Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Number of Averages
Hochgeladen von
phoneme790 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten1 Seitevibration averages
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenvibration averages
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten1 SeiteNumber of Averages
Hochgeladen von
phoneme79vibration averages
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
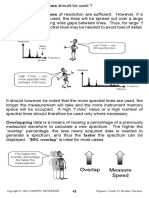
The parameter “number of averages” determines the number of
consecutive spectra used for averaging. The larger the number of
spectra used for averaging, the more noise spikes are smoothed out
and the more accurately true spectral peaks are represented.
However, the larger the “number of averages”, the more data needs to
be collected, and therefore the longer it takes to obtain the “average
spectrum”. A “number of averages” of 4 is sufficient for most cases.
The larger the number
of spectra used for
averaging, the slower
the measurement.
Number of Measure
Averages Speed
Collected data is usually not directly used to generate a spectrum, but
is often modified beforehand to cater for certain limitations of the FFT
process (the process that transforms the data into a spectrum). Data is
usually modified by multiplication with a correction window. This
prevents spectral lines from “smearing” or “leaking” into one another.
“Window type” is the parameter that determines the kind of window
that is used. The “Hanning” window is usually used. If the
“rectangular” window is used, the data will effectively not be modified.
Amplitude Amplitude
Hanning window No window
used used
Frequency Frequency
Copyright 2003 COMMTEST INSTRUMENTS 44 Beginner’s Guide To Machine Vibration
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SoundMagic AU Manual PDFDokument14 SeitenSoundMagic AU Manual PDFmcain93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisVon EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Signal Processing - Sync Vs Asynch and FFT WindowsDokument17 SeitenSignal Processing - Sync Vs Asynch and FFT WindowsPauloNavarreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRA4Picoscope SettingsDokument2 SeitenFRA4Picoscope Settingseng.fabio.griloNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper Understanding Data Averaging Modes en 5545142 PDFDokument3 SeitenWhite Paper Understanding Data Averaging Modes en 5545142 PDFMuhammad Fahmi MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Signal Processing for Effective Machinery AnalysisDokument11 SeitenVibration Signal Processing for Effective Machinery AnalysisMario Alfonso Zaragoza ZuñigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR EFFECTIVE VIBRATION ANALYSISDokument11 SeitenSIGNAL PROCESSING FOR EFFECTIVE VIBRATION ANALYSISmicky1389Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ac RecDokument47 SeitenAc RecHimanshu ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Setting Up Your Oscilloscope To Measure Jitter: Gary GiustDokument2 SeitenSetting Up Your Oscilloscope To Measure Jitter: Gary GiustUziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Use of Statistical Models To Establish and Update Vibration AlarmDokument11 SeitenEffective Use of Statistical Models To Establish and Update Vibration AlarmMohammadreza GalebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choosing the Right Windowing Function for Fourier AnalysisDokument19 SeitenChoosing the Right Windowing Function for Fourier AnalysisAbderrahim AbarayNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use A Spectrum AnalyzerDokument3 SeitenHow To Use A Spectrum Analyzer0limperoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Wiener Filter Making Signals Orthogonal: March 2019Dokument7 SeitenApplication of Wiener Filter Making Signals Orthogonal: March 2019Aqsa RamzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectral Density Estimation - WikipediaDokument9 SeitenSpectral Density Estimation - WikipediaEn Iyisi İnşaat MühendisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aliasing - Siemens PLM Community - 367750Dokument8 SeitenAliasing - Siemens PLM Community - 367750Vili KamenovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrum Analyzer ThesisDokument7 SeitenSpectrum Analyzer Thesistiffanysurrattlittlerock100% (2)
- Vibration Field Tehcnician GuideDokument21 SeitenVibration Field Tehcnician Guidebudiharyatno100% (1)
- Automatic Speech Recognition For Resource-Constrained Embedded SystemsDokument2 SeitenAutomatic Speech Recognition For Resource-Constrained Embedded SystemsmstevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Record-423Dokument54 SeitenAc Record-423NARENDRANoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Signal Analysis - FFTDokument20 Seiten04 Signal Analysis - FFTJohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis de Vibraciones Mecanicas SKFDokument31 SeitenAnalisis de Vibraciones Mecanicas SKFJhonathan GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dresser RandDokument71 SeitenDresser RandLong Nguyen100% (1)
- AN10073 How To Setup A Real Time Oscilloscope To Measure JitterDokument12 SeitenAN10073 How To Setup A Real Time Oscilloscope To Measure JitterMOHSENNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP SamplingDokument36 SeitenDSP Samplingin_visible100% (1)
- Audio Enhancement and Denoising Using Online Non-Negative Matrix Factorization and Deep LearningDokument9 SeitenAudio Enhancement and Denoising Using Online Non-Negative Matrix Factorization and Deep LearningIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unfiltered Audio Specops Manual enDokument19 SeitenUnfiltered Audio Specops Manual enHigaru KawasakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender Recong Paper 2Dokument4 SeitenGender Recong Paper 2Kumara SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis Dictionary: AccelerationDokument36 SeitenVibration Analysis Dictionary: Accelerationkamal arabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project PropoalDokument11 SeitenProject PropoalTadese AtomssaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDN - Real Spectrum Analysis With Octave and MATLAB - Steve HagemanDokument23 SeitenEDN - Real Spectrum Analysis With Octave and MATLAB - Steve HagemanRadh KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving The Effectiveness of The Median Filter: Kwame Osei Boateng, Benjamin Weyori Asubam and David Sanka LaarDokument13 SeitenImproving The Effectiveness of The Median Filter: Kwame Osei Boateng, Benjamin Weyori Asubam and David Sanka Laarammayi9845_930467904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation of Different Averaging Based Filter Designs Using Digital Signal Processor and Its Synthesis On FPGADokument18 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of Different Averaging Based Filter Designs Using Digital Signal Processor and Its Synthesis On FPGAअमरेश झाNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFDokument10 SeitenInspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFHari KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel VoiceDokument22 SeitenNovel VoicerasoolreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swerleins AlgorithmDokument14 SeitenSwerleins AlgorithmnomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoizer3 ManualDokument17 SeitenStereoizer3 ManualsaladeaulamusicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100-04 Noise Vibration and HarshnessDokument15 Seiten100-04 Noise Vibration and HarshnessAngy SalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Complete Guide To Machine Learning For Sensors and Signal Data PDFDokument31 SeitenThe Complete Guide To Machine Learning For Sensors and Signal Data PDFlykecu100% (1)
- Talview Project DescriptionDokument3 SeitenTalview Project DescriptionfforappfforNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Transform, Wavelets, Prony Analysis: For Harmonics and Quality PowerDokument6 SeitenFourier Transform, Wavelets, Prony Analysis: For Harmonics and Quality PowerMilan PetrikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replacer ManualDokument4 SeitenReplacer ManualCris Riffo EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CZT Introduction - EmbeddedDokument6 SeitenCZT Introduction - EmbeddedJohn Bofarull GuixNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiomedicalDokument3 SeitenBiomedicalNavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Field Tehcnician Guide PDFDokument21 SeitenVibration Field Tehcnician Guide PDFadnane adnaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glosario Términos de Análisis de VibracionesDokument34 SeitenGlosario Términos de Análisis de VibracionesgabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero PaddingDokument5 SeitenZero Paddingtommaso850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application Note #64 An Introduction To The DER2018 FFT EMI ReceiverDokument8 SeitenApplication Note #64 An Introduction To The DER2018 FFT EMI ReceiverpatopickNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFT GuideDokument7 SeitenFFT GuideJuan Cruz RaccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ann LA2 ProjectDokument23 SeitenAnn LA2 ProjectDimitri MolotovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Speech Recognition using Correlation AnalysisDokument5 SeitenAutomatic Speech Recognition using Correlation AnalysisTra LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Are Enveloping Spectra Plots ProcessedDokument1 SeiteHow Are Enveloping Spectra Plots ProcessedPPMNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Defeat Advanced Malware: New Tools for Protection and ForensicsVon EverandHow to Defeat Advanced Malware: New Tools for Protection and ForensicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Target Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsVon EverandAutomatic Target Recognition: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Test Methods for SRAMs: Effective Solutions for Dynamic Fault Detection in Nanoscaled TechnologiesVon EverandAdvanced Test Methods for SRAMs: Effective Solutions for Dynamic Fault Detection in Nanoscaled TechnologiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Digital Signal Processing and ApplicationsVon EverandApplied Digital Signal Processing and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolutionary Algorithms and Neural Networks: Theory and ApplicationsVon EverandEvolutionary Algorithms and Neural Networks: Theory and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Track-Before-Detect Using Expectation Maximisation: The Histogram Probabilistic Multi-hypothesis Tracker: Theory and ApplicationsVon EverandTrack-Before-Detect Using Expectation Maximisation: The Histogram Probabilistic Multi-hypothesis Tracker: Theory and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Short Term Memory: Fundamentals and Applications for Sequence PredictionVon EverandLong Short Term Memory: Fundamentals and Applications for Sequence PredictionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule Management PlanDokument1 SeiteSchedule Management Planphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule Management PlanDokument1 SeiteSchedule Management Planphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work Breakdown StructureDokument1 SeiteWork Breakdown Structurephoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network DiagramDokument1 SeiteNetwork Diagramphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Stakeholder Register: 8 Initiating FormsDokument1 Seite1.2 Stakeholder Register: 8 Initiating Formsphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Is Data Collected?: Itself. To Do This, Measurements Are Usually Recorded On TheDokument1 SeiteHow Is Data Collected?: Itself. To Do This, Measurements Are Usually Recorded On Thephoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement.: 2003 Commtest Instruments Beginner'S Guide To Machine VibrationDokument1 SeiteMeasurement.: 2003 Commtest Instruments Beginner'S Guide To Machine Vibrationphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cage Defect Frequency: Modulation, Frequency Modulation, and ModulationDokument1 SeiteCage Defect Frequency: Modulation, Frequency Modulation, and Modulationphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Data Displayed in Spectrum AnalysisDokument1 SeiteHow Data Displayed in Spectrum Analysisphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Requirements Management PanDokument1 SeiteRequirements Management Panphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Backlash DefinitonDokument1 SeiteBacklash Definitonphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Beating DefinitionDokument1 SeiteBeating Definitionphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spectram LinesDokument1 SeiteSpectram Linesphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seal ApplicationsDokument1 SeiteSeal Applicationsphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machinery Health Sensors: White PaperDokument1 SeiteMachinery Health Sensors: White Paperphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Predict CorrosionDokument1 SeitePredict Corrosionphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- SC: Stepper Rich Limit:: FORM 6354-1Dokument1 SeiteSC: Stepper Rich Limit:: FORM 6354-1phoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Max Ferequrency Seleti9onDokument1 SeiteMax Ferequrency Seleti9onphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Water Pipe Flows PDFDokument1 SeiteDesign of Water Pipe Flows PDFphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Water Hammer CalcsDokument1 SeiteWater Hammer Calcsphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Important Note: Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Can Often Be VeryDokument1 SeiteImportant Note: Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI) Can Often Be Veryphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Steel Pipe Standards 1Dokument1 SeiteCarbon Steel Pipe Standards 1phoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Esp SoftwareDokument1 SeiteEsp Softwarephoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Characteristics of Pipe Fittings KL ValuesDokument1 SeiteHydraulic Characteristics of Pipe Fittings KL Valuesphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Characteristics of Pipe Fittings and FlowDokument1 SeiteHydraulic Characteristics of Pipe Fittings and Flowphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Straub Couplings: STRAUB-GRIP vs STRAUB-FLEXDokument1 SeiteTypes of Straub Couplings: STRAUB-GRIP vs STRAUB-FLEXphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sintakote JointDokument1 SeiteSintakote Jointphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Information: Serial Numbers and Engine NameplateDokument1 SeiteGeneral Information: Serial Numbers and Engine Nameplatephoneme79100% (1)
- Lean Maintenance PhasesDokument1 SeiteLean Maintenance Phasesphoneme79Noch keine Bewertungen