Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lear-70-SSD Spec Characteristics Gdlnes
Hochgeladen von
rpagarwal2Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lear-70-SSD Spec Characteristics Gdlnes
Hochgeladen von
rpagarwal2Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 1 of 10
1.0) Scope/Purpose: This document is intended to define special characteristics for use within Lear
Seating Systems Divisions and provide guidelines for appropriate controls and PPAP submission
for the special characteristics to Lear Seating Systems Division Plants. This process could be used
for component parts or sub-assemblies. All Customer unique assembly could use the customer
symbols.
2.0) Responsibility
2.1) Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) Team: Which shall include but is not limited
to, design responsible engineers; manufacturing and process engineers; manufacturing,
operations and quality engineers; is responsible for the deployment of special characteristics
including validation, PPAP, control methods and periodic review.
2.2) Design Responsible Engineer: Is responsible for identifying potential special characteristics
during the design phase and incorporating the special characteristics into the design failure
mode and effects analysis (DFMEA). The Design Responsible Engineer should use of sound
engineering methods to, when possible, develop robust designs to eliminate the need for
special characteristics; validating potential special characteristics during the design validation
(DV) of a product; insuring special characteristics are incorporated into the design record and
assist the APQP team in efforts to improve the design and process to eliminate special
characteristics.
2.3) Manufacturing and/or Process Engineer: Is responsible for incorporating the special
characteristics into the process failure mode and effects analysis (PFMEA); the use of sound
engineering methods to, when possible, develop robust processes to eliminate the need for
special characteristics; and developing capable processes and controls for Special
Characteristics that cannot be eliminated.
2.4) Quality Engineer: Is responsible for developing robust controls for all special characteristics
and insures that they are included in the Control Plan; conducting initial process studies for
capability analysis; compiling documents and information to prepare PPAP; and submitting
PPAP to the customer.
2.5) Manufacturing and/or Operations: Is responsible to produce the product in accordance
with the controlled process documented in the PPAP and working with the APQP team to
improve processes to eliminate the need for special characteristics.
3.) Definitions
3.1) Special Characteristic: A product characteristic or manufacturing process parameter that
can affect safety or compliance with regulations, fit, function, performance, or subsequent process
of product. Special Characteristics are also known as Key Characteristics.
3.2) Standard Characteristic: A product characteristic that is not noted as a Special
Characteristic.
3.2.1) Notes: Standard characteristics shall have appropriate controls; the absence of a
special characteristic does not waive the requirement to control the characteristic.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 2 of 10
3.2.2) Loss Function: The loss function for the standard characteristic shows no incremental
economic or customer satisfaction within the tolerance. Further, it shows no significant
increase immediately outside the tolerance.
3.3) <LK-SC> Lear Key Safety Characteristic: A special characteristic related to those product
requirements (Dimensions, Specifications, Tests or process parameters) which can affect
compliance with government regulations or safe Vehicle/Product Function.
3.3.1) Notes: Normally these characteristics are a 9 or 10 for severity on FMEA. The term is
synonymous with the AIAG APQP manual term Key Characteristic with Safety or Legal
Considerations.
3. 3.2) Correlation to OEM Special Characteristics: The <LK-SC> correlates to Ford’s
Critical Characteristic, CC and DCX’s Shield <S>.
3.4) <LK-PC> Lear Key Product Characteristic: A special characteristic that identifies those
product parameters and requirements that are important for customer satisfaction with a focus on
capability to maximize customer satisfaction.
3.4.1) Notes. Normally these characteristics are a 6, 7 or 8 for severity on FMEA. The term
is synonymous with the AIAG APQP manual term Key Characteristic without Safety or Legal
Considerations.
3.4.2) Correlation to OEM Special Characteristics: <LK-PC> correlates to GM’s KPC,
Ford’s Significant Product Characteristics, (SC) and DCX’s Diamond <D>.
3.4.3) Loss Function: A <LK-PC > Is a characteristic that has shown that the reasonable
anticipated variation is likely to significantly affect customer satisfaction.
3.5) <LK-FF> Key Fit and Function Characteristic: A special characteristic where deviation of
the characteristic outside of the specified tolerances may severely affect subsequent operations.
Key Fit and Function Characteristics are related to parameters that severely affect the operation of
the process or subsequent operations if they are outside of specification tolerance. It is limited to
highlighting characteristics where verification is mandatory, but where ongoing process control is
not automatically mandated.
3.5.1) Notes: Normally these characteristics are a 6, 7 or 8 in severity on FMEA. There is
no synonymous term in the AIAG APQP manual.
3.5.2) Correlation to OEM Special Characteristics: The <LK-FF> correlates to the Ford
High Impact (HI) Characteristic and the GM Product Quality Characteristic (PQC). There is
no similar DCX characteristic.
3.5.3) Loss Function: The loss function represented by the <LK-FF> is when the customer
is equally satisfied across the entire specification, but the loss function is steep just outside of
the specification.
4.0) Procedure: APQP teams work together in each phase of the APQP process to deploy special
characteristics. The PPAP process is used to communicate the initial process capabilities for
special characteristics.
4.1) Concept, Development, and Planning Phase (Pre Award): During this phase, the APQP
team focuses on using historical warranty and quality data and customer specifications to identify
preliminary special characteristics. These preliminary special characteristics should be considered
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 3 of 10
as targets for elimination through robust design practices or improved manufacturing processes.
The team considers the preliminary special characteristics in the Feasibility Review, Engineering
and Manufacturing Analysis, and Design Validation Plan.
4.2) Planning (Post Award) – Selection of Potential Special Characteristics: During this
phase, the APQP team focuses on the characteristics and their elimination through robust design
practices. The team reviews the product design and manufacturing process requirements for
characteristics that affect regulatory compliance, safe vehicle or product function, customer
satisfaction and machine/assembly operator safety. The APQP and product design team identifies
the system or a component feature that may require special actions or controls to insure the
product meets these requirements. These actions and controls are documented in the APQP
section of LPMP.
4.2.1) <LK-SC>: Design analysis is required to establish design margin and validate with
testing. This characteristic represents a regulated product safety requirement. Design
Validation (DVP&R) testing and reporting is required.
4.2.2) <LK-PC>: Design analysis is required to establish design margin and validation with
testing. This characteristic represents an element of the design that defines a unique
characteristic that is essential to the design intent. This characteristic should be controlled in
the design and may be applied based on best practice, warranty data or experience with
similar products. Design Validation (DVP&R) testing and reporting is required.
4.2.3) <LK-FF>: Design analysis is required in establishing variation between mating parts
and validation testing.
4.2.4) Additional Care: Some parts may require additional care, including product
verification and traceability, special handling, functional checks, and safety/compliance
certification. Any requirements for additional care shall be included in the design record.
4.3) Prototype Phase – Validation of Potential Special Characteristics: The development of a
Design FMEA (DFMEA) will identify actions that reduce or eliminate risk through employing robust
design practices and the identification of potential Special Characteristics. The design goal is to
eliminate Special Characteristics through design actions that improve the product robustness.
Special Characteristics are confirmed only after all design and process alternatives are exhausted
and when special controls are identified.
4.3.1) <LK-SC>: Design Validation (DVP&R) testing and reporting is required. The APQP
team must identify special controls. Special controls, especially those for surrogate
characteristics, may have to be included in design notes.
4.3.2) <LK-PC>: Design Validation (DVP&R) testing and reporting is required.
4.3.3) <LK-FF>: Notes.
4.3.4) Additional Care: For parts that require additional care, as specified in the design
record, conformance and capability to those requirements should be checked during the
prototype builds.
4.4) Pilot – Process Development for Capability and Control of Special Characteristics:
Characteristics are cascaded to the manufacturing process if the design is unable to fully control
the characteristic. The development of a Process FMEA (PFMEA) will identify actions that reduce
or eliminate risk through robust process practices and characteristics controls. The goal is to design
and define Special Characteristics controls that will always be employed until the design process
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 4 of 10
removes the “Special Characteristic” requirement from the FMEA through design and testing
exercises. Process design standards, machine design standards, and process FMEA’s will be
appropriately populated with the Lear symbols defined herein.
Local manufacturing facilities are engaged in the application of Special Characteristics as defined
on drawings, design and process FMEA’s. Local manufacturing facilities develop control plans,
work instructions, records of inspection, plant layouts and visual controls that are consistent with
this procedure.
4.4.1) <LK-SC>: Efforts should be directed at measuring the specific safety parameter of the
characteristic. If this parameter cannot be directly measured, a surrogate characteristic that
correlates (with verified testing) may be used. It is not intended for the manufacturing or
assembly facility to possess testing equipment that is certified or capable of performing
regulated safety testing. Key Safety Characteristics or surrogate characteristics must be
included in the control plan.
4.4.2) <LK-PC>: If the specific parameter cannot be directly measured, a surrogate
characteristic that correlates (with verified testing) may be used. Special Characteristics or
surrogate characteristics must be included in the control plan.
4.4.3) <LK-FF>: Manufacturing controls are required to verify conformance through
measurement, error proofing or functional testing.
4.5) Launch – Control the Special Characteristics: The APQP team executes the control plan
and reviews the PFMEA during launch to insure the control and capability of special characteristics.
4.6) Post Launch – Reduce Variation, Review, and Eliminate Special Characteristics: After
launch, the APQP team works to reduce variation and improve controls. The APQP process is
done in advance of the actual production process, additional characteristics may be found during
the manufacturing process. These characteristics must be identified by the team and appropriate
controls and documentation shall be implemented. The manufacturing process may demonstrate
higher levels of capability than anticipated and may support the reduction of the frequency of
special controls with customer approval.
The design responsible engineers shall review their lists of preliminary, potential, and identified
special characteristics for use in future programs.
4.7) PPAP: Special characteristics require initial process studies for PPAP. Special
characteristics that do not follow the methods established in the AIAG manuals for PPAP,
Measurement Systems Analysis, and Statistical Process Control require customer approval.
4.7.1) <LK-SC> - Variable Data: Surrogate characteristics shall be noted in the design
record. For characteristics that have a loss function that follow that of a <LK-PC>, submission
and controls follow the guidelines for the <LK-PC>
4.7.2) <LK-SC> - Attribute Data: Surrogate characteristics shall be noted in the design
record.
4.7.3) <LK-PC> - Variable Data: By their nature, <LK-PC>s should be made capable.
Where they are not capable, then errorproofing or 100% inspection strategies that control the
characteristic to a fraction of the available tolerance are required to optimize customer
satisfaction.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 5 of 10
4.7.4) <LK-PC> - Attribute Data: Normally attribute data should not be used to control <LK-
PC>s. When this is not possible, then error proofing and 100% inspection strategies that
control the characteristic to a fraction of the available tolerance are required to optimize
customer satisfaction. Calculations for process capability shall have customer approval.
4.7.5) <LK-FF>: Manufacturing controls are required to verify conformance through
measurement, error proofing or functional testing once capability has been demonstrated.
Calculations for process capability shall have customer approval
5.0) History
5.1) Revision History.
6.0) Forms / Examples
6.1) Customer – Lear Special Characteristics Cross Reference
6.2) Special Characteristics Management Model
6.3) Special Characteristics Recommended Controls Cross Reference / Preferred Controls
6.4) Loss Function Matrix
6.5) Special Characteristics – Recommended Controls Cross Reference
7.0) Reference
7.1) Ford Motor Company Customer Specific Requirements ISO/TS 16949 November 2003
7.2) GM Customer Specifics – ISO/TS 16949 December 2003
7.3) DaimlerChrysler (Chrysler Group) Customer Specific Requirements February 2005
7.4) FMEA Handbook Version 4.1, Ford motor Company, © 2004
7.5) Key Characteristics Designation System, 3rd Revision, GM1805 QN, General Motors
Corporation, March 2003
7.6) Reference Notes for Customer & Industry Specifications
5.1) Revision History
Revision Date Description of Revision Approved By
Released This procedure has been developed to meet Quality Margaret Lewis
5/12/06 System requirements for SSD divisions and supersedes
any similar procedure issued to date.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 6 of 10
6.1) Customer – Lear Special Characteristics Cross Reference
Key Characteristics Cross Reference Matrix
Lear Key Characteristics Ford Special DCX GM KCDS
characteristics
<LK-SC> Key Safety / (CC) – Critical Shield - <S> No equivalent.
Compliance Characteristic Characteristic
A product characteristic with Are those product Safety characteristics are GM KCDS requires that
reasonable anticipated requirements (Dimensions, defined as engineering parts (not characteristics)
variation may affect regulatory Specifications, Tests or designated specifications or be reviewed for
compliance or safe vehicle or process parameters) that can product requirements requirements for additional
product function. This affect compliance with applicable to component care. Additional care may
characteristic may drive either government regulations or material, assembly include testing for
capability or errorproofing and safe Vehicle/Product operation(s) which require safety/compliance,
usually implies additional Function. Special controls are special manufacturing functional checks, product
requirements such as identified on the Control plan control to assure compliance verification and
traceability and product and are defined as assembly with governmental vehicle traceability, and special
verification. process methods, safety, emissions, noise, or handling practices.
administrative actions, theft prevention
techniques and tests, beyond requirements
normal and customary
controls used to detect and
contain defects.
<LK-PC> Key Product (SC) – Significant Product Diamond - <D> KPC – Key Product
Characteristics – Characteristic Characteristic
Application of a Diamond to
A product characteristic with The product parameters and key design characteristic A product characteristic
reasonable anticipated requirements that are mandates that the inspection with anticipated variation
variation, including variation important for customer method, sample size and is likely to significantly
within tolerance, is likely to satisfaction. Special controls frequency be documented in affect customer
affect customer satisfaction or are identified on the Control a Control Plan. It does not satisfaction. The loss
subsequent operations. This plan and are defined as define how measurements function within the
characteristic drives a focus on assembly process methods, should be made and does tolerance drives a focus
process capability. administrative actions, not automatically invoke capability to minimize
techniques and tests, beyond SPC. The Control Plan is customer dissatisfaction.
normal and customary the governing document as Requires minimizing
controls used to detect and the methodology of variation within tolerance.
contain defects. conformance.
<LK-FF> Key Fit and (HI) – High Impact No equivalent. PQC – Product Quality
Function Characteristic Characteristic Characteristic
The Pentagon is no longer
A product characteristic which Are related to parameters that used. A product characteristic
variation outside of tolerance severely affect the operation which variation outside of
may significantly affect the of the process or subsequent the tolerance may
customer satisfaction or operations if they are outside significantly affect
subsequent operations. This of specification tolerance. customer satisfaction.
characteristic drives a focus on (Related to improper
errorproofing. manufacturing or assembly
operations affecting down
stream activities)
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 7 of 10
6.2) Special Characteristics Management Model
KC Deployment Flow
Product Engineering
Designs and validates <LK-SC> LK -PC
Product to achieve an executable system Ingredients DFMEA
that meets customer, regulatory and Lear
Commercial requirements Standards
Identifies areas of the design LK-SC
Drawings
<LK-FF>
that require additional attention
To reliably achieve the product ’s mission LK-PC
(Normal & customary controls inadequate)
Key Characteristics
By :
Stability Fatigue
Durability FMVSS
Sound / vibration
Fit & function
Identifies areas of the manufacturing process
that require additional controls LK-SC
To reliably achieve the product’s mission
(Normal & customary controls inadequate)Define for Deployment std. controls Flow Plan
M-pact
-
LK-FF
Process & Manufacturing
Engineering
Collaborates in the design phase with plants & <LK-SC> LK -PC
Product Engineering to develop Manufacturing PFMEA
System that meets customer, regulatory and M-pact
-
Lear commercial requirements <LK-FF>
LK-SC
LK-FF Local Plant Manufacturing
Control Plan Executes Key Characteristics
M-pact
- methodology per AIAG
Core tools and Lear standard
““KC”
Work instructions Controls.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 8 of 10
6.3) Special Characteristics – Recommended Controls Cross Reference
Safety or Loss Characteristics Preferred Controls Capability Methods
Non Safety For PPAP
Function
Mistake proofing device with a 100% inspection strategies
tightened tolerance that does not that control the characteristic
allow the defect to pass thru to a fraction of the available
process, 100% automated tolerance are required to
inspection with a tightened optimize customer
LK-PC tolerance. The tightened satisfaction. Calculations for
Loss Function
Non Safety
tolerances need to be process capability shall have
constructed to reduce the loss. customer approval. * See
Below
Ongoing continuous Process capability to CPK of
improvement with statistical 1.67 or customer approval.
control to continually reduce the
loss function.
Ongoing continuous Process capability to CPK of
improvement with statistical 1.67 or customer approval.
Safety
control to continually reduce the
loss function.
LK-SC Mistake proofing device that 100% inspection strategies
does not allow the defect to pass that control the characteristic.
No Loss Function
thru process, 100% automated Calculations for process
inspection with a lock box for capability shall have customer
defects. approval. * See below.
Mistake proofing device that 100% inspection strategies
Non Safety
does not allow the defect to pass that control the characteristic.
thru process. Calculations for process
capability shall have customer
approval. * See below.
LK-FF Ongoing statistical control to Process capability to CPK of
insure defects are not 1.67 or customer approval.
manufactured,
*Variable methods of proving capability are preferred but when not practical alternative strategies should be used.
Example 1) Using a Statistical Z table we find +/- 3 sigma has of a probability of .0027. That means, assuming no inspection errors, 384 pieces
with no defects is similar to a CPK of 1.00. Finding +/- 4 sigma on the Z table has a probability of .000063. That means (assuming no gage
error) 15873 with no defects is similar to a CPK of 1.33
Example 2) Supplier installs a mistake proof that will insure that defective parts can not be made or can not leave the process. This mistake
proof device must be qualified with an attribute gage study. The gage study should include a substantial number of defects in the sample group.
See AIAG MSA.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 9 of 10
6.4) Loss Function Matrix
The loss function establishes a measure of the user dissatisfaction with a product's performance as it
deviates from a target value. Thus, both average performance and variation are critical measures of
quality. Selecting a product design or a manufacturing process that is sensitive to controlled sources of
variation improves quality.
Simply put, the loss function is a way to show how each non-perfect part produced, results in a loss of
customer satisfaction. Deming states that it shows a minimal loss at the nominal value, and an ever-
increasing loss with departure either way from the nominal value.
W. Edwards Deming Out of the Crisis. p.141.
Symbol Action Plan
Key Product Characteristic : LISL USL
A key Product Characteristic is a
E Reduce Variation
Product Characteristic where the loss
Function has shown that the reasonably
LK-PC about a Target
Anticipated variation is likely to significantly Location
Affect customer satisfaction with a product.
Product Quality Characteristic:
A product Quality Characteristic is
LSL USL
LK-FF
one in which the customer is equally
satisfied across the entire specification, Process Control +/- 3 σ
but the loss function is steep just outside
of the specification limits.
Standard Product characteristic: LSL USL Meet Tolerance (+/- 3 σ)
A Standard Product Characteristics is one
in which the customer is equally satisfied
NONE
(Standard Care)
across the entire specification. And the
loss function is flat just outside of
specification.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Seating Systems Divisional Procedure Manual
l Lear SSD Special Characteristics Guideline SSD-DPM 20.3
Release Date: May 12, 2006
Effective Date: May 12, 2006 Owner: SSD Divisional Quality Department Page: 10 of 10
6.5) Special Characteristics – Recommended Controls Cross Reference
Definitions
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, pages 6-3. “Special Characteristics can be classified as Critical,
Significant, Operator Safety, or High Impact.”
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, pages 6-5 and 6-6. Definitions listed for each Ford special
characteristic.
Importance to Eliminate Special Characteristics
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, pages 6-8. “Every effort must be made to eliminate Special
Characteristics and Special Controls through design actions to improve product robustness,
or through process improvements that focus on improving process capability and safety.”
Hierarchy of Controls for Special Characteristics
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, pages 6-7. “Special Controls are those manufacturing and assembly
process methods, administrative actions, techniques and tests beyond the normal and
customary controls used to detect and/or contain Special Characteristic-related product
defects. This type of controls will prevent the shipment of a product not acceptable to the
end customer and is part of the quality system shown on the control plan.”
Incorporation into PFMEA
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, page 6-4. A table provides criteria for selection of special
characteristics based on the FMEA severity and occurrence scores.
Incorporation into Control Plan
• Ford: FMEA Handbook, pages 6-3. “Special Product Characteristics (<CC> and <SC>) must
be designated and included in control plans.”
Use of Customer Symbols
• Ford Customer Requirements, Nov 2003, Section 4.21 Symbols. “The organization is to
contact Ford Engineering to obtain concurrence for the use of Ford Motor Company special
characteristics symbols defined in the glossary of this document.”
• GM Customer Requirements Dec 2003, Section 4.1.5 Special Characteristics. “The
organization shall use General Motors Key Characteristic Designation System definitions
and symbols to comply with ISO/TS 16949:2002 special characteristics requirements (e.g.
cl. 7.2.1.1), and as provided in 4.2.2, General Procedures and Other Requirements, and
4.2.2.1 1, Key Characteristic Designation System (KCDS), (GM1805 QN) which defines
GM’s approach to special characteristics.
PPAP Requirements
• Ford: TBD.
• GM Customer Requirements Dec 2003, Section 4.1.8 Part Approval Process. “The supplier
shall comply with the Chrysler, Ford, GM Production Part Approval Process manual to
comply with cl. 7.3.6.3”.
©2003 Printed Copy for Reference Only
LearNet document is Controlled
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Spec Characteristics GdlnesDokument2 SeitenSpec Characteristics Gdlnessathyabalaraman0% (1)
- AS052Dokument12 SeitenAS052krishna kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fit/Function KPC:: Special Characteristics 11.1 Key Product Characteristic (KPC) DefinitionsDokument3 SeitenFit/Function KPC:: Special Characteristics 11.1 Key Product Characteristic (KPC) Definitions57641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Page 46 - 2.3: (Make Short Notes and Try A Flowchart)Dokument28 SeitenPage 46 - 2.3: (Make Short Notes and Try A Flowchart)Sonali DalviNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCCAF Handbook A4Dokument37 SeitenSCCAF Handbook A4William Autometal100% (1)
- Supplier Quality Assurance Manual: Special Devices, Incorporated Daicel Safety Systems America Arizona, IncDokument14 SeitenSupplier Quality Assurance Manual: Special Devices, Incorporated Daicel Safety Systems America Arizona, IncJeelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powertrain Global Quality RequirementsDokument6 SeitenPowertrain Global Quality RequirementsCarlos CarranzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 272Dokument14 Seiten272Ioana AlexandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unity FSP MFG 06 V01R00Dokument83 SeitenUnity FSP MFG 06 V01R00sowjanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1e1 S4hana2022 BPD en EsDokument60 Seiten1e1 S4hana2022 BPD en EsJulio CalacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCCAF Handbook - LetterDokument42 SeitenSCCAF Handbook - LetterBruno Debonnet78% (9)
- Validation Master Plan ExampleDokument11 SeitenValidation Master Plan ExampleAjay GangakhedkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMW15049 Agst 2016Dokument12 SeitenGMW15049 Agst 2016Gabriel Medina Encalada75% (4)
- ES-1007 Engineering SpecificationDokument5 SeitenES-1007 Engineering Specificationmoez manderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Characteristics Designation System: KCDS Pyramid KCDS PyramidDokument33 SeitenKey Characteristics Designation System: KCDS Pyramid KCDS PyramidmichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etq 114Dokument12 SeitenEtq 114Alex Acosta100% (1)
- Apqp Stages AIAG-1Dokument49 SeitenApqp Stages AIAG-1Jose Antonio Santoyo RayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure - Special CharacteristicsDokument13 SeitenProcedure - Special Characteristicsalexandru.ghiniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design With Strut-And-tie Models - ExamplesDokument101 SeitenDesign With Strut-And-tie Models - Examplesdeyu90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aqpaxi Phase 2.rev13Dokument7 SeitenAqpaxi Phase 2.rev13Isabel SierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM 1805Dokument33 SeitenGM 1805Hector Calle100% (1)
- Apqp Report2Dokument32 SeitenApqp Report2Angel MuruetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saep 349Dokument41 SeitenSaep 349Abdul Ahad LoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saep 1626Dokument13 SeitenSaep 1626paul cafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- APQP OS Procedure ExampleDokument8 SeitenAPQP OS Procedure Exampleali qaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ford ApqpDokument17 SeitenFord ApqpmageroteNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEEsqapDokument30 SeitenIEEEsqapDavid WessmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sop-Special Characteristics IdentificationDokument3 SeitenSop-Special Characteristics IdentificationSaravana kumar NagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manjulas Kitchen Best of Indian Vegetarian Recipes Free SampleDokument81 SeitenManjulas Kitchen Best of Indian Vegetarian Recipes Free SampleVasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saep 397Dokument9 SeitenSaep 397munnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- APQP Check ListDokument17 SeitenAPQP Check ListmdjeckelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Design and DevelopmentDokument13 SeitenProduct Design and DevelopmentGeorgiana BusuiocNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP 5 Supplier Quality ProcessesDokument187 SeitenGP 5 Supplier Quality ProcessesNeumar Neumann0% (1)
- Process Audit Check ListDokument47 SeitenProcess Audit Check ListAnas NazriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabp Z 002Dokument5 SeitenSabp Z 002Eagle SpiritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saep 349 PDFDokument41 SeitenSaep 349 PDFRami ElloumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Qualification Requirements 2.0Dokument3 SeitenProduct Qualification Requirements 2.0Amit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irqb Guideline 6 Special Processes Rev01Dokument22 SeitenIrqb Guideline 6 Special Processes Rev01Delong KongNoch keine Bewertungen
- VDA Special CharacteristicsDokument45 SeitenVDA Special Characteristicsrenato fabbri100% (11)
- VAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - Template PDFDokument10 SeitenVAL - 170401 - BMAA VAL Activity 3 URS - Template PDFDineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- L02-What Is Software QualityDokument30 SeitenL02-What Is Software QualityLee StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- G6a 0011 00Dokument14 SeitenG6a 0011 00Angelo Carlo MalabananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Characteristics DefinitionsDokument2 SeitenSpecial Characteristics Definitions57641100% (2)
- User Requirements SpecificationDokument5 SeitenUser Requirements SpecificationpriyabrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Process ReviewDokument33 SeitenDesign & Process ReviewFarm AgrobotNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Deere Design, Process, and Assembly ReviewDokument33 SeitenJohn Deere Design, Process, and Assembly ReviewcucuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerPoint Presentation FAI AS9102Dokument29 SeitenPowerPoint Presentation FAI AS9102Danny Fydm OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1e1 S4hana1909 BPD en MXDokument63 Seiten1e1 S4hana1909 BPD en MXfreddie mirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 PFMEA & Control Plan 1 of 7Dokument8 Seiten6 PFMEA & Control Plan 1 of 7P G Suman100% (1)
- OsageDokument40 SeitenOsageFederico MoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabp G 008Dokument78 SeitenSabp G 008Anonymous EarAM2100% (1)
- FaureciaDokument34 SeitenFaureciaIonut Eduard100% (2)
- ANPQP 2.1 - ChangesDokument25 SeitenANPQP 2.1 - ChangeskoalaboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - ASQ Symposium Core Tools Apr 12 BDokument69 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - ASQ Symposium Core Tools Apr 12 Brameshdesign67% (3)
- APQP Check ListDokument17 SeitenAPQP Check Listhmp90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Process Planning (CAPP): 2nd EditionVon EverandComputer Aided Process Planning (CAPP): 2nd EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 382 L6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsDokument42 SeitenCE 382 L6 - Shear and Moment DiagramsAydın Göğüş100% (2)
- Is.11865.2006 - Water IngressDokument9 SeitenIs.11865.2006 - Water Ingressrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ais 046Dokument13 SeitenAis 046jmmshahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is.13944.1994 Window RetensionDokument13 SeitenIs.13944.1994 Window Retensionrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Practice For Bus Body Design and Approval PDFDokument105 SeitenCode of Practice For Bus Body Design and Approval PDFrpagarwal2100% (1)
- Vichiensamuth 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 46 012034Dokument11 SeitenVichiensamuth 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 46 012034rpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is 737 2008Dokument18 SeitenIs 737 2008Arjuna ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS-063 - Requirement of School BusesDokument13 SeitenAIS-063 - Requirement of School Busesrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Code of Practice For Bus Body Design and Approval PDFDokument105 SeitenCode of Practice For Bus Body Design and Approval PDFrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ais 05Dokument71 SeitenAis 05rpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIS-031 RegulationsDokument22 SeitenAIS-031 RegulationsVirajNoch keine Bewertungen
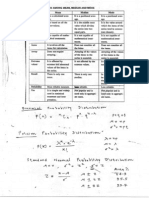
- Scan Formula's of StatDokument2 SeitenScan Formula's of Statrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical DataDokument32 SeitenTechnical Datarpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tatin CelikDokument52 SeitenTatin Celikgoran073Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Standard Is CodeDokument4 SeitenIndian Standard Is CodeGaganpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymers: Vacuum Thermoforming Process: An Approach To Modeling and Optimization Using Artificial Neural NetworksDokument17 SeitenPolymers: Vacuum Thermoforming Process: An Approach To Modeling and Optimization Using Artificial Neural NetworksSuresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP-ISO - 3302 - 1 - Rubber Tolerances For Products PDFDokument13 SeitenNP-ISO - 3302 - 1 - Rubber Tolerances For Products PDFluis martinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIIE Managerial Finance Exam QuestionsDokument10 SeitenIIIE Managerial Finance Exam Questionsrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CompaniesDokument13 SeitenTypes of Companiesrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3M VHB Tape Design Guide HiResDokument20 Seiten3M VHB Tape Design Guide HiResrpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chennai Travel GuideDokument15 SeitenChennai Travel Guiderpagarwal2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is:4990-1993, Plywood For Concrete Shuttering Work - SpecificationDokument22 SeitenIs:4990-1993, Plywood For Concrete Shuttering Work - Specificationrpagarwal2100% (1)
- Indian Standard Is CodeDokument4 SeitenIndian Standard Is CodeGaganpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - BD - Introduction To Big DataDokument83 SeitenUnit 1 - BD - Introduction To Big DataRishab kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercializing Process TechnologiesDokument11 SeitenCommercializing Process TechnologiesBramJanssen76Noch keine Bewertungen
- Green Building ProposalDokument22 SeitenGreen Building Proposalsarvadh100% (1)
- JN UG 3066 Integrated Peripherals APIDokument410 SeitenJN UG 3066 Integrated Peripherals APItalelkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Introduction To The Engineering Profession: Engr. Roman M. Richard, MengDokument13 SeitenUnit 2: Introduction To The Engineering Profession: Engr. Roman M. Richard, MengRoman MarcosNoch keine Bewertungen
- WAMP Server and PHP ZeroMQ Extension InstallationDokument2 SeitenWAMP Server and PHP ZeroMQ Extension InstallationGautambuddha AirportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of ThingsDokument243 SeitenInternet of ThingsWallie BillingsleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Africa Cyber Security Report 2017Dokument88 SeitenAfrica Cyber Security Report 2017kskabuye100% (1)
- Coveo For Sitecore Project Guide Version 2 PDFDokument54 SeitenCoveo For Sitecore Project Guide Version 2 PDFmaldonado.ogNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument4 SeitenNew Text Documentjutt1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 TriesDokument10 Seiten12 TriesNikhil 20528Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Reflecting Surface Practical Phase ShiftDokument5 SeitenIntelligent Reflecting Surface Practical Phase ShiftVarsha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive ActiveHybrid - V.4 GA8P70HZDokument15 SeitenDrive ActiveHybrid - V.4 GA8P70HZTimur GorgievNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ekip Bluetooth 1sdh000903r0002Dokument10 SeitenEkip Bluetooth 1sdh000903r0002Gary MokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es19btech11024 HW1Dokument3 SeitenEs19btech11024 HW1Salam RockybhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em 1110 1 1000Dokument371 SeitenEm 1110 1 1000ingaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat 2 STSDokument424 SeitenCat 2 STSVardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yokogawa MKR 10000Dokument60 SeitenYokogawa MKR 10000Jay SanchaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet of Things For Smart Healthcare: Technologies, Challenges, and OpportunitiesDokument24 SeitenInternet of Things For Smart Healthcare: Technologies, Challenges, and OpportunitiesSriharsha SarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium ProfileDokument23 SeitenAluminium ProfileRobert CedeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Fashion Shopping Questionnaire Final VersionDokument10 SeitenOnline Fashion Shopping Questionnaire Final VersionCao Mỹ HằngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Capabilities in Microsoft Dynamics NAVDokument3 SeitenManufacturing Capabilities in Microsoft Dynamics NAVAtanacia Ilagan100% (1)
- Elon Musk and Twitter - TBADokument11 SeitenElon Musk and Twitter - TBASibghatullah SiyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Codigo Cummins c-FMI-PID-SID-1Dokument35 SeitenCodigo Cummins c-FMI-PID-SID-1Claudivan FreitasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidance On Complying With Section IX, QG-106: Updated To Address Revisions in The 2021 EditionDokument5 SeitenGuidance On Complying With Section IX, QG-106: Updated To Address Revisions in The 2021 EditionSurat ButtarasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- B06 HydroProfiler-M eDokument2 SeitenB06 HydroProfiler-M eJamjamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow-X Flow ComputerDokument12 SeitenFlow-X Flow ComputerKuan Yue ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aw2.9bk6 12ax1 ManualDokument63 SeitenAw2.9bk6 12ax1 ManualjassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bluetooth Low Energy Device: Using The MT8852B To Test A Controlled Through A Proprietary InterfaceDokument7 SeitenBluetooth Low Energy Device: Using The MT8852B To Test A Controlled Through A Proprietary InterfaceAlberto SaldivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMEADokument3 SeitenFMEAyadiNoch keine Bewertungen