Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Title: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-Supplier
Hochgeladen von
Deepak DasOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Title: Minimum Requirements On Welding From Supplier and Sub-Supplier
Hochgeladen von
Deepak DasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
1 of 10
1.0 Scope
1.1 To establish the minimum Sulzer Pumps Equipment requirements for Weld Procedure Specifications,
Weld Procedure Qualification Record, Welder Qualification and other weld related information’s. This
regulation does not seek to limit the degree of testing carried out during procedure qualification,
welder qualification or production, welder qualification or production welding, only to ensure a global
minimum supplier standard.
1.2 This specification applies to all welded fabrication and foundry-level casting repairs for Sulzer. This
includes, but is not limited to, the welding of pump casings, piping, vessels, castings, wear rings and
baseplates. These requirements apply to welding performed by contractors, fabricators, foundries,
and their sub-suppliers. Responsibility for implementation at Sub-suppliers is laying within the
Supplier who receive the Sulzer Purchase Order
1.3 The supplier shall refer to supporting documentation such as e.g. (PS) Purchasing Specification, (PO)
Purchase order, (ITP) Inspection Test Plan, (SQS) Sulzer quality Standards and / or others for
additional requirements.
1.4 Job-specific requirements may take precedence over or add to the requirements of this document. In
the event that requirements appear to conflict, the more stringent requirements shall prevail and any
conflict or question shall be brought to the attention of Sulzer.
1.5 Any required deviation to this document shall be submitted to Sulzer for review and approval.
1.6 All relevant construction codes must be adhered to with all welded items. The requirements in this
document are in addition to the code requirements. The code shall be always of latest edition unless
otherwise specified.
1.7 At any time a welding related document may be reviewed by Sulzer for compliance with contract
specifications and engineering requirements. Welder qualification (WPQ) , Weld procedures (WPS)
and or Procedure qualification records (PQR`s)or any other such as (PWHT procedures) or others not
named here, which do not meet contract specifications or engineering requirements may be rejected
at any time.
1.8 Welding of certain items is not addressed by this specification. This items include:
1.8.1 Specific noncritical, non-structural items including guards, fans, clamps, oil-retaining shields and non-
structural stands.
1.8.2 All relevant construction codes must be adhered to with these items.
2.0 General Notes
2.1 This document shall be considered when qualifying welding procedures for use on Sulzer equipment
such as, but not limited to pump casing fabrications, wear rings, lube oil systems, casting repairs,
baseplates etc. Suppliers shall nevertheless have welding programs which meet Codes and
Standards applicable to the project and this document..
2.2 If suppliers want to subcontract any welding activity, the chosen sub- supplier must fulfil all
requirements as specified in this and all other related documents. The subcontracting of welding
activities must be communicated to Sulzer and prior acceptance must be given in written prior to any
work start.
2.3 A site is a single manufacturing facility that extends as far as it has operational control of the welding
activities performed.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
2 of 10
3.0 References
3.1 All standards, codes and norms refer to the last published edition and addenda, which has to be
adopted if customer is not requiring a former version.
ASME BPVC IX American society of mechanical engineers Boiler and pressure vessel
code (Section: 9 “Welding and brazing qualifications”)
ASME BPVC II-C Specification for welding rods, electrodes and filler metals.
ASME BPVC VIII American society of mechanical engineers Boiler and pressure vessel
code (Section: 8“Rules of construction for pressure vessels”)
EN ISO 15614-1 Specification and qualification of welding procedures for metallic
materials - Welding procedure test - Part 1: Arc and gas welding of
steels and arc welding of nickel and nickel alloys
EN ISO 9606-1 to 4 Qualification testing of welders (Fusion welding)
NORSOK M-601 Welding and Inspection of Piping
ASTM A 488 Standard practices for steel castings, welding, qualification of
procedures and qualification
AWS D1.1 Structural welding code “steel”
ASME B 31.3 American society of mechanical engineers (Process piping)
ASME B 31.1 American society of mechanical engineers (Power piping)
EN ISO 5817 Welding - Fusion-welded joints in steel, nickel, titanium and their
alloys (beam welding excluded) - Quality levels for imperfections
SQS 0006 Handling of stainless steel
SQS 0007 Guideline for welding duplex materials
SQS 0008 Welding of martensitic stainless steels
4.0 Responsibility
4.1 Responsibility for compliance with this specification shall be defined within each supplier and or sub-
supplier site. Each supplier shall define implementation of these requirements in a written procedure
which shall define who in the organization is responsible for conducting, evaluating and approving
weld tests as well as responsibilities for records and communication towards Sulzer. One designated
point of contact at the supplier is preferred.
5.0 Weld Procedure Specification (WPS)
5.1 All welding activities must be covered by a qualified PQR and the necessary WPS must be
established. The only exceptions are welding on fasteners, and other non-loaded, non-pressure
boundary components and or structures.
5.1 Each WPS shall be in a format that contains all the relevant information and variables required by the
code against which it is qualified. All WPS shall be rationally titled and revision controlled. When WPS
is submitted to Sulzer corresponding documents must be attached and rationally named or labelled
for clear traceability.
5.2 As a minimum the use of English language is required. Bilingual translations are preferred (Local
language and English).
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
3 of 10
5.3 The necessary WPS for the job must be present in the shop at the time of welding and be understood
in fully by the welder and or welding operator.
5.4 The only option to use pre-qualified WPS is if the requirements from AWS D 1.1 or the EN ISO 1090
is implemented and documented in fully. The use of pre-qualified procedures shall be approved in
writing by Sulzer prior to the commencement of welding. The welder qualification must be in
accordance to ASME BPVC IX or EN ISO 9606. The AWS D1.1 only if applicable.
5.5 At any time a weld procedure may be reviewed by Sulzer for compliance with contract specifications
and engineering requirements. Weld procedures or PQRs which do not meet contract specifications
or engineering requirements may be rejected at any time.
6.0 Weld Procedure Qualification Record (WPQR)
6.1 Each WPQR shall be in a format that contains all the relevant information and variables required by
the code against which it is qualified. This code may be ASME IX, EN ISO 15614 The AWS D1.1 only
if applicable.
6.2 All internal supporting documentation shall be kept with the qualification record. This may include but
shall not be limited to: NDE reports, laboratory test reports, as-run records (including inter-pass
temperature information).
6.3 Test according to recognized standards and with the recommended soundness attained by
ISO 17025 accreditation. For all PQR testing. This requirement does not apply for production NDT
(Non-destructive testing).
6.4 Where it is required by local regulation, customer requirement or for other reasons, the WPQR shall
be witnessed and / or approved by a recognised jurisdictional, third party or verification body such as
Lloyds Register, Bureau Veritas or local equivalent. Where EU directives such as PED apply, then it
is mandatory for WPQR’s to be verified by a verification body.
6.5 Testing required for the qualification of WPQR shall be in accordance with Table 1 of this procedure.
6.6 Where testing per Table 1 does not meet local or project specific requirements, then additional testing
shall be carried out.
6.7 Each site is responsible for conducting the test required by the standard used to qualify the
procedures that are used in the construction of components under the rules of the codes, standards,
and specifications that reference the code applied. A site is having responsibility for operational
control of the material-joining methods used. Exchange of such documents shall be done for
reference only and not for production. Unless this scenario is approved in writing by the customer and
Sulzer prior to work start.
6.8 WPS and PQR records shall be maintained for lifetime of the production facility. For newly qualified
WPQR’s, any additional material of welded coupons shall be retained to allow supplementary testing
to be carried out at a later date, should it be required. Remaining specimen`s for PQR shall be
properly labelled, stamped if necessary and stored as long as the respective document is in use.
7.0 Welder and welding operator qualification
7.1 All welding must be performed by qualified welder and welding operator. Welders shall be qualified in
accordance with the code to which they will be welding. This code may be ASME IX, EN ISO 9606-1,
DIN EN ISO 14732, AWS D1.1 or other recognised standard prior to any work start.
7.2 Welder qualification for duplex materials shall include the equal corrosion tests as done for PQR as
stated in Table 1: “WPQR Testing requirements”
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
4 of 10
7.3 Welder qualification shall be done in a position that reflects the position of the daily work. The best
proof for skill is a welder qualification in ASME 6G but shall only be requested if applicable in
production.
7.4 All welding activities including preparations like tack welding, fabrication and repair work shall be
done by qualified welders only with the aid of a WPS. This also applies to tack welds which will be
removed before the completion of the weld.
7.5 A welder continuity log must be established in accordance to applied code or standard. The log must
be up to date at any time.
7.6 A written examination for welders on the theory, safety, and processes for welding is recommended.
The so called “job knowledge test” shall be done whenever a new welder qualification takes place or
at least every second year.
7.7 If a job knowledge test program is not available at a supplier site, the current applied training content
and frequency of trainings take place shall be presented to gain understanding and trust in the
qualification and skill of the welders.
7.8 A welder maintenance log documenting continuity of welder qualification shall be maintained in
accordance to the standard applied.
7.9 Independent of the applied standard and or code. It is recommended to renew the welder qualification
every 5 Years latest. This applies independently of the welder maintenance log status.
7.10 The vendor will immediately remove any welder or welding operator from work on Sulzer’s
components when, in the opinion of Sulzer, the welder does not possess the required competency or
attention to produce sound welds.
8.0 Post weld heat treatment (PWHT)
8.1 As a condition of supplier qualification, suppliers shall provide a PWHT procedure to Sulzer for
approval. The following minimum information shall be included in the procedure:
8.1.1 Place of heat treatment (address and company) Name, date and signature of operator.
8.1.2 Any required supporting in the furnace or other practices to prevent warping.
8.1.3 Thermocouple types, number, and locations.
8.1.4 Method of thermocouple attachment.
8.1.5 Full heat treat cycle information including heating and cooling rates, hold times and temperatures,
and cooling methods
8.1.6 A time-temperature record for PWHT is necessary. This record chart shall be attached to the heat
treatment report.
8.2 If PWHT is applied it is essential that the heat treatment parameters or a reference number to the
heat treatment procedure is available on the WPS. Referencing documents to be attached.
8.3 All PWHT equipment inclusive recording systems and related sensors must be regularly calibrated.
8.4 All closed heating chambers (e.g. furnace) require a temperature uniformity calibration. In accordance
to ASTM A991.
8.5 Any required NDE, including hardness testing, shall be carried out after final PWHT (if PWHT is
required). At suppliers option, for internal purposes, suppliers may choose to perform additional NDE
prior to PWHT, in order to identify defects before PWHT.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
5 of 10
9.0 General welding requirements
9.1 Suppliers shall be technically competent to perform all proposed welding.
9.2 Suppliers are fully responsible and liable for any welding which they subcontract to 3rd Party vendors
or welders.
9.3 Suppliers shall define an employee (or department) as the single point of contact for welding-related
questions and issues which may be raised by Sulzer Welding Engineering. This employee may be
retained as a part-time, full-time, or contract employee. This employee shall be competent to answer
technical questions relating to the vendor’s welding program and shall be empowered by
management to make any needed changes, if necessary. If this employee cannot be defined, or is
not sufficiently technically competent for the type of welding being done by the supplier, the supplier’s
welding qualifications may be partially or completely revoked.
9.4 Suppliers of pump component fabrications including barrels, cans, and discharge heads shall prepare
a fabrication maps for each component including:
9.4.1 Supplier Letterhead
9.4.2 PO Number and line item
9.4.3 Sulzer Sales Order Number
9.4.4 Proposed weld procedures for each joint inclusive thickness and preparation shape.
9.4.5 This is not required for baseplates, unless required by client requirement.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
6 of 10
10.0 Welding processes
10.1 Welding process description:
Below table shall clarify process details and application for the process on Sulzer components or
products. Independent on process a qualified procedure must be available.
In general shall the semi-automatic processes (131, 135, 136) only be applied on non-pressure
application such as baseplates or other structural components.
Process terminology according to (EN ISO 4063 / Common US terms according to AWS A2.4):
Process Application
(131 [MIG] / GMAW) with a solid wire filler Only to be applied for non-pressurized
and is shielded by inert gasses (Ar, He). Aluminium materials components.
(135 [MAG] / GMAW) with a solid wire filler To be used as Root and Hot pass for vertical
and is shielded by active gas mixture (Ar, He pump and or thick low load structural
2 2
with CO or O ). application. Also acceptable for coupling
guards or fans. Not allowed to use on any
pressure retaining components.
(136 [MAG] / FCAW-G) with a flux filled Preferred for baseplates and fill and cover
tubular wire and is shielded by active gasses passes on vertical pump components. The
2 2
(Ar with CO or O ). process is not allowed for small diameter
pipes.
(114 / FCAW-S) (without Gas) with a flux Not acceptable for any Sulzer component
filled tubular wire create shielding gas by unless specifically requested in PO or
burning the flux. agreed otherwise.
(141 / GTAW) Gas tungsten arc welding with Acceptable for any Sulzer component.
inert gas shielding.
(111 / SMAW) Shield metal arc welding Acceptable for any Sulzer component.
(12 / SAW) Submerged arc welding Acceptable for any Sulzer component.
(15 / PTA) Plasma tungsten arc welding with Especially useful for overlay, buttering and
inert and active gasses. hard facing.
(311 / OAW) Oxyacetylene welding Acceptable for wear application (e.g.
Stellite). Not acceptable for any pressure
retaining or structural application.
(52 / LBW) Laser welding Acceptable for any Sulzer component.
(441 / EXW) Explosion welding Acceptable where specified.
(78 / SW) Arc stud welding Acceptable for support and stand fastener.
(2 / RW) Resistance welding Acceptable where specified.
Others like (HVOF and its variations) Acceptable where specified.
Above list is not exhaustive, not mentioned processes or process combinations shall be qualified
according to code and presented to Sulzer for approval prior to any use.
10.2 All welding and related auxiliary equipment must be regularly maintained and calibrated. A sticker
shall indicate the expiry date on the equipment. A calibration certificate must be available on request.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
7 of 10
11.0 Filler metals and consumable
11.1 All suppliers shall have a written weld filler control procedure outlining the control and handling of
weld filler. This procedure shall be submitted on request for approval as a condition of qualification.
The procedure shall define clearly:
11.1.1 The method used to maintain identity of filler to prevent metal mixing.
11.1.2 The method of issuing filler to the welder.
11.1.3 Disposition of filler metal certs
11.1.4 The storage and handling of filler materials and its conditions. Furthermore handling of flux and flux
coated or cored filler materials with parameters for storage and re-drying.
12.0 Weld joint preparation
12.1 Tack welds at the root of the joint shall be made with filler metal equivalent to that which will be used
in the root pass. Tack welds shall be made by qualified welders and shall be fused with the root pass
or removed before welding. Cracked tack welds shall be removed by grinding, not welded over.
12.2 Surfaces to be welded and adjacent surfaces shall be dry, clean, and free of contamination (dirt, oil,
grease, scale, paint, slag, chemicals, low melting point metals, etc.) before welding. The clean area
shall extend at least 1 inch (25 mm) beyond the weld joint in all directions. Cleaning is required on
both the inside and outside surfaces. For pipe, this includes both the OD and ID.
12.3 Surfaces which have been prepared by thermal cutting or gouging methods shall be ground, filed, or
machined to remove oxidation and scale at least 1/16 inch or 1,5mm independent of service condition
of the surface.
12.4 Surfaces of P-No 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, and 4X that have been prepared using thermal cutting our gouging
shall have at least 1/16” of material beyond the cut surface removed by grinding or machining.
12.5 Any deviation from the weld joint preparation as specified in the related WPS is only acceptable if the
dimension is increasing. Any decrease of dimensions on the joint preparation is not permissible.
13.0 Welding technique requirements
13.1 Arc strikes and weld starts and stops shall be confined to the weld joint. Arc strikes outside the weld
joint shall be removed by grinding and examined for cracks using the inspection method required for
that surface, VT at minimum. Grinding shall not reduce the wall thickness to less than the minimum
design wall thickness. This rule applies independently of material.
13.2 GTAW “washing” without filler material is not allowed.
13.3 Crater cracks shall be removed by grinding. Crater cracks shall not be welded over.
13.4 The visual appearance of welds is very important to the confidence of the users of Sulzer’s pumps.
Suppliers shall make every reasonable effort to ensure that visible welds have a visually appealing
appearance. As a minimum standard all welding seams must be cleaned as needed and brushed
after welding, all spatter and or slag shall be removed. Also all edges shall be deburred or chamfered.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
8 of 10
14.0 NDE requirements
14.1 All NDE requirements are given in the respective TP (Test procedure) mentioned in the ITP
(Inspection and test plan) and the PO (Purchase Order).
14.2 All welding (100%) shall be visually inspected (Sulzer TP 0012, 0014 and 0015 as applicable)
independent of the additional requirements given in ITP, QQP or PO and all deviations must be
corrected prior to shipping to Sulzer. For any discontinuity’s will be found by visual incoming
inspection at Sulzer the supplier is liable and will be charged for any re-work effort necessary. A
report for the visual inspection is not necessary unless it is required by the PO or its related
documents such as ITP or QQP.
14.3 Examination of a weld repair area or a repair to a weld shall use, at minimum, the NDE method
required for the surface. This requirement applies both to a cavity prepared for welding, and to the
completed repair weld.
14.4 All requirements given in the TP must be fulfilled.
15 Various material and component related requirements
15.1 Requirements for welding on hardened martensitic stainless steel wear rings.
E.g. CA40 @ 400HB (casting defect repair or build up after miss machining)
15.1.1 PQRs intended to be used for hardened martensitic stainless steel wear rings require PQR testing
per the governing code, for material in the standard annealed or tempered condition, to demonstrate
that the weld is correctly fused.
15.1.2 Welds require filler with matching chemistry to the base metal. Use of austenitic stainless steel filler
metals is not allowed.
15.1.3 All welds require PWHT to establish the correct hardness level.
15.1.4 Wear rings manufactured from hardened martensitic stainless steel with a minimum specified
hardness above 300 HB require a full reaustinitize and temper Post-Weld Heat Treatment. This full
reheat treatment is required in order to restore HAZ hardness levels.
15.2 Requirements for welding Duplex Stainless Steel (DSS) and Super Duplex Stainless Steel (SDSS).
15.2.1 All requirements defined below apply for DSS and SDSS. Where requirements are defined
specifically for SDSS, they are allowed but not mandatory for DSS.
15.2.1.1 “DSS” is defined as austenitic-ferritic stainless steel with a PREN ≥ 34. Generally these alloys have
22% chromium.
15.2.1.2 “SDSS” is defined as austenitic-ferritic stainless steel with a PREN ≥ 40. Generally these alloys have
25% chromium.
15.2.1.3 Sulzer considers grades with UNS Numbers S32550 (Ferralium-255 and F61) and ACI Grade 1B to
be “Duplex” grades.
15.2.1.4 The alloy UNS S31803 is an obsolete version of this material grade and is not acceptable for Sulzer.
Use the UNS S32205 for welding only. Deviations to PO must be brought to Sulzers attention and
approved in writing.
15.2.2 Weaving is not allowed for any kind of Duplex welds, with the exception that the root pass only for
open-root welds may have a weave of no more than 2.5x the wire diameter, or if clearly recorded
according to PQR.
15.2.3 Heat input of production welds shall not exceed the heat input qualified in the PQR, unless the
completed weld is solution annealed.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
9 of 10
15.2.3.1 Heat input for DSS shall not exceed 2,50 kJ/mm (55 kj / in).
15.2.3.2 Heat input for SDSS shall not exceed 1,5 kJ/mm (37 kj / in).
15.2.4 Prequalification of DSS and SDSS weld procedures per AWS D1.1 is not allowed. DSS and SDSS
weld procedures require testing per the requirements of Table 1 of this document.
15.2.5 PQRs done on SDSS allow the welding of DSS, with an appropriate filler metal adjustment. PQRs
done on DSS allow the welding of DSS but not SDSS. Unless stated otherwise by other related
document.
15.2.6 Sulzer recommendation is not to use FCAW wire larger than 0.045” (1.2 mm) for DSS or SDSS.
Unless the related PQR values are achieved as described in Table 1.
16 General notes.
16.1 All certification and delivery advice documentation shall include the Sulzer Purchase Order number,
line item number and material number.
16.2 All documentation shall be provided on or prior to delivery of the material.
16.3 Acceptance of the material shall be on satisfactory compliance to the Purchase Order requirements.
16.4 All standards and Sulzer documents referenced shall be current issues unless stated otherwise.
16.5 Failure to comply with the above requirements could result in rejection or delayed payment of
invoices.
17 Sulzer attitude
17.1 This document has been established to provide minimum requirements on welded components for
Sulzer. If you have a need for further information or on clarification of technical details, please do not
hesitate to get in contact with the responsible Sulzer representative.
17.2 Our all future relies on the quality of the components and equipment we deliver our customer today.
Do not assume, know, clarify and help us to exceed our customer’s expectation and convince him
about our products by deliver what we promise and more, but never less.
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Purchase Specification
Technical Quality
Sulzer Pumps
Page:
Title: Minimum requirements on welding from supplier and sub-supplier
10 of 10
Table 1. Sulzer recommended WPQR Testing Requirements
Intergranular corrosion
LP or MP Examination
ASME IX / EN 15614 /
RT or UT Examination
ASTM G48 Corrosion
Other recognised std.
Macro-examination
Micrographic-
Impact Tests
Ferrite count
ASTM A262
examination
Hardness
Test
test
Carbon Steel ● ● ● ○
Note 1, 7, 8
Low Temperature Carbon
Steel ● ● ● ● ●
Note 7, 8
2.5% Cr Steel ● ● ● ○
Note 7, 8
12% Cr Steel ● ● ● ●
Note 7, 8
304 / 304L ● ● ● ○
Note 2, 7, 8
316 / 316L ● ● ● ○ ○ ○
Note 1, 7, 8
22% Cr Duplex ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
Notes 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
25% Cr Duplex ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
Notes 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
CuNi ● ● ●
Note 7, 8
6Mo ● ● ●
Note 7, 8
● Mandatory Requirement.
○ Optional Requirement
Note 1 - Hardness testing shall be carried out where compliance with NACE is required.
Note 2 - For cryogenic service impacts shall be carried out at -196°C (-321°F)
Note 3 - Max. hardness 28 HRC (22% Cr) and 32 HRC (25% Cr)
Note 4 – ASTM G48 shall be at 25°C (77°F) for 24 hours.
Accept: No pitting, 4.0 g/m2 (0.00082 lb/ft2) max. weight loss
Note 5 - Impact tests required at -46°C (-51°F). Accept 45J (single reading 35J) minimum
(Except for 3A and 1B material no Impact testing is required)
Note 6 - Ferrite balance shall be in the range of 35-65% for weld metal and HEZ heat effected zone.
Note 7 - Where a test is not defined in the table, or where it is not defined either as mandatory or optional, then that
test may be carried out at the discretion of the site performing the qualification.
Note 8 – Whenever a new PQR is performed the specimen shall be longer than needed for additional testing with
values different from what we qualify. It is best practice to do the WPQR with a test specimen of extended size in
order to have sufficient material left for further tests. This PQR specimen’s shall be stored properly and stamped for
easy identification as well as from 3rd party inspector if applicable
Note 9- ASTM G48 shall be at: 40°C (104°F) for 24 hours if in the as welded condition.. 50°C (122°F) for 24 hours if
PWHT is applied. Accept: No pitting, 4.0 g/m2 (0.00082 lb/ft2) max. weight loss
Revision: 0 Date: 04-01-2017 Amendment: Initial issue
This document has been prepared & published under the authority of the QESH Core Team Doc No: PS 4008
Uncontrolled valid at time of printing
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MTC Sample Dia 36 Inch Heat 639914 4130Dokument2 SeitenMTC Sample Dia 36 Inch Heat 639914 4130emadabdelsattarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPS-43 - Gtaw & Smaw Tig + SmawDokument19 SeitenWPS-43 - Gtaw & Smaw Tig + SmawAvinash ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)Dokument1 SeiteQap Wo 7 r0 (Ion Exchange)KailasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report on Welding Procedure Specifications for Single V-Groove JointsDokument15 SeitenReport on Welding Procedure Specifications for Single V-Groove JointsAvishek Gupta100% (1)
- IRN - 18.07.2019 - Harshad Panchal - Revision-0 - Furnace Fabrica - JNK - PORVAIR - RIL PDFDokument3 SeitenIRN - 18.07.2019 - Harshad Panchal - Revision-0 - Furnace Fabrica - JNK - PORVAIR - RIL PDFsaptarshi jashNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME PQR - MMA/SMAW Fillet Welds on OGAP Supplies PartsDokument1 SeiteASME PQR - MMA/SMAW Fillet Welds on OGAP Supplies Partssathi_mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4130, 75 Ksi (517 Mpa), Forging/Barstock, H2S Compatible: Doc No: M21509 Rev: O Page 1 of 3Dokument3 Seiten4130, 75 Ksi (517 Mpa), Forging/Barstock, H2S Compatible: Doc No: M21509 Rev: O Page 1 of 3Anonymous ZSne5ChQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alstom IRDokument4 SeitenAlstom IRkasi reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry & Facilities Inspection ReportDokument10 SeitenIndustry & Facilities Inspection Reportkbpatel123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Certificate AnalysisDokument1 SeiteTest Certificate AnalysisSagar KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flange 10 & 12 InchDokument2 SeitenFlange 10 & 12 InchreniNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTHE-BFCCU-TUV-00103-LHP-IRN 01 DT - 02.06.2018Dokument1 SeiteLTHE-BFCCU-TUV-00103-LHP-IRN 01 DT - 02.06.2018bappadittaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 694Dokument1 Seite694Mauricio Ramirez100% (1)
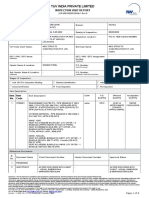
- Tuv India Private Limited: Inspection Visit ReportDokument8 SeitenTuv India Private Limited: Inspection Visit ReportAbhay KarandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IVR-8117994011-01 - Rev.00Dokument6 SeitenIVR-8117994011-01 - Rev.00Abhay KarandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. WpsDokument14 SeitenP. WpsIsmiArdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write WPS ISO 15614Dokument10 SeitenWrite WPS ISO 15614Hoang LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubular Butt Joint Configurations For Welder Qualification (With and Without Backing)Dokument21 SeitenTubular Butt Joint Configurations For Welder Qualification (With and Without Backing)attaulla100% (1)
- SS SAW Welding Flux Sample MTCDokument1 SeiteSS SAW Welding Flux Sample MTCKunal AjgaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spec Sheet - Handler 187Dokument4 SeitenSpec Sheet - Handler 187Hobart Welding ProductsNoch keine Bewertungen
- JNK SOP for Weld Visual InspectionDokument17 SeitenJNK SOP for Weld Visual InspectionAvishek GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QAP Seamless PipeDokument2 SeitenQAP Seamless Pipechetan85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wps Mma PipeDokument2 SeitenWps Mma PipeDimitris NikouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Product Data SheetDokument4 SeitenMaterial Product Data SheethungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Insection ReportDokument4 SeitenWelding Insection ReportRanjeet MouryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thread GageDokument30 SeitenThread GageRosendo RizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gta+sma PQRDokument3 SeitenGta+sma PQRRahul MoottolikandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of Steel Parts: Rev Ecn No. Date Reviewed by Approved by StatusDokument15 SeitenHeat Treatment of Steel Parts: Rev Ecn No. Date Reviewed by Approved by StatusAnonymous ZSne5ChQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Module 4Dokument6 SeitenCourse Module 4Makise AghataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabari Engineering PQRDokument3 SeitenSabari Engineering PQRAdvanced Quality Centre AQC100% (1)
- Welding Procedure Qualification Record: Shipyard LogoDokument4 SeitenWelding Procedure Qualification Record: Shipyard LogoGökhan TEZCAN100% (1)
- 4130wog0913 - Rev14Dokument3 Seiten4130wog0913 - Rev14Quality controller100% (1)
- Draft Wps Astm A 743 GR - Ca6nmDokument2 SeitenDraft Wps Astm A 743 GR - Ca6nmIlham PaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procurement Services: Industry & Facilities DivisionDokument6 SeitenProcurement Services: Industry & Facilities DivisionVikas Mani TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine necessary preheat temperature for steel weldingDokument11 SeitenDetermine necessary preheat temperature for steel weldingromanosky11Noch keine Bewertungen
- LPT As Per Asme & IsoDokument2 SeitenLPT As Per Asme & IsosbmmlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aws 001Dokument1 SeiteAws 001akshay sarfareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarma Tub Inox Certificat PDFDokument1 SeiteSarma Tub Inox Certificat PDFJacob HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPQ Is 2062 Haresh Shah W1Dokument1 SeiteWPQ Is 2062 Haresh Shah W1Anand KesarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison ASTM A 3388 & ISO 11496Dokument1 SeiteComparison ASTM A 3388 & ISO 11496Rahul MoottolikandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 90mm 316l Peeled and PolishedDokument1 Seite90mm 316l Peeled and PolishedB.M Industrial WorksNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPS for FCAW Welding of SteelDokument2 SeitenWPS for FCAW Welding of SteelHamid MansouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BK91 1310 CPF VED 003 QAC H03 0001 - A NDE Procedure For Centrifugal PumpsDokument69 SeitenBK91 1310 CPF VED 003 QAC H03 0001 - A NDE Procedure For Centrifugal PumpsPanneer SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASMEDokument38 SeitenASMEshazanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Werkszeugnis Altena Blech Vom 17.06.PDF 1Dokument2 SeitenWerkszeugnis Altena Blech Vom 17.06.PDF 1MuzammilNoch keine Bewertungen
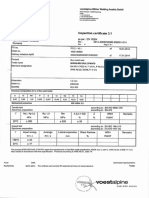
- Certified Material Test Report for EN 19-T Steel ForgingsDokument4 SeitenCertified Material Test Report for EN 19-T Steel ForgingsashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS 3103Dokument9 SeitenPS 3103JayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joints (Qw-402) DetailsDokument3 SeitenJoints (Qw-402) DetailsNaqqash SajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- EIL - Formats - PMI PDFDokument53 SeitenEIL - Formats - PMI PDFABHISHEK SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 121 T BW FPDokument4 Seiten121 T BW FPA. ΒρατσισταNoch keine Bewertungen
- WPS ISO 15614-1 WeldNote MetricDokument1 SeiteWPS ISO 15614-1 WeldNote MetricVirgil SorcaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Dokument2 SeitenWelding Procedure Specification (WPS)Abdulmecit YetisNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Caravan Trading and Contracting (Oil & Gas Division) : Initial Equipment Inspection ReportDokument1 SeiteUnited Caravan Trading and Contracting (Oil & Gas Division) : Initial Equipment Inspection Reportfali2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- OMR pipe fittings certificate analysisDokument1 SeiteOMR pipe fittings certificate analysisslimane AIT-IDIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welder Qualification CertificateDokument2 SeitenWelder Qualification CertificateNguyen Thanh BinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTAW Welding of CP Titanium and Ti6Al4VDokument1 SeiteGTAW Welding of CP Titanium and Ti6Al4VDeepak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Report: CPP-RM-PO-0180Dokument4 SeitenInspection Report: CPP-RM-PO-0180ANIL PLAMOOTTIL0% (1)
- Welding Procedure Qualification Certificate EN ISO 15614-1: 2017Dokument3 SeitenWelding Procedure Qualification Certificate EN ISO 15614-1: 2017dcsamaraweera100% (1)
- 1.2 Resistance and Special WeldingDokument14 Seiten1.2 Resistance and Special WeldingnikhilbathamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10080-1-SS-MT-007Dokument34 Seiten10080-1-SS-MT-007SURAJ PRSADNoch keine Bewertungen
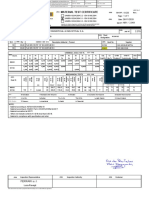
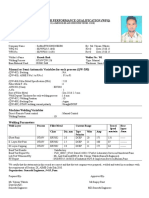
- Print ListDokument1 SeitePrint ListDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Dokument2 SeitenImpeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qap - Kongsberg - NabDokument4 SeitenQap - Kongsberg - NabDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- EHS Objectives 21-22Dokument3 SeitenEHS Objectives 21-22Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Dokument2 SeitenImpeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balloon Drawing 50A3 ImpellerDokument1 SeiteBalloon Drawing 50A3 ImpellerDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rdi Af Blank ApplicationDokument10 SeitenRdi Af Blank ApplicationDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 212GM 2,3,4Dokument2 Seiten212GM 2,3,4Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accepted Impeller Casting Inspection ReportDokument2 SeitenAccepted Impeller Casting Inspection ReportDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Dokument2 SeitenImpeller 50A3 2112T-7 & 8Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concession Request For Impeller 50A3Dokument3 SeitenConcession Request For Impeller 50A3Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accepted Impeller Casting Inspection ReportDokument2 SeitenAccepted Impeller Casting Inspection ReportDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller 50A3 2111R-6 & 7Dokument2 SeitenImpeller 50A3 2111R-6 & 7Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection reportDokument1 SeiteImpeller inspection reportDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller 50A3 2111R-6 & 7Dokument2 SeitenImpeller 50A3 2111R-6 & 7Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller inspection report meets specificationsDokument2 SeitenImpeller inspection report meets specificationsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller A29-5 2115K-2Dokument1 SeiteImpeller A29-5 2115K-2Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller casting quality requirementsDokument1 SeiteImpeller casting quality requirementsDeepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller A29-5 2115K-2Dokument1 SeiteImpeller A29-5 2115K-2Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller A29-5 2115K-2Dokument1 SeiteImpeller A29-5 2115K-2Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller A29-5 2115K-2Dokument1 SeiteImpeller A29-5 2115K-2Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concession Request For Impeller 56A3Dokument3 SeitenConcession Request For Impeller 56A3Deepak DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On Occupational Safety and Health in Construction, Operation and Maintenance of Biogas Plant 2016Dokument76 SeitenGuidelines On Occupational Safety and Health in Construction, Operation and Maintenance of Biogas Plant 2016kofafa100% (1)
- Last Clean ExceptionDokument24 SeitenLast Clean Exceptionbeom choiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RUJUKANDokument3 SeitenRUJUKANMaryTibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharp Ar5731 BrochureDokument4 SeitenSharp Ar5731 Brochureanakraja11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Petty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForDokument3 SeitenPetty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForCrizhae OconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperDokument14 SeitenInorganica Chimica Acta: Research PaperRuan ReisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestDokument8 SeitenFederal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestAnonymous Pb39klJNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP in Health 4Dokument15 SeitenDLP in Health 4Nina Claire Bustamante100% (1)
- Clark DietrichDokument110 SeitenClark Dietrichikirby77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biagioli Did Galileo Copy The TelescopeDokument28 SeitenBiagioli Did Galileo Copy The TelescopeGregory HooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8dd8 P2 Program Food MFG Final PublicDokument19 Seiten8dd8 P2 Program Food MFG Final PublicNemanja RadonjicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Briana SmithDokument3 SeitenBriana SmithAbdul Rafay Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simply Put - ENT EAR LECTURE NOTESDokument48 SeitenSimply Put - ENT EAR LECTURE NOTESCedric KyekyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UAPPDokument91 SeitenUAPPMassimiliano de StellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ujian Madrasah Kelas VIDokument6 SeitenUjian Madrasah Kelas VIrahniez faurizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DECA IMP GuidelinesDokument6 SeitenDECA IMP GuidelinesVuNguyen313Noch keine Bewertungen
- GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT STATISTICS (Report) - Powerpoint PresentationDokument37 SeitenGROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT STATISTICS (Report) - Powerpoint PresentationCyryhl GutlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaked David Fry II Conversation Regarding Loopholes and Embezzlement at AFK Gamer LoungeDokument6 SeitenLeaked David Fry II Conversation Regarding Loopholes and Embezzlement at AFK Gamer LoungeAnonymous iTNFz0a0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Guide To Sports Training PDFDokument105 SeitenComplete Guide To Sports Training PDFShahana ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms For Image Processing and Computer Vision: J.R. ParkerDokument8 SeitenAlgorithms For Image Processing and Computer Vision: J.R. ParkerJiaqian NingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery Lecture - 01 Asepsis, Antisepsis & OperationDokument60 SeitenSurgery Lecture - 01 Asepsis, Antisepsis & OperationChris QueiklinNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesDokument16 SeitenApril 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- Marine Engineering 1921Dokument908 SeitenMarine Engineering 1921Samuel Sneddon-Nelmes0% (1)
- LM1011 Global ReverseLogDokument4 SeitenLM1011 Global ReverseLogJustinus HerdianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Computer ScienceDokument3 SeitenUnit 3 Computer ScienceradNoch keine Bewertungen
- En dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFDokument24 SeitenEn dx300lc 5 Brochure PDFsaroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- FX15Dokument32 SeitenFX15Jeferson MarceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movement and Position: Question Paper 4Dokument14 SeitenMovement and Position: Question Paper 4SlaheddineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyDokument20 SeitenSoftware Requirements Specification: Chaitanya Bharathi Institute of TechnologyHima Bindhu BusireddyNoch keine Bewertungen