Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
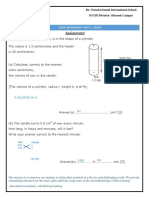
16.wireless Mouse PDF
Hochgeladen von
naglocOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
16.wireless Mouse PDF
Hochgeladen von
naglocCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
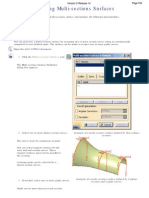
Wireless Mouse
Surfaces
Design & Communication Graphics
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ....................................................................................................................... 1
Introduction …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………2
Mouse Body….………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………3
Edge Cut …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….12
Centre Cut..………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..14
Wheel Opening………………………………………………………………………………..…………………………………15
Wheel Location…………………………………………………………………………………………………..………………16
Laser…..………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………18
Wheel…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………18
Mouse Mat………………………………………………………………………………………..……………………………….20
Assembly…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….21
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 1
Wireless Mouse
Introduction
Surface modelling is clearly a lot more work than solid modelling. Surface modelling
forces you to work face by face and faces must fit together. These action are all performed
automatically in solid modelling. Where Surface techniques become beneficial is in a
situations where solid modelling become clumsy or inefficient, or when a given modelling
task is simply impossible with solids. The focus of this exercise is to add to the skills based
on the advanced surface modelling materials and explore further the functionality of
surfacing tools.
Learning Intentions
In addition to the normal command the following commands will be
used.
o Splines
o Projected Curves
o Lofted Surfaces
o Filled Surfaces
o Knit Surfaces
o 3D Sketch Convert Entity
o Create Solid
o Dome
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 2
Mouse Body
The part is symmetrical with respect to the Right reference
plane. Open a new part and name it Mouse. Select the Top
reference plane and sketch a rectangle as shown. Exit the sketch
and rename the sketch Reference Dim. This sketch will help you
sketch the free-form splines approximately the correct size.
Bottom Edge
Open a new sketch on the Top reference plane, and sketch a
5-point spline as shown to represent the bottom edge of the
mouse. Draw only half of the outline. Make sure that the
endpoints of the spline are Coincident with the corners of the
rectangle in the Reference Dim sketch.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 3
Add Relations
Use relations on the handles at the ends of the spline to create tangency across the
line of symmetry. Add Horizontal relations to the Spline handles
Tangent Relation
To make the spline tangent to the rectangle, sketch a short construction line Tangent
to the spline itself, not to a handle or a spline point. Add a Vertical relation to the
construction line. Make the Endpoint of the construction line Coincident with the
rectangle.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 4
Adjusting the shape of the spline
In the Reference Dim Sketch Adjust the shape of the Spline
by dragging the interpolant points. Select fully define the
Spline. Exit the sketch and rename the sketch Base Edge
Sketch top profile of the parting line.
Open a new sketch on the Top reference plane. Sketch a
spline which lies slightly outside the Base Edge sketch. The
endpoints of this spline should have Vertical relation with
respect Base Edge sketch and should be dimensioned as
shown. Add relations to the end handles as you did in the
previous sketch. Notice the use of Show Inflection Points
on the spline to help to define the area of slightly reversed
convexity. Exit the sketch and name it Profile Top
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 5
Sketch the side profile of the parting line.
Open a new sketch on the Right reference plane, and draw a spline shown below.
The ends of the spline should have Vertical relations with respect to the
Endpoints of the spline in the Profile top. Add a Horizontal relation to the handle at
the end of the spline furthest from the Origin. Exit the sketch and name it Profile
Side.
Project Curve
Search for the Project Curve command
and drag the command into the sketch
toolbar. Use the Sketch onto Sketch
Option. Select the Profile Side and
Profile Top. Rename the projected curve
Projected Curve
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 6
Create loft profile sketch.
Open a new sketch on the Right reference plane, and sketch a pair of arcs as shown.
The arc near the Origin should be tangent to a line 15 degrees from horizontal and
the other arc should simply have a radius of 10 mm.
Both arcs should be Coincident to the ends of the Base Edge sketch and be pierced
by the Projected Curve.
Note
Using the Selection Manager, multiple, disjoint profiles in a single sketch are
manageable and valid.
Create third loft profile.
Create a new plane parallel to the Front reference
plane through a spline point from the Base Edge
sketch. Rename this plane Mid Plane.
Mid Profile.
Open a new sketch on the Mid Plane reference plane.
Sketch an arc. Add a Coincident relation between the bottom
endpoint and the spline point the plane was created from.
Add a Pierce relation between the top endpoint and the
Projected Curve. Draw a construction line between the
endpoints of the arc. Using the Smart Dimension tool, select
the construction line, and then hold down the Shift Key and
select the Arc. This will give a dimension as if the Min arc
condition in the dimension properties was used. 1.25 mm. Exit
the sketch and name it Mid Profile
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 7
Create the Surface Loft.
Use the Selection Manager to select open profiles at the ends.
The Mid Profile sketch will not require the Selection Manager.
For Guide Curves, select Projected Curve and Bottom Edge
Edge. For Start/End Constraints, use Normal to Profile for both
ends so that it is smooth across the plane of symmetry.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 8
Top curve of the mouse.
Open a sketch on the Right reference
plane and sketch a partial ellipse at an
angle. Sketch a construction line from the
centre of the ellipse to the end of the
minor axis to control the angle. Add Pierce
relations between the endpoints of the
ellipse and the Projected Curve Add a
Coincident relation between the end of
the major axis and the rightmost endpoint
of the ellipse.
Extrude a reference surface.
Filled Surface requires a reference
surface to define the tangency condition
along the top. Extrude the partial ellipse
sketch away from the rest of the model.
The distance doesn’t matter.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 9
Filled surface
Click the Filled Surface. Select the Edge of the extruded surface and the edge of the
lofted surface. Use the end condition Tangent for the extruded surface and Contact
for the lofted surface. Notice that with Optimize surface selected, the surface again
becomes degenerate. This is because the Optimize surface option applies a
simplified surface patch that is similar to a lofted surface.
Clear Optimize surface and you will get a better, four-sided patch. Click OK.
Hide the Extruded Surface
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 10
Mirror the surface bodies.
Click Mirror on the Features toolbar. Select the Right reference
plane as the mirror plane. In the Bodies to Mirror selection list,
select the lofted and filled surfaces to be mirrored Uncheck Knit
surfaces. Leaving the Knit surfaces option cleared this way there
is no confusion about what will or will not knit by the Mirror
feature
Planar surface.
Select the edges of the lofted surface and mirrored loft on
the bottom and create a planar surface.
Knit
Knit the five surface bodies into a solid Save the Part Select
Try to form Solid
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 11
Edge Cut (Extrude Cut)
Select the Right plane and draw a rectangle
on the Left hand side to the dimensions
shown exit the sketch.
Convert Sketch Top Plane
Select the top plane and use the
convert entity command to the top
plane
3D Sketch Convert Entity
Select 3D Sketch and use the Convert Entity
command for the curve.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 12
Edge Cut
Select the Swept Cut command Select the
Profile Path and Guide Curve
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 13
Centre Cut
Select the Right plane and
use the Convert Entity
sketch command and trim
the line to the dimension
shown.
Note: A vertical construction line at the centre.
Use the Section View command to assist in the create the centre line
Create a Plane on the end of the trimmed sketch.
Sketch a square to the dimensions shown
Select the Swept Cut to create the mid Centre Cut
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 14
Wheel Opening
Select the Right plane and create sketch
to the dimensions shown
Plane Creation
Create a plane at the end of the
construction line
Straight Slot
Use the Straight Slot command to create a sketch to the dimension shown and
Extrude 21mm
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 15
Fillet 5mm
Create a fillet 5mm
Wheel Location
Select the Right plane and reference the
Midpoint of the wheel slot create a line 12.5mm and a
circle radius 2mm. Use the Extrude Cut command and
select midpoint extrude distance of 14 mm
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 16
Base Pads
Select the base of the mouse body and create
the location of the mouse pads to the
dimension given. Extrude the four pads to a
dimension of .25mm. Select the Extrude Cut
command to create the laser opening
dimension 4mm
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 17
Laser (New Part)
Sketch a circle of 2mm radius extrude to a distance of
1mm. Use the Dome command to create the top of the
laser
Wheel Hub (New Part)
Create the sketch to the dimensions below and revolve to create the
wheel hub. Create a circle of 2mm on the mid plane and use the
Mid Plane End Condition to a distance of 14mm
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 18
Wheel Hub Design
Create a sketch to the dimensions shown and
Extrude Cut to depth of 5mm. Create an Axis and
using the Circle Pattern command create the
design with the number of instances equal to 4.
Wheel (New Part)
Create the sketch and using the
Revolve Command to create the wheel
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 19
Mouse Mat
Create a rectangle 200mm by 160 mm and
Extrude to a distance of 5mm and fillet the
edges. Apply Decals to the mouse mat.
Assembly
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 20
Apply Appropriate Appearances to all parts. Create an assembly.
DCG - Wireless Mouse Page 21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)Von EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)Noch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Tesla Roadster Ebook 03Dokument30 SeitenSolidWorks Tesla Roadster Ebook 03ivan abreguNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Tesla Roadster Ebook 02Dokument36 SeitenSolidWorks Tesla Roadster Ebook 02ivan abreguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keyboard Button.: Surface ModellingDokument15 SeitenKeyboard Button.: Surface Modellingapi-189878770Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1: Mouse Model: Design IntentDokument26 SeitenExercise 1: Mouse Model: Design IntentDaniel RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assemblies AeroplaneDokument23 SeitenAssemblies AeroplaneEdison BreggerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3 PDFDokument20 SeitenExercise 3 PDFMarko MillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Aston Martin Ebook 03 WorkshopDokument34 SeitenSolidWorks Aston Martin Ebook 03 WorkshopMohamed AlgharibNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolidWorks Aston Martin Ebook 02Dokument31 SeitenSolidWorks Aston Martin Ebook 02Aan WidyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Horn SolidWorksDokument11 SeitenShoe Horn SolidWorksnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & CAD-II Lab (MEEN-3238)Dokument29 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Machine Design & CAD-II Lab (MEEN-3238)Sarmad HafeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tesla Roadster Ebook 2 RoofDokument35 SeitenTesla Roadster Ebook 2 RoofTECH TUBENoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 12: StarshipDokument13 SeitenExercise 12: StarshipAbd Elrahman HamdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Model Shoe Horn Sketch PicturesDokument10 SeitenSurface Model Shoe Horn Sketch PicturesnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybride - Modeling - Desktop FanDokument19 SeitenHybride - Modeling - Desktop FanFaisal AbdulazizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3 PDFDokument20 SeitenExercise 3 PDFSameer AmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 2 EngDokument12 SeitenCourse 2 Engkrishnaram1233Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual: Cad 3DDokument25 SeitenLab Manual: Cad 3DnaveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Solidworks Software Lesson 9: Peters Township High School Mr. Burns & Mr. Walsh Cadd OnlineDokument30 SeitenTeaching Solidworks Software Lesson 9: Peters Township High School Mr. Burns & Mr. Walsh Cadd OnlineHuntemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unigraphics NX8 - SketchingDokument242 SeitenUnigraphics NX8 - SketchingBoy Doland75% (4)
- Blend Target Bypass RingDokument5 SeitenBlend Target Bypass RingPaulo MarausNoch keine Bewertungen
- VXmodel - Tutorial 1 - Scan-to-CAD 1 - ENDokument25 SeitenVXmodel - Tutorial 1 - Scan-to-CAD 1 - ENshahnawaz875Noch keine Bewertungen
- GampaDokument21 SeitenGampaALEX MPELLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Solid Modelling Using: Inventor 7Dokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Solid Modelling Using: Inventor 7George SmyrnakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginner SolidWorks - USB KeyDokument24 SeitenBeginner SolidWorks - USB KeyKarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Surfaces - Plastic Medicine Spoon PDFDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Surfaces - Plastic Medicine Spoon PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Whistle PDFDokument6 Seiten06 Whistle PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens NX Helmet Exercise Guide: Version(s) Supported: NX 12.XDokument38 SeitenSiemens NX Helmet Exercise Guide: Version(s) Supported: NX 12.XMarcelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sphere StarccmDokument25 SeitenTutorial Sphere StarccmbabmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cavity Block Exercise: Prerequisite KnowledgeDokument8 SeitenCavity Block Exercise: Prerequisite KnowledgeSaish VerenkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Notes and Exercises Advanced 02Dokument223 Seiten3D Notes and Exercises Advanced 02VENKATRAMAN A RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Adaptive Swept Surfaces PDFDokument7 SeitenCreating Adaptive Swept Surfaces PDFBorralla CinzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Christopher F. SikoraDokument120 SeitenBy Christopher F. SikoraZakirUllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 5: Modeling A Rocker Device (Using Sketch Curves) : PrerequisitesDokument20 SeitenProject 5: Modeling A Rocker Device (Using Sketch Curves) : PrerequisitessamihakhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drone Handout Up To Session 3Dokument43 SeitenDrone Handout Up To Session 3Krishnanunni Karayil UllasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad 2D Tips: Circular ViewportDokument12 SeitenAutocad 2D Tips: Circular ViewportDanny ArimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Solidworks Basics: Materials Tech. WoodDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Solidworks Basics: Materials Tech. WoodKarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Activity 2 - Sketching and Reference Geometry - SDSMacaraegDokument21 SeitenLaboratory Activity 2 - Sketching and Reference Geometry - SDSMacaraegDaniel S. MacaraegNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProfilesDokument5 SeitenProfilesHOD FOE Civil EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 210 Mechanical Engineering Drawing & Graphics: Reference Planes Vertical Bearing SupportDokument20 SeitenME 210 Mechanical Engineering Drawing & Graphics: Reference Planes Vertical Bearing SupportEbrahim HanashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect6 Rhino Arch ModelingDokument10 SeitenLect6 Rhino Arch ModelingDavid lemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Sections Surfaces PDFDokument11 SeitenMulti-Sections Surfaces PDFBorralla CinzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4inventor 201 Part 3Dokument12 Seiten4inventor 201 Part 3empty_shake5319Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testdrive SeDokument214 SeitenTestdrive Sevul1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Google Sketchup Tutorial PacketDokument11 SeitenGoogle Sketchup Tutorial PacketJhon VelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autodesk - Training - Using SplinesDokument18 SeitenAutodesk - Training - Using Splinescristianalonso3259Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practica 13Dokument23 SeitenPractica 13OnePiece ZoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- VXmodel - Tutorial 2 - Scan-to-CAD 2 - ENDokument15 SeitenVXmodel - Tutorial 2 - Scan-to-CAD 2 - ENshahnawaz875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Part ModelDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Part Modelsmg26thmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 罗技鼠标 犀牛建模教程 英文Dokument15 Seiten罗技鼠标 犀牛建模教程 英文Thomas WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucf - Solidworks IIIDokument60 SeitenUcf - Solidworks IIIameg15100% (1)
- Solid WorksDokument65 SeitenSolid WorkssumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 SFC Module07ExercisesDokument14 Seiten0 SFC Module07ExercisesDaniel RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Design TechniquesDokument23 SeitenAdvanced Design Techniquesapi-3748063Noch keine Bewertungen
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingVon EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)Von EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flower Pot - Circular Patterna PDFDokument20 SeitenFlower Pot - Circular Patterna PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Model Shoe Horn Sketch PicturesDokument10 SeitenSurface Model Shoe Horn Sketch PicturesnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.int Solidworks Spatula Booklet PDFDokument24 Seiten15.int Solidworks Spatula Booklet PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Horn SolidWorksDokument11 SeitenShoe Horn SolidWorksnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Surfaces - Plastic Medicine Spoon PDFDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Surfaces - Plastic Medicine Spoon PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseball Cap PDFDokument13 SeitenBaseball Cap PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Revolve - A Glass PDFDokument11 SeitenIntro To Revolve - A Glass PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Sweep - Part (A) Allen Keys PDFDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Sweep - Part (A) Allen Keys PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Surfaces - Keyboard Button PDFDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Surfaces - Keyboard Button PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculator PDFDokument6 SeitenCalculator PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07.chocolate Bar Linear Pattern PDFDokument9 Seiten07.chocolate Bar Linear Pattern PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- What'S New in Solidworks 2013: View SelectorDokument1 SeiteWhat'S New in Solidworks 2013: View SelectornaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08.lego Block PDFDokument22 Seiten08.lego Block PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03.digital Camera PDFDokument15 Seiten03.digital Camera PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Guidelines 80810Dokument4 SeitenLaser Guidelines 80810PepabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desk Tidy Exercise: ExtrudeDokument9 SeitenDesk Tidy Exercise: Extrudeapi-189878770Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04.model House Extrude PDFDokument12 Seiten04.model House Extrude PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.advanced SolidWorks CPD-Surface Modelling PDFDokument43 Seiten17.advanced SolidWorks CPD-Surface Modelling PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Whistle PDFDokument6 Seiten06 Whistle PDFnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Parametric Modeling SW 2009 Memo BlockDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To Parametric Modeling SW 2009 Memo Blockapi-189878770Noch keine Bewertungen
- My Construction PortfolioDokument1 SeiteMy Construction PortfolionaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dvhu&Xwwlqj XlgholqhvDokument4 SeitenDvhu&Xwwlqj XlgholqhvnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enable 3D ViewDokument1 SeiteEnable 3D ViewnaglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digitalfab-Tutorial-2 Print From AutoCADDokument2 SeitenDigitalfab-Tutorial-2 Print From AutoCADMridul HakeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 24Dokument42 SeitenSection 24naglocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseDokument30 SeitenBig Data Analytics & Technologies: HbaseWong pi wenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop 2 Electrical Installations Single PhaseDokument3 SeitenWorkshop 2 Electrical Installations Single PhaseDIAN NUR AIN BINTI ABD RAHIM A20MJ0019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dover Artificial Lift - Hydraulic Lift Jet Pump BrochureDokument8 SeitenDover Artificial Lift - Hydraulic Lift Jet Pump BrochurePedro Antonio Mejia Suarez100% (1)
- MX3Dokument154 SeitenMX3Dung Nguyen0% (1)
- Faculty: Geology Exploration Specialty: Geology Engineering Group: 123.6 Student: Asef Sadiqov Teacher: Afet Israfilova Theme: The EarthDokument16 SeitenFaculty: Geology Exploration Specialty: Geology Engineering Group: 123.6 Student: Asef Sadiqov Teacher: Afet Israfilova Theme: The EarthKenan RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierDokument3 SeitenClass - B Complementary Symmetry Power AmplifierAnonymous SH0A20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Movements 06-26-2019 - Full ScoreDokument5 SeitenAir Movements 06-26-2019 - Full ScoreMichael CrawfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Big TEGO. Products Services Data Sheets-75-150-16!76!31-61Dokument31 SeitenThe Big TEGO. Products Services Data Sheets-75-150-16!76!31-61DWI RAHMASARI FATMAWATINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 AssignmentDokument6 SeitenChapter 6 AssignmentRohit RajeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Report Guideline EEE250Dokument8 SeitenPractical Report Guideline EEE250MOHD ASYRAAF BIN SAIDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- 145Kv Sf6 Circuit Breaker Type Ltb145D1/B List of Drawings: Description Document Reference NO. SRDokument13 Seiten145Kv Sf6 Circuit Breaker Type Ltb145D1/B List of Drawings: Description Document Reference NO. SRneeraj100% (1)
- Ug CR RPTSTDDokument1.014 SeitenUg CR RPTSTDViji BanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research Lecture 4aDokument26 SeitenNursing Research Lecture 4asyamsul anwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesDokument38 SeitenCHMT 2009 Week 5 Coal PropertiesTiisetso MokwaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathDokument2 SeitenMathWessam ElmongyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomechanic of Foot PDFDokument8 SeitenBiomechanic of Foot PDFMichealowen BabygoalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel NotesDokument9 SeitenExcel NotesAhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL-PRF-85704C Turbin CompressorDokument31 SeitenMIL-PRF-85704C Turbin CompressordesosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTL8139D DataSheetDokument60 SeitenRTL8139D DataSheetRakesh NettemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 WholeDokument344 Seiten02 WholeedithgclemonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Manual HEIDENHAIN Conversational Format ITNC 530Dokument747 SeitenUser's Manual HEIDENHAIN Conversational Format ITNC 530Mohamed Essam Mohamed100% (2)
- فيزياء لغات ثانوية عامة أنجليزى-webDokument462 Seitenفيزياء لغات ثانوية عامة أنجليزى-webMohamed RayanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-7 - Line CodingDokument14 SeitenLecture-7 - Line CodingFahim Hasan AlifNoch keine Bewertungen
- V. Activities: A. Directions: Do The Activity Below. (20 PTS.) Note: Work On This OfflineDokument7 SeitenV. Activities: A. Directions: Do The Activity Below. (20 PTS.) Note: Work On This OfflineKeith Neomi CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infinera Ds Isfp Timedivision Multiplexing ModulesDokument3 SeitenInfinera Ds Isfp Timedivision Multiplexing ModulesAnonymous bpf0OZSd9Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADA Practical File: Kartik KatariaDokument34 SeitenADA Practical File: Kartik KatariaKilari TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism NotesDokument14 SeitenMagnetism Notesapi-277818647Noch keine Bewertungen
- S Energy SN 72 Cell Series Solar Panel Datasheet V 01Dokument2 SeitenS Energy SN 72 Cell Series Solar Panel Datasheet V 01infercomNoch keine Bewertungen
- X500Dokument3 SeitenX500yu3zaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abr Sinai Onshore Gas Pipeline PDFDokument42 SeitenAbr Sinai Onshore Gas Pipeline PDFhamza2085100% (1)