Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exercise Vernier Caliper
Hochgeladen von
mexflozia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten10 Seitenylp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenylp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten10 SeitenExercise Vernier Caliper
Hochgeladen von
mexfloziaylp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
SUNG SIEW SECONDARY SCHOOL
YEARLY LESSON PLAN 2019 SCIENCE FORM 1
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map / HEBAT
K
Theme1:Scientific Methodology (12 hours)
Chapter1 : Introduction to Scientific Investigation
1.1 Science is part of daily life 1.1.1 relate daily activities to Science. Circle map
(1.5 hour) 1.1.2 generalise the meaning of Science.
1.1.3 summarise the importance of science in everyday life.
1.1.4 describe the fields of Science.
1.1.5 communicate about careers in Science.
1.1.6 relate subjects to be studied with science careers of interest.
1&2 1.1.7 Describe innovation in technology.
1.2 Your science laboratory 1.2.1 identify and state functions of the apparatus. Tree map
(2 hours) 1.2.2 identify symbols and examples of hazardous materials in the laboratory.
1.2.3 draw and label apparatus commonly used in the laboratory and classify
based on how it is used
1.2.4 Justify the regulations and safety measures in the laboratory.
1.3 Physical quantities and their 1.3.1 identify and use the correct units for different physical quantities. Bridge map
units 1.3.2 identify the symbols and values of prefixes use in measurement.
(2 hours) 1.3.3 convert base quantity units for mass, length and time such as grams to
kilograms, centimeters to meters, seconds to hours and vice versa.
1.3.4 Justify the importance of the use of S.I. units in daily life.
1.4 The use of measuring 1.4.1 use the right measuring instrument and use it in the rightway, to measure Tree map
instruments, accuracy, accurately and consistently the quantities of length, mass, time, temperature
consistency,sensitivity and electric current.
and errors (1 hour 30 min)
1.4.2 use measuring instruments with higher accuracies and compare the
3&4 (4 hours)
measurements in terms of accuracy, consistency and sensitivity.
(1 hour)
1.4.3 explain how to overcome systematic errors and random errors.
(30 min)
1.4.4 estimate the length, area, mass or volume of an object before taking actual
measurements.
(30 min)
1.4.5 explain with examples innovations of various types of measuring instruments
through a multimedia presentation.
(30 min)
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
1.5 Density 1.5.1 arrange sequentially materials based on density. Circle map
(3 hours) 1.5.2 predict whether the materials will float and sink according to density.
1.5.3 define operational definition of density.
5 1.5.4 calculate density using formula (density = mass/ volume) and water
Displacement method.
1.5.5 explain the phenomena related to the density difference in everyday life.
1.5.6 Innovate objects, food or beverage using the concept of density. (*Project 1)
1.6 Steps in a scientific 1.6.1 differentiate each science process skills. Flow map
investigation 1.6.2 make a sequence on the steps of carrying out a scientific investigation in the Model 21
(1 hour) correct order.
6 1.6.3 Conduct a scientific investigation to solve a simple problem.
(CNY 1.7 Scientific attitudes and 1.7.1 support scientific attitudes and values practiced by scientists.
), 7 values in carrying out 1.7.2 justify the need to practice scientific attitudes and values when carrying out an
scientific investigation investigation. Circle map
(30 min) 1.7.3 practice scientific attitudes and values while carrying out a scientific
investigation.
Theme2: Maintenance and Continuity of Life (28 hours)
Chapter2 :Cell as the basic unit of life
2.1 Cell–structure, function 2.1.1 explain that living things are made up of cells that carry out life’s functions Model 23
and organization and undergo cell division.
(5.5 hours) (1 hour)
2.1.2 demonstrate the preparation of slides of animal cells and plant cells using the Bubble map
correct procedures.
(1 hour)
2.1.3 communicate about each structures in cells with their functions as well as
compare and contrast animal cells with plant cells.
(1 hour)
2.1.4 explain with examples the characteristics of unicellular and multicellular
8, 9 organisms for animal cells and plant cells.
(1 hour) Double bubble map
2.1.5 differentiate the types and functions of animal cells and plantc ells.
(30 min)
2.1.6 conceptualise the formation of a plant and an animal with reference to the
sequence of cell organization:
Cell tissue organ system organism
(30 min)
2.1.7 appreciate and be amazed by the existence of various organisms
(30 min)
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
2.2 Cell respiration and 2.2.1 communicate about the process of cellular respiration. Circle map
photosynthesis (20 min)
2.2.2 communicate about the process of photosynthesis.
(2 hours) (1 hour)
9 2.2.3 differentiate the process of cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
(20 min)
2.2.4 explain how the process of cellular respiration and the process of
photosynthesis complement each other.
(20 min)
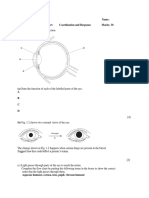
Chapter3 :Coordinationandresponses
3.1 Homeostasis in living things 3.1.1 communicate about homeostasis. Flow map
(2 hours) (30 min)
3.1.2 explain with examples the systems involved with homeostasis in humans and
animals
9, 10 (30 min)
3.1.3 explain with examples the systems involved in plant homeostasis.
(30 min)
3.1.4 appreciate the importance of homeostasis in humans and living things.
(30 min)
Chapter4 : Reproduction
4.1 Sexual and asexual 4.1.1 compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction in animals and
reproduction plants.
(1 hour) 4.1.2 reason the importance of reproduction. Double bubble map
4.1.3 be grateful for the ability to reproduce and the continuation of life as a gift
from God
4.2 Human reproductive system 4.2.1 identify the structures and function of the male and female reproductive
(1.5 hours) systems. Model 11
11 (1 hour)
(US1) 4.2.2 communicate about the physical changes that occur during puberty. Bubble map
12 (15 min)
4.2.3 compare and contrast the male gamete with the female gamete in the Double bubble map
reproductive system.
(15 min)
4.3 Menstrual cycle 4.3.1 communicate about the menstrual cycle and the sequence of changes in the
(1 hour) uterus lining during menstruation. Flow map
4.3.2 relate the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle to the process of fertilisation.
4.3.3 justify the importance of personal hygiene during menstruation.
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
14 4.4 Fertilisation and pregnancy 4.4.1 communicate about the process of fertilisation and the implantation of
(1 hour) embryo.
4.4.2 justify the importance and functions of placenta and umbilical cord. Flow map
4.4.3 describe the development of a zygote into an embryo and subsequently into a
foetus during pregnancy until birth.
4.5 Factors affecting the 4.5.1 relate the importance of taking nutritious food during pregnancy to the Bubble map
development of a foetus and health of both motherand foetus.
baby 4.5.2 justify the importance of avoiding the intake of harmful substances to the
(1 hour) foetus.
4.5.3 justify the benefits of breastfeeding compared to formula milk on the
infant’s development.
4.5.4 realise that every living creature has a right to live even if its in the womb.
4.6 Infertility and contraception 4.6.1 communicate the meaning of infertility and how to overcome them. Bubble map
(1 hour) (15 min)
4.6.2 differentiate methods of contraception. Circle map
(15 min)
4.6.3 realise the importance of practicing frequent health screening and to get
immediate treatment for problems related to reproductive system.
(15 min)
4.6.4 criticise the abuse of knowledge on contraception methods and its effect to
society.
(15 min)
15 4.7 Plant reproduction 4.7.1 communicate about the structure and function of each part of a flower. Circle map
&16 (4 hours) (30 min)
4.7.2 justify the pollination process. Bubble map
Good (30 min)
Friday 4.7.3 describe the process of fertilisation and explain the formation of seeds and Flow map
fruits in plants.
(1 hour) Multi-Flow Map
4.7.4 describe the germination process of a seed.
(1 hour 30 min)
4.7.5 solve problems if germination does not occur
(30 min)
Week 13 – Mid-Semester 1 Holiday ; Week 17, 18 – Mid-Year Examination
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
Theme3 Exploration Of Elements In Nature (24 hours)
Chapter 5 : Matter
5.1 Matterin nature 5.1.1 state that almost everything that exists in nature is matter. Tree map
(2.5 hours) (30 min)
5.1.2 prove that living things and non-living things have mass and occupy space.
19 (30 min)
5.1.3 differentiate the physical properties and chemical properties of matter.
(1 hour)
5.1.4 classify materials by the different characteristics.
(30 min)
20, 21 5.2 Three states of matter 5.2.1 generalise that matter consists of particles. Tree map
(4 hours) (20 min)
Wesak 5.2.2 compare and contrast three states of matter based on the kinetic theory in
Day terms of the arrangement and movement of particles.
(30 min)
5.2.3
use space-time relationships to compare rate of diffusion in three
states of matter.
(1 hour)
5.2.4 describe the change in state of matter, in terms of movement of particles
Modul 18
caused by the absorption and the release of heat, based on kinetic theory. Modul 30
(30 min)
Modul 7
5.2.5 conclude that temperature remains constant during melting / freezing and
boiling.
(40 min)
5.2.6 conclude that the mass remains constant during physical changes.
(40 min)
5.2.7 explain with examples the changes of the state of matter in daily life
(20 min)
Week 22&23 – Mid-Year Holiday * Kaamatan * Hari Raya
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
Chapter6 : Periodic Table
6.1 Classification of element 6.1.1 conclude that all matterconsists of atoms. Modul 29
(3 hours) (10 min)
6.1.2 differentiate between atoms and molecules as well as elements and Bubble map
compounds.
(50 min)
6.1.3 identify the position of metal, non-metal and inert gases in the periodic table.
(30 min)
6.1.4 differentiate the characteristics of metals and non-metals.
(1 hour)
6.1.5 appreciate the order of elements that exist in nature that has allowed people to Modul 6
organize them in the form of a table.
(30 min)
6.2 Mixture 6.2.1 communicate about examples of mixtures in daily life
(1 hour) (10 min)
24, 25 6.2.2 solve problem of separating mixtures through activities based on the Circle map
different characteristics of material and physical methods
(50 min)
6.3 Compound 6.3.1 communicate about compounds in daily life.
(1.5 hours) (10 min)
6.3.2 demonstrate the formation of compounds between metal and non- metal.
(30 min) Circle map
6.3.3 conclude that mass is conserved during chemical change.
(10 min)
6.3.4 separate compounds through chemical methods.
(20 min)
6.3.5 differentiate between chemical change and physical change.
(10 min)
6.3.6 differentiatebetween mixturesand compounds.
(10 min)
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
Chapter7: Air
26 7.1 Composition of Air 7.1.1 plan ways to determine and record the composition of air.
(2.5 hours) (1 hour)
7.1.2 synthesise the composition of air from a pie chart. Brace Map
(20 min)
7.1.3 justify the importance of oxygen, nitrogen carbon dioxide and inert gases in Modul 16
daily life.
(20 min)
7.1.4 appreciate the carbon cycle and the oxygen cycle in maintaining the
composition of gases in the air.
(20 min)
7.1.5 solve problems when there is/are interferences to the oxygen and the
carbon cycle.
(30 min)
27 7.2 Combustion 7.2.1 conclude about the conditions needed for combustion. Bubble map
(1 hour) (40 min)
7.2.2 relate the conditions of combustion with the principles used in the
manufacture of fire extinguishers.
(10 min)
7.2.3 practice safety measures to prevent the occurrence of fire which can lead to
the destruction of life and property. Modul 6
(10 min)
28 US 2
29 7.3 Air Pollution 7.3.1 define air pollution and air pollutants. Multi-Flow Map
(2 hours) (30 min)
7.3.2 communicate about air pollutants and the causes.
(30 min)
7.3.3 justify steps to prevent and control air pollution.
(30 min)
7.3.4 solve problems on the adverse effects of air pollution.
(30 min)
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
Theme 4: Energy and sustainability of life(22 hours)
Chapter 8 : Lights and optic
8.1 The use ofmirrors 8.1.1 differentiate between a real image and a virtual image. Bubble map
(3.5 hours) (20 min)
8.1.2 Communicate about the characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror,
concave mirror and convex mirror.
(1 hour)
8.1.3 state that the object distance is equal to the image distance in a plane mirror
(20 min)
8.1.4 use the plane mirror to apply the concept of reflection of light.
(30 min)
8.1.5 justify the application of concave mirror and convex mirror in daily life.
(30 min)
8.1.6 construct an optical instruments to appreciate the use these of optical
instruments to enhance the ability of the human senses.
30, 31 (30 min)
8.1.7 solve problems in daily life involving the application of plane mirror,
concave mirrorand convex mirror.
(30 min)
8.2 Properties of light 8.2.1 communicate about the properties of light. Circle Map
(30 min) (30 min)
8.3 Reflection of light 8.3.1 state the characteristics of image formed by a plane mirrors Bubble map
(1 hour) (10 min)
8.3.2 communicate about the Law of Reflection.
(20 min)
8.3.3 draw ray diagrams to show the reflection of light
(20 min)
8.3.4 solve problems in daily life with the application of reflection of light
(10 min)
32 8.4 Refraction of light 8.4.1 Generalise that refraction occurs when light moves through medium of Circle Map
(2 hours) different densities.
(20 min)
8.4.2 draw ray diagrams to show refraction of light when light propagate from one
medium to another medium of different densities.
(40 min)
8.4.3 generalise the relationship between the angle of incidence,i and angle of
refraction,r, when lighttravels from a medium of low density to a medium of
high density.
(40 min)
8.4.4 justify the applications of refraction of light in daily life.
(20 min)
8.5 Dispersion of light 8.5.1 communicate about the dispersion of light. Circle Map
(1 hour) (30 min)
32
8.5.2 explain with an example the dispersion of light in daily life.
(30 min)
33 Mid-Semester 2 Holiday
8.6 Scattering of light 8.6.1 communicate about scattering of light Circle Map
(1 hour) (30 min)
8.6.2 explain withan example scattering of light in daily life
(30 min)
8.7 Addition and subtraction of 8.7.1 identify primary colours (10 min)
light 8.7.2 identify the addition of primary colours to produce secondary colours. Modul 27
(2 hours) (20 min)
8.7.3 communicate about subtraction of light. Circle Map
34
(30 min)
8.7.4 record the colours formed on the screen when light passes through colour
filters.
(20 min)
8.7.5 differentiate the addition and subtraction of light.
(20 min)
8.7.6 explain with examples addition and subtraction of light in daily life.
(20 min)
Theme 5: Exploration of Earth and Space (13 hours)
Chapter 9 : Earth
9.1 System and structure of 9.1.1 communicate about the system of the Earth
the Earth (50 min) Modul 14
(1.5 hours) 9.1.2 explain differences in Earth layers based on its composition and physical
characteristics. Circle Map
(20 min)
9.1.3 realise that Earth is the only place that can sustain life based on its physical
35
characteristic
(20 min)
9.2 Substance of the Earth 9.2.1 explain type and characteristic of rocks. Double bubble map
(30 min) (15 min)
9.2.2 communicate on how to differentiate the process of rock formation
(15 min)
WEE Content Standard Learning Content iThink Map
K
35 9.3 Main processes of the 9.3.1 explain the different Earth processes that effect the changes on Earth. Flow Map
Nation Earth (30 min)
al Day (1 hour) 9.3.2 communicate about exogenicand endogenic processes
(30 min)
9.4 Geohazard phenomena 9.4.1 communicate about geohazard. Multi-Flow Map
(1 hour) (20 min)
9.4.2 generate ideas on how science and technology are used to prepare for
geohazards.
(20 min)
9.4.3 realise that enviromental disasters effect human livelihood.
36 (20 min)
9.5 Age of the Earth 9.5.1 communicateaboutgeological time scaleoftheEarth. Circle Map
Awal
(1 hour) (15 min)
Muhar
9.5.2 explain the method to determine the age of the Earth. Modul 15
ram
(15 min)
9.5.3 communicate about fossils.
(15 min)
9.5.4 reason about the importance of fossils in the advancement of contemporary
science.
(15 min)
37 9.6 Earth resources and 9.6.1 explain surface waterand its risks. Multi-Flow Map
applied geology (15 min)
(1.5 hours) 9.6.2 explain theimportance of underground water and its risks.
(15 min)
9.6.3 communicate about economic minerals.
(15 min)
9.6.4 explain the formation of petroleum and coal.
(15 min)
9.6.5 communicate about the hydrothermal process.
(15 min)
9.6.6 solve problems about the negative effects of unplanned human activities on
all living things on Earth.
(15 min)
37, 38 Revision
39-41 Year-End Examination
42-47 Revision
Prepared by Mdm Petronella GR 28 November 2018
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ylp Remove 2018Dokument5 SeitenYlp Remove 2018mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Harian Science T1 - 2021Dokument14 SeitenRancangan Harian Science T1 - 2021g-90227065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation: Theme 1: Scientific Methodology (12 Hours)Dokument14 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction To Scientific Investigation: Theme 1: Scientific Methodology (12 Hours)Anonymous ESQwNOtfe6Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Sains T1 2023 (Bi)Dokument14 SeitenRPT Sains T1 2023 (Bi)REHAN SUWARNI BINTI ABU BAKAR KPM-GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Form 1 2017 SemesraDokument15 SeitenRPT Science Form 1 2017 Semesracikgu ayu100% (3)
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Science Form 1 2019 (Dlp-English)Dokument14 SeitenRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Science Form 1 2019 (Dlp-English)Nur IzzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science StandardsDokument2 SeitenScience Standardsapi-369625583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated ScienceDokument26 SeitenIntegrated ScienceMedlyn CeesayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan SC f1Dokument16 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan SC f1Mary IdrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated ScienceDokument26 SeitenIntegrated ScienceAris TotleNoch keine Bewertungen
- YEARLY SCIENCE LESSON PLAN FORM 1Dokument14 SeitenYEARLY SCIENCE LESSON PLAN FORM 1noor mazitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFDokument24 SeitenWASSCE WAEC Integrated Science Syllabus PDFKojo Yeboah Enchill100% (1)
- Sow f1 Igcse Phy 2021Dokument21 SeitenSow f1 Igcse Phy 2021Immy MaysmeekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hour (S) Content Standard Learning Standard Basic Addition Complementary Theme: Inquiry in Science 1.0 Scientific SkillsDokument5 SeitenHour (S) Content Standard Learning Standard Basic Addition Complementary Theme: Inquiry in Science 1.0 Scientific SkillsIqbal N SalmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal Cell LAPDokument2 SeitenPlant and Animal Cell LAPewolramnasomitelimusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Standards MN 2009 005263Dokument3 SeitenScience Standards MN 2009 005263api-369643865Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0610 Topic QuestionsDokument302 Seiten0610 Topic QuestionsFor GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work For Form 1 ScienceDokument22 SeitenScheme of Work For Form 1 ScienceJila NfmNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseDokument2 SeitenIGCSE Biology Worksheet - Coordination and ResponseAnand Kumar ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabus-AnaDokument10 SeitenCourse Syllabus-AnaMariamiraluz Khalidryan Sevilla-BurlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Things and Their Environment JHSDokument34 SeitenLiving Things and Their Environment JHSLiza YanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 ProfEd 08 Grade 6 Science 2nd Quarter TOS II 24 BSCIE BIOLOGYDokument4 Seiten02 ProfEd 08 Grade 6 Science 2nd Quarter TOS II 24 BSCIE BIOLOGYRen ManalotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TheoryDokument2 SeitenCell TheoryKai SarabusabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugasan Isl Sce 3101Dokument9 SeitenTugasan Isl Sce 3101Hamidah JamaludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIFE SCIENCES WINTER CLASSES LEARNERS BOOKLET (Final)Dokument43 SeitenLIFE SCIENCES WINTER CLASSES LEARNERS BOOKLET (Final)Magadani FhatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science - Unifying ThemesDokument6 SeitenEarth and Life Science - Unifying ThemesBarbeicaht SallinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ylp Science f1 2024 Fara Asrab GoayDokument17 SeitenYlp Science f1 2024 Fara Asrab Goayg-90227065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional PlanningDokument6 SeitenInstructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Anatomy Book ProjectDokument2 SeitenComparative Anatomy Book Project장서아Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SC Year 1Dokument8 SeitenRPT SC Year 1Kilimoly BalakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S7Lt - Iic - 3 S7Lt - Iid - 4 S7Lt - Iie - 5: Week 3Dokument1 SeiteS7Lt - Iic - 3 S7Lt - Iid - 4 S7Lt - Iie - 5: Week 3Gen Dee100% (2)
- BOW ScienceDokument10 SeitenBOW ScienceRUTH MIASCONoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisa Histologie 2019 2020 MG ENGL Sem IDokument7 SeitenFisa Histologie 2019 2020 MG ENGL Sem IUrsu GeorgianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- YLP Science F1 2017 CompleteDokument32 SeitenYLP Science F1 2017 CompletesitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal MicrosDokument4 SeitenAnimal MicrosespantocdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Grade 10Dokument6 SeitenYearly Plan Grade 10hanatabbal19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated ScienceDokument6 SeitenIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- B.course ContentDokument3 SeitenB.course ContentAaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Sc. 7-8Dokument103 SeitenGeneral Sc. 7-8Maki ErkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex 2B To Deped Order.42.S.2016: I. ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenAnnex 2B To Deped Order.42.S.2016: I. ObjectivesCristina MaquintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Unit PlanDokument15 SeitenScience 10 Unit Planapi-537568147Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Dokument23 Seiten1989 Paper 1 Question 5 (B)Kin Long Chris WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan 4 2011Dokument12 SeitenScience Yearly Plan 4 2011Zulkhairi AbidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Science Scheme of Work 2019Dokument5 SeitenGrade 7 Science Scheme of Work 2019ramloghun veer100% (1)
- 7 E's LP Bio. 7Dokument3 Seiten7 E's LP Bio. 7Jen Lorejas100% (1)
- Scheme of Work and Suggested Activities Formula A pt3 KSSM Science Form 1Dokument25 SeitenScheme of Work and Suggested Activities Formula A pt3 KSSM Science Form 1Thivya RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 11 Wolkow PDFDokument653 SeitenBiology 11 Wolkow PDFمنیر سادات100% (7)
- Penguin Unit ADokument25 SeitenPenguin Unit Aapi-334151244Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Performance StandardsDokument1 SeiteCells, Tissues, Organs and Systems Performance StandardsColesio, Maria Elaine M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perancangan Takwim Amali Sains 2022Dokument4 SeitenPerancangan Takwim Amali Sains 2022Conan X-FileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Science: Benchmarks, Skills & Knowledge, and Assessment TasksDokument3 SeitenElementary Science: Benchmarks, Skills & Knowledge, and Assessment TasksPerihan SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Scope and SequenceDokument11 SeitenBiology Scope and SequenceNabeela NargisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFDokument51 Seiten2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFJosh MagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Secondary Science 7 Scheme of WorkDokument21 SeitenLower Secondary Science 7 Scheme of WorksumnamundethNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntegratedScience WB1 SamplepagesDokument7 SeitenIntegratedScience WB1 SamplepagesCHRISTOPHER SCALENoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Work Grade 5Dokument1 SeiteBudget of Work Grade 5Maria Concepcion TuvillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Els For Co1Dokument5 SeitenDLP Els For Co1jefferson cristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI Sci DOK Levels 09-27-07Dokument6 SeitenMI Sci DOK Levels 09-27-07lchamblessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 11 - Curiosity (M-F/7:45 - 8:45) Grade 12 Jacinto (M-F/12:30 - 1:30)Dokument4 SeitenGrade 11 - Curiosity (M-F/7:45 - 8:45) Grade 12 Jacinto (M-F/12:30 - 1:30)Lowel AndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH (31 Dis - 7 Jan)Dokument1 SeiteRPH (31 Dis - 7 Jan)mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STIMULI AND RESPONSESDokument12 SeitenSTIMULI AND RESPONSESaidilubaidillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Read Vernier CalipersDokument2 SeitenHow to Read Vernier CalipersAverroes ShineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penilaian SKPMGDokument1 SeitePenilaian SKPMGmexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Week 5Dokument20 SeitenRPH Week 5mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Science in Daily LifeDokument13 SeitenImportance of Science in Daily LifemexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH (31 Dis - 7 Jan)Dokument11 SeitenRPH (31 Dis - 7 Jan)mexflozia100% (1)
- SM Sung Siew Sandakan Jadual Penyediaan Kbat/ I-Think (Junior) Sains & Matematik 2018 Tingkatan 1Dokument2 SeitenSM Sung Siew Sandakan Jadual Penyediaan Kbat/ I-Think (Junior) Sains & Matematik 2018 Tingkatan 1mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains 1B latihanDokument23 SeitenSains 1B latihanmexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Item 2017 (1d)Dokument12 SeitenAnalisis Item 2017 (1d)mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBLDokument1 SeitePBLmexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Week 4Dokument16 SeitenRPH Week 4mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Week 24Dokument7 SeitenRPH Week 24mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Week 30Dokument8 SeitenRPH Week 30mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH Week 16Dokument5 SeitenRPH Week 16mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeostasis Hands-on Activity: Negative Feedback Pathways in the Human BodyDokument16 SeitenHomeostasis Hands-on Activity: Negative Feedback Pathways in the Human BodymexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ERPH 2017 (17 April - 28 April)Dokument14 SeitenERPH 2017 (17 April - 28 April)mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Year Test IDokument24 SeitenMid Year Test ImexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 HeatDokument6 SeitenChapter 7 HeatchernzhongNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH SainsDokument3 SeitenRPH SainsmexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- f1 Chapter 2Dokument36 Seitenf1 Chapter 2mexfloziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resources On EarthDokument6 SeitenResources On EarthNg Kok ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadual WAKTU 1EDokument1 SeiteJadual WAKTU 1Eanon_990952259Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods in Rock MechanicsDokument24 SeitenNumerical Methods in Rock Mechanicsali100% (2)
- Tartarus Magistery Manfred JuniusDokument10 SeitenTartarus Magistery Manfred JuniusJanWillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mastercool - FluorescentDye (Em Ingles)Dokument8 SeitenMastercool - FluorescentDye (Em Ingles)Luis Henrique MarangãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Configuration NotesDokument4 SeitenElectron Configuration NotesapriantokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07apr Mat183 Mat193 Mat421Dokument6 Seiten07apr Mat183 Mat193 Mat421Ahmad Mustaqim100% (1)
- Time DilationDokument17 SeitenTime DilationJimmy JoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centurion University of Technology and Management: Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering (Rdme - 2019)Dokument5 SeitenCenturion University of Technology and Management: Recent Developments in Mechanical Engineering (Rdme - 2019)Babuli KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copia de GranulometriaDokument1 SeiteCopia de GranulometriaSantiago GiraldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hatch Cover Analysis of Capesize Bulk CarriersDokument6 SeitenHatch Cover Analysis of Capesize Bulk CarriersBasem TamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index of Physics Lab Report on Refraction of LightDokument6 SeitenIndex of Physics Lab Report on Refraction of LightSnehal VinodNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP A08e15 Od01 - DS - 0 0 5 PDFDokument2 SeitenFP A08e15 Od01 - DS - 0 0 5 PDFYura DankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microphone Calibration by Transfer Function Comparison MethodDokument5 SeitenMicrophone Calibration by Transfer Function Comparison MethodJulian A. TinaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Energy Analysis For Open Systems Compatibility ModeDokument35 SeitenChapter 5 - Energy Analysis For Open Systems Compatibility ModekhameesmarwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRP Column AbaqusDokument14 SeitenFRP Column AbaqusAlvin PurmawinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bearing Capacity of Footings On Coarse SoilsDokument11 SeitenThe Bearing Capacity of Footings On Coarse SoilsMattNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS (GCE) Instant Revision of ChemistryDokument130 SeitenAS (GCE) Instant Revision of ChemistryOlivia Panterka Vainilla100% (4)
- Doob, The Development of Rigor in Mathematical Probability (1900-1950) PDFDokument11 SeitenDoob, The Development of Rigor in Mathematical Probability (1900-1950) PDFFardadPouranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Techniques Julia C. Drees Alan H. B. WuDokument36 SeitenAnalytical Techniques Julia C. Drees Alan H. B. WuBetrearon SileshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Method 1Dokument3 SeitenNumerical Method 1Er SarbeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field and Magnetic Effects of Current: Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenMagnetic Field and Magnetic Effects of Current: Assignment 2HaRryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldox 1100 Structural SteelDokument2 SeitenWeldox 1100 Structural SteelAndrewFranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration BookDokument152 SeitenVibration Bookrez_babu7430Noch keine Bewertungen
- FHWA Drilled Shafts Construction Procedures and LRFD Design Methods APP-CDokument14 SeitenFHWA Drilled Shafts Construction Procedures and LRFD Design Methods APP-CmalangpeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile RefereneDokument24 SeitenPile RefereneamazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 MCB Key PDFDokument19 SeitenUnit 2 MCB Key PDFDafne Fertig88% (32)
- 12-Story Steel Building AnalysisDokument505 Seiten12-Story Steel Building Analysissysyphus01100% (1)
- Flixborough - The Disaster and Its Aftermath PDFDokument31 SeitenFlixborough - The Disaster and Its Aftermath PDFAlessio Scarabelli100% (2)
- Contacts Modeling in AnsysDokument74 SeitenContacts Modeling in Ansyssudhirm16100% (2)
- A Review of Melt Extrusion Additive Manufacturing Processes I. Process Design and ModelingDokument13 SeitenA Review of Melt Extrusion Additive Manufacturing Processes I. Process Design and ModelingFernando AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Physics 1: Brwebberandchwbarnes Michaelmas Term 2008Dokument73 SeitenTheoretical Physics 1: Brwebberandchwbarnes Michaelmas Term 200821260paco61Noch keine Bewertungen