Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lead-Acid Battery No. 2
Hochgeladen von
Kuo Garol Sarong0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten5 SeitenBattery
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
ODT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBattery
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als ODT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten5 SeitenLead-Acid Battery No. 2
Hochgeladen von
Kuo Garol SarongBattery
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als ODT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
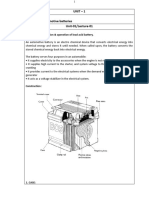
How a Lead Acid Cell Works
Basic Lead Acid Cell Construction
While battery manufacturers will employ different construction techniques and technologies, all lead
acid batteries have the same three fundamental components.
These three fundamental components rely on the physical laws associated with their chemistry to
provide a behavior that is relatively consistent from manufacturer to manufacturer.
The three fundamental components are:
Anode – This is the also known as the negative electrode or terminal. It is made of lead.
Cathode – This is known as the positive electrode or terminal. It is made of lead dioxide.
Electrolyte – This is a mixture of sulfuric acid and water. If you have the type of lead acid battery
known as a flooded cell, the electrolyte is the liquid that is sloshing around on the inside.
Definition and Discussion of Open Circuit
Output Voltage
There are two ways to measure the output voltage on a battery. The first is to take the measurement
with the battery disconnected. The second is to take the measurement with the battery powering
various devices.
Taking a voltage measurement with the battery disconnected from devices will provide what is known
as an open circuit output voltage. Sometimes this will be referred to as a “no load’ condition. That is to
say, there are no devices placing a demand on the battery.
Taking the same voltage measurement with the battery providing power to devices is taking the
measurement of the battery under load. This can be a more difficult measurement to interpret as the
voltage of a battery under load will vary depending on the amount of current being provided.
In some cases, it is far simpler to analyze the state of a battery by taking an open circuit voltage
measurement.
Lead Acid Cell versus Lead Acid Battery
A single cell is a single combination of a lead, lead dioxide and and electrolyte composed of sulfuric
acid and water. It’s output and behavior are governed by this chemistry. A single cell will provide an
open circuit output voltage of about 2.13 volts when fully charged and will be considered discharged
when its open circuit output voltage drops to 1.95 volts.
A battery may be a single lead acid cell or it may be several connected lead acid cells.
For example, a 12 volt car battery is made up of six lead acid cells that are connected in series. The
total open circuit output voltage from these cells when full charged is approximately 12.78 volts. It is
generally considered to be fully discharged when its open circuit output voltage drops to 11.7 volts.
Two Cycles of a Lead Acid Battery
The two cycles of a lead acid battery are referred to as a discharge cycle and a charge cycle.
During the discharge cycle, the battery is connected to a device and it is supplying power to that device.
It accomplishes this by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. While in this cycle, the
battery is considered to be acting as a Galvanic Cell. When the useable electrical energy within the
battery has been completed, the battery is considered to be fully discharged.
During the charge cycle, a power source (like a charger or alternator) is connected to battery and
supplies the battery with an electrical current. During this process, electrical energy is being converted
into stored chemical energy. While being charged, the battery is often considered to be acting as an
electrolytic cell. When the battery has reached its chemical energy storage capacity, it is considered to
be fully charged.
Functional Description of Lead Acid Battery
Discharge Cycle
Electrical power depends on a difference of electrons between two points. The fully charged battery has
more electrons at the negative terminal and fewer at the positive terminal.
When a fully charged battery is connected to a device (or load), the battery begins its discharged cycle.
During this cycle, electrons are leaving the negative terminal, powering the device and re-entering the
battery at the positive terminal. With the battery, the electrolyte is working to keep maintain the
difference of electrons between the negative terminal and positive terminal.
During this process, the electrolyte and the electrodes begin to change chemically begin exhausting
their ability to supply electrical power. When that ability to supply electrical power has been depleted,
the battery is said to be discharged.
When the battery is completely discharged, the electrolyte will be water and the electrodes will have
been transformed into lead sulfate.
What’s important to know here is that a dead battery will still have voltage when measured
by a meter. If devices are connected to the battery when the measurement is taken, the
battery will read about 10.5 volts. If devices are not connected, the voltage will be about
11.7 Volts.
Functional Description of Lead Acid Battery
Charge Cycle
The second cycle is known as the charge cycle. Its essentially the reverse of the discharge cycle.
During this cycle a a charger is connected to the battery. The charger output voltage is set to a voltage
that is higher than that of the battery. Current is essentially forced through the battery in the opposite
direction. Like the discharge cycle, a chemical change is occurring within the battery.
When the battery is completely charged, the negative electrode will be lead, the positive electrode will
be lead dioxide and the electrolyte will return to a mixture of sulfuric acid and water.
http://all-about-lead-acid-batteries.capnfatz.com/all-about-lead-acid-batteries/lead-acid-battery-
fundamentals/how-a-lead-acid-cell-works/
https://www.scribd.com/doc/140348858/UPSC-Chemical-Engineering-Fluid-Mechanics-Multiple-
Choice-Objective-Type-Questions-With-Answers-1
https://www.scribd.com/document/329271518/multiple-choice-questions-on-open-channel-flow
https://www.scribd.com/doc/140353116/Fluid-Mechanics-Multiple-choice-questions-for-engineers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 1 - Automotive Batteries ConstructionDokument62 SeitenChapter 1 - Automotive Batteries ConstructionMsaiful MiyoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BATTERIESDokument14 SeitenBATTERIESwagnerjames028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test, Charge and Replace Batteries and Jump-Start VehiclesDokument11 SeitenTest, Charge and Replace Batteries and Jump-Start Vehiclesajay100% (1)
- 12v DC To 230v Ac Inverter 1Dokument34 Seiten12v DC To 230v Ac Inverter 1Aman Shaik100% (1)
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDokument31 SeitenBasic Electronic ComponentsEngr. CasmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Battery ChargerDokument16 SeitenAutomatic Battery ChargerJULIET MOKWUGWONoch keine Bewertungen
- The Battery: SubjectDokument36 SeitenThe Battery: SubjectporkfaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Lead Acid BatteriesDokument8 SeitenAbout Lead Acid BatteriesAurvin SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment OneDokument10 SeitenExperiment Oneمحمد القدوميNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dokument82 SeitenModul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dzakwan LikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batteries HandDokument5 SeitenBatteries HandSyeda FarvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsDokument5 SeitenEngr. Jayde Paolo Castro Mirandilla Batteries: MIDTERM - ECE00 Basic ElectronicsRomuel Villanueva AlmeydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dokument49 SeitenModul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dzakwan LikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dokument33 SeitenModul Electrical System SMS III - 2020Dzakwan LikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Sizing - Open ElectricalDokument11 SeitenBattery Sizing - Open ElectricalJoseph GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 PDFDokument24 SeitenChapter 2 PDFbroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead Acid BatteriesDokument5 SeitenLead Acid BatteriesRanjan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Battery ServicingDokument24 SeitenAutomotive Battery ServicingEmmanuel Lucena100% (1)
- Charging and Starting Systems Unit 8 ChaDokument14 SeitenCharging and Starting Systems Unit 8 ChaDaniel AsratNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1Dokument9 SeitenUNIT 1 Moodle Lecture 1aryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1Dokument12 SeitenReport 1onkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2Dokument12 SeitenLec 2Joseph MagonduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Sources of DCDokument7 Seiten5 Sources of DCAparna RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery PresentationDokument56 SeitenBattery PresentationSandeep JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Correctly Charge A Battery - Microtex EnergyDokument19 SeitenHow To Correctly Charge A Battery - Microtex EnergySelva RengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions Battery (Resky)Dokument4 SeitenDefinitions Battery (Resky)Resky AprilianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Vehicle 3rd ModuleDokument25 SeitenElectric Vehicle 3rd ModuleSimi BaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Automotive BatteryDokument45 SeitenThe Automotive Batteryمحمد القدوميNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term PaperDokument3 SeitenTerm PaperJonie MatienzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery ManagementDokument53 SeitenBattery ManagementSovan Ghosh100% (1)
- Servicing Automotive BatteryDokument35 SeitenServicing Automotive BatteryYvan Lopez100% (3)
- The Critical Nature of Stationary Battery MaintenanceDokument7 SeitenThe Critical Nature of Stationary Battery MaintenancealfianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - ME467 Engine ElectricDokument21 Seiten3 - ME467 Engine Electricnoman88407Noch keine Bewertungen
- BattryDokument38 SeitenBattrynatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How A Battery Is MadeDokument11 SeitenHow A Battery Is MadejatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batteries and Fuel CellsDokument15 SeitenBatteries and Fuel CellsZulvana Anggraeni HarvianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Do The Calculation?: Figure 1. Stationary Batteries On A Rack (Courtesy of Power Battery)Dokument10 SeitenWhy Do The Calculation?: Figure 1. Stationary Batteries On A Rack (Courtesy of Power Battery)kritikasharma88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument18 SeitenChemistry ProjectMd RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolytic CellDokument12 SeitenElectrolytic CellabcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electricity 03Dokument31 SeitenBasic Electricity 03Tanvir AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3 Chemical Effect - Electric CellsDokument36 Seiten5.3 Chemical Effect - Electric CellsSho baconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrity TestingDokument0 SeitenIntegrity Testingjesus_hfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batteries Electricity Though Chemical ReactionsDokument6 SeitenBatteries Electricity Though Chemical ReactionsMuhammad Umar SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell and BatteryDokument5 SeitenCell and BatteryKrishnaSahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of EnergyDokument19 SeitenSources of EnergyYashwanth S DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inDokument12 SeitenPaper Battery Full Seminar Report On WWW Way2project inPhebe PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 057 PDFDokument16 Seiten2 057 PDFManny AnacletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive BatteryDokument25 SeitenAutomotive BatteryRichard I. de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Battery MainDokument23 SeitenPaper Battery MainSwati SinghalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BATTERIESDokument27 SeitenBATTERIESchintanpNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJARCCE5J A Rashmi Varma Automatic Battery Charger PDFDokument4 SeitenIJARCCE5J A Rashmi Varma Automatic Battery Charger PDFParu LechuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument31 SeitenModule 4Pragati ShindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.07 John Kim - Lead Acid Battery Charging Important Part of A Reliable Power Backup SystemDokument4 Seiten12.07 John Kim - Lead Acid Battery Charging Important Part of A Reliable Power Backup Systemgustavo RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Vehicle 3rd ModuleDokument18 SeitenElectric Vehicle 3rd Modulegirishvadde10Noch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Drives Function Blocks For Siemens PLCs Quick Start-Up Guide A A4Dokument40 SeitenABB Drives Function Blocks For Siemens PLCs Quick Start-Up Guide A A4ElafanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.cell in Series and ParallelDokument5 Seiten9.cell in Series and ParallelCarmella Mae QuidiligNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher: MR - Seale Student: Destineé JonesDokument7 SeitenTeacher: MR - Seale Student: Destineé JonesDwight JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELLS AND BATTERIES AllDokument18 SeitenCELLS AND BATTERIES AllVictor mulotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument6 Seiten1Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day 2Dokument2 SeitenDay 2Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- DocxDokument3 SeitenDocxKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument6 Seiten2Kuo Garol Sarong100% (1)
- Day 3 PICHEDokument13 SeitenDay 3 PICHEKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scanned With CamscannerDokument1 SeiteScanned With CamscannerKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiffusionDokument1 SeiteDiffusionKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics 3Dokument1 SeiteStatics 3Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample ProblemDokument1 SeiteSample ProblemKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transfer - 20190902115750Dokument1 SeiteMass Transfer - 20190902115750Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Thermo 1Dokument1 SeiteIntro To Thermo 1Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To ThermoDokument1 SeiteIntro To ThermoKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entropy ChangeDokument1 SeiteEntropy ChangeKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative AnalysisDokument1 SeiteQualitative AnalysisKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital Statistics - 20190720122838Dokument1 SeiteVital Statistics - 20190720122838Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics 5Dokument1 SeiteStatics 5Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics 4Dokument1 SeiteStatics 4Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics 1Dokument1 SeiteStatics 1Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dark Side of The Moon Roe v. WadeDokument4 SeitenThe Dark Side of The Moon Roe v. WadeKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- StaticsDokument1 SeiteStaticsKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Flow For Used Up BatteryDokument1 SeiteProcess Flow For Used Up BatteryKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cory Conjuangco - Aquino (Agrarian Reform)Dokument3 SeitenCory Conjuangco - Aquino (Agrarian Reform)Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- History 2Dokument13 SeitenHistory 2Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- EvaporationDokument1 SeiteEvaporationKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Doc 2019-06-17 11.18.06 - 20190617111842Dokument1 SeiteNew Doc 2019-06-17 11.18.06 - 20190617111842Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead-Acid Battery No. 1Dokument5 SeitenLead-Acid Battery No. 1Kuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civilian Home Defense ForcesDokument15 SeitenCivilian Home Defense ForcesKuo Garol SarongNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkDokument4 SeitenHow Magnetic Induction Lamps WorkMarlon BoucaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charger M HDokument4 SeitenCharger M HgeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor UsingDokument9 SeitenSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction Motor UsingPantech ElectricalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.1 The Bipolar-Junction Transistor: Basic PrinciplesDokument25 Seiten12.1 The Bipolar-Junction Transistor: Basic PrinciplessamuraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp1 Measuring Resistance Using The VA MethodDokument5 SeitenExp1 Measuring Resistance Using The VA MethodMuhammad EsleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Crystallinity of Polyethylene With Diffe PDFDokument13 SeitenEffect of Crystallinity of Polyethylene With Diffe PDFKhaled Saif AldinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mic 2514Dokument6 SeitenMic 2514Ashwin RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wideband Rec FDokument9 SeitenWideband Rec FMontaha BouezzeddineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Pentium Pro Is A SixthDokument12 SeitenThe Pentium Pro Is A SixthHemant MakwanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mtl7000 Series: Ultra-Slim Safety Barriers That Can Be Used Like TerminalsDokument13 SeitenMtl7000 Series: Ultra-Slim Safety Barriers That Can Be Used Like TerminalsDharmilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Non MetalsDokument10 SeitenMetals and Non MetalsKaran MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Inspiration Office LED Lighting Interactive Guide INTDokument28 SeitenApplication Inspiration Office LED Lighting Interactive Guide INTEddy Suyono ArchitectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- B10100Dokument4 SeitenB10100Francisco SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPS Sample Physics ProjectDokument24 SeitenCPS Sample Physics ProjectSHAIVYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Hybrid Digital: Four Phase PWM Controller For Intel Vr12.5™ CpusDokument47 SeitenGreen Hybrid Digital: Four Phase PWM Controller For Intel Vr12.5™ CpusIgorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 45 - 6575 - EE231 - 2013 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 231 - Lect - 01Dokument18 Seiten45 - 6575 - EE231 - 2013 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 231 - Lect - 01athomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester IV IPH-251 Physics-IV Geometrical and Wave Optics: Theory 4 Credits 3-1-0 Unit-IDokument12 SeitenSemester IV IPH-251 Physics-IV Geometrical and Wave Optics: Theory 4 Credits 3-1-0 Unit-IRahul ChhimpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12bDokument67 Seiten12bDan FarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected Failure Mechanisms of Modern Power ModulesDokument16 SeitenSelected Failure Mechanisms of Modern Power ModulesSoumitra KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Luminescence, Plasmonic, and Magnetic Properties of Doped Semiconductor NanocrystalsDokument17 SeitenLuminescence, Plasmonic, and Magnetic Properties of Doped Semiconductor NanocrystalsTrần ChứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heathkit IT-1121 Curve Tracer ManualDokument107 SeitenHeathkit IT-1121 Curve Tracer ManualdonsterthemonsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course OutlineDokument4 SeitenCourse Outlinemralex11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Thin FilmsDokument25 SeitenReport On Thin FilmsAbhisikta MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics Book 1 Electronic Devices and Circuit ApplicationsDokument28 SeitenFundamentals of Electronics Book 1 Electronic Devices and Circuit Applicationsjuan lopexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timing Aware Dummy Metal Fill MethodologyDokument3 SeitenTiming Aware Dummy Metal Fill MethodologyraveneyesdeadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zno ApplicationDokument5 SeitenZno ApplicationGauri PuranikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATV61HD30N4Dokument4 SeitenATV61HD30N4BlAdE 12Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPRS Module 3 - Basic ElectronicsDokument43 SeitenCPRS Module 3 - Basic ElectronicsLawrence Cada NofiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument26 SeitenPDFpooja waghmareNoch keine Bewertungen