Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
New L Valency Table
Hochgeladen von
ZarbEChishtiOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
New L Valency Table
Hochgeladen von
ZarbEChishtiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
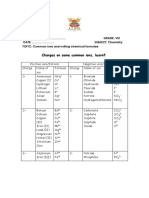
NAME.....................................
USEFUL VALENCIES, IONS AND FORMULAE FOR GCSE
METALS
ION = +1 ION = +2 ION = +3
VALENCY OF 1 VALENCY OF 2 VALENCY OF 3
Li lithium Mg magnesium Al aluminium
Na sodium Ca calcium Fe iron (III)
K potassium Ba barium
Cu copper (I) Fe iron (II)
Ag silver Ni nickel
Cu copper (II)
H hydrogen * Zn zinc
NH4 ammonium * Pb lead (II)
* these ions are not actually of metals but behave as such by forming
positive ions
NON - METALS
ION = -1 ION = -2 ION = -3
VALENCY OF 1 VALENCY OF 2 VALENCY OF 3
F fluoride O oxide N nitride
Cl chloride S sulphide PO4 phosphate
Br bromide SO4 sulphate
I iodide CO3 carbonate
OH hydroxide VALENCY OF 4
NO3 nitrate C carbon
HCO3 hydrogencarbon Si silicon
ate
HSO4 hydrogensulph These do not form ions
ate
OTHER FORMULAE
The formulae of ionic compounds (compounds formed between metals and non-
metals) is given by balancing the relative numbers of positive and negative ions
needed to achieve a neutral compound.
The formulae of acids and of more covalent molecules is not easy to predict using
valencies. The following should be learnt as a matter of course.
Common Gases Common Acids Other
H2 hydrogen HCl hydrochloric H2 O water (l)
O2 oxygen HNO3 nitric NH3 ammonia (g)
N2 nitrogen H2SO4 sulphuric F2 fluorine (g)
Cl2 chlorine H3PO4 phosphoric Br2 bromine (l)
CO2 carbon dioxide HCOOH methanoic I2 iodine (s)
(weak)
SO2 sulphur CH3COO ethanoic CO carbon monoxide
dioxide H (weak) (g)
NAME.....................................
CH4 methane H2CO3 carbonic C2 H 4 ethene (g)
(weak)
REACTIVITY SERIES OF SOME METALS
K > Na > Li > Ca > Mg > Al > [C] > Zn > Fe > Pb > [H] > Cu > Ag > Au
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Name of Atom Common Ionic ChargeDokument2 SeitenName of Atom Common Ionic ChargeMichael Rey MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.9 Polyatomic CompoundsDokument3 Seiten5.9 Polyatomic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Formula of IonsDokument6 SeitenTest 1 Formula of IonsSEAW FUI MINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 EquationsDokument11 SeitenLecture 1 Equationsmerabamoding11Noch keine Bewertungen
- WS 1 Mole - FormulaDokument6 SeitenWS 1 Mole - FormulaSEAW FUI MINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsDokument11 SeitenElements, Compounds and Chemical EquationsKasman Kasonde MumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 CBSE ChemistryDokument67 Seiten10 CBSE ChemistryAlifiyah HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApsummerDokument5 SeitenApsummerLayleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenChem Nomenclature Updated PDFDokument2 SeitenGenChem Nomenclature Updated PDFCamille AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Chemical FormulaeDokument14 Seiten1.1 Chemical FormulaeShyamal DlrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsDokument1 SeiteSymbols and Names For Common Polyatomic IonsElixirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021Dokument5 SeitenSummer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021shelly zhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Ions and Their ChargesDokument2 SeitenCommon Ions and Their ChargesTristanEvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 2 Module 3Dokument6 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 3Jason Vinluan CarinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4.3 Chemical Formula and Naming Practice QuestionsDokument7 Seiten2.4.3 Chemical Formula and Naming Practice Questionsphat.vuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cation and AnionDokument1 SeiteCation and Anionsumityadav742008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chm361-Chapter 5Dokument34 SeitenChm361-Chapter 5atikah roshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical NomenclatureDokument7 SeitenChemical NomenclatureQuỳnh NgânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision NotesDokument3 SeitenRevision NotesKay MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Name and FormulasDokument35 SeitenChemical Name and FormulasSara HdaifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chm361 Chapter 5Dokument34 SeitenChm361 Chapter 5syamimiafrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cha 11Dokument11 SeitenCha 11Tun Lin AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asm 33333333333Dokument2 SeitenAsm 33333333333p5jp29697cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)Dokument5 SeitenChemistry Class 10 Lecture 1 (3 April)allroundersaksham304Noch keine Bewertungen
- JRS Tutorials: Chemistry IITDokument58 SeitenJRS Tutorials: Chemistry IITtusharr11.mobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valency TableDokument2 SeitenValency TableashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1, Naming CompoundsDokument19 SeitenChapter 1, Naming CompoundsKurdishNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM& 161 - Tran - Winter 2021 Elements and Ions: What Does This Tell Us? An Element On This List Exists As ADokument2 SeitenCHEM& 161 - Tran - Winter 2021 Elements and Ions: What Does This Tell Us? An Element On This List Exists As AНиколай ЛиксуновNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Compounds and Formula WorksheetDokument4 SeitenIonic Compounds and Formula WorksheetKemoy FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Info SheetDokument3 SeitenChemistry Info SheetClara GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDokument16 SeitenShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationSHARIN HANUM AB RAHMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenICSE Selina Solution For Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 1ABHISHEK THAKURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std. 8 Chemistry ProjectDokument8 SeitenStd. 8 Chemistry ProjectEnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDokument3 SeitenValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common IonsDokument3 SeitenCommon IonsabdallaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1.0 - Questions 1. Write Standard Atomic Notation For H Ca F Li ODokument16 SeitenLesson 1.0 - Questions 1. Write Standard Atomic Notation For H Ca F Li OThai NgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete NomenclatureDokument10 SeitenComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Coordination CompoundDokument36 SeitenChapter 5 Coordination Compoundammar zakariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Polyatomic IonsDokument1 SeiteCommon Polyatomic IonsRoddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Cations and AnionsDokument2 SeitenList of Cations and AnionsArvin MagtotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Writing and Naming of CompoundsDokument1 SeiteFormula Writing and Naming of CompoundsMon ColinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgeDokument2 SeitenNomenclature: General Chemistry Pro-KnowledgemohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming CompoundsDokument2 SeitenNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2tables As ReferencesDokument10 SeitenMODULE 2tables As ReferencesJuneyale Padilla100% (1)
- CHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFDokument59 SeitenCHM361-CHAPTER 5 Coordination Compound PDFEhaz100% (1)
- Physical Sciences GR 10 Revision Term 2 - 2023Dokument22 SeitenPhysical Sciences GR 10 Revision Term 2 - 2023lethimpilondhlovuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsDokument2 SeitenSymbols and Charges For Monoatomic IonsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes PT 3 4Dokument53 SeitenChemistry Notes PT 3 4Eunice Kyla MapisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicDokument2 SeitenIvan Zaman: Element (Metal) Symbol Valency Atomic Element Symbol Valency AtomicJobayer Mahin100% (1)
- Chemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersDokument4 SeitenChemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersAbdullah HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valency SheetDokument3 SeitenValency SheetBex JacobsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main - Acids Bases and Salts Formulas and Names Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenMain - Acids Bases and Salts Formulas and Names Cheat SheetLorens NorNoch keine Bewertungen
- HydrogenDokument3 SeitenHydrogenanon-60242100% (2)
- Chapter 2 StoichiometryDokument111 SeitenChapter 2 StoichiometryNORMASLAILA JAAFARNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Q) Elements Symbols Valances Compounds Formula Common NamesDokument14 Seiten(Q) Elements Symbols Valances Compounds Formula Common Namesshihab shoronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Stoichiometry - StudentDokument105 SeitenChapter 1 Stoichiometry - StudentNur AlisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1a ChemistryDokument10 SeitenExercise 1a Chemistryapi-533545229Noch keine Bewertungen
- Garam Bab 8Dokument29 SeitenGaram Bab 8ctohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionVon EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - Xii Society, Religion and Temple: /j-U-V-/J-U-V-/J-u-u-u-u-u-u-u-U-U-U-u-U-U-VJ-VJ-U-U-U-U-U-U-U-VJDokument35 SeitenChapter - Xii Society, Religion and Temple: /j-U-V-/J-U-V-/J-u-u-u-u-u-u-u-U-U-U-u-U-U-VJ-VJ-U-U-U-U-U-U-U-VJZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dream in IslamDokument8 SeitenDream in IslamZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazrat Laal Shahbaz Qalandar: Translated by Hafeez AnwarDokument78 SeitenHazrat Laal Shahbaz Qalandar: Translated by Hafeez AnwarZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yaad e HusainDokument3 SeitenYaad e HusainZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Al Quran Surah-An-Nisa (4), Aayah 85) : Haya Imaan HaiDokument6 Seiten(Al Quran Surah-An-Nisa (4), Aayah 85) : Haya Imaan HaiZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anas B. Malik Reported: I Saw Allah's Apostle ( ) Squatting and Eating Dates. Sahih Muslim 2044 A In-Book Reference: Book 36, Hadith 205Dokument1 SeiteAnas B. Malik Reported: I Saw Allah's Apostle ( ) Squatting and Eating Dates. Sahih Muslim 2044 A In-Book Reference: Book 36, Hadith 205ZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valency TableDokument2 SeitenValency TableZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jarah Wa Tadeel Usul Ul Hadith Science of HadithDokument44 SeitenJarah Wa Tadeel Usul Ul Hadith Science of HadithZarbEChishtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 1411: Generic Heating/Cooling CurveDokument19 SeitenChemistry 1411: Generic Heating/Cooling CurveKinal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 14 Bonding HL NotesDokument26 SeitenTopic 14 Bonding HL NotesaabbccNoch keine Bewertungen
- P13Dokument8 SeitenP13Dana CapbunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics SemiconductorsDokument22 SeitenElectronics SemiconductorsA B ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry I Module 2 Week 2Dokument7 SeitenGeneral Chemistry I Module 2 Week 2Arth LubayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Generation and Electrical SourcesDokument33 SeitenChapter 1 - Generation and Electrical SourcesDEM2A F2014RAXON RAJ A/L SURESHRAJKUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- l-3 c-163 1344837023407Dokument79 Seitenl-3 c-163 1344837023407Kommraju Sravan Kumar100% (1)
- Rlhudson o Ring GuideDokument214 SeitenRlhudson o Ring GuideAndré RiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDokument4 Seiten11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureAkhed100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding 1Dokument81 SeitenChemical Bonding 1RIMMY AUGUSTINE 2138110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ions and Radicals TextDokument2 SeitenIons and Radicals Textameerfati76Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Chemistry SyllabusDokument2 Seiten11th Chemistry SyllabusFreQuency Career InsTituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professor Dr. D. Hellwinkel (Auth.) - Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - A Directory To Comprehension and Application of Its Basic Principles (2001)Dokument238 SeitenProfessor Dr. D. Hellwinkel (Auth.) - Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry - A Directory To Comprehension and Application of Its Basic Principles (2001)Lenin Fernandez ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsDokument14 SeitenCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsAswar ShaileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraDokument11 SeitenCourse 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraanoopNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - MELC 5 Week 3Dokument11 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 1 Activity Sheet Quarter 2 - MELC 5 Week 3Melyn Kaye LedesmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit PlanDokument8 SeitenUnit PlanKayla RhodesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric AnalysisDokument39 SeitenVolumetric AnalysisNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Review: Vocabulary Section 6.3Dokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Review: Vocabulary Section 6.3Christopher HurtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Plan 2.1Dokument3 SeitenLearning Plan 2.1Shielo Marie CardinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonds: Forming IonsDokument10 SeitenChemical Bonds: Forming IonsShiela LumbagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table - 62760 - 2023 - 05 - 06 - 21 - 02Dokument31 SeitenPeriodic Table - 62760 - 2023 - 05 - 06 - 21 - 02Tae KookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications OF Artificial Intelligence FOR Organic ChemistryDokument203 SeitenApplications OF Artificial Intelligence FOR Organic ChemistryMichael RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Coordination Compounds PDFDokument7 Seiten9 Coordination Compounds PDFShatabdi MahendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ca ReviewDokument12 SeitenCa ReviewNaresh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Structure OftheatomDokument15 Seiten4 Structure OftheatomVaibhav V VeenajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form FourDokument55 SeitenChemistry Form FourNorazlin UjangNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Transitional Metal ChemistryDokument131 SeitenAn Introduction To Transitional Metal ChemistryHafsa KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Compounds: Grade 9Dokument21 SeitenCarbon Compounds: Grade 9Rosalyn RayosNoch keine Bewertungen