohammed ramzi CHAHBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Meshing ANSYS R2Dokument39 SeitenMeshing ANSYS R2Alvaro CujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Meshing Users Guide PDFDokument498 SeitenANSYS Meshing Users Guide PDFvivekzz100% (1)
- ANSYS PresentationDokument48 SeitenANSYS Presentationmagi100% (1)
- 2 Tetra Meshing - 13Dokument11 Seiten2 Tetra Meshing - 13Varun ChaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Course Material For HRDDokument142 SeitenSolidWorks Course Material For HRDWai Phyo MaungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Optimization Formula SAE DrivetrainDokument21 SeitenDesign and Optimization Formula SAE DrivetrainIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Modeling and Analysis GlossaryDokument40 SeitenFinite Element Modeling and Analysis GlossaryAda DarmonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Technology For Marine Design and ProductionDokument15 SeitenAdvanced Technology For Marine Design and Productionmaang alleija100% (1)
- ANSYS Explicit Dynamics 120 Workshop 01Dokument33 SeitenANSYS Explicit Dynamics 120 Workshop 01Jaime Domínguez Soto100% (1)
- AnsysDokument151 SeitenAnsyspraveen06apr67% (3)
- Basic Vibration Analysis in AnsysDokument30 SeitenBasic Vibration Analysis in AnsysmanjunathbagaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Explicit Dynamics - Ashish JaiswalDokument57 SeitenANSYS Explicit Dynamics - Ashish JaiswalPeriNumerics100% (1)
- Part Modeling Best PracticesDokument3 SeitenPart Modeling Best PracticesBryan BritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altair's Student Guides - Instructor's Manual - CAE For Simulation of Sheet Metal FormingDokument26 SeitenAltair's Student Guides - Instructor's Manual - CAE For Simulation of Sheet Metal FormingKFourMetrics100% (13)
- Slocum, Alex Fundamentals of Design Mit PDFDokument75 SeitenSlocum, Alex Fundamentals of Design Mit PDFvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adm SimulationDokument273 SeitenAdm SimulationSamir2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- AWS90 Structural Nonlin Ch03 ContactDokument78 SeitenAWS90 Structural Nonlin Ch03 ContactRaki Rock100% (2)
- Miltronics The Probe 2 wire-Manual-Spanish (FN.117) PDFDokument59 SeitenMiltronics The Probe 2 wire-Manual-Spanish (FN.117) PDFJuan MontufarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Unigraphics NX - 09 The Master ModelDokument13 SeitenManual Unigraphics NX - 09 The Master ModelthiagomcasimiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solidworks 2018 Reference Guide: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 250 Standalone TutorialsDokument70 SeitenSolidworks 2018 Reference Guide: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 250 Standalone TutorialsInnabilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Probe Level Monitor: Instruction Manual PL-517 January 2001Dokument20 SeitenThe Probe Level Monitor: Instruction Manual PL-517 January 2001horacio mondragon100% (1)
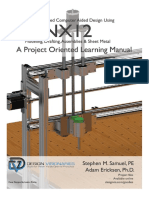
- Mountainboard Design Project Student 2010 LR ENG PDFDokument541 SeitenMountainboard Design Project Student 2010 LR ENG PDFjvs11021102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contactos AnsysDokument78 SeitenContactos AnsyssergiogigiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whitepaper - Bolted ConnectionsDokument18 SeitenWhitepaper - Bolted ConnectionsOğuzhan KocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Forming of Tubes-A ReviewDokument11 SeitenFlow Forming of Tubes-A Reviewdr_kh_ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Modelling and Analysis of Hot Turning OperationDokument55 SeitenFinite Element Modelling and Analysis of Hot Turning OperationSangar LingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing and Manufacturing Ruled Surface Blades: Peter Klein, CAM Software Director, Concepts NRECDokument6 SeitenDesigning and Manufacturing Ruled Surface Blades: Peter Klein, CAM Software Director, Concepts NRECCésarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCDM-Intro 17.0 Module04 FEA ModelingDokument29 SeitenSCDM-Intro 17.0 Module04 FEA Modelingmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCDM-Intro 17.0 Module03 Repairing GeometryDokument40 SeitenSCDM-Intro 17.0 Module03 Repairing Geometrymarcosandia1974100% (1)
- Workshop 01 - Transfer ChuteDokument38 SeitenWorkshop 01 - Transfer Chutemarcosandia1974100% (1)
- SCDM-Intro 17.0 Module05 CFD ModelingDokument21 SeitenSCDM-Intro 17.0 Module05 CFD Modelingmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 M03 Global Mesh ControlsDokument24 SeitenMesh-Intro 17.0 M03 Global Mesh Controlsmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 WS1.1 CFD ANSYS WB Meshing BasicsDokument21 SeitenMesh-Intro 17.0 WS1.1 CFD ANSYS WB Meshing Basicsmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 WS2.1 CFD ANSYS Meshing MethodsDokument35 SeitenMesh-Intro 17.0 WS2.1 CFD ANSYS Meshing Methodsmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 M02 Meshing MethodsDokument38 SeitenMesh-Intro 17.0 M02 Meshing Methodsmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- CFX-Intro 14.5 WS07 Centrifugal-Pump PDFDokument24 SeitenCFX-Intro 14.5 WS07 Centrifugal-Pump PDFmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Giw Conversion Slurry PumpsDokument2 SeitenGiw Conversion Slurry Pumpsmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rocky Manual PDFDokument211 SeitenRocky Manual PDFRaghul Ravi88% (8)
- CFX-Intro 14.5 L11 Transient PDFDokument22 SeitenCFX-Intro 14.5 L11 Transient PDFmarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jaw BrochureDokument12 SeitenJaw Brochuremarcosandia1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad 2010. Manual de PersonalizacionDokument646 SeitenAutocad 2010. Manual de Personalizaciondeportia8981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testas 3Dokument238 SeitenTestas 3Rishabh Tiwari100% (1)
- VISI ModellingDokument176 SeitenVISI Modellinggoatack100% (3)
- Telangana TS EdCET Syllabus and Exam PatternDokument43 SeitenTelangana TS EdCET Syllabus and Exam PatternpavaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti CollisionDokument22 SeitenAnti CollisionJohn Jairo Simanca CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class X Maths 2015 Set 1 PDFDokument5 SeitenCBSE Class X Maths 2015 Set 1 PDFNitish MehraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 4,5 HDE - Cylinderical & Spherical Co-OrdinatesDokument24 SeitenLecture - 4,5 HDE - Cylinderical & Spherical Co-OrdinatesHew LetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Mathematics 6 q3 ST Final PrintingDokument9 Seiten6 Mathematics 6 q3 ST Final PrintingRANDY ALVARONoch keine Bewertungen
- Timoshenko (26 31)Dokument22 SeitenTimoshenko (26 31)Khalid YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Application of IntegrationDokument10 SeitenH2 Application of IntegrationSiya LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios de Repaso para El ExamenDokument20 SeitenEjercicios de Repaso para El ExamenDanielMalpicaCuevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume of A Solid of RevolutionDokument14 SeitenVolume of A Solid of RevolutionChristine Ann MumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 1Dokument8 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Set 1the back benchers showNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0580 s17 QP 43Dokument20 Seiten0580 s17 QP 43yuke kristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Areas and Volumes (MCH - 13) TestDokument2 SeitenSurface Areas and Volumes (MCH - 13) TestradivyapriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HE LAB MANUAL (Repaired) PDFDokument224 SeitenHE LAB MANUAL (Repaired) PDFDarshan DaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse 10 March13 Maths Question Paper With Solution 2023Dokument40 SeitenIcse 10 March13 Maths Question Paper With Solution 2023RIYAN THAKURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aplikasi Intergral Tententu - Volume Benda PutarDokument20 SeitenAplikasi Intergral Tententu - Volume Benda PutarRita SuzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot Math 6 Q3 W8Dokument15 SeitenCot Math 6 Q3 W8Gladys TonogNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 External PressureDokument6 Seiten05 External PressureNitesh SardarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2210 PDFDokument18 SeitenIs 2210 PDFShailendra ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 430 Ope 08-04changedDokument25 Seiten430 Ope 08-04changedNéstor CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 Multiple IntegralsDokument134 SeitenChapter 14 Multiple IntegralsRosalina KeziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 AU521 Descriptive GeometryDokument3 Seiten14 AU521 Descriptive GeometryBrayan BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coupling GuardsDokument10 SeitenCoupling Guards최승원Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arithmetic 1Dokument15 SeitenArithmetic 1arman malikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of InertiaDokument17 SeitenMoment of Inertiasubhankarsarthak1100% (1)
- Preboards 1 MeslDokument4 SeitenPreboards 1 MeslRonaldRajumNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS Course ContentsDokument5 SeitenANSYS Course ContentsVikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge IGCSEDokument60 SeitenCambridge IGCSEV PNoch keine Bewertungen