Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Micro Eportfolio Competition Spreadsheet Data-Fall 18
Hochgeladen von
api-334921583Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Micro Eportfolio Competition Spreadsheet Data-Fall 18
Hochgeladen von
api-334921583Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Microeconomics Course Assignment
In fulfillment of Course ePortfolio and CSIS requirement
This Assignment is required and totals 100 points
Part 1 Perfect Competition Analysis
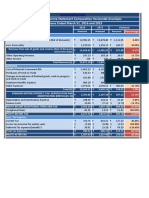
Costs of Production and Profit Maximization Analysis for the Perfect Competitive Market Structure
Total Total Average Average Average
Total Fixed Variable Fixed Variable Total Marginal Market Price Total
Output/h Costs Cost Total Cost Costs Costs Costs Costs Perfect Revenue
r (TFC) (TVC) (TC) (AFC) (AVC) (ATC) (MC) Competition (TR)
0 $ - $ - $6.00 $ -
1 $ 12.00 $ 6.00 $ 18.00 $ 12.00 $6.00 $18.00 $18.00 $6.00 $ 6.00
2 $ 12.00 $ 9.00 $ 21.00 $ 6.00 $4.50 $10.50 $3.00 $6.00 $ 12.00
3 $ 12.00 $ 11.00 $ 23.00 $ 4.00 $3.67 $7.67 $2.00 $6.00 $ 18.00
4 $ 12.00 $ 12.00 $ 24.00 $ 3.00 $3.00 $6.00 $1.00 $6.00 $ 24.00
5 $ 12.00 $ 14.00 $ 26.00 $ 2.40 $2.80 $5.20 $2.00 $6.00 $ 30.00
6 $ 12.00 $ 17.00 $ 29.00 $ 2.00 $2.83 $4.83 $3.00 $6.00 $ 36.00
7 $ 12.00 $ 21.00 $ 33.00 $ 1.71 $3.00 $4.71 $4.00 $6.00 $ 42.00
8 $ 12.00 $ 26.00 $ 38.00 $ 1.50 $3.25 $4.75 $5.00 $6.00 $ 48.00
9 $ 12.00 $ 32.00 $ 44.00 $ 1.33 $3.56 $4.89 $6.00 $6.00 $ 54.00
10 $ 12.00 $ 39.00 $ 51.00 $ 1.20 $3.90 $5.10 $7.00 $6.00 $ 60.00
11 $ 12.00 $ 47.00 $ 59.00 $ 1.09 $4.27 $5.36 $8.00 $6.00 $ 66.00
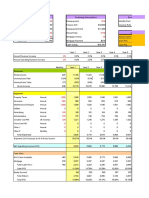
Correct Level of Output
Total Costs of Production Highest Profit
$70.00
$60.00
$50.00
Marginal Costs = Marginal Revenue
Dollar Costs
$40.00
$30.00
$20.00
$10.00
$-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Output
Total Fixed Costs (TFC) Total Variable Cost (TVC)
Total Cost (TC)
Long Run Profit Maximizing Output Level
Average Total Cost
D=AR=MR
Price Perfect Competition Ma
Five Characteristics:
1. Many firms produce i
Marginal Cost 2. Large number of buye
3. Sellers and buyers ha
about the produc
4. No barriers to entry o
5. The Seller is a Price ta
Quantity
The ultimate goal of this market structure is to establish an equilibrium between
demand and supply. In perfect competition the market is saturated with suppliers
each firm is a price taker and maximize the profit by mananging the quantity they
produce. In order to maximize profits in a perfectly comptetitive market, firms set
marginal revenue equals to marginal cost (MR=MC). In the long-run, economic profit
cannot be sustained. The new firms in the market causes the demand curve of each
individual firm to shift downard, bringing down the price, the average revenue and
marginal revenue curve. Therefore, in the long-run, the firm will make zero economic
profit.
Average Costs of Production
$20.00
$18.00
$16.00
$14.00
Production Costs
$12.00
$10.00
$8.00
Total Marginal $6.00
Profit Revenue $4.00
(TP) (MR)
$2.00
$0.00
$-
($12.00) 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
($9.00) 6 Output
($5.00) 6
$0.00 6 Average Fixed Costs (AFC) Average Variable Costs (AVC)
$4.00 6 Average Total Costs (ATC) Marginal Costs (MC)
$7.00 6
$9.00 6 Profit Maximization
$10.00 6 $70.00
Reve n u e an d C o st s
$10.00 6 $60.00
$9.00 6 $50.00
$40.00
$7.00 6 $30.00
$20.00
$10.00
Highest Profit $-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Output
Total Cost (TC) Total Revenue (TR)
Costs = Marginal Revenue
Measuring Total Profits
20
18
Price and Cost Per Unit
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Output
Average Total Costs (ATC) Marginal Costs (MC)
Marginal Revenue (MR)
6
Price a
4
2
0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Output
Average Total Costs (ATC) Marginal Costs (MC)
Marginal Revenue (MR)
Perfect Competition Market Structure
Five Characteristics:
1. Many firms produce identical products
2. Large number of buyers and sellers
3. Sellers and buyers have all relevant information to make rational decisions
about the product being bought and sold
4. No barriers to entry or exit
5. The Seller is a Price taker
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 05-Back To Basics - Your Guide To Manufacturing Excellence (Series On Resource Management) - Steven PDFDokument213 Seiten05-Back To Basics - Your Guide To Manufacturing Excellence (Series On Resource Management) - Steven PDFPoya KhNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM Standard For C Q E2500Dokument5 SeitenASTM Standard For C Q E2500GerifalteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loan Modification CalculatorDokument4 SeitenLoan Modification CalculatorElizabeth ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Amortization Schedule With Irregular Payments v.2Dokument75 SeitenExcel Amortization Schedule With Irregular Payments v.2azertyytrezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Cash SheetDokument1 SeiteDaily Cash Sheethowieg43100% (2)
- M&a Case Study SolutionDokument3 SeitenM&a Case Study SolutionSoufiane EddianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 7 Solutions 2 PDFDokument5 SeitenHW 7 Solutions 2 PDFUmerSaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRP Nigel SlackDokument18 SeitenMRP Nigel Slackwanara_seta3384Noch keine Bewertungen
- Property Info: Operation CostsDokument2 SeitenProperty Info: Operation CostsKilogram LossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Reporting PackageDokument50 SeitenExecutive Reporting PackageArthsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format of Financial Statements Under The Revised Schedule VIDokument97 SeitenFormat of Financial Statements Under The Revised Schedule VIDebadarshi RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1 SwanDavisDokument4 SeitenCase 1 SwanDavissilly_rabbit0% (1)
- Capital Budgeting by Group 1 PDFDokument54 SeitenCapital Budgeting by Group 1 PDFSXCEcon PostGrad 2021-23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Walmart Inc. - Operating Model and Valuation - Cover Page and NavigationDokument24 SeitenWalmart Inc. - Operating Model and Valuation - Cover Page and Navigationmerag76668Noch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Skills - Loan Calculation & Analysis TemplateDokument57 SeitenExcel Skills - Loan Calculation & Analysis TemplateCyprienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalbudgeting 151105130320 Lva1 App6892Dokument40 SeitenCapitalbudgeting 151105130320 Lva1 App6892Mrvive JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Company Process v6 SYDokument65 SeitenInter Company Process v6 SYrikizalkarnain88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Financials SampleDokument19 SeitenComparative Financials SampleNadia.ishaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Use JK PDFDokument9 SeitenMixed Use JK PDFAnkit ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cma of HostelDokument128 SeitenCma of HostelkolnureNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEM Reporting DashboardDokument21 SeitenTEM Reporting DashboardLawrence BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income Statement Horizontal Analysis TemplateDokument2 SeitenIncome Statement Horizontal Analysis TemplateSope DalleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Law Firms in The US: Due ProcessDokument35 SeitenLaw Firms in The US: Due ProcessCraigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled SpreadsheetDokument816 SeitenUntitled SpreadsheetrakhalbanglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Detailed Financial Projections Template 8821 UpdatedDokument27 SeitenIC Detailed Financial Projections Template 8821 UpdatedRozh SammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Answer 3Dokument14 SeitenBest Answer 3Chelsi Christine TenorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFH Rental AnalysisDokument6 SeitenSFH Rental AnalysisA jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial CalculatorDokument58 SeitenFinancial CalculatorAngela HarringtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Template Detailed ModelDokument20 Seiten1) Template Detailed Modelabdul5721Noch keine Bewertungen
- Property Reality - Bond Statement TemplateDokument21 SeitenProperty Reality - Bond Statement TemplateOwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personlig BudgetDokument6 SeitenPersonlig BudgetAnn SundkvistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gail India Oil and GasDokument38 SeitenGail India Oil and GasKumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Existing Building AnalysisDokument15 SeitenExisting Building AnalysisAmir H.TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capital Budgeting Analysis For Medical Services USA: Purpose of SpreadsheetDokument71 SeitenCapital Budgeting Analysis For Medical Services USA: Purpose of SpreadsheetSalman FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dabur Financial Modeling-Live Project.Dokument47 SeitenDabur Financial Modeling-Live Project.rahul1094Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tax CalculaterDokument2 SeitenTax CalculaterMahimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pro FormaDokument1 SeitePro FormaSuavekBartosinski100% (2)
- Balanced ScorecardDokument13 SeitenBalanced Scorecardatulmir50% (2)
- Management Accounting SampleDokument25 SeitenManagement Accounting SampleEdward Baffoe100% (1)
- Tati Nomination FormsDokument16 SeitenTati Nomination FormsAl Manar PetroleumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting KpisDokument6 SeitenAccounting KpisHOCININoch keine Bewertungen
- Appropriations Dividend To Shareholders of Parent CompanyDokument30 SeitenAppropriations Dividend To Shareholders of Parent Companyavinashtiwari201745Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Consolidation Package - TemplateDokument369 Seiten7 Consolidation Package - TemplateOUSMAN SEIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolling Budget and Forecast : Model KeyDokument2 SeitenRolling Budget and Forecast : Model KeyomernoumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pay Slip TemplateDokument1 SeitePay Slip TemplateJohn Rheymar TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Rental Analysis WorksheetDokument8 SeitenBasic Rental Analysis WorksheetGleb petukhovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation, and MaintenanceDokument111 SeitenBusiness Application System Development, Acquisition, Implementation, and MaintenanceSudhir PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business ValuationDokument2 SeitenBusiness Valuationahmed HOSNYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model #14 M - A Model (Mergers and Acquisitions)Dokument11 SeitenModel #14 M - A Model (Mergers and Acquisitions)Rahul GopanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management CalculationsDokument35 SeitenFinancial Management CalculationsfossacecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blu Containers Worksheet - IntermediateDokument13 SeitenBlu Containers Worksheet - Intermediateahmedmostafaibrahim22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Merger Model PP Allocation BeforeDokument100 SeitenMerger Model PP Allocation BeforePaulo NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Feasibility of Product ADokument4 SeitenFinancial Feasibility of Product AMuhammad AsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule of Duties and Professional Charges For Quantity SurveyingDokument4 SeitenSchedule of Duties and Professional Charges For Quantity SurveyingJared MakoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water PPPS: Training & WorkshopDokument23 SeitenWater PPPS: Training & WorkshopShreyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mortgage Calculator Excel TemplateDokument13 SeitenMortgage Calculator Excel TemplateHamid MansouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standalone Financial Results For September 30, 2016 (Result)Dokument10 SeitenStandalone Financial Results For September 30, 2016 (Result)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Statement Model: Strictly ConfidentialDokument9 Seiten3 Statement Model: Strictly ConfidentialAshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smilehouse Financial Model 051114Dokument84 SeitenSmilehouse Financial Model 051114Nguyen Thi Mai LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yates Financial ModellingDokument18 SeitenYates Financial ModellingJerryJoshuaDiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4 Notes Easy NotesDokument91 Seiten3.4 Notes Easy Notesapi-3813392Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Model - SolutionDokument6 SeitenFinancial Model - SolutionOssama AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Eportfolio Monopoly Spreadsheet Data - SPG 18 1Dokument3 SeitenMicro Eportfolio Monopoly Spreadsheet Data - SPG 18 1api-334921583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eportfolio AssignmentDokument17 SeitenEportfolio Assignmentapi-409603904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Eportfolio Monopoly Spreadsheet Data - SPG 18 1Dokument3 SeitenMicro Eportfolio Monopoly Spreadsheet Data - SPG 18 1api-334921583Noch keine Bewertungen
- EportfolioDokument4 SeitenEportfolioapi-334921583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Economic PresentationDokument13 SeitenEconomic Presentationapi-334921583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Sachin Tandukar Class: Severe and Hazardous Weather Professor: Derek Mallia Fire in The Earth System David M. J. S. BowmanDokument9 SeitenName: Sachin Tandukar Class: Severe and Hazardous Weather Professor: Derek Mallia Fire in The Earth System David M. J. S. Bowmanapi-334921583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 5Dokument4 SeitenQuiz 5Nguyet T NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABC AnalysisDokument6 SeitenABC AnalysisPankaj GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsDokument33 SeitenBasic Cost Management ConceptsMarcela Nichol RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap013 Target Costing Cost MNGTDokument49 SeitenChap013 Target Costing Cost MNGTramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean Thi Nki NG: Single Minute Exchange of Dies: Literature ReviewDokument11 SeitenLean Thi Nki NG: Single Minute Exchange of Dies: Literature ReviewBhanuj VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scrum Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteScrum Cheat Sheetmohitmcm100% (3)
- PCB Book v5.0.4 e Demo WDokument56 SeitenPCB Book v5.0.4 e Demo Whlgc63100% (1)
- Which of The Following Falls Under The Activity-Based Management Umbrella?Dokument17 SeitenWhich of The Following Falls Under The Activity-Based Management Umbrella?naddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management System and ISODokument15 SeitenQuality Management System and ISODana Goan100% (1)
- 8D Template Hussey Schnaider FormatDokument37 Seiten8D Template Hussey Schnaider FormatJuan Carlos Lekuona-Muñoz CarrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Conversion Cycle: Introduction To Accounting Information Systems, 7eDokument44 SeitenThe Conversion Cycle: Introduction To Accounting Information Systems, 7eontykerlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaizen Case StudyDokument2 SeitenKaizen Case Studykirti_27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bus 359.Q2.2021.22 - Eoq Rop - HWDokument2 SeitenBus 359.Q2.2021.22 - Eoq Rop - HWTrần Hữu ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Athletic Knit: A Case Study On Inventory ControlDokument9 SeitenAthletic Knit: A Case Study On Inventory ControlAnagha BhatkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPP MRP 18mayDokument12 SeitenPPP MRP 18mayuddindjmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 8502 - 4-2000Dokument22 SeitenIso 8502 - 4-2000smupy_122-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Six Sigma (Vijayvignesh N S 2020606042)Dokument12 SeitenSix Sigma (Vijayvignesh N S 2020606042)N S Vijay VigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens PLM Siemens I DT MC CON Cs Z6Dokument4 SeitenSiemens PLM Siemens I DT MC CON Cs Z6rasgeetsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing PlanDokument49 SeitenManufacturing PlanRiad BoudehriNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGM - TVS PresentationDokument19 SeitenLGM - TVS Presentationsuraj nairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart-1Dokument1 SeiteSheet Metal Gauge Size Chart-1rahil_sangNoch keine Bewertungen
- OeeDokument6 SeitenOeesingh1984_09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cost of Quality (Compatibility Mode)Dokument39 SeitenCost of Quality (Compatibility Mode)esivaks2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 4432 (1988) : Case Hardening Steels (MTD 16: Alloy Steels and Forgings)Dokument15 SeitenDisclosure To Promote The Right To Information: IS 4432 (1988) : Case Hardening Steels (MTD 16: Alloy Steels and Forgings)Selvaraji Muthu50% (2)
- TQM IntroductionDokument32 SeitenTQM Introductionshivashankar sgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaduna State University: PGD in AccountingDokument12 SeitenKaduna State University: PGD in AccountingPAUL TIMMYNoch keine Bewertungen