Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
01 - How Plants Grow
Hochgeladen von
solo_sudhanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
01 - How Plants Grow
Hochgeladen von
solo_sudhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
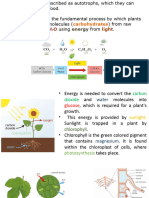
How Plants Grow
The willow tree experiment:
17th Century – Joannes Baptistia – concluded that [water = mass of plant]
Test for Starch:
Starch found as Colourless grains in plant cell. Very difficult to see.
By adding Iodine solution, the starch turns blue-black. This process makes starch visible.
Testing a leaf for starch:
Problem with Normal Leaf
o Cell wall does not allow iodine into the cell
o Green pigment masks colour change
Leaf is treated with boiling water – This makes easy for any solution to enter the cell
Treat with ethanol – Removes green pigment chlorophyll, makes leaf crisp.
If we add iodine solution, the leaf will turn blue-back if starch was available in the leaf.
Destarching a plant:
If a plant is left in darkness for 2 or 3 days, then the plants will become starch free.
Carbon dioxide properties:
Soda lime absorbs carbon dioxide, take it out of air
Sodium hydrogen carbonate solution release carbon dioxide into air.
Experiment to find effect of carbon dioxide:
Two destarched plant were taken
In one plant a small dish of soda lime is added.
In another plant a small dish of sodium hydrogen carbonate is added.
The plants were sealed with transparent plastic bags.
Plants were left in daylight for few hours.
The leaf from each plant is tested for starch.
Result:
o The plant with dish of soda lime did not contain starch.
o The plant with dish of sodium hydrogen carbonate contains starch.
Conclusion:
o Carbon dioxide is required for starch production.
Oxygen Properties:
When a glowing splint is brought near oxygen, the splint re-lighted. This shows that gas contains more oxygen than
normal air.
Experiment to find out oxygen production in plants:
Two samples of Canadian pondweed were setup (Ref figure)
One was put in dark and the other was put in a sunny place.
No gas is collected in the plant which is kept in dark.
The gas collected in sunlight is tested with glowing splint. The splint re-lighted which proves that oxygen is produced
during photosynthesis.
Experiment to find out the use of Light in starch production:
Take a destarched plant.
Cover one leaf with aluminium foil and another leaf with transparent plastic cover.
Leave the setup in sunlight for 4 hours.
The two leaves are then removed and tested for starch.
Result:
o The leaf covered with aluminium did not contain starch.
o The leaf covered with plastic paper contains starch
Conclusion:
o Light is required for starch production.
Energy transfer diagram for photosynthesis:
Light Energy Chlorophyll Stored chemical energy.
Biomass:
Mass of living thing.
Used to monitor the environment.
Any change in total biomass indicates environmental change.
Dry Biomass – Mass of dead living thing in which has no water (Water dried out)
Wet biomass- mass of a living thing which contains water (water not dried out)
Minerals:
Required by plant for survival.
Eg: Potassium phosphate and calcium nitrate.
Dissolves in the water in the soil.
Taken by the plants through roots.
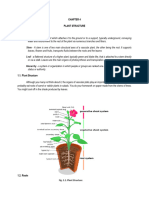
Root Hair:
Projection of root is called root hair.
Tip of the root hair grows out into the spaces between soil particles.
500 root hairs in square centimetre.
Greatly increase the surface area of the root, so that large quantities of water pass through them.
Water in the soil is drawn to replace water that is lost through evaporation.
Plants do not use energy to take in water.
Mineral Salt transportation:
Mineral salt are dissolved in water.
Plants has to use energy to take mineral salt in
Energy is provided by the root, by respiration process. (oxygen is taken in by the plant during respiration process)
Root gets oxygen from the air spaces between the soil particles.
Transporting water tubes:
Cells form columns in the plants. When they die the walls between them breakdown to form tubes.
Xylem – Water conducting tube.
A group of vessels form xylem tissue, which makes vascular bundle.
Xylem runs from root through stem to leaf where they from leaf veins.
The cell structure of leaf:
Epodermis – The upper and lower surface. Made up of one layer thick cell.
Wax coating – The upper layer is coated with Wax to pervert water passing out of the leaf.
Stomata – Small holes in the lower side of the leaf.
Palisade Tissue
o Found below upper epidermis
o Mainly involved in making food.
Spongy mesophyll:
o Found below Palisade Tissue
o Makes food but also provide a surface for evaporation of water.
Veins:
o Vascular bundles made up of xylem tissue.
o Carries water to leaf.
Phloem Tissue:
o Carry away food from leaf.
Test for Water:
Cobalt chloride paper turns pink if tested with water.
Water movement:
Water evaporates from cells in the spongy mesophyll layer.
If water vapour is less outside, then water vapour from the cell will diffuse through stomata.
When water is lost in spongy mesophyll, then it takes more water from xylem tissue in stem and root.
Transpiration:
o The process by which plants lose water from their leaves
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Year 9 Science C1Dokument44 SeitenYear 9 Science C1Ventus TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionDokument14 SeitenIGCSE Biology 4.2 Plant NutritionsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutrition & TransportDokument21 SeitenPlant Nutrition & TransportKim-Elaine Pohatu100% (1)
- Biology Notes PDFDokument79 SeitenBiology Notes PDFSaket GudimellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Science Notes-1Dokument258 SeitenCombined Science Notes-1Premier Car Sales67% (3)
- Major Classification of PlantsDokument19 SeitenMajor Classification of PlantsJhoy Angeles PinlacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic BotanyDokument346 SeitenForensic BotanyHebertnevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- LET Reviewer in BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE Part 11 PDFDokument1 SeiteLET Reviewer in BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE Part 11 PDFaileen a. maputeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is BlockchainDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Blockchainsolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxonomy and ClassificationDokument91 SeitenTaxonomy and ClassificationshakiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To PlantsDokument78 SeitenIntroduction To PlantsAzizah ManzurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant NutritionDokument7 SeitenPlant NutritionVedant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Biological Processes in Plants NoteDokument9 SeitenMain Biological Processes in Plants NoteNicola HerathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114Dokument12 SeitenGrade 08 English Medium Science - Copy (53114onmd2435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Describe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaDokument16 SeitenDescribe & Draw The Plant Cell (Work Sheet) o Nucleus, Cell Wall, Cell Membrane, Chloroplast, Large Vacuole, MitochondriaStudy's AnayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Revision Notes - Photosynthesis and TranspirationDokument1 SeiteBiology Revision Notes - Photosynthesis and TranspirationHusen Ibn IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument23 SeitenChapter 1Cheong JkNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF DocumentDokument28 SeitenPDF Documentkaleb.kgzlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFDokument10 SeitenPlant Nutition - 230204 - 212736 PDFashraf alaqilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preig Point 8 Unit1Dokument30 SeitenPreig Point 8 Unit1myatthirisan2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resumen de Bio - Plant NutritionDokument2 SeitenResumen de Bio - Plant NutritionramirosaracenielguezabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisDokument5 SeitenThis Chapter Looks at PhotosynthesisGiuseppe CondelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUTRITION - PlantDokument8 SeitenNUTRITION - PlantKekeletsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument3 SeitenUntitledKathrynn NaipaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life ProcessesDokument36 SeitenLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDokument15 SeitenPhotosynthesisSultana KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO PRACTICAL 10 Class CBSE IndiaDokument12 SeitenBIO PRACTICAL 10 Class CBSE Indiaroshni.ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument4 SeitenChapter 10Mahir ShahriyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of A LeafDokument82 SeitenStructure of A Leaflevie agacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of RootsDokument10 SeitenFunctions of RootsRufi RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wDokument5 SeitenTopic 6 Revision Notes Prd58wSeve ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)Dokument7 SeitenNutrition in Plants: 2 (G) 2 (L) 6 12 6(s) 2 (G)John Renzo MolinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: BiologyDokument7 SeitenDioxide and Water Using Energy From Sunlight: ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-21 Notes CH: 1 Photosynthesis Grade: 8 Subject: Biologyanish kanthethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28 02 14 The Exchange System in PlantsDokument53 Seiten28 02 14 The Exchange System in Plantsapi-263322904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant NutritionDokument31 SeitenPlant NutritionAbhay BhingradiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 2 Notes CH 6-1Dokument4 SeitenPart 2 Notes CH 6-1Technical AyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap: Life Processes Important Notes (Continued) Class 2Dokument4 SeitenChap: Life Processes Important Notes (Continued) Class 2Technical AyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plants and PhotosynthesisDokument3 SeitenPlants and PhotosynthesisUpeka WeerasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesDokument50 SeitenAlwadi International School Biology Grade-9 6.plant Nutrition NotesMohammed HelmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis and Transpiration - Copy - 031804Dokument13 SeitenPhotosynthesis and Transpiration - Copy - 031804chibamboallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Revision NotesDokument19 SeitenBio Revision NotesRamya SundaresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About PhotossynthesisDokument7 SeitenAll About Photossynthesisapi-341032878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in PlantsDokument5 SeitenTransport in Plantsbaone segaetshoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutrition 2021Dokument8 SeitenPlant Nutrition 2021lowkeydeadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Revision Notes - Photosynthesis and TranspirationDokument1 SeiteBiology Revision Notes - Photosynthesis and TranspirationanggaadildarmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Nutrition NoteDokument5 SeitenPlant Nutrition NoteYolanda JesslinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 BioDokument2 SeitenLab 8 BioDavid HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Class 10Dokument14 SeitenPhotosynthesis Class 10shreya morajkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- مذكرة شرح الوحدة الرابعةDokument9 Seitenمذكرة شرح الوحدة الرابعةmoatazosmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 - Unit 6 - Presentation - Lesson 6Dokument28 SeitenYear 8 - Unit 6 - Presentation - Lesson 6zahra.abbas140110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 PhotosynthesisDokument99 SeitenChapter 6 Photosynthesisjzdf2d9nnvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Lab 3Dokument7 SeitenGroup Lab 3Trần Xuân QuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Dokument24 SeitenUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6,8 BiologyDokument4 SeitenChapter 6,8 BiologyParshvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhotosynthesisDokument4 SeitenPhotosynthesisananya workNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Transport in PlantDokument15 SeitenUnit 2 - Transport in PlantAbdelrahman GhanimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Unit 1Dokument14 SeitenScience Unit 1SadakatMalihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2979 - 20220918 - 085545 - 2728 - Photosynthesis and Gaining Water and MineralsDokument25 Seiten2979 - 20220918 - 085545 - 2728 - Photosynthesis and Gaining Water and MineralscorporolrexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Unit 6Dokument2 SeitenBiology Unit 6Emma FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant NutritionDokument9 SeitenPlant Nutritionakshai.ar13Noch keine Bewertungen
- 07 PlantPhysiology ReadingDokument4 Seiten07 PlantPhysiology ReadingMahaletchumyKavidasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument5 SeitenChapter 2Hend HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fm3 Bio NotesDokument42 SeitenFm3 Bio Notesthankyoubeast71Noch keine Bewertungen
- C4 - Directive Principles of State PolicyDokument1 SeiteC4 - Directive Principles of State Policysolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Ad Test Paper 1 - 7007 PDFDokument24 SeitenClass 7 Ad Test Paper 1 - 7007 PDFsolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 7 Ad Test Paper 1 - 7000 PDFDokument24 SeitenClass 7 Ad Test Paper 1 - 7000 PDFsolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology Forecasting and Assessment - 1Dokument4 SeitenTechnology Forecasting and Assessment - 1solo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Organisation BehaviourDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To Organisation Behavioursolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics AssignmentDokument6 SeitenEconomics Assignmentsolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To International BusinessDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To International Businesssolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Kingdoms of Life: Lesson OneDokument48 SeitenChapter 2: Kingdoms of Life: Lesson OneIrene Miranda FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)Dokument8 SeitenActivity 1 - The Plant Kingdom (6th Grade)David JustinicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Biology Week 1 Lesson 2 Worksheet 2 and SolutionsDokument3 SeitenGrade 10 Biology Week 1 Lesson 2 Worksheet 2 and SolutionsJamie LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateDokument6 SeitenScience Form 3 Chapter 3: Name: Class: DateTeng Pei ErNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSSM Form 5 Biology Textbook-84-105Dokument22 SeitenKSSM Form 5 Biology Textbook-84-105Fatin Liyana AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Water Relations - Absorption Transport and Control MechanismsDokument29 SeitenPlant Water Relations - Absorption Transport and Control MechanismsJacoSkinfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vascular PlantDokument1 SeiteVascular PlantPRINTDESK by DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 BotanyDokument10 SeitenLesson 1 BotanyKaizenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Chapter 9 Plant DiversityDokument28 SeitenLife Chapter 9 Plant DiversityvaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant CellDokument4 SeitenPlant CellKenneth FungoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument5 SeitenChapter 4Lebanan Aprille MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyDokument13 SeitenActivity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyHerlyn SabulaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Vascular and NonDokument4 SeitenDifference Between Vascular and NonJanine ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 3:plant ClassificationDokument5 SeitenBIO 3:plant ClassificationTers MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 9 10Dokument40 SeitenModule 9 10kevoarcher093Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BotanyDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To BotanybagongonjeremiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 171 Plants - Fungi and Colonization of LandDokument15 Seiten171 Plants - Fungi and Colonization of LandJuwita RahmaningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying PlantsDokument2 SeitenClassifying PlantsJanelle BerkemeierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Plant DiversityDokument100 SeitenLecture 9 Plant DiversityDon TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDokument2 SeitenDifference Between Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDat HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Class ScienceDokument10 Seiten7th Class ScienceM Saadat SaeediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire SampleDokument16 SeitenQuestionnaire SamplerhonnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seedless PlantsDokument52 SeitenSeedless PlantsEdnin Francisco100% (1)
- Biology-WPS OfficeDokument2 SeitenBiology-WPS OfficeLyca FelicisimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in PlantsDokument14 SeitenTransport in PlantsMuhammad Faizan KaleemNoch keine Bewertungen