Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ccna 1 Mind Map
Hochgeladen von
Hp SlateOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ccna 1 Mind Map
Hochgeladen von
Hp SlateCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
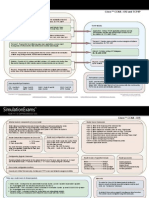
PDU: Data Stream Protocols:
• This layer serves as the source and destination of
Protocols: communications across data networks. TCP UDP
[Type text]
• Directly accessing the underlying processes that
DNS: used to resolve Internet names to IP
addresses. manage and deliver communication to the human
HTTP: used to transfer files that make up the network.
Web pages of the World Wide Web. • Enabling users to interact with the data network in a
SMTP: used for the transfer of mail messages way that is meaningful and effective.
and attachments (MUA MTA, MTA MTA)
POP: mail delivery protocols. They deliver e-
mail from the e-mail server (MDA) to the client
OSI Reference
(MUA)
Model
Telnet: terminal emulation protocol used to PDU: Segment
provide remote access to servers and 7. Application
networking devices.
6. Presentation
Encoding the bits for transmission and decoding them at the 5. Session Dividing data received from an application into segments
destination. Adding a header to identify and manage each segment
4. Transport
Describing the physical, electrical, and mechanical Using the header information to reassemble the segments
characteristics of the physical media and connectors that 3. Network back into application data
interconnect network devices. Passing the assembled data to the correct application
2. Data Link
Enabling data to be directed to the correct application
PDU: bits 1. Physical running on end devices using port numbers.
Variousdifferent
Notes: media and Physical
media layerfiber,
(copper, protocols have different
wireless)
advantages/disadvantages of each kind. When is
data-carrying capacities. Raw data bandwidth tothe
usetheoretical
ST/Cross? PDU: Packet Protocols: IPv4, IPv6
upper
And howlimit of athe
to tell bit difference
transmission. Throughput
between them. and goodput are
PDU: Frame Notes:
different measures of observed
Preparing data layer
Network transfer over for
packets a specific
period of time. placement onto the physical media that L3 uses logical addresses to
transports data. Carrying data from one host to another regardless of identify and route traffic from one
Notes: the type of data. network to another.
Layer 3 IP routing does not guarantee reliable Network/subnet address.
L2 uses physical addresses to identify nodes and deliver
delivery or establish a connection before data is Broadcast address. Host address.
frames in the local network/segment.
transmitted. This connectionless and unreliable Subnet mask.
Ethernet is the most widely used LAN technology.
communication is fast and flexible, but upper layers Public vs. private addresses
CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, Token passing must provide mechanisms to guarantee delivery of Default Gateway
data if it is needed. Purpose of the routing table
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CCNA ICND2 CheatsheetDokument10 SeitenCCNA ICND2 CheatsheetLulzim BruçajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CLI CheatsheetDokument2 SeitenCisco CLI CheatsheetNg Chin Chong100% (1)
- CCNA Cheat SheetDokument3 SeitenCCNA Cheat Sheetnarenprasad88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mindmap OSPFDokument1 SeiteMindmap OSPFmohanraj_ponnusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Mind MapDokument1 SeiteCCNA Mind MapMahmoud Reda100% (2)
- CCNA Command Cheat SheetDokument33 SeitenCCNA Command Cheat SheetLumin Han100% (1)
- CCNA CheatSheet PDFDokument19 SeitenCCNA CheatSheet PDFpranali50% (2)
- CCNP - FlashcardsDokument19 SeitenCCNP - Flashcardsnacho_456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Cram SheetDokument6 SeitenCcna Cram SheetDevistated100% (1)
- (CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #1 - Boubakr Tech PDFDokument4 Seiten(CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #1 - Boubakr Tech PDFPrabhashKumarJha100% (2)
- CCNA Notes FinalDokument41 SeitenCCNA Notes FinalNabi Bakhsh100% (2)
- Cheat Sheet On CCNA TerminologiesDokument12 SeitenCheat Sheet On CCNA Terminologiesdevdas100% (1)
- CCNP Class Notes (Ospf)Dokument20 SeitenCCNP Class Notes (Ospf)Bashri MabyouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Networking Interview QuestionsDokument8 SeitenCisco Networking Interview Questionsajit8279Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ipv4 MulticastDokument1 SeiteIpv4 MulticastopexxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingDokument8 SeitenCCNA Cheat Sheet: Experts in NetworkingHeribertus BudhihartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nokia SRC Scalable IP Exam Sample Questions Document enDokument7 SeitenNokia SRC Scalable IP Exam Sample Questions Document enabc100% (1)
- TCP/IP Networking Interview Questions, Answers, and Explanations: TCP/IP Network Certification ReviewVon EverandTCP/IP Networking Interview Questions, Answers, and Explanations: TCP/IP Network Certification ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- CCNA Security, Final ExamDokument22 SeitenCCNA Security, Final ExamMarco Antonio Vera Marin100% (1)
- Cisco Cheat SheetDokument1 SeiteCisco Cheat SheetParulSawhneySethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Cram Sheet - ICND 1 PDFDokument2 SeitenCCNA Cram Sheet - ICND 1 PDFadkadimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic SubnettingDokument7 SeitenBasic Subnettingandreas100% (6)
- Network Training Ppt1Dokument277 SeitenNetwork Training Ppt1aravindanjulie100% (1)
- Spanning Tree Protocol MindMapDokument1 SeiteSpanning Tree Protocol MindMapJonathan MonteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- FortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide-Online CompressedDokument388 SeitenFortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide-Online CompressedAngel GuzmánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) SecurityVon EverandVoice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) SecurityNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #3Dokument8 Seiten(CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #3researcherjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 300-101 Exam QuestionsDokument22 Seiten300-101 Exam QuestionsAdnaan Ahmad100% (1)
- Cisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)Dokument40 SeitenCisco TAC Entry Training - 9 - Network Address Translation (NAT)FerasHamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3he15239aaadtqzza01 - v1 - 7750 SR MG and CMG Cli Reference Guide r11.0.r7Dokument2.142 Seiten3he15239aaadtqzza01 - v1 - 7750 SR MG and CMG Cli Reference Guide r11.0.r7Username SOCIALNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRKSPG 2206Dokument89 SeitenBRKSPG 2206abaheabaheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Administering Cisco QoS in IP Networks: Including CallManager 3.0, QoS, and uOneVon EverandAdministering Cisco QoS in IP Networks: Including CallManager 3.0, QoS, and uOneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Routing Switching SyllabusDokument8 SeitenCCNP Routing Switching Syllabuskrishna100% (1)
- CCNA 2 Exams SolvedDokument70 SeitenCCNA 2 Exams Solvedvisky100% (9)
- CUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitectureDokument10 SeitenCUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitecturesenthilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 200-301 Ultima VersionDokument1 SeiteCcna 200-301 Ultima VersionmayraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtcre 1 4Dokument4 SeitenMtcre 1 4Silvano F. Rocha100% (1)
- Ccna v4 Lab GuideDokument48 SeitenCcna v4 Lab GuideRVR IT SERVICES100% (1)
- CCNP Route Lab ManualDokument44 SeitenCCNP Route Lab ManualAdeoso Adeboye0% (1)
- DOCSIS Evolution and How 3.1 Will Change EverythingVon EverandDOCSIS Evolution and How 3.1 Will Change EverythingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- SemSim CCNA Cram SheetsDokument9 SeitenSemSim CCNA Cram SheetsMohan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #4 - Boubakr TechDokument3 Seiten(CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #4 - Boubakr TechPrabhashKumarJhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Advanced Eigrp PDFDokument13 Seiten05 Advanced Eigrp PDFAbdelhakGhalmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spanning TreeDokument2 SeitenSpanning TreealhersalNoch keine Bewertungen
- (CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #5 - Boubakr TechDokument4 Seiten(CCNA) Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet #5 - Boubakr TechPrabhashKumarJhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 3Dokument434 SeitenCcna 3Siau HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSHOOT 15min GuideDokument13 SeitenTSHOOT 15min GuidejuliosistemasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Dokument47 SeitenEigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Sándor PetrócziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Exercise: SubnettingDokument27 SeitenLab Exercise: SubnettingMahmmoud MahdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAT and PAT PDFDokument4 SeitenNAT and PAT PDFtanzimshamsuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Topics Need To KN 2. Videos 3. Revision: 1.0 Network Fundamentals 20%Dokument4 SeitenExam Topics Need To KN 2. Videos 3. Revision: 1.0 Network Fundamentals 20%meeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP RouteDokument96 SeitenCCNP RouteAlexander GarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Ios CommandsDokument3 SeitenCisco Ios CommandsRrustem BejtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco SD-Access - Integrating With Your Existing Network - Vedran HafnerDokument91 SeitenCisco SD-Access - Integrating With Your Existing Network - Vedran HafnerMaheshBangera100% (1)
- Network Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandNetwork Segmentation Strategy A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandIP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandSIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna1 Chapter7 RobrigginsDokument7 SeitenCcna1 Chapter7 RobrigginsHp SlateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template Created by Terri Street Questions & Answers Entered by Katherine DouglasDokument37 SeitenTemplate Created by Terri Street Questions & Answers Entered by Katherine Douglassolecito89Noch keine Bewertungen
- SEM1 Final JeopardyDokument33 SeitenSEM1 Final JeopardyHp SlateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetaminophen Chart PDFDokument2 SeitenAcetaminophen Chart PDFHp SlateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA1 Final Answered Oct 2009 100 PercentsDokument22 SeitenCisco CCNA1 Final Answered Oct 2009 100 PercentsDiego Mogrovejo NarváezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cours BY PART 3Dokument69 SeitenCours BY PART 3ibou100% (1)
- Introduction To DoS & DDoS AttacksDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To DoS & DDoS Attacksanon_611052707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hltapi STC ReadmeDokument2 SeitenHltapi STC ReadmeVenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi LayerDokument5 SeitenOsi LayerJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure VRF Leaking On Cisco IOS XEDokument13 SeitenConfigure VRF Leaking On Cisco IOS XEIvan MachuzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 - OSPF Full LabDokument21 SeitenLab 5 - OSPF Full LabCésar CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Console Output CLI ConsoleDokument9 SeitenConsole Output CLI ConsoleJuan Carlos YepezNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTPDokument16 SeitenRTPsamyu83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title:: Write A Program To Demonstrate Subnetting and Find The Subnet MasksDokument10 SeitenTitle:: Write A Program To Demonstrate Subnetting and Find The Subnet MasksDarshan DerleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.6.1 Packet Tracer - Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default RoutesDokument4 Seiten15.6.1 Packet Tracer - Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default RoutesHạnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRKSPG 2518 PDFDokument133 SeitenBRKSPG 2518 PDFHoward ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network PosterDokument1 SeiteNetwork PosterShahzad Farooq100% (1)
- Collaboration Meeting Rooms (CMR) Cloud Enterprise Deployment Guide (WBS31)Dokument46 SeitenCollaboration Meeting Rooms (CMR) Cloud Enterprise Deployment Guide (WBS31)Cark86Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install An SSL Certificate From A Commercial Certificate Authority - DigitalOceanDokument27 SeitenHow To Install An SSL Certificate From A Commercial Certificate Authority - DigitalOceanramakrishnanpisharodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connection Log - PreviousDokument72 SeitenConnection Log - PreviousSergio BranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 192.168.100.0 /25, 2 Subnets, 126 Hosts / Subnet 192.168.100.0 /28, 16 Subnets, 14 Hosts / SubnetDokument1 Seite192.168.100.0 /25, 2 Subnets, 126 Hosts / Subnet 192.168.100.0 /28, 16 Subnets, 14 Hosts / SubnetTenzin DorjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 07b Inter-Vlan (Latihan 2)Dokument5 SeitenModul 07b Inter-Vlan (Latihan 2)Niken LarasatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud HubDokument7 SeitenCloud HubJhony AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista de Trakers UTorrentDokument11 SeitenLista de Trakers UTorrentLary RaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Job Interview Questions - AnswerDokument6 SeitenCCNP Job Interview Questions - Answermdtanvirkhan1279618Noch keine Bewertungen
- HCIE-Routing & Switching V3.0 考试大纲 PDFDokument8 SeitenHCIE-Routing & Switching V3.0 考试大纲 PDFAlexey PrisyagnyukNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMWARE V5 Platform System Log MessageDokument220 SeitenCOMWARE V5 Platform System Log Messageserge.dudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Shortest Path First OspfDokument64 SeitenOpen Shortest Path First OspfAsif AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JM 20337Dokument2 SeitenJM 20337spikelinuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- EthernetDokument30 SeitenEthernetokboyinbodeNoch keine Bewertungen