Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Math Strategies and Tactics
Hochgeladen von
hiii0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten3 SeitenOriginaltitel
Math Strategies and Tactics.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
42 Ansichten3 SeitenMath Strategies and Tactics
Hochgeladen von
hiiiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Math Strategies and Tactics
Tactic 1: Draw a diagram
Tactic 2: If a diagram has been drawn to scale, trust it (unless it says Note: figure not drawn
to scale)
Tactic 3: If a diagram has been drawn to scale, redraw it
Tactic 4: Add a line to a diagram
Tactic 5: Test the Choices Starting with B or C
Tactic 6: Replace Variables with Numbers
Tactic 7: Choose an Appropriate Number
Tactic 8: Eliminate Absurd Choices, and Guess
Tactic 9: Subtract to Find Shaded Regions
Tactic 10: Don’t Do More Than You Have To
Tactic 11: Pay Attention to Units
Tactic 12: Use Your Calculator
Tactic 13: Know When Not to Use Your Calculator
Tactic 14: Systematically Make a List
Tactic 15: Trust All Grids and Charts
Tactic 16: Add Equations
Reviewing Mathematics
Key Fact A1:
For any number a, exactly one of the following is true:
a is negative
a=0
a is positive
Key Fact A2:
For any number a and a positive b:
a =b a=b or a = -b
<b -b< a< b
>b a< -b or a > b
Key Fact A3:
For any number a: a x 0= o. Conversely, if the product of two or more numbers is 0, at least
one of them must be 0.
If ab= 0, then a= 0 or b= 0
If xyz= 0, then x= 0 or y= 0 or z= 0
Key Fact A4:
The product and quotient of two positive numbers or two negative numbers are positive; the
product and quotient of a positive number and a negative number is negative.
Key Fact A5:
The product of an even number of negative factors is positive
The product of an odd number of negative factors is odd
Key Fact A6:
The reciprocal of any nonzero number a is
The product of any number and its reciprocal is 1.
Key Fact A7:
The sum of two positive numbers is positive
The sum of two negative numbers is negative
To find the sum of a positive and negative number, find the difference of their
absolute values and use the sign of the number with the larger absolute value
Key Fact A8:
The sum of any number and its opposite is 0.
Key Fact A9:
To subtract signed numbers, change the problem to an addition problem by changing the sign
(KCC).
Key Fact A10:
Every integer has a finite set of factors (or divisors) and an infinite set of multiples
Ex: 2, 3,4,5,7,11,13,17
Key Fact A11:
Every integer greater than one that is not a prime can be written as a product of primes.
Key Fact A12:
The product of the GCF and LCM of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers
Key Fact A13:
To find the GCF and LCM of two or more integers, first get their prime factorization
Key Fact A14:
For any number b: b =b
For any number b and integer n>1: b =b x b….where b is used as a factor n times
Key Fact A15:
For any numbers b and c and positive integers m and n:
bm=
b
b
(b ) =b
b c = (bc)
b
c
Key Fact A16:
For any positive number n:
0 =0
If a is positive, a is positive
If a is negative a is positive if n is even, and negative if n is odd
English Words Mathematical Meaning Symbol
Is, was, will be, had, has, will Equals =
have, is equal to, is the same
as
Plus, more than, increased Addition +
by, added to, exceeds,
received, got older than,
farther than, greater than
Minus, fewer, less than, Subtraction -
difference, decreased by,
subtracted from, younger
than, gave, lost
Times, of product, multiplied Multiplication x
by
Divided by, quotient, per, for Division
More than, greater than Inequality >
At Least Inequality >
Fewer than, less than Inequality <
At most Inequality <
What, how many, etc. Unknown Variable X (or some other variable)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- ASME Boiler Feed WaterDokument30 SeitenASME Boiler Feed WaterHendri KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Model QuestionsDokument12 SeitenInvestment Model Questionssamuel debebe0% (1)
- PIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.2 (Mechanics) FinalDokument82 SeitenPIA B2 - Module 2 (PHYSICS) SubModule 2.2 (Mechanics) Finalsamarrana1234679Noch keine Bewertungen
- Central Tendency, Position, and VariationDokument37 SeitenCentral Tendency, Position, and VariationCeline Joy PolicarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Structure - 16 - 30 - FianalDokument26 SeitenHydraulic Structure - 16 - 30 - FianalMahmood YounsNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDS-PAGE PrincipleDokument2 SeitenSDS-PAGE PrincipledhashrathNoch keine Bewertungen
- V-RAY 2.0 Option Editor Overview (SketchUp)Dokument14 SeitenV-RAY 2.0 Option Editor Overview (SketchUp)thonethoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsm2300a SeriesDokument324 SeitenBsm2300a SeriesIBRAHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUTOSAR SWS UDPNetworkManagementDokument103 SeitenAUTOSAR SWS UDPNetworkManagementStefan RuscanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remote Sensing of Environment: SciencedirectDokument28 SeitenRemote Sensing of Environment: SciencedirectAmmara HabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of ConvertersDokument1 SeiteClassification of ConvertersJon BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Simulation of A QCA 2 To 1 MultiplexerDokument5 SeitenDesign and Simulation of A QCA 2 To 1 MultiplexerzubifayazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zalzalah Cesar Thesis 2016Dokument72 SeitenZalzalah Cesar Thesis 2016feezy11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmel 0038Dokument1 SeiteAtmel 0038namerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTB-BOL VetrificadoDokument19 SeitenGTB-BOL VetrificadoelduenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Chemistry MCQ (Haloalanes & Haloarenrs)Dokument7 SeitenXii Chemistry MCQ (Haloalanes & Haloarenrs)SanjanasanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juki Revised Top BotDokument12 SeitenJuki Revised Top BotFabio GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Physics Exemplar PDFDokument130 Seiten12 Physics Exemplar PDFPRATIM SADHU100% (1)
- The Network+ Cram Sheet: Networking ConceptsDokument4 SeitenThe Network+ Cram Sheet: Networking ConceptsISTAKHAR UDDIN AHAMED100% (1)
- Zipato MQTTCloudDokument34 SeitenZipato MQTTClouddensasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chameleon ChipDokument2 SeitenChameleon ChipChetan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Navier Stokes To Black Scholes - Numerical Methods in Computational FinanceDokument13 SeitenFrom Navier Stokes To Black Scholes - Numerical Methods in Computational FinanceTrader CatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen-Bradley RSLogix 500 PDFDokument6 SeitenAllen-Bradley RSLogix 500 PDFGanda PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuesTeksFerriumC61C64andC6 PDFDokument23 SeitenQuesTeksFerriumC61C64andC6 PDFEmily MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- STP10NK80Z - STP10NK80ZFP STW10NK80ZDokument11 SeitenSTP10NK80Z - STP10NK80ZFP STW10NK80ZAnkitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract of Talk by Dr. Nitin Oke For National Conference RLTDokument2 SeitenAbstract of Talk by Dr. Nitin Oke For National Conference RLTnitinNoch keine Bewertungen
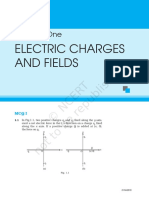
- Kluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Dokument9 SeitenKluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Rex KalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowDokument20 SeitenRodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowShara MotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4.damping ElementsDokument5 SeitenWeek 4.damping ElementsTrophie NilemoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KDW1.1 100 300 W1 220 Mainspindle Drive Indramat ManualDokument146 SeitenKDW1.1 100 300 W1 220 Mainspindle Drive Indramat ManualSven TackNoch keine Bewertungen