Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exercise Salts
Hochgeladen von
Ida Yuni SukadiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exercise Salts
Hochgeladen von
Ida Yuni SukadiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SPM 2008
(a) Diagram 3.1 shows the results of an experiment to investigate the movement of bromine
particles in air.
Diagram 3.1
(i) State the name of the process involved in this experiment. [1 mark]
(ii) State the type of particle present in bromine gas, Br2.[1 mark]
(iii)Explain the observation in this experiment based on the kinetic theory of matter.[3 marks]
(iv) This experiment is repeated at a higher temperature. Predict the time taken for the bromine
vapour to spread throughout the space in both gas jars.[1 mark]
SPM 2010
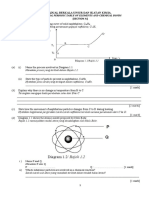
Diagram 1 shows the inter-conversion of the three states of matter, X, Y and Z of water.
Diagram 1
(a) What type of particle is found in water? [1 mark]
(b) Under the room temperature, at what temperature does ice change to water? [1 mark]
(c) What is the physical state labelled Z?[1 mark]
(d) Name the process when water changes from state X to state Y.[1 mark]
(e) When water changes from state Y to state Z, state the changes in:
(i) The energy of the particles. [1 mark]
(ii) The forces of attraction between the particles.[1 mark]
(f) The smell of curry cooking in the kitchen spreads to the living room. Based on the kinetic
theory of matter, state the process involved. Explain your answer. [3 marks]
TRIAL JOHOR 2010
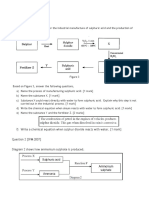
Graph 2 shows the temperature against time when solid P is heated.
(a) Based on Graph 2, answer the following questions:
(i) What is meant by melting point?[1 mark]
(ii) State the melting point of substance P. [1 mark]
(iii) State the physical state of P from time t1 to t2 [1 mark]
(iv) Explain why the temperature remains constant from time t1 to t2.[2 marks]
(v) Diagram 2 shows the set-up of apparatus used by a student to determine the
melting point of substance P.
Identify one mistake in the diagram. Explain why.[2 marks]
(b) When solid iodine is heated, it changes to purple fume.
(i) Name the process involved.[1 mark]
(ii) Name one isotope of iodine and state its use.[2 marks]
SPM 2008
(a) Diagram 3.1 shows the results of an experiment to investigate the movement of bromine
particles in air.
Diagram 3.1
(v) State the name of the process involved in this experiment. [1 mark]
(vi) State the type of particle present in bromine gas, Br2.[1 mark]
(vii) Explain the observation in this experiment based on the kinetic theory of matter.[3
marks]
(viii) This experiment is repeated at a higher temperature. Predict the time taken for the
bromine vapour to spread throughout the space in both gas jars.[1 mark]
SPM 2010
Diagram 1 shows the inter-conversion of the three states of matter, X, Y and Z of water.
Diagram 1
(g) What type of particle is found in water? [1 mark]
(h) Under the room temperature, at what temperature does ice change to water? [1 mark]
(i) What is the physical state labelled Z?[1 mark]
(j) Name the process when water changes from state X to state Y.[1 mark]
(k) When water changes from state Y to state Z, state the changes in:
(iii) The energy of the particles. [1 mark]
(iv) The forces of attraction between the particles.[1 mark]
(l) The smell of curry cooking in the kitchen spreads to the living room. Based on the kinetic
theory of matter, state the process involved. Explain your answer. [3 marks]
TRIAL JOHOR 2010
Graph 2 shows the temperature against time when solid P is heated.
(a) Based on Graph 2, answer the following questions:
(v) What is meant by melting point?[1 mark]
(vi) State the melting point of substance P. [1 mark]
(vii) State the physical state of P from time t1 to t2 [1 mark]
(viii) Explain why the temperature remains constant from time t1 to t2.[2 marks]
(v) Diagram 2 shows the set-up of apparatus used by a student to determine the
melting point of substance P.
Identify one mistake in the diagram. Explain why.[2 marks]
(b) When solid iodine is heated, it changes to purple fume.
(iii) Name the process involved.[1 mark]
(iv) Name one isotope of iodine and state its use.[2 marks]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Example Form 1 Science Paper (With Answers)Dokument10 SeitenExample Form 1 Science Paper (With Answers)Kenny Cheah Soon Lee100% (8)
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachDokument49 SeitenIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approachtevin sessa100% (1)
- Nyjc H2 Math P2Dokument6 SeitenNyjc H2 Math P2jimmytanlimlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding The Polytropic Index N' For Adiabatic and Isothermal CompressionDokument8 SeitenFinding The Polytropic Index N' For Adiabatic and Isothermal CompressionaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Biology Chapter 6Dokument32 SeitenSPM Biology Chapter 6birinthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProgressionsDokument23 SeitenProgressionsHayati Aini AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Dokument7 SeitenExercise Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Syazwan AkidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using A Ticker Timer Tape To Calculate VelocityDokument2 SeitenUsing A Ticker Timer Tape To Calculate VelocityIrwinKumarAsoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsDokument34 SeitenMPHG2009-Chapter 9 ElectronicsMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- 39-Article Text-131-1-10-20191111Dokument9 Seiten39-Article Text-131-1-10-20191111berlian gurningNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.1 (B) Soluble SaltsDokument23 Seiten8.1 (B) Soluble SaltsFidree AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORM 4 Additional Mathematics MODULE 1Dokument2 SeitenFORM 4 Additional Mathematics MODULE 1ALAN LIEW KOK PINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration SPM ADokument1 SeiteIntegration SPM ARosmizar Ahmad0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaDokument14 SeitenJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomical TerminologyDokument3 SeitenAnatomical TerminologyRura DangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 3 Chapter 4Dokument7 SeitenForm 3 Chapter 4Lau Lee LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Test 1 2018 SECTION BDokument7 SeitenChem Test 1 2018 SECTION BAmirah Noor AffandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Dokument21 SeitenChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ima 2Dokument8 SeitenIma 2Punitha ArumughamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simultaneous Equations by Substitution CodebreakerDokument1 SeiteSimultaneous Equations by Substitution Codebreakerayesha125865Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Dokument1 Seite2019 JC1 H2 Math Term 2 Revision Test (Questions)Timothy HandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Math Mid Year SPM Form 5 P2 2015Dokument18 SeitenAdd Math Mid Year SPM Form 5 P2 2015smkpthoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- f4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011Dokument12 Seitenf4 Chem Mid-Year Exam 2011matleNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMATH DifferentiationDokument16 SeitenAMATH DifferentiationLeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- E (I) Circular Measures 1Dokument8 SeitenE (I) Circular Measures 1Wong Jing KaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 49 Question Trial SPM ChemistryDokument1 Seite49 Question Trial SPM ChemistrychongpeisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Dokument11 SeitenAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Dokument16 Seiten3 (Movement of Substances Across Plasma Membrane)Jia YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerDokument6 Seiten1 Thermo and Equil - Remedial - AnswerNur Afiqah Mohd ZakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec 3 NA Science (Physics) September 2014 Holiday HomeworkDokument6 SeitenSec 3 NA Science (Physics) September 2014 Holiday HomeworkMavis LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 JC1 Promo RevisionDokument477 Seiten2012 JC1 Promo RevisionVincent SeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Physics Terms and DefinitionDokument12 SeitenSPM Physics Terms and Definitionnursuhailah100% (3)
- Paper 2 QuestionDokument15 SeitenPaper 2 QuestionNoridaAnisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerDokument36 SeitenUlangkaji Akhir Menjelang SPM AnswerHee Ting Wong100% (1)
- Final Report (Parking Project) PDFDokument148 SeitenFinal Report (Parking Project) PDFBassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technique To Answer Biology Paper 3Dokument6 SeitenTechnique To Answer Biology Paper 3李友志100% (1)
- AMATH StatisticsDokument17 SeitenAMATH StatisticsLeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Tingkatan 4Dokument1 SeiteKimia Tingkatan 4Rohana YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Log & Indices - Set1@2011Dokument2 SeitenLog & Indices - Set1@2011Hayati Aini AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 SPM Physics: Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Scalar and VectorDokument73 Seiten2020 SPM Physics: Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Scalar and VectorsharveenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Biodiversity (SC f2)Dokument2 SeitenExercise Biodiversity (SC f2)Mastura Haji Ariffin0% (1)
- Linear LawDokument4 SeitenLinear LawJoann NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul A+ Set 1Dokument14 SeitenModul A+ Set 1ZANARIAH BINTI LIHAT MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pada Titik Yang Manakah, Naftalena Bermula Untuk Melebur? (1 Mark)Dokument2 SeitenPada Titik Yang Manakah, Naftalena Bermula Untuk Melebur? (1 Mark)Victoria PetrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS IX 4th Sem AftermidDokument12 SeitenPHYSICS IX 4th Sem AftermidShahidul Hassan MontiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 2 - Chemical ReactionsDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 2 - Chemical ReactionsDaniel Ngenokesho WandyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Paper 2Dokument13 SeitenPhysics Paper 2Adam K C Tiong100% (1)
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDokument30 SeitenPaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesaganbasmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDokument30 SeitenPaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery Practicesaganbasm100% (1)
- Lesson Exercise 5h 20 September 2016 Past Year Questions Winter 2006 Paper 3Dokument13 SeitenLesson Exercise 5h 20 September 2016 Past Year Questions Winter 2006 Paper 3Tee Xin RuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Chem 2407Dokument2 SeitenX Chem 2407pankaj brownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Perfect Score Module Form 5Dokument48 SeitenPhysics Perfect Score Module Form 5jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Dokument4 SeitenAnswer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Liana Jalil100% (1)
- Chapter 1Dokument11 SeitenChapter 1kenenathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Dokument59 SeitenBengkel Teknik Menjawab Fizik SPM 2016Suriyati Yusoff100% (2)
- 1W1Q Set1Dokument3 Seiten1W1Q Set1Rafiq IrdhinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDokument15 SeitenThe Particulate Nature of Matterabhilasha sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY VIII P2 BEFORE MID 2nd SemsDokument10 SeitenPHY VIII P2 BEFORE MID 2nd SemsShahidul Hassan MontiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KAMAL Assignment July Phy&ChemDokument3 SeitenKAMAL Assignment July Phy&ChemSHERIFF LAWALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checkpoint Revision (Part 2) : Plants Need To Absorb Water and Transport It To All of Their Living PartsDokument15 SeitenCheckpoint Revision (Part 2) : Plants Need To Absorb Water and Transport It To All of Their Living PartsMark ZuckerburgNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2223 Level L Chemistry Course QuestionsDokument56 Seiten2223 Level L Chemistry Course QuestionsZyteckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: SCIENCE Paper - 1Dokument9 SeitenPhysics: SCIENCE Paper - 1chaituNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterDokument41 Seiten2.1 (A) Kinetic Theory of MatterIda Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draf Jadual Kem Halaqah Ilmi 3.0Dokument2 SeitenDraf Jadual Kem Halaqah Ilmi 3.0Ida Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Rate of ReactionsDokument3 SeitenQuiz Rate of ReactionsIda Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Exercise 1Dokument2 SeitenSalt Exercise 1Ida Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugasan CNY Manufactured SubstancesDokument4 SeitenTugasan CNY Manufactured SubstancesIda Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collision TheoryDokument61 SeitenCollision TheoryIda Yuni Sukadi50% (2)
- To Investigate The Diffusion of Particles in A GasDokument2 SeitenTo Investigate The Diffusion of Particles in A GasIda Yuni SukadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab On Hess LawDokument7 SeitenIB Lab On Hess LawBraulioMolinaFloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data For SA Series DehumidifiersDokument2 SeitenData For SA Series Dehumidifiersmustafa elfatihNoch keine Bewertungen
- RacDokument3 SeitenRacofficial vrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class VIII Heat Gain and Heat LossDokument5 SeitenClass VIII Heat Gain and Heat LossEdu TainmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 7 Entropi: NugrahaDokument33 SeitenBab 7 Entropi: NugrahaGilbert SihombingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melting Boiling/evaporation: Freezing CondensationDokument32 SeitenMelting Boiling/evaporation: Freezing CondensationSiti Norliana JohariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH03 & CH04 Technical DataDokument32 SeitenCH03 & CH04 Technical DataKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat Capacity BaruDokument23 Seiten4.2 Understanding Specific Heat Capacity BarureanizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freeze Drying Guide Vol2Dokument49 SeitenFreeze Drying Guide Vol2Keval PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUNDAMENTALS OF HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 7th EDITION BY FRANK P. INCROPERA-458Dokument1 SeiteFUNDAMENTALS OF HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 7th EDITION BY FRANK P. INCROPERA-458Endru MourishioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correlations For LiquidDokument5 SeitenCorrelations For LiquidElmer HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry 2nd Edition Ball Solution ManualDokument17 SeitenPhysical Chemistry 2nd Edition Ball Solution Manualrobyn96% (27)
- A Review of Heat Pipe Systems For Heat Recovery and Renewable Energy ApplicationsDokument11 SeitenA Review of Heat Pipe Systems For Heat Recovery and Renewable Energy ApplicationsJoao MinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CO - CoolingDokument43 SeitenCO - CoolingOral McnarrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation Checklist: Instructions 1. Outdoor Air IntakesDokument6 SeitenVentilation Checklist: Instructions 1. Outdoor Air IntakesUntung SuropatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial # 1 Energy and Energy BalanceDokument1 SeiteTutorial # 1 Energy and Energy Balancea mustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hvac Rpoblems NewDokument20 SeitenHvac Rpoblems NewGrace Joy CariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termistor ValueDokument4 SeitenTermistor ValueGabor KomuvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME341 Lab Report 1 PDFDokument11 SeitenME341 Lab Report 1 PDFSatvik SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 3 (Material Balances)Dokument76 SeitenCHAPTER 3 (Material Balances)Ali Imran Mohamad0% (1)
- Calculating Equilibrium ConstantsDokument3 SeitenCalculating Equilibrium ConstantsChastine CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 5 SolutionDokument36 SeitenSheet 5 SolutionJoseph CorderoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR and Blower Doors For Building Commissioning-SteinbronnDokument16 SeitenIR and Blower Doors For Building Commissioning-Steinbronnalexander100% (1)
- Phase Diagrams - Progress in Solid State Chemistry (10) 1975 PeltonDokument37 SeitenPhase Diagrams - Progress in Solid State Chemistry (10) 1975 PeltonJunior Lima100% (1)
- Airconditioning System Part 1Dokument11 SeitenAirconditioning System Part 1Educational PurposesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Florida Heat Pump EM SeriesDokument2 SeitenFlorida Heat Pump EM SeriesWilliam RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5-Humidification Enthalpy ProblemsDokument17 SeitenLecture 5-Humidification Enthalpy ProblemsWasim NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporative Cooling Equations 1589983721 PDFDokument10 SeitenEvaporative Cooling Equations 1589983721 PDFAbdulhamit KAYYALINoch keine Bewertungen