Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
L2 Drafting Details PDF
Hochgeladen von
abhishekOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
L2 Drafting Details PDF
Hochgeladen von
abhishekCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drafting
Drafting system
• 3over 3 arrangement of rollers
• Two drafting zones
• Bottom rollers fluted
• Top rollers synthetic rubber Back roller
covered
28 2 28
• Draft limits Front 5
Maximum : 20- 22 roller Condens
28 er 25
Conde
Minimum : 5-6 25 nser
High draft : Lot of drafting irregularity Bottom apron
Low draft : High drafting force due to 2mm
large mass of fibre 2mm
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 2
Apron drafting
Elements of drafting system
• Drafting rollers
• Bottom rollers made of steel
• Top rollers synthetic rubber covered)
• Aprons
• Cradle
• Nose bar
• Condenser
• Spacer
• Weighting system
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 3
Aprons
Tensioning device
• Aprons are used to guide the fibres in the
drafting zone
• The aprons are made of synthetic rubber or
leather of 1mm in thickness .
Nose bar • The top apron extends over the drafting
Tension zone and held taut by tensioning device .
Pulley
• The bottom apron runs over smooth guide
bar ( nose bar ). The lower part of bottom
apron runs over a pulley.
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 4
Cradle
• The extension of the aprons within the draft
zone is known as cradle length ( a) .
Cradle Fibre length (mm)
length (a) Cotton Synthetic
40 36 33
43 33 50
50 - 60
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 5
• The top rollers and aprons get their drive from bottom rollers.
• The middle bottom roller drives
• bottom apron and
• top roller along with its apron due to frictional contact between them.
• Rollers are pressed against each other at 100-250N force to guide
fibres
• Aprons are also pressed against each other
• Top rollers weighing:
• spring pressure
• Pneumatic pressure
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 6
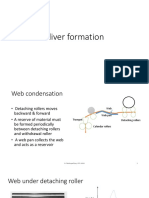
Spacing between top & bottom aprons
• Fibre guidance depends upon this pressure and
spacing between the aprons
• The pressure should be moderate.
X Roving
• Too much pressure
• extremely high drafting force leading to uneven drafting
and fibre breakage.
• Too less pressure
Bottom apron • inadequate guidance.
• Spacing should be adapted to fibre volume present
between the aprons
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 7
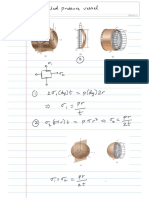
Apron pressure control
• The gap (X) between two aprons is adjusted by
spacers ( clip M) of variable height
• These are inserted between the nose bar of lower
apron and the cradle edge of top apron
• The pressure between aprons is adjusted by
inserting small clips known as “ spacers”.
• Spacers of various sizes are available to suit the
different fibre volume.
X Roving
• These are inserted between the nose bar of
bottom apron and cradle edge of top apron.
Bottom apron
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 8
X Roving
Bottom apron
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 9
Roller Pressure adjustment
• The set load stage can be
read on the pressure adjusting
cam in the form of
• numbers or
• color markings
Lever of the top weighting arm
2 Adjusting key 3 Pressure
adjusting cam
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 10
Fibre guidance by condenser
Drafted fibres tends to spread out . Condenser
Consequence : fly liberation & unevenness
They need to be brought back and hence
condensers.
• Three condensers
• Rear condenser (13)
• break draft condenser (14), and
• main draft condenser (15)
• The rear and back zone condensers have reciprocating
motion to spread out wear of top roller surfaces.
• The main zone condenser floats in draft field
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 11
Condenser Break draft
condenser
Rear condenser
Reference values for the break draft condenser
a (mm) b (mm) Color
10 12 14 3 3 3 green yellow red (standard)
Reference values for the rear condenser
a (mm) b (mm) Color Main draft zone condenser
12 3 transparent
16 3 red (standard)
20 5 yellow
28 5 green
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 12
Roller overhang
• The front roller overhang over bottom roller is 6 – 8mm . It is done
to accommodate 3mm condenser.
• The middle top apron roller is given 2mm back overhang from its
bottom roller to ensure satisfactory movement of bottom and top
aprons.
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 13
Drafting Front
roller
6-8
mm
Back roller
28
28 25 28
• It is essentially a two zone drafting
system consisting of 3 over 3 or 4 over Roving
4 drafting rollers. 28
30 25 28
Bottom
apron
• In the case of 4 over 4 rollers , a
neutral zone ( draft ≈ 1) separates the 49 /60/76mm 60 - 90mm
front and back zone. Middle
Front zone Back zone
zone
• The mass of fibre to be drafted being
large , inter fibre friction produces
large drag between fibres during
drafting.
4 over 4 drafting system
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 14
Significance of back Front
6-8
mm
Back roller
zone draft roller
28
28 25 28
Roving
• No effective control to be exerted in back zone . 28
30 25 28
• Purpose of the draft: To straighten out fibres in Bottom
sliver so as to ensure an even flow of slightly apron
tensioned well parallelized fibres into the main
49 /60/76mm 60 - 90mm
draft zone.
• Total draft = 10 -12 ( usually)
This is achieved by
• Wide back zone setting • Back zone draft = 1.2 – 1.4
• Low rear zone draft
• ( 1.05 – 1.15 for cotton, and
• 1.1 – 1.3 for synthetic). Most of the drafting is
performed in front zone
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 15
Significance of setting Front
6-8
mm
Back roller
roller
28
28 25 28
• Setting Roving
• Front zone : Fibre length +3mm - 5 mm 28
30 25 28
• Back zone : Fibre length + 10mm - 16 mm Bottom
apron
• Front zone setting must be of adequate
width to permit an undisturbed drafting 49 /60/76mm 60 - 90mm
operation. Otherwise, the drag may
become too strong to overcome by the
drawing force of the front pair of rollers
leading to undrafted portions.
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 16
6-8 mm Back
roller
Front
roller
2828 25 28
Roving
28 28
30 25
Bottom apron
49 /60/76mm 60 - 90mm
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 17
Drive to drafting rollers
Back roller
Middle roller
Front roller
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 18
End
R Chattopadhyay, IITD 2018 19
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Moisture Comfort - TXL750 PDFDokument188 SeitenMoisture Comfort - TXL750 PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ah! Ventures Startup Support ServicesDokument22 SeitenAh! Ventures Startup Support ServicesabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Mangala Joshi Course CoordinatorDokument20 SeitenDr. Mangala Joshi Course CoordinatorabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Venture Capital Firms in LondonDokument3 SeitenList of Venture Capital Firms in LondonabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ollala OllaDokument371 SeitenOllala OllaabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond Hi Bond HaDokument30 SeitenBond Hi Bond HaabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aecdea PDFDokument22 SeitenAecdea PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garment Fit Comfort TXL750 PDFDokument66 SeitenGarment Fit Comfort TXL750 PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7 Production Draft Calculation PDFDokument12 SeitenLesson 7 Production Draft Calculation PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6 Noil Extraction Theory PDFDokument20 SeitenLesson 6 Noil Extraction Theory PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Someka Templates InfoDokument7 SeitenSomeka Templates InfoabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Banking Sample Cover LetterDokument1 SeiteInvestment Banking Sample Cover LetterabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Intro Roving Frame PDFDokument8 SeitenL1 Intro Roving Frame PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument2 SeitenLecture 3abhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chetan Bhagat - Three Mistakes of My LifeDokument144 SeitenChetan Bhagat - Three Mistakes of My LifeGayathri ParthasarathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aecdea PDFDokument22 SeitenAecdea PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Properties TXL110Dokument31 SeitenFiber Properties TXL110abhishek100% (1)
- 7th AprilDokument12 Seiten7th AprilabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Age CEO CFO COODokument6 SeitenAge CEO CFO COOabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture7 Failure TheoriesDokument7 SeitenLecture7 Failure TheoriesabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleaching NPTELDokument16 SeitenBleaching NPTELabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25th Cvl100 Letc 9aDokument18 Seiten25th Cvl100 Letc 9aabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Western Region DirectoryDokument3 SeitenWestern Region DirectoryabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex-I: With Other Students by Applying The Formula of Their University, If Officially Provided by The UniversityDokument2 SeitenAnnex-I: With Other Students by Applying The Formula of Their University, If Officially Provided by The UniversityRichard GaurabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument5 SeitenLecture 1abhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Value of Education: Springboard For SuccessDokument28 SeitenThe Value of Education: Springboard For SuccessabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 35 - 2 PDFDokument23 SeitenLecture 35 - 2 PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minor-I Solution PDFDokument5 SeitenMinor-I Solution PDFabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Coastal Site Solutions GuideDokument35 SeitenCoastal Site Solutions GuideSandy PaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric SampleDokument2 SeitenRubric SampleAlexander James Pascua100% (5)
- Fosroc Conplast SP430: Constructive SolutionsDokument2 SeitenFosroc Conplast SP430: Constructive SolutionsDhrubajyoti DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positioner Serie XL - Vlatb048Dokument16 SeitenPositioner Serie XL - Vlatb048Felipe Gamboa GálvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Compaq LA2205wg PDFDokument8 SeitenHP Compaq LA2205wg PDFJerson A. Encarnacion ManceboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbinas A Gas EjerciciosDokument4 SeitenTurbinas A Gas EjerciciosEdwin Titirico ApazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEMM Drill02Dokument644 SeitenHEMM Drill02miningnova2Noch keine Bewertungen
- B7100HST-D 60164Dokument180 SeitenB7100HST-D 60164Juan MayorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of A Reviewer Manual in Mechanical Engineering With Theories and 5,001 Solved Problems and Answered Questions (Elements) : For Computerized Mechanical Engineering Licensure Examination PDFDokument13 SeitenDevelopment of A Reviewer Manual in Mechanical Engineering With Theories and 5,001 Solved Problems and Answered Questions (Elements) : For Computerized Mechanical Engineering Licensure Examination PDFTristan Tabago Consolacion33% (3)
- Kenmore Elite Microwave ManualDokument45 SeitenKenmore Elite Microwave ManualjibjabtooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome Newcomer To SLPDokument10 SeitenWelcome Newcomer To SLPnxgenoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conbextra EP10TG PDFDokument2 SeitenConbextra EP10TG PDFAcho SupraholicNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Catalogue Crucible GlobalDokument7 SeitenE Catalogue Crucible GlobalSylab InstrumentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eir July2017Dokument1.559 SeitenEir July2017Rakesh JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0409 - Water Temperature Sensor InstructionsDokument4 Seiten0409 - Water Temperature Sensor Instructionsyehaa_01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acc Gearbox Manual PDFDokument47 SeitenAcc Gearbox Manual PDFRESIMEN MAHASISWA SATUAN 605 / PWBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksDokument15 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2marksAbdul rahumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flywheel UPS PresentationDokument34 SeitenFlywheel UPS PresentationcarlosmandopintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emisiones AtmosféricasDokument64 SeitenEmisiones AtmosféricasHernán Santiago Effio LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev.0 21-1-14 TechDokument22 SeitenRev.0 21-1-14 Techjorge de oliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Parking Lot Design: Pdhonline Course C620 (6 PDH)Dokument51 SeitenComplete Parking Lot Design: Pdhonline Course C620 (6 PDH)Sahit NgjeçiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Technology - Implementation & Benefit For PLNDokument16 SeitenSmart Grid Technology - Implementation & Benefit For PLNrendroyoko100% (1)
- Kaeser - CSDx140SFCDokument11 SeitenKaeser - CSDx140SFCdheerajdorlikar100% (1)
- Digital Field Trip ReflectionDokument4 SeitenDigital Field Trip ReflectionZainab FarrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping QuestionsDokument8 SeitenPiping Questionsjijimon85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of The November 2017 ExamDokument5 SeitenAnalysis of The November 2017 Examtapera_mangeziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gl1200 BackfiringDokument4 SeitenGl1200 BackfiringPuican IulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressive Architecture-1965-01Dokument208 SeitenProgressive Architecture-1965-01Andréa CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiGas 4000 Light E 08.02Dokument2 SeitenDiGas 4000 Light E 08.02manit1963Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renewable Energy in North SulawesiDokument10 SeitenRenewable Energy in North SulawesiSeptian AnggoroNoch keine Bewertungen