Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Separation Procces For Natural Gas
Hochgeladen von
Miller Guerrero0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten2 SeitenThis are some caracteristics of the medium in the procces of gravity separation of gas
Originaltitel
Separation Procces for Natural Gas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis are some caracteristics of the medium in the procces of gravity separation of gas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten2 SeitenSeparation Procces For Natural Gas
Hochgeladen von
Miller GuerreroThis are some caracteristics of the medium in the procces of gravity separation of gas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
BROWNIAN MOVEMENT a Brownian particle and computing its insoluble particles is suspended
average behavior. throughout another substance). Although
Brownian motion, also called Brownian
the terms colloid and emulsion are
movement, any of various physical COALESCENCE
sometimes used interchangeably,
phenomena in which some quantity is
Coalescence is a process in which two emulsion should be used when both
constantly undergoing small, random
phase domains of the same composition phases, dispersed and continuous, are
fluctuations. It was named for the Scottish
come together and form a larger phase liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the
botanist Robert Brown, the first to study
domain. In other words, the process by dispersed phase) is dispersed in the other
such fluctuations (1827).
which two or more separate masses of
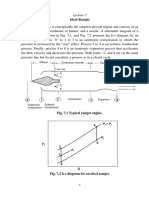
PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE
If a number of particles subject to miscible substances seem to "pull" each
Medium-pressure separators usually
Brownian motion are present in a given other together should they make the
operate at pressures ranging from 230 to
medium and there is no preferred slightest contact.
250 up to 600 to 700 psi. This pressure
direction for the random oscillations, then
This is highly supported by the Brownian need to be regulated to prevent un-safe
over a period of time the particles will
motion in this case due to the situations for the personnel or the vessel
tend to be spread evenly throughout the
environment in which the particles of itself.
medium. Thus, if A and B are two adjacent
water and gas (in a lower proportion
regions and, at time t, A contains twice as Heat as a form of energy that is
compared to the oil particles), bounce all
many particles as B, at that instant the transferred from one body to another
over the emulsion, making up small
probability of a particle’s leaving A to enter results in a difference in temperature. This
packages called domains, the domains
B is twice as great as the probability that a reduces surface tension and viscosity of
formed need to be separated in order to
particle will leave B to enter A. The the oil and thus assists in releasing gas that
make “profit” of the materials obtained.
physical process in which a substance is hydraulically retained in the oil. A
tends to spread steadily from regions of EMULSION spreader plate that disperses the oil into
high concentration to regions of lower small streams or rivulets increases the
concentration is called diffusion. Diffusion An emulsion is a mixture of two or more effectiveness of the heated-water bath.
can therefore be considered a macroscopic liquids that are normally immiscible. Upward flow of the oil through the water
manifestation of Brownian motion on the Emulsions are part of a more general class bath affords slight agitation, which is
microscopic level. Thus, it is possible to of two-phase systems of matter called helpful in coalescing and separating
study diffusion by simulating the motion of colloids (a colloid is a mixture in which entrained gas from the oil. This
one substance of microscopically dispersed
temperature is stabled in the range of 50-
60ºC
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Lateral Earth Pressure Due To Vibratory Rollers PDFDokument11 SeitenLateral Earth Pressure Due To Vibratory Rollers PDFchutton681Noch keine Bewertungen
- 212.nozzle Load Stress Analysis Using WRC 107 and WRC 297Dokument4 Seiten212.nozzle Load Stress Analysis Using WRC 107 and WRC 297jeronimo113Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis of Circular CylindricDokument243 SeitenVibration Analysis of Circular CylindricAlfonso BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GỐC 431-SC02Dokument123 SeitenGỐC 431-SC02Hoàng Hồng Dương100% (1)
- Final Round and ClincherDokument8 SeitenFinal Round and Clincherponcatoera0% (2)
- 155 MM Drag and Exterior BallisticDokument40 Seiten155 MM Drag and Exterior Ballisticoso5755Noch keine Bewertungen
- FEMA 451 Compl - Struct Analysis Performance-BasedDokument85 SeitenFEMA 451 Compl - Struct Analysis Performance-BasedGeorge Sanches100% (2)
- Trapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingDokument7 SeitenTrapezoidal Sheet As A Bracing Preventing Flat Trusses From Out-Of-Plane BucklingWilliam Pol100% (1)
- Architectural Structures (G G Schierle, 2006) - NoRestrictionDokument227 SeitenArchitectural Structures (G G Schierle, 2006) - NoRestrictionVlad Ghiriti100% (1)
- Periodic TableDokument2 SeitenPeriodic TableMiller GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Structure AX4Dokument2 SeitenMolecular Structure AX4Miller GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 333 PDFDokument26 Seiten333 PDFdineshhissarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A "Unit Operation"?Dokument7 SeitenWhat Is A "Unit Operation"?Miller GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Assignment1Dokument7 SeitenPhy Assignment1AakashRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bossard White Paper Material Fatigue enDokument16 SeitenBossard White Paper Material Fatigue enHeviiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer TableDokument1 SeiteHeat Transfer TablehydarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods in Heat Transfer: Satyajit Mojumder Dept. of Mechanical Engineering BUET, Dhaka-1000Dokument40 SeitenNumerical Methods in Heat Transfer: Satyajit Mojumder Dept. of Mechanical Engineering BUET, Dhaka-1000Anonymous 17ihTauS5100% (1)
- 2nd Year Breakdown + ReviewDokument7 Seiten2nd Year Breakdown + ReviewSuperman6424Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Dynamics AssignmentDokument6 SeitenFluid Dynamics AssignmentUzair ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optoelectronic Devices and Systems: Second EditionDokument11 SeitenOptoelectronic Devices and Systems: Second EditionDEVINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vierendeel Truss: Past and Present of An Innovative TypologyDokument19 SeitenThe Vierendeel Truss: Past and Present of An Innovative TypologyLoris LorisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture12 2019 Harmonic Potential PDFDokument26 SeitenLecture12 2019 Harmonic Potential PDFMatt AllsopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument4 SeitenLecture 7minoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationDokument27 Seiten2.A Study On Stress ConcentrationRameez FaroukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Simulation ReportDokument10 SeitenFlow Simulation Reportaloph denyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Through Quantum Dots: Lecture Notes DPG-School Electronic Nanostructures' Oct 8-12, 2001, Bad Honnef (Germany)Dokument34 SeitenTransport Through Quantum Dots: Lecture Notes DPG-School Electronic Nanostructures' Oct 8-12, 2001, Bad Honnef (Germany)Azhar MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet ME307Dokument6 SeitenFormula Sheet ME307Eren ÇamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Raves: Tremor Observations From An Electronic Dance Music FestivalDokument8 SeitenSeismic Raves: Tremor Observations From An Electronic Dance Music FestivalMaría MarchianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 4Dokument31 SeitenProblem Set 4Joakin Bahamondes100% (1)
- Chapter 3 (MEC681) - MHI PDFDokument71 SeitenChapter 3 (MEC681) - MHI PDFمحمد فائزNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Spindle Motor Selection: 9/30/2018 Aruna Kumar.p 1Dokument19 SeitenMain Spindle Motor Selection: 9/30/2018 Aruna Kumar.p 1srinivas murthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering Systems 4th Edition by Houghtalen - Compress PDFDokument6 SeitenSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering Systems 4th Edition by Houghtalen - Compress PDFpotineNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3.scalar and VactorsDokument18 Seiten1.3.scalar and Vactorsmardel11Noch keine Bewertungen