Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Gravitational and Kinetic Energies
Hochgeladen von
DanKimberleyCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Gravitational and Kinetic Energies
Hochgeladen von
DanKimberleyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
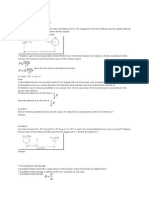
Gravitational potential and kinetic energies
GPE is the energy an object has due to its position in a gravitational field. KE is the energy an object
has due to its movement. When objects rise or fall, GPE is converted into KE and visa versa.
Gravitational Potential Energy
GPE is calculated using the equation:
GPE = mass (kg) * g (Nkg-1) * height (m)
Usually, GPE is considered as a change caused by a change in height, thus:
∆𝐸𝑝 = 𝑚𝑔∆ℎ
e.g. A brick of mass 2.2kg is lifted by 1.24m therefore GPE = 2.2*9.81*1.24 = 26.98J
Kinetic Energy
KE is calculated using the equation:
KE = 0.5 * mass(kg) * speed2(m2s-2)
1
𝐸𝑘 = 𝑚𝑣 2
2
e.g. A jet has a cruising speed of 900km/h and a flight mass of 400 tonnes. It’s KE can be calculated
as such:
Conversion between KE and GPE
Due to the principle of conservation of energy, we can never lose or gain energy out of nowhere.
This means one is always converted to the other:
By dividing out the mass, how fast an object will be travelling after falling a certain distance from
rest can be calculated:
𝑣 = √2𝑔∆ℎ
Or how high an object could rise if projected upwards at a certain speed:
𝑣2
∆ℎ =
2𝑔
e.g.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grade 8 - KE & PEDokument43 SeitenGrade 8 - KE & PEThea Cassius FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Stored EnergiesDokument92 SeitenLesson 4 Stored EnergiesareebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Chapter 6.4 Energy CalculationsDokument16 SeitenPhysics Chapter 6.4 Energy CalculationsSei loriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 8 Understanding EnergyDokument27 SeitenScience 8 Understanding EnergyFirst name Last nameNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkDokument6 SeitenWorkjoei ArqueroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyDokument20 SeitenLesson 1 - Kinetic and Gravitational Potential EnergyMouli MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Gravitational Potential Energy StoresDokument16 Seiten1 Gravitational Potential Energy Storesd.gwynne4740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics WorkoutsDokument14 SeitenPhysics Workoutsoziyan alemnewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Work Energy and PowerDokument31 SeitenChapter 2 Work Energy and PowerGimarino Lahra MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SummaryDokument4 SeitenPhysics SummarymiauneitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Work and PowerDokument18 SeitenEnergy, Work and PowerChristian AbordoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Power and EnergyDokument4 SeitenWork, Power and EnergyJeya Plays YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy PowerDokument68 SeitenWork Energy PowerSky Drive100% (1)
- Roller Coaster ProjectDokument35 SeitenRoller Coaster ProjectVanitta RangsitananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 Energy NotesDokument17 SeitenYear 8 Energy Notescyuzuzo1912Noch keine Bewertungen
- P6 Part 5Dokument10 SeitenP6 Part 5Kenneth DuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 Work and EnergyDokument7 SeitenLesson 5 Work and EnergyAnna kris DulfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Work Energy PowerDokument7 SeitenModule 4 Work Energy PowerGreen BrainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and PowerDokument21 SeitenWork, Energy and Powerdela2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energy (Physics)Dokument90 SeitenEnergy (Physics)Christina SterlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strand 2.1 - Energy (Yr 12 Phy)Dokument12 SeitenStrand 2.1 - Energy (Yr 12 Phy)Sumeet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy and PowerDokument42 SeitenWork Energy and PowerKryschan CaditeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument4 SeitenEnergyjessa ferrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 W1 Asynchronous Tasks AND NOTESDokument5 SeitenQ4 W1 Asynchronous Tasks AND NOTESsy.valNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 GravitationDokument71 SeitenChapter 7 GravitationWendy TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Energy & The Work Energy TheoremDokument1 SeiteKinetic Energy & The Work Energy Theoremferas.barbar06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSDokument3 SeitenKinetic Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy - HONORSMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument29 SeitenChapter 5Muhamad DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes Work Done, Energy, PowerDokument5 SeitenPhysics Notes Work Done, Energy, PowerJennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Problems: Potential EnergyDokument18 SeitenSample Problems: Potential EnergyJet TejadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Total Mechanical EnergyDokument11 SeitenKinetic Total Mechanical EnergyAriel KedemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - KE and GPEDokument14 SeitenLesson 2 - KE and GPETalha HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics SummaryDokument145 SeitenPhysics SummaryAnurag PattekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potential Energy Problems PDFDokument3 SeitenPotential Energy Problems PDFJiyan LitohonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic EnergyDokument6 SeitenKinetic EnergyMary Ann MalaguitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Power and EnergyDokument33 SeitenWork Power and EnergyYfel UndagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work and Energy Lesson PlanDokument20 SeitenWork and Energy Lesson PlanNhoj Kram AlitnacnosallivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Energy ESTDokument32 SeitenChapter 3 - Energy ESTsamuel.moryoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy MYP3Dokument68 SeitenEnergy MYP3Soha RamadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Is Defined As The Capacity To Do Work or Transfer Heat. For Us To Understand TheDokument11 SeitenEnergy Is Defined As The Capacity To Do Work or Transfer Heat. For Us To Understand ThemayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo q6Dokument1 SeiteThermo q6Single UserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guía PhysicsDokument31 SeitenGuía PhysicsJojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Power and Energy PDFDokument9 SeitenWork Power and Energy PDFaratan jrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gun Powder RocketsDokument3 SeitenGun Powder RocketsWagner OñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes by Derek LauDokument110 SeitenPhysics Notes by Derek LauLynn BlackNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORK and EnergyDokument7 SeitenWORK and EnergyLeonard NdlovuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Science 1Dokument8 Seiten10th Science 1Daulatrao ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Level Chapter 5 NotesDokument17 SeitenAs Level Chapter 5 NotesVivehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited Today... ENPHYS Module 2 Work Energy and Power 1Dokument8 SeitenEdited Today... ENPHYS Module 2 Work Energy and Power 1Ashlie JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanicalenergy 140323133410 Phpapp02Dokument14 SeitenMechanicalenergy 140323133410 Phpapp02levie agacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Physics - Energy, Work, and PowerDokument28 SeitenGrade 12 Physics - Energy, Work, and PowerJabez CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work and EnergyDokument6 SeitenWork and EnergyThetMon HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeDokument10 SeitenRotational Kinetic Energy: Learning OutcomeBouatake HedstromNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Calculate Kinetic EnergyDokument22 SeitenHow To Calculate Kinetic EnergyMerlinda Aquino Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes - Space: "The Weight of An Object Is The Force of Gravity Acting On It"Dokument7 SeitenPhysics Notes - Space: "The Weight of An Object Is The Force of Gravity Acting On It"Jonathan ZhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Power and EnergyDokument9 SeitenWork Power and Energyhimadri.banerji60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and PowerDokument23 SeitenWork, Energy and Powervibgyorislight100% (1)
- General Physics ReviewerDokument15 SeitenGeneral Physics ReviewerArviNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Festivals and FastingDokument4 SeitenOn Festivals and FastingOrangeGuitaristNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Problem of EvilDokument1 SeiteThe Problem of EvilDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pascal's WagerDokument1 SeitePascal's WagerDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kalam Cosmological ArgumentDokument1 SeiteKalam Cosmological ArgumentDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indoctrination of ChildrenDokument1 SeiteIndoctrination of ChildrenDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDokument1 SeiteLord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDokument2 SeitenWaking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDokument1 SeiteCore Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves 2Dokument1 SeiteWaves 2DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- StamitzDokument2 SeitenStamitzDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force Against Velocity: Circular MotionDokument1 SeiteForce Against Velocity: Circular MotionDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDokument1 SeitePaper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Errors and UncertaintyDokument1 SeiteErrors and UncertaintyDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding ForcesDokument1 SeiteAdding ForcesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDokument1 SeiteGravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 9 Take 2Dokument3 SeitenPractical 9 Take 2DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding ForcesDokument2 SeitenAdding ForcesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spreadsheet 5Dokument3 SeitenSpreadsheet 5DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding ForcesDokument2 SeitenAdding ForcesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gcse WavesDokument1 SeiteGcse WavesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluorescent TubesDokument1 SeiteFluorescent TubesDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 9Dokument2 SeitenPractical 9DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDokument3 SeitenCore Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Practical 9Dokument4 SeitenCore Practical 9DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Practical 5Dokument3 SeitenCore Practical 5DanKimberley100% (1)
- Core Practical 4Dokument4 SeitenCore Practical 4DanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDokument2 SeitenSemiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power in Electric CircuitsDokument1 SeitePower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power in Electric CircuitsDokument4 SeitenPower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Movement: Laminar FlowDokument2 SeitenFluid Movement: Laminar FlowDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen