Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction to Microprocessors
Hochgeladen von
Harshit Goyal0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten3 SeitenA computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads binary instructions from its memory, accepts binary data as input,processes the data according to those instructions and provides results as output. It is a programmable device made up of both hardware and software. A computer that is designed using a microprocessor as its CPU is known as a microcomputer.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Introduction
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenA computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads binary instructions from its memory, accepts binary data as input,processes the data according to those instructions and provides results as output. It is a programmable device made up of both hardware and software. A computer that is designed using a microprocessor as its CPU is known as a microcomputer.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
36 Ansichten3 SeitenIntroduction to Microprocessors
Hochgeladen von
Harshit GoyalA computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads binary instructions from its memory, accepts binary data as input,processes the data according to those instructions and provides results as output. It is a programmable device made up of both hardware and software. A computer that is designed using a microprocessor as its CPU is known as a microcomputer.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
INTRODUCTION
Computer: A computer is a multipurpose programmable machine that reads
binary instructions from its memory , accepts binary data as input ,processes
the data according to those instructions and provides results as output. It is a
programmable device made up of both hardware and software. The various
components of the computer are called hardware. A set of instructions written
for the computer to solve a specific task is called program and collection of
programs is called software .
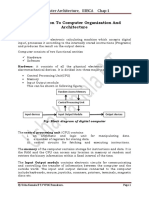
The computer hardware consists of four main components. The central
processing unit which acts as computer’s brain. Input unit through which
program and data can be entered to computer, output unit on which the
results of the computations can be displayed. Memory in which data and
program are stored.
Fig 1. Block diagram of a microcomputer
A computer that is designed using a microprocessor as its CPU , is known as a
microcomputer.
Microprocessor or ‘Computer on Chip’ first became a commercial reality in
1971 with the introduction of the 4 bit 4004 by Intel. A byproduct of
Microprocessor development was Microcontroller. The same fabrication
technology and programming concept that make the general purpose
microprocessor also yielded the Microcontroller.
Microprocessors
A microprocessor is a general purpose digital computer central processing unit
(CPU). Although known as a ‘Computer on Chip’ the Microprocessor in no
sense a complete digital computer. Block diagram of a Microprocessor CPU
which contains ALU; Program counter (PC), a stack pointer (SP) ,some working
registers , a clock timing circuit and interrupt circuit s is shown in the following
figure
Arithmetic and Logic
Unit
Accumulator
Working Register
Program Counter Stack Pointer
Clock Circuit Interrupt Circuits
Fig.2.Block Diagram of a Microprocessor
The microprocessor can be viewed as a programmable logic device that can
be used to control processes or to turn on /off devices. On the other hand
microprocessor can be viewed as a data processing unit or a computing unit
of a computer. The microprocessor is a programmable integrated device that
has computing and decision making capability similar to that of the CPU od a
computer. A microprocessor is a multipurpose, programmable, clock-driven,
register based electronic device that reads binary instructions from a storage
device called memory; accepts binary data as inputs and process data
according to those instructions, and provide results as output.
To make a computer microcomputer one must add memory usually RAM
and ROM, memory decoders , an oscillator and a number of Input ,Output
devices such as serial and parallel ports. In addition special purpose devices
such as interrupt handler and counters may be added to relieve the CPU from
time consuming counting or timing cores. When the Microcomputer is
equipped with mass storage devices , I/O peripherals such as a key board and a
display CRT it yields a small computer that can be applied to a range of general
purpose applications.
The hardware design of a microprocessor is arranged such that a very
small or very large system can be configured around the CPU as the application
demands as shown in Fig1. The prime use of the Microprocessor is to read data
, perform extensive calculations on that data, and store those calculations in a
mass storage device or display the results for human use. The programs used
by microprocessor are stored in the mass storage device and loaded into RAM
as user directs. A few microprocessor program are stored in ROM . The ROM
based programs are primarily small fixed programs that operate peripherals
and other fixed devices that are connected to the system.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction to Microprocessor and Computer OrganizationDokument26 SeitenIntroduction to Microprocessor and Computer OrganizationVishal GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontrollers: An IntroductionDokument10 SeitenMicrocontrollers: An IntroductionAjay YANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Architecture of Computer SystemDokument30 SeitenThe Basic Architecture of Computer SystemAnnie GloryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1 Introduction To MiocroprocessorDokument21 SeitenLec 1 Introduction To Miocroprocessor21201151Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The 68Hc12 MicrocontrollerDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To The 68Hc12 Microcontrollerahetdhaezh100% (2)
- Introduction - Unit I MCDokument35 SeitenIntroduction - Unit I MCKirthi RkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSDokument292 SeitenCSSantanu Kumar SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of a Digital Computer: Key Components and FunctionsDokument24 SeitenAnatomy of a Digital Computer: Key Components and FunctionsanilkumarosmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comupet Science AssisnmentDokument11 SeitenComupet Science AssisnmentHari BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co Module1Dokument22 SeitenCo Module1Ashika RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOC-20210330-WA0010.Dokument12 SeitenDOC-20210330-WA0010.v5kbkrmdfpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDokument55 SeitenUnit I Introduction To 8085 Microprocessorkiran sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Logic And Computer Organization UNIT – II 2.0) IntroductionDokument32 SeitenDigital Logic And Computer Organization UNIT – II 2.0) IntroductionJit AggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology Booklet Section 1-3Dokument251 SeitenInformation Technology Booklet Section 1-3randyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To MPDokument22 SeitenIntro To MP211902020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDokument22 SeitenMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers6012 ANILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor: Mbeya University of Science and Technology Department of Electronics and Telecommunication EngineeringDokument30 SeitenMicroprocessor: Mbeya University of Science and Technology Department of Electronics and Telecommunication EngineeringEM NemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features, functions and uses of different types of computersDokument13 SeitenFeatures, functions and uses of different types of computersnoiseaholic22Noch keine Bewertungen
- KTU - CST202 - Computer Organization and ArchitectureDokument22 SeitenKTU - CST202 - Computer Organization and ArchitectureJoel K SanthoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroprocessorDokument11 SeitenMicroprocessornave101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Micro Lect3Dokument21 SeitenIntroduction To Micro Lect3Annalyn SoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers explained in 40 charactersDokument2 SeitenDifferences between microprocessors and microcontrollers explained in 40 charactersustad2121Noch keine Bewertungen
- Co 1st ChapterDokument12 SeitenCo 1st ChapterPriyanka H VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3Dokument8 SeitenLab 3bilalkhan.ak12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor - Introduction To Basic MicroprocessorDokument21 SeitenMicroprocessor - Introduction To Basic MicroprocessorTanveer Ahmed HakroNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Language BasicsDokument61 SeitenC Language BasicsinfotainmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDokument3 SeitenCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecpc-308 15Dokument140 SeitenEcpc-308 15chinusood08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop - I Lab ManualDokument36 SeitenWorkshop - I Lab Manualatulya singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDokument3 SeitenCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDokument55 SeitenUnit I Introduction To 8085 Microprocessorsheriffwoody123Noch keine Bewertungen
- KTU CST202 Computer Organization Module 1Dokument22 SeitenKTU CST202 Computer Organization Module 1Akhil KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 2 Computer Architecture Notes EnglishDokument4 SeitenChapter - 2 Computer Architecture Notes EnglishAshish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Organisation of A Micro ProcessorDokument8 SeitenGeneral Organisation of A Micro ProcessornelsrodrigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computer OrganizationDokument66 SeitenIntroduction To Computer OrganizationShaina GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Notes Chapter1Dokument28 SeitenCA Notes Chapter1Nithyan NithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDokument8 SeitenChapter 1 - IntroductionRoshan NandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture and OrganizationDokument46 SeitenComputer Architecture and OrganizationAdeeti Chopra SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer StudiesDokument29 SeitenComputer StudiesPatson BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsDokument33 SeitenHardware Organisation of Computers and MicroprocessorsUchenna OgunkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsDokument12 SeitenHI M2 Introduction To Computer ConceptsErickson SongcalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Dokument34 SeitenLecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Tushar VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1&M2 MixedDokument135 SeitenM1&M2 MixedRoopa B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MicroprocessorDokument39 SeitenIntroduction To MicroprocessorDeepika BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Peripherals and Interfacing LectureDokument23 SeitenIntroduction to Peripherals and Interfacing Lectureabu sayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zimsec Computer Science NotesDokument19 SeitenZimsec Computer Science NotesTaguma TahwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture & OrgDokument23 SeitenComputer Architecture & OrgIkawa AfueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro ProcesserDokument1 SeiteIntro ProcesserAMIT KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Computer and Its OperationsDokument11 SeitenBasics of Computer and Its OperationsKingashiqhussainPanhwerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)Dokument40 SeitenCO - OS Unit-1 (Part1)ffjsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Ion To 8085 MicroprocessorDokument56 SeitenUnit 1 Ion To 8085 Microprocessorrosecar6100% (1)
- Unit 1Dokument205 SeitenUnit 1rohanrec92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3: Programmable Logic Devices (PLDS) Introduction To Micro-Processors and Micro-ControllersDokument36 SeitenModule 3: Programmable Logic Devices (PLDS) Introduction To Micro-Processors and Micro-ControllersDhanish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computers, Microprocessors, and Microcontrollers: An IntroductionDokument65 SeitenComputers, Microprocessors, and Microcontrollers: An IntroductionHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Basic Computer EngineeringDokument27 SeitenUnit 1 - Basic Computer EngineeringVikas JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microcontroller&Its Applications 2021 NotesDokument38 SeitenMicrocontroller&Its Applications 2021 NotesAnirban MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 BCCDokument47 SeitenPart 1 BCCKyla FlorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Course for Advanced Computer StudiesVon EverandFoundation Course for Advanced Computer StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesVon EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Von EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motor BasicsDokument23 SeitenMotor BasicsHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2980245C HVAC Handbook 2013 WebDokument35 Seiten2980245C HVAC Handbook 2013 WebomeshchemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2980245C HVAC Handbook 2013 WebDokument35 Seiten2980245C HVAC Handbook 2013 WebomeshchemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-DOF Forced Vibration Frequency ResponseDokument95 Seiten1-DOF Forced Vibration Frequency ResponseTaher Abu SeirNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-Life Vehicle Recovery in ChinaDokument8 SeitenEnd-Of-Life Vehicle Recovery in ChinaHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- UB BlueSealDokument1 SeiteUB BlueSealHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- End of Life Vehicle Recovery in EgyptDokument9 SeitenEnd of Life Vehicle Recovery in EgyptHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Life Vehicle Recovery in EgyptDokument9 SeitenEnd of Life Vehicle Recovery in EgyptHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Wind TunnelsDokument25 SeitenTypes of Wind TunnelsHarshit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginning Embedded ElectronicsDokument119 SeitenBeginning Embedded ElectronicsHarshit Goyal100% (1)
- 901 Cpu Book Cp3 Cpu enDokument167 Seiten901 Cpu Book Cp3 Cpu enSandigai MariosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5 Instruction Formats: Three-Address MachinesDokument4 Seiten3.5 Instruction Formats: Three-Address Machinesلطيف احمد حسنNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atpg Overview: Ashokraj YellamrajuDokument37 SeitenAtpg Overview: Ashokraj Yellamrajuashokraj108100% (2)
- Ca 2 Marks & Big Ques PDFDokument96 SeitenCa 2 Marks & Big Ques PDFsathya priyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- @@D@-@ @@d@-@/na20d@-@: Cp1e-E Cp1e-NDokument44 Seiten@@D@-@ @@d@-@/na20d@-@: Cp1e-E Cp1e-NEDEVALDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Cod Unit 4Dokument50 SeitenCod Unit 4anilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel Case Study - PresentationDokument26 SeitenIntel Case Study - Presentationravinder_bhandari080% (1)
- Positive&Negative LogicDokument12 SeitenPositive&Negative LogicMahesh GonuguntlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macintosh 128k.512kDokument79 SeitenMacintosh 128k.512kmatthew katzensteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- INLINE 5 Adapter Reflash InstructionsDokument6 SeitenINLINE 5 Adapter Reflash InstructionsAngel Amaya AsencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4G Transceiver NRF24L01 Module User's Manual v2.0Dokument12 Seiten2.4G Transceiver NRF24L01 Module User's Manual v2.0Nina FloydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Terminology 2Dokument7 SeitenParallel Terminology 2maxsen021Noch keine Bewertungen
- DDCA Ch5Dokument101 SeitenDDCA Ch5Dheer MehrotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Books For 3 SemDokument2 SeitenReference Books For 3 SemVikram Rao100% (1)
- Intel 8-Mbit SV Boot Block GuideDokument58 SeitenIntel 8-Mbit SV Boot Block GuideuserscrybdNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLC FatekDokument36 SeitenPLC FatekM7mud M7mdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Micro Controller 8051Dokument20 SeitenUnit 4 Micro Controller 8051Anbalagan Guru100% (1)
- MPU/MMU in ARM structure overviewDokument34 SeitenMPU/MMU in ARM structure overviewcalvin6789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interrupts PDFDokument4 SeitenInterrupts PDFHermain Fayyaz KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 140 Avi 030 00Dokument40 Seiten140 Avi 030 00Sergio Mauricio Acuña BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report on Embedded System Lab2Dokument22 SeitenLab Report on Embedded System Lab2Saroj KatwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard Brochure G31 v1.1Dokument1 SeiteMotherboard Brochure G31 v1.1Akanksha KhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pic16f877 Microcontroller PDFDokument12 SeitenPic16f877 Microcontroller PDFShrikant ChamlateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guangzhou HC Bluetooth Module Data SheetDokument14 SeitenGuangzhou HC Bluetooth Module Data Sheetivan10mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Memory Address TranslationDokument4 SeitenVirtual Memory Address TranslationNitin SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is GPU Computing? - Understanding GPU Accelerated ComputingDokument4 SeitenWhat is GPU Computing? - Understanding GPU Accelerated ComputingSam RonnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compal Confidential AMD FP2 Processor with DDRIII + Husdon M3 FCH SchematicsDokument50 SeitenCompal Confidential AMD FP2 Processor with DDRIII + Husdon M3 FCH SchematicsYadi MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Operating Systems 5th Edition Mchoes Test BankDokument25 SeitenUnderstanding Operating Systems 5th Edition Mchoes Test BankGaryBaxterbwse100% (32)
- Exercise - Problems ch3 PDFDokument16 SeitenExercise - Problems ch3 PDFchandlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart MemoriesDokument11 SeitenSmart MemoriesHari KrishNoch keine Bewertungen