Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
OSPF Is A Link
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous Th1S33Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OSPF Is A Link
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous Th1S33Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
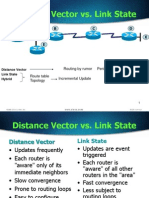
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that calls for the sending of link-state
advertisements (LSAs) to all other routers within the same hierarchical area. Information
on attached interfaces, metrics used, and other variables are included in OSPF LSAs. As
OSPF routers accumulate link-state information, they use the SPF algorithm to calculate
the shortest path to each node.
SPF Algorithm
The shortest path first (SPF) routing algorithm is the basis for OSPF operations. When an
SPF router is powered up, it initializes its routing-protocol data structures and then waits
for indications from lower-layer protocols that its interfaces are functional.
After a router is assured that its interfaces are functioning, it uses the OSPF Hello
protocol to acquire neighbors, which are routers with interfaces to a common network.
The router sends hello packets to its neighbors and receives their hello packets. In
addition to helping acquire neighbors, hello packets also act as keep-alives to let routers
know that other routers are still functional.
On multiaccess networks (networks supporting more than two routers), the Hello protocol
elects a designated router and a backup designated router. Among other things, the
designated router is responsible for generating LSAs for the entire multiaccess network.
Designated routers allow a reduction in network traffic and in the size of the topological
database.
When the link-state databases of two neighboring routers are synchronized, the routers
are said to be adjacent. On multiaccess networks, the designated router determines which
routers should become adjacent. Topological databases are synchronized between pairs of
adjacent routers. Adjacencies control the distribution of routing-protocol packets, which
are sent and received only on adjacencies.
Each router periodically sends an LSA to provide information on a router's adjacencies or
to inform others when a router's state changes. By comparing established adjacencies to
link states, failed routers can be detected quickly and the network's topology altered
appropriately. From the topological database generated from LSAs, each router calculates
a shortest-path tree, with itself as root. The shortest-path tree, in turn, yields a routing
table.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Open Shortest Path FirstDokument6 SeitenOpen Shortest Path FirstDaniel EpureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework - OSPF - RogandoDokument9 SeitenHomework - OSPF - RogandoRussel Jazz RogandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsci OspfDokument68 SeitenBsci OspfEhsan YazdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing and Switching Essentials Lecture 5 Note (Via Netcad Modules)Dokument42 SeitenRouting and Switching Essentials Lecture 5 Note (Via Netcad Modules)Shivend MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ospf NotesDokument17 SeitenOspf NotesIwllnu UwillnweNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA2 Chap 10 SummaryDokument2 SeitenCCNA2 Chap 10 SummarydlpleasantNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPFDokument2 SeitenOSPFsupermonkey21Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Summary: The Characteristics of OSPF FollowDokument7 SeitenOSPF Summary: The Characteristics of OSPF FollowarubenlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Routing Protocols: Submitted By: Saeed Ali Shahani (Intern)Dokument15 SeitenMajor Routing Protocols: Submitted By: Saeed Ali Shahani (Intern)Saeed Ali ShahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ospf Basics: Characteristic Ospf Ripv2 Ripv1Dokument8 SeitenOspf Basics: Characteristic Ospf Ripv2 Ripv1piyu_43Noch keine Bewertungen
- How OSPF Protocol Works & Basic Concepts - OSPF Neighbor, TopologDokument4 SeitenHow OSPF Protocol Works & Basic Concepts - OSPF Neighbor, TopologSanjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)Dokument33 SeitenOSPF (Open Shortest Path First)sachin prajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Definition: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Is A RoutingDokument14 SeitenOSPF Definition: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Is A RoutingBaah geooffrey JnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link StateDokument4 SeitenLink StateBetty Belicia ArfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF ThesisDokument9 SeitenOSPF ThesisShubham BaranwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Ospf Routing and AclDokument63 Seiten1 Ospf Routing and AclAshok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Tutorial: December 3rd, 2010Dokument8 SeitenOSPF Tutorial: December 3rd, 2010Sajith SubrahmanyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 7: OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)Dokument15 SeitenPractical 7: OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)Suktey Tuljaram. ArjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking StudyDokument5 SeitenNetworking Study2888shashankNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF - Open Shortest Path FirstDokument28 SeitenOSPF - Open Shortest Path FirstsatyamgNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)Dokument21 SeitenOSPF (Open Shortest Path First)José Luis PomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)Dokument21 SeitenOSPF (Open Shortest Path First)José Luis PomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPFDokument9 SeitenOSPFhim2000himNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cnap 3 Mod 2Dokument79 SeitenCnap 3 Mod 2api-3748967Noch keine Bewertungen
- OpenOSPFD - PaperDokument26 SeitenOpenOSPFD - PaperbzanajNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rebirth of The Router by Henry OsborneDokument8 SeitenThe Rebirth of The Router by Henry Osbornesicarii13Noch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkLab 1exDokument14 SeitenNetworkLab 1exMadan Prabhu DuraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial OspfDokument9 SeitenTutorial OspfYuri VelezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Dynamic RP Link StateDokument34 SeitenLecture 9 Dynamic RP Link StateCalvinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Open Shortest Path FirstDokument63 SeitenOSPF Open Shortest Path FirstPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 (Part - 2) : Unicast Routing ProtocolsDokument31 SeitenLecture 5 (Part - 2) : Unicast Routing ProtocolsesraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPFDokument19 SeitenOSPFMihret BerheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Shortest Path First: By: - Harsh KumarDokument20 SeitenOpen Shortest Path First: By: - Harsh KumarHarsh Kumar KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 2 Ospf PDFDokument4 SeitenCcna 2 Ospf PDFmacgyver_AdonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ros Ospf 110522 1928 406Dokument23 SeitenRos Ospf 110522 1928 406Raul Cespedes IchazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link State Routing ?: Link-State Routing Protocols Are One of The Two Main Classes ofDokument6 SeitenLink State Routing ?: Link-State Routing Protocols Are One of The Two Main Classes ofNikunj PatniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain OSPF in Detail?Dokument4 SeitenExplain OSPF in Detail?mystuff stuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 IP RoutingDokument13 Seiten9 IP RoutingChis LebroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 LabDokument7 SeitenLecture 7 LabSerin AskecNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Crash Course Day 03Dokument125 SeitenCCNA Crash Course Day 03JJohnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study The Working of RIP and OSPFDokument11 SeitenStudy The Working of RIP and OSPFJeevanreddy MamillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Basic Routing ConceptsDokument4 SeitenLecture 4 - Basic Routing ConceptsOge EstherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Short Path Protocol - OSPFDokument78 SeitenOpen Short Path Protocol - OSPFomarkhanfar2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Routing: Routing Is The Process of Selecting Paths in A Network Along Which To Send Network Traffic. Routing IsDokument8 SeitenRouting: Routing Is The Process of Selecting Paths in A Network Along Which To Send Network Traffic. Routing IsMuslim Abdul Ul-AllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing ProtocolDokument24 SeitenRouting Protocolgomathisankar.v1978Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITNW3101 Lecture7Dokument57 SeitenITNW3101 Lecture7mdarifsiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA-Day3 and 5 Fifth Day Start at 129 SlideDokument188 SeitenCCNA-Day3 and 5 Fifth Day Start at 129 SlideAtique Reza0% (1)
- Distance Vector vs. Link State: A B C D X EDokument125 SeitenDistance Vector vs. Link State: A B C D X EAtique RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link-State Routing Protocol FeaturesDokument3 SeitenLink-State Routing Protocol FeaturesShakeel AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acn OspfDokument10 SeitenAcn OspfApoorva H PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Routing ProtocolsDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Routing ProtocolsAhmet OZERENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 10-1 Network Layer - Interior Gateway Routing Protocols - OSPFDokument20 SeitenComputer Communication Networks CS-418: Lecture 10-1 Network Layer - Interior Gateway Routing Protocols - OSPFAli MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Routing and OSPF (Part 1)Dokument48 SeitenDynamic Routing and OSPF (Part 1)deepank singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Shortest Path First: State Advertisements (Lsas)Dokument16 SeitenOpen Shortest Path First: State Advertisements (Lsas)Prabha GaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Ospf: Robert Pradeepan SrilankaDokument142 SeitenConfiguring Ospf: Robert Pradeepan Srilankanvbinh2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSPFv3 Technology White PaperDokument21 SeitenOSPFv3 Technology White PaperVictoria E Pulido CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsVon EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONVon EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Literature Review Paper On Different Techniques Used in Vehicle Over Speed DetectionDokument3 SeitenA Literature Review Paper On Different Techniques Used in Vehicle Over Speed DetectionAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resource Management in Wireless Access Networks: A Layer-Based Classification - Version 1.0Dokument24 SeitenResource Management in Wireless Access Networks: A Layer-Based Classification - Version 1.0Anonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Criticality CharacterizationDokument1 SeiteTraffic Criticality CharacterizationAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive Radio SystemDokument10 SeitenCognitive Radio SystemAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research ProjectDokument54 SeitenResearch ProjectAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Channel Assignment Scheme 2 PDFDokument29 SeitenChannel Assignment Scheme 2 PDFAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Physics/Physics and Measurement: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDokument4 SeitenFundamentals of Physics/Physics and Measurement: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Definition - What Does Mean?: Line of Sight (Los)Dokument1 SeiteDefinition - What Does Mean?: Line of Sight (Los)Anonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- ExercisesDokument6 SeitenExercisesAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Entropy (Information Theory)Dokument3 SeitenEntropy (Information Theory)Anonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Propagation DefinitionDokument5 SeitenRadio Propagation DefinitionAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Error Probability Analysis For Convolutional Codes: - BER & Coding SchemesDokument3 SeitenError Probability Analysis For Convolutional Codes: - BER & Coding SchemesAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Binary Symmetric ChannelDokument14 SeitenBinary Symmetric ChannelAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Analog DiscoveryDokument9 SeitenIntroduction To The Analog DiscoveryAnonymous Th1S33Noch keine Bewertungen