Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Usi 6a D Americanrevolution
Hochgeladen von
api-3275513030 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
260 Ansichten6 SeitenThe document discusses the key causes of the Revolutionary War, including England's desire to control and tax the American colonies to finance wars and maintain troops. This led to colonial dissatisfaction as the colonies had no representation in Parliament and resented restrictions on their legislatures and westward expansion. England imposed taxes like the Stamp Act to raise revenue from the colonies.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
usi-6a-d-americanrevolution
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe document discusses the key causes of the Revolutionary War, including England's desire to control and tax the American colonies to finance wars and maintain troops. This led to colonial dissatisfaction as the colonies had no representation in Parliament and resented restrictions on their legislatures and westward expansion. England imposed taxes like the Stamp Act to raise revenue from the colonies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
260 Ansichten6 SeitenUsi 6a D Americanrevolution
Hochgeladen von
api-327551303The document discusses the key causes of the Revolutionary War, including England's desire to control and tax the American colonies to finance wars and maintain troops. This led to colonial dissatisfaction as the colonies had no representation in Parliament and resented restrictions on their legislatures and westward expansion. England imposed taxes like the Stamp Act to raise revenue from the colonies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
R 31 – USI – 6a Notes
Causes of the Revolutionary War – USI 6a
As England expanded control over the American
colonies, many colonists became dissatisfied and
rebellious.
England’s reason for control –
England’s desire to remain a world power.
England imposed taxes, such as the Stamp Act, to
raise revenue (money) to pay the cost of the
French and Indian War.
England’s reason for taxation –
To help finance the French & Indian War.
To help with the maintenance of English troops in
the colonies.
Sources of colonial dissatisfaction –
Colonies had no representation in Parliament.
Some colonists resented the power of colonial
governors.
England wanted strict control over colonial
legislatures (law-makers for colonies.)
Colonies opposed taxes.
The Proclamation of 1763 hampered (restricted)
the westward movement of settlers.
R 32 – Sets to the Revolution
R 33 Notes – USI 6b – Declaration of Independence
USI – 6b – Declaration of Independence Notes
John Locke – philosopher who stated that people are born with natural
rights that cannot be taken away. Jefferson borrowed this idea when he
wrote the Declaration of Independence.
New political ideas led to a desire for independence and a democratic
government in the 13 American colonies.
The Declaration of Independence proclaimed independence from Great
Britain. It stated that people have natural (inherent) rights to life,
liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
Ideas of European Philosophers:
People have a right to life, liberty, and property. (Locke)
Government is created to protect the rights of people and has only
limited and specific powers the people consent (permission) to
give it.
Key philosophies in the Declaration of Independence
People have “certain unalienable rights” (rights that cannot be taken
away)—to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
People establish governments to protect those rights.
Government derives power from the consent of the people.
People have a right and a duty to change a government that violates
their rights.
R 36 – Key People – USI6c
Who were some key individuals in the American Revolution?
King George III : British king during the Revolutionary era
John Adams: Championed the cause of independence
George Washington: Commander of Continental Army
Thomas Jefferson: Major author of the Declaration of
Independence
Patrick Henry: Outspoken member of the House of
Burgesses; inspired colonial patriotism with his “Give me
liberty or give me death” speech
Benjamin Franklin: Prominent member of the Continental
Congress; helped frame the Declaration of Independence;
helped gain French support for American independence
Lord Cornwallis: British General who surrendered at
Yorktown.
Phillis Wheatley: Enslaved African American who wrote
poems and plays supporting American independence and
who eventually gained her freedom
Paul Revere: Patriot who made a daring ride to warn
colonists of British arrival
Thomas Paine: Wrote the pamphlet, “Common Sense,”
urging people to fight for independence
R 37 – Key Events – USI-6c
What were some of the key events that occurred during the
Revolutionary War period?
Boston Massacre : Colonists in Boston were shot after
taunting British soldiers.
Boston Tea Party : Samuel Adams and Paul Revere led
patriots in throwing tea into Boston Harbor to protest tea
taxes.
First Continental Congress : Delegates from all colonies
except Georgia met to discuss problems with Great Britain
and to promote independence.
Lexington and Concord : The first armed conflicts of the
Revolutionary War
Approval of the Declaration of Independence : The
colonies declared independence from Great Britain (July
4, 1776).
Battle of Saratoga : This American victory was the turning
point in the war.
Surrender at Yorktown : This was the colonial victory over
forces of Lord Cornwallis that marked the end of the
Revolutionary War.
Signing of the Treaty of Paris : Great Britain recognized
American independence in this treaty.
R 39 – 6d – Colonial Advantages
USI – 6 d notes – Colonial Advantages
Defense of the colonists’ own land, strong beliefs, and capable leadership
contributed to the American victory in the Revolutionary War.
Colonial Advantages –
Colonists defending their own land, principles, and beliefs.
Support from France and Spain.
Strong leadership – George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Benjamin
Franklin, etc.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Reconstruction Amendments: The Essential Documents, Volume 2Von EverandThe Reconstruction Amendments: The Essential Documents, Volume 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guided Notes-The Articles of Confederation With Fill-In-The-BlanksDokument2 SeitenGuided Notes-The Articles of Confederation With Fill-In-The-Blanksapi-429964456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Andrew Jackson: Heroic Leader or Cold-hearted Ruler?Von EverandAndrew Jackson: Heroic Leader or Cold-hearted Ruler?Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Civil War DBQDokument10 SeitenCivil War DBQKevin Earlie100% (1)
- The Fathers of the Constitution: A Chronicle of the Establishment of the UnionVon EverandThe Fathers of the Constitution: A Chronicle of the Establishment of the UnionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The War of 1812 - Assessment AnswersDokument6 SeitenThe War of 1812 - Assessment Answersapi-285312776Noch keine Bewertungen
- DBQ Early Presidential Policies 13Dokument9 SeitenDBQ Early Presidential Policies 13zackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manifest Destiny Vocabulary Power PointDokument21 SeitenManifest Destiny Vocabulary Power PointlaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Two Harriets Heroines of Abolition 970lDokument2 SeitenThe Two Harriets Heroines of Abolition 970lapi-299636499Noch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of The Civil War Webquest WorksheetDokument4 SeitenCauses of The Civil War Webquest Worksheetapi-93717200100% (1)
- Lesson 18 An Era of ReformDokument34 SeitenLesson 18 An Era of Reformfishertr1100% (1)
- Exam Form 2Dokument23 SeitenExam Form 2Didi Gump EddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- French and Indian War DBQ Extra CreditDokument8 SeitenFrench and Indian War DBQ Extra CreditsofaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Revolution Webquest - JHDokument7 SeitenAmerican Revolution Webquest - JHapi-3724678100% (1)
- Lesson 5 Toward - IndependenceDokument28 SeitenLesson 5 Toward - Independencefishertr1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Sources - Lincolns Emancipation Proclamation 770lDokument3 SeitenPrimary Sources - Lincolns Emancipation Proclamation 770lapi-299636499Noch keine Bewertungen
- Northern Reformers Dossiers - StudentDokument8 SeitenNorthern Reformers Dossiers - Studentapi-2673413790% (1)
- Anish Goli - AMSCO 7.2 & 7.3 World War I Reading & G.O 20-21Dokument6 SeitenAnish Goli - AMSCO 7.2 & 7.3 World War I Reading & G.O 20-21Anish gNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBQ On Civil WarDokument7 SeitenDBQ On Civil WarMegan RitchieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manifest DestinyDokument2 SeitenManifest DestinyMark JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Westward Expansion DBQDokument4 SeitenWestward Expansion DBQapi-309456562100% (1)
- ss8h3 Causes of The Am Rev Stations OnesheetDokument2 Seitenss8h3 Causes of The Am Rev Stations Onesheetapi-473034142Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching With Text Boston Massacre InvestigationDokument18 SeitenTeaching With Text Boston Massacre Investigationapi-341830053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civil WarDokument1 SeiteCivil Warapi-318949993Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Social Reforms of The Antebellum EraDokument4 Seiten3 Social Reforms of The Antebellum Eraapi-294843376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of The Civil WarDokument34 SeitenCauses of The Civil Warapi-321559404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hooking Lesson Taxes From The KingDokument11 SeitenHooking Lesson Taxes From The Kingapi-341830053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Inquiry Lesson: Pontiac's RebellionDokument3 SeitenVisual Inquiry Lesson: Pontiac's RebellionNicole McIntyreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 GuideDokument2 SeitenUnit 3 Guidemia racicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes and Effects of The War of 1812Dokument12 SeitenCauses and Effects of The War of 1812Sadiq Habib100% (1)
- Causes of Wwi - ImadunceDokument12 SeitenCauses of Wwi - ImaduncekmsochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of The American Revolution Unit CalendarDokument3 SeitenCauses of The American Revolution Unit Calendarapi-341830053Noch keine Bewertungen
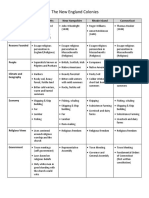
- ColoniesreferencechartDokument3 SeitenColoniesreferencechartapi-328472919100% (1)
- Road To Revolution TestDokument4 SeitenRoad To Revolution Testapi-315723574Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Battles of The American Revolutionary War - Rank em - ws-1Dokument2 SeitenNotes - Battles of The American Revolutionary War - Rank em - ws-1api-236682830Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jacksonian Era OutlineDokument2 SeitenJacksonian Era Outlineapi-293174357Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Washington AdamsDokument41 Seiten5 Washington Adamsapi-294843376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Webquest:The Effects of The Transcontinental RailroadDokument9 SeitenWebquest:The Effects of The Transcontinental RailroadLara LandryNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Good StartDokument18 SeitenA Good Startapi-328120679100% (1)
- Picture The Preamble ProjectDokument2 SeitenPicture The Preamble Projectapi-2487625700% (1)
- The Impact of Westward ExpansionDokument4 SeitenThe Impact of Westward Expansionapi-445112426Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Jackson 1Dokument20 Seiten4 Jackson 1api-294843376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Persons of Interest CardsDokument1 SeitePersons of Interest Cardsapi-293174357Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 French Indian WarDokument30 Seiten1 French Indian Warapi-294843376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ags PP 155-158Dokument4 SeitenAgs PP 155-158api-421695293Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weapons of ww1 Web QuestDokument4 SeitenWeapons of ww1 Web Questapi-350901417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colonial America OutlineDokument2 SeitenColonial America Outlineapi-293174357Noch keine Bewertungen
- To Play The Game, Click Here!: Template by Bill Arcuri, WCSDDokument67 SeitenTo Play The Game, Click Here!: Template by Bill Arcuri, WCSDJayson100% (1)
- Bill of Rights Crossword PDFDokument2 SeitenBill of Rights Crossword PDFryannodveithNoch keine Bewertungen
- President Cereal Project RubricDokument3 SeitenPresident Cereal Project Rubricapi-266941933Noch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American RevolutionDokument11 SeitenPowerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American Revolutionapi-261440325100% (1)
- zp315 Westward-ExpansionDokument50 Seitenzp315 Westward-Expansionapi-266559121Noch keine Bewertungen
- Age of JacksonDokument11 SeitenAge of Jacksonapi-305127889Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Presidency of George Washington Slotted Notes Editable 1Dokument3 SeitenThe Presidency of George Washington Slotted Notes Editable 1Zainab LawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Republic NotesDokument3 SeitenEarly Republic Notesapi-305127889Noch keine Bewertungen
- War of 1812 Scavenger HuntDokument3 SeitenWar of 1812 Scavenger HuntJR WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitutional Convention Simulation 2Dokument4 SeitenConstitutional Convention Simulation 2api-294843376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gettysburg Address PowerDokument43 SeitenGettysburg Address Powerapi-321698435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tci CH 12 PlacardsDokument8 SeitenTci CH 12 Placardsapi-300100207Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trails To The West Travel BrochureDokument2 SeitenTrails To The West Travel Brochureapi-266559121100% (1)
- Notes - Ce13-14Dokument4 SeitenNotes - Ce13-14api-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Ce12Dokument4 SeitenNotes Ce12api-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Ce11Dokument4 SeitenNotes Ce11api-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ce-9-Court System-NotesDokument1 SeiteCe-9-Court System-Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade6 Usi7 NotesDokument1 SeiteGrade6 Usi7 Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit3 NotesDokument9 SeitenUnit3 Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 NotesDokument5 SeitenUnit 2 Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Usi NotesDokument8 SeitenUsi Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 NotesDokument2 SeitenUnit 1 Notesapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pence Usi IntroDokument2 SeitenPence Usi Introapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pence Ce IntroDokument2 SeitenPence Ce Introapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8th SyllabusDokument2 Seiten8th Syllabusapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6th SyllabusDokument1 Seite6th Syllabusapi-327551303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Executive Summary of The Mission Handbook: Periodic Paper #1Dokument9 SeitenExecutive Summary of The Mission Handbook: Periodic Paper #1Catholic Mission Association USANoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter On Hazard Pay PDFDokument2 SeitenLetter On Hazard Pay PDFAravella SimotasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banana, The Green GoldDokument22 SeitenBanana, The Green Goldachiever06Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1twe PDFDokument360 Seiten1twe PDFAsad SamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Developments in EconomyDokument193 SeitenCurrent Developments in EconomygandhingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 CV 01966 Document7 5 - 12 4 14Dokument3 Seiten14 CV 01966 Document7 5 - 12 4 14PixelPatriotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis For Culinarian CookwareDokument23 SeitenCase Analysis For Culinarian Cookwarevisakhboban100% (1)
- 2022-2023 Fillable ISFAADokument5 Seiten2022-2023 Fillable ISFAAKouassi Thimotée YaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Opinion Strategies - Fairfax and Loudoun Counties PollDokument2 SeitenPublic Opinion Strategies - Fairfax and Loudoun Counties PollThe FederalistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batf/Irs - Criminal Fraud William Cooper - CAJI News ServiceDokument16 SeitenBatf/Irs - Criminal Fraud William Cooper - CAJI News ServiceAlex Moore-Minott100% (1)
- Phil Iri Reading Screening Test For Grade 10Dokument7 SeitenPhil Iri Reading Screening Test For Grade 10Angela Solivio100% (1)
- Foreign Policy: Chapter OutlineDokument32 SeitenForeign Policy: Chapter OutlineRaven BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- 800 Yds Gramer Kelime SorusuDokument67 Seiten800 Yds Gramer Kelime SorusuHande100% (1)
- Foreign Policy Convergence in Pacific Asia: The Evidence From Voting in The UN General AssemblyDokument18 SeitenForeign Policy Convergence in Pacific Asia: The Evidence From Voting in The UN General AssemblyWaayija SalmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Briefing On - Bonus 3392-181Dokument6 SeitenBriefing On - Bonus 3392-181Mike OwensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article I of The Us Constitution Guiding QuestionsDokument2 SeitenArticle I of The Us Constitution Guiding Questionsapi-262416934Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 George Garvey Et Al V City of New York Et Al DECISION ORDER On 37Dokument13 Seiten2022 George Garvey Et Al V City of New York Et Al DECISION ORDER On 37Jamie WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- China Task Force Presentation DeckDokument19 SeitenChina Task Force Presentation DeckChina Task ForceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alimah To Imamah Muslim Women S Approaches To RelDokument113 SeitenAlimah To Imamah Muslim Women S Approaches To ReljazzeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Notes - Superpowers - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDokument7 SeitenEssential Notes - Superpowers - Edexcel Geography A-LevelSashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of The Revolutionary WarDokument2 SeitenCauses of The Revolutionary Warapi-177192937Noch keine Bewertungen
- Two Boys Kissing Letter 2014 - Fauquier HSDokument2 SeitenTwo Boys Kissing Letter 2014 - Fauquier HSncacensorshipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabadbaran City Ordinance No. 2009-15Dokument3 SeitenCabadbaran City Ordinance No. 2009-15Albert CongNoch keine Bewertungen
- An American Genocide The United States ADokument1 SeiteAn American Genocide The United States AgjaramillovNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Family Advantage National Bank of Canada 2018Dokument84 SeitenThe Family Advantage National Bank of Canada 2018Business Families FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 54 Mark Twain and Henry James: Humorism and CosmopolitanismDokument16 SeitenUnit 54 Mark Twain and Henry James: Humorism and CosmopolitanismMary Garcia SolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erno : Anthony Knerr & Viktor BöhmDokument36 SeitenErno : Anthony Knerr & Viktor BöhmBialet MasseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Study GuideDokument2 SeitenChapter 1 Study Guideapi-288748017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Timeline of Trump's HateDokument42 SeitenTimeline of Trump's HateRex David100% (1)
- Life of Indigenous People in AmericaDokument13 SeitenLife of Indigenous People in AmericaAnshika GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Russia Hoax: The Illicit Scheme to Clear Hillary Clinton and Frame Donald TrumpVon EverandThe Russia Hoax: The Illicit Scheme to Clear Hillary Clinton and Frame Donald TrumpBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- Stalin's Daughter: The Extraordinary and Tumultuous Life of Svetlana AlliluyevaVon EverandStalin's Daughter: The Extraordinary and Tumultuous Life of Svetlana AlliluyevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darkest Hour: How Churchill Brought England Back from the BrinkVon EverandDarkest Hour: How Churchill Brought England Back from the BrinkBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (31)
- The War after the War: A New History of ReconstructionVon EverandThe War after the War: A New History of ReconstructionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Devil at My Heels: A Heroic Olympian's Astonishing Story of Survival as a Japanese POW in World War IIVon EverandDevil at My Heels: A Heroic Olympian's Astonishing Story of Survival as a Japanese POW in World War IIBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- The Smear: How Shady Political Operatives and Fake News Control What You See, What You Think, and How You VoteVon EverandThe Smear: How Shady Political Operatives and Fake News Control What You See, What You Think, and How You VoteBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (16)
- Stonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonVon EverandStonewalled: My Fight for Truth Against the Forces of Obstruction, Intimidation, and Harassment in Obama's WashingtonBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- All the Gallant Men: An American Sailor's Firsthand Account of Pearl HarborVon EverandAll the Gallant Men: An American Sailor's Firsthand Account of Pearl HarborBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (37)
- Where the Birds Never Sing: The True Story of the 92nd Signal Battalion and the Liberation of DachauVon EverandWhere the Birds Never Sing: The True Story of the 92nd Signal Battalion and the Liberation of DachauBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarVon EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- The Shadow War: Inside Russia's and China's Secret Operations to Defeat AmericaVon EverandThe Shadow War: Inside Russia's and China's Secret Operations to Defeat AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Unknown Valor: A Story of Family, Courage, and Sacrifice from Pearl Harbor to Iwo JimaVon EverandUnknown Valor: A Story of Family, Courage, and Sacrifice from Pearl Harbor to Iwo JimaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (7)
- The Only Thing Worth Dying For: How Eleven Green Berets Fought for a New AfghanistanVon EverandThe Only Thing Worth Dying For: How Eleven Green Berets Fought for a New AfghanistanBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- Never Call Me a Hero: A Legendary American Dive-Bomber Pilot Remembers the Battle of MidwayVon EverandNever Call Me a Hero: A Legendary American Dive-Bomber Pilot Remembers the Battle of MidwayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- The Saboteur: The Aristocrat Who Became France's Most Daring Anti-Nazi CommandoVon EverandThe Saboteur: The Aristocrat Who Became France's Most Daring Anti-Nazi CommandoBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (18)
- Thomas Jefferson: Author of AmericaVon EverandThomas Jefferson: Author of AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (107)
- Dead Reckoning: The Story of How Johnny Mitchell and His Fighter Pilots Took on Admiral Yamamoto and Avenged Pearl HarborVon EverandDead Reckoning: The Story of How Johnny Mitchell and His Fighter Pilots Took on Admiral Yamamoto and Avenged Pearl HarborNoch keine Bewertungen
- Every Man a Hero: A Memoir of D-Day, the First Wave at Omaha Beach, and a World at WarVon EverandEvery Man a Hero: A Memoir of D-Day, the First Wave at Omaha Beach, and a World at WarBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (10)
- The Courage to Be Free: Florida's Blueprint for America's RevivalVon EverandThe Courage to Be Free: Florida's Blueprint for America's RevivalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saving Freedom: Truman, the Cold War, and the Fight for Western CivilizationVon EverandSaving Freedom: Truman, the Cold War, and the Fight for Western CivilizationBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (11)
- The Weird Middle Ages: A Collection of Mysterious Stories, Odd Customs, and Strange Superstitions from Medieval TimesVon EverandThe Weird Middle Ages: A Collection of Mysterious Stories, Odd Customs, and Strange Superstitions from Medieval TimesBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (39)
- Dunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureVon EverandDunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- Sacred Duty: A Soldier's Tour at Arlington National CemeteryVon EverandSacred Duty: A Soldier's Tour at Arlington National CemeteryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- Modern Warriors: Real Stories from Real HeroesVon EverandModern Warriors: Real Stories from Real HeroesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- No Better Friend, No Worse Enemy: The Life of General James MattisVon EverandNo Better Friend, No Worse Enemy: The Life of General James MattisBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)