Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Growth Point 6
Hochgeladen von
api-3463240740 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten11 SeitenOriginaltitel
growth point 6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten11 SeitenGrowth Point 6
Hochgeladen von
api-346324074Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
422|Page
ACTIVITIES
ACTIVITY 4.9 TWO-DIGIT MULTIPLICATION:
RELATING TO A KNOWN FACT
OVERVIEW:
In this activity students use multiplication facts that they know to help
them multiply other numbers. Students can use basic multiplication facts
and understanding of place value: for example 3 x 20 = 3.x 2 tens = 6 tens
= 60. Or a student may know that 4 x 25 = 100 and use this to calculate 5
x 25.
MATERIALS:
Calculators can be used for checking,
THE ACTIVITY:
1, Write the calculation 9 x 25 on the board. Invite students to calculate
this mentally and to explain their strategies. Emphasise the facts they
knew that they used to assist them.
2. Write some responses on the board, for example:
+ Known facts: 4 x 25 = 100; 9=2x4+1.
+ Known facts: 9 x 5 = 45, 9 x 20 = 180.
+ Known facts: 10 x 25 = 250, 9 = 10-1.
3. Write several calculations on the board, for example: 30 x 6, 5 x 25, 15
8,19 x6,50x9, 13 x7.
4, Invite students to calculate one or more of them and to record the
known facts that they used. Students can use calculators to help check
their calculations.
COMMENTS ON THE ACTIVITY:
‘The main purpose is to show that one uses multiplication facts one knows
in order to do calculations, and that these facts, and therefore one’s
mental strategies, vary from person to person. A secondary purpose is for
Some students to acquire strategies that they may not have thought of
previously.
ASSESSING PROGRESS:
+ Students can calculate some multiplications by using known facts,
+ Students can identify the known facts that they use.* Students widen
‘the range of strategies open to them when calculating mentally.
\Wih permission: Meinosh (2004) Montal Computations: Two-Digt Whole Numbers Module 4
123|Page
PRACTICE EXAMPLE:
1 40x5 6.30x7
2 15 x6 7.8x19
3. 5x36 8.48x5
4 23x8 9.4x35
5 7x50 10. 25x7
ACTIVITY 4.10 TWO-DIGIT MULTIPLICATION:
USE EXTENSIO! -DIGIT STARTEGIES
OVERVIEW:
Module 3 introduced strategies for multiplying single-digit by single-
digit numbers. These strategies are also equally appropriate for
multiplying two-digit by single-digit numbers. Each single digit has a
strategy associated with it.
MATERIALS:
Calculators can be used for checking,
THE ACTIVITY:
1. Before extending each of these strategies, check that students can
use them with single digit calculations, Then invite students to extend
their use to two-digit examples. Calculators can be used to check results.
For example:
+ Strategy: 5 x = half of 10 x
+ Single-digit example: 5 x 7 = half of 10 x 7 = half of 70 = 35.
+ Two-digit example: 5 x 46 = half of 10 x 46 = half of 460 = 230.
+ Check result with calculator
This table gives an example of each strategy with a single-digit example,
followed by some two-digit calculations which students can be asked to
perform using the same strategy.
Strategy Singie-digit Two-digit
by single-digit by single-digit
33,242, 2x57
2 x= Doubles 2x4 2
3xe2x+1 multiple 3x6=12+6
4x2x6:12.24
dxe2x
Sx=halfofl0x 3X9: 90,45
6x=5x+ one multiple 6X7: 35 +7
TxeSxt2x Tx: 2048 ve ieeeu aa
Bx=2x2x2x 8x7: 14, 28, 56 8x35, 9x32, 816
peoree 9x 16.9% 34,947
9x= 10 ~ I multiple
{1h pormissin: Mefatash (2004) Mental Computations: TWo- Digit Whale Numbers Madu 4
124|Page
2. Invite students to write other two-digit calculations with explanations
of how these can be done using these strategies.
COMMENTS ON THE ACTIVITY:
This activity assumes that students can already use each of the
strategies with single digit numbers, and they now need practice in
extending their use to multiplying two-digit numbers. For practice with
single digits, use Module 3,
ASSESSING PROGRESS:
+ Students can use each strategy to perform a two-digit calculation.
+ Students can explain their use of each strategy.
+ Students can calculate two-digit by one-digit calculations using the
appropriate strategies
ACTIVITY 4.11 TWO-DIGIT MULTIPLICATION:
SKIP COUNTING
OVERVIEW:
‘Students have practiced skip counting with single digits in Module 3. This
activity extends this to some two-digit numbers, for which skip counting
is relatively simple, for example 15, 20, 25, 40.
MATERIALS:
Calculators can be used for checking,
THE ACTIVITY:
1. Establish a sequential order from student to student round the class
‘and back to the first student. Choose a simple two-digit number, such as
10, and have the class count up in tens in the established order until 100
is reached. Continue round, now starting at 20 and counting by 20s until
200 is reached.
2. Continue similarly with 30, 40,
3, Now count up in 15s, 25s,
4. Show students how to use a calculator to check skip counting, For
example, to skip count in 15s, enter 0+ 15 =, Now each time the =’ button
is pressed the calculator adds 15: 15, 30, 45, 60,
{1 permission: Melntosh (2004) Mental Computations: Two-Digt Whole Numbers Mocs 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Wednesday 5 AprilDokument4 SeitenWednesday 5 Aprilapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hpe Forward Planning DocumentDokument8 SeitenHpe Forward Planning Documentapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Forward Planning DocumentDokument8 SeitenScience Forward Planning Documentapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Forward Planning DocumentDokument11 SeitenEnglish Forward Planning Documentapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Forward Planning DocumentDokument17 SeitenMaths Forward Planning Documentapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
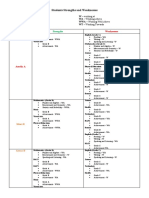
- Students Strengths and WeaknessesDokument6 SeitenStudents Strengths and Weaknessesapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reconciliation WeekDokument10 SeitenReconciliation Weekapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Early Years Learning FrameworkDokument5 SeitenEarly Years Learning Frameworkapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- How The World WorksDokument9 SeitenHow The World Worksapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokument9 SeitenRoles and Responsibilitiesapi-346324074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)