Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cloud Computing - An Exploration
Hochgeladen von
Vincent VijayOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cloud Computing - An Exploration
Hochgeladen von
Vincent VijayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cloud Computing - An Exploration
Charles D. Gnanesh
VP-Technology, SRA Systems
100, Valluvarkottam High Road,
Chennai - 600034, India
Abstract: It is my earnest desire that everyone should have a basic
understanding of what cloud computing is and what it offers to everyone. This
paper attempts to put together a fundamental understanding of what is cloud
computing in simple layman terms. Wherever necessary, the usual jargons
associated with the new domain have been deliberately avoided, to ensure
everyone has a good read and is able to comprehend the basics. For any further
study on the domain or focus topics such as Amazon’s AWS or Microsoft’s Azure
cloud platforms please approach the author.
Contents
Introduction
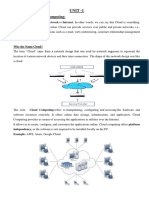
What is Cloud Computing
Types of Clouds
Advantages of using the cloud
Issues to be addressed by the cloud
Conclusion
References
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 1 Charles D. Gnanesh
Introduction
Over the past 6 months, it’s been an exciting journey attending many seminars,
reading whitepapers and watching success stories on cloud computing. Cloud
Computing has arrived and is here to stay, definitely for the next decade. This
paper will serve as a primer to whoever is interested to dive into this new service
paradigm and is also looking for avenues to expand his/her knowledge in this
area a bit more.
Hospitality has been a lifeline in many of our families in India. Every other day we
get guests from various known/unknown sources of our relations/friends etc and
it’s been our sincere and cherished tradition to feed them
with our best. But over the past few years a new trend has
come up, if the guests arrive at a volume more than 5, we
usually order food at our local fast food shop or our well
known food bhavans. We are no longer concerned about
how much of food we need to prepare, how much rice to
buy, how many dishes to make, when to cook, when to
microwave and so on…. its all outsourced! Cloud
computing attempts to solve the very same problems, but
in a virtual world, with the option to pay as per our usage, scale when required,
get more computing power on a need basis and so many such facilities, all at a
low cost, compared to having our own setup.
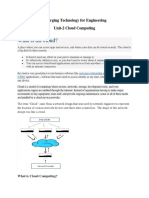
Cloud, usually refers to the Internet and in our case, refers to any hardware or
software resource that does not reside on our own infrastructure or premises, but
at a location which is deemed to be safe and available at all times for our use.
Computing is added along with Cloud to imply that the primary aim of the
providers of these clouds, is computing power at a low cost. Lets explore this
further.
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 2 Charles D. Gnanesh
What is Cloud Computing?
In 2006, post the dot-com bubble, Amazon came out with a concept of Elastic
Compute Cloud (EC2), offering everyone, who had a credit card, incredible
amounts of computing power, storage space and software resources, which until
then was being obtained at huge costs. They could do this, because they already
had huge data centers with millions of commodity type servers to support their
cyber bookstore. They quickly started building more such clouds in various parts
of the world and came out with valuable combinations of these resources as
offerings for the industry.
There are thousands of such data centers with unused or underutilized
computing power, which can be sold to users who really are looking for such high
capacities for economies of scale. That was the beginning of the cloud-
computing story. Following Amazon, Internet giant Google also joined in, to get
this market booming.
“Cloud computing is a style of computing in which dynamically scalable and often
virtualized resources are provided as a service over the Internet” says Wikipedia.
Just to make it legible to a normal mind, Cloud computing offers an endless
supply of computing power, along with storage space, as long as you can pay for
it and all this would be provided over an internet connection. And this computing
power that you get, may be from a server that shares its resources with many
other users like you, so as to completely utilize the entire power its got. This is
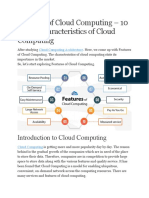
primarily known as virtualization of the physical resources. Some of the attributes
of Cloud computing is depicted below, as given by the Gartner Research Group.
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 3 Charles D. Gnanesh
Types of Clouds
Public Cloud – A service provider, who maintains huge data centers, will
provision computing resources for our usage and we will pay him on a pay-per-
use basis. We will not care about where the systems are located, nor have
physical access or control over where our data is stored. This is an offsite model
of the cloud.
Private Cloud – A huge enterprise can consolidate its servers into a local data
center and employ virtualization techniques to provision machines and storage
space as required by the enterprise. Or if the enterprise wishes, they can also
approach a provider to offer them a cloud, which is accessible only by them and
would be part of their own network, thereby allowing the enterprise to manage
the cloud and its security/access points. The machines provisioned by the cloud
service provider, in this case, will be only used for this particular enterprise and
will not be shared or accessible to the public.
Hybrid Cloud – Having a combination of an in-house cloud and also a tie up with
multiple cloud service providers can offer the enterprise with having a more
secure, vendor independent cloud, commonly referred to as a hybrid cloud. This
will not lock the enterprise to one particular service provider but enable them to
take advantage of the multiple offerings from various providers, while building a
solid cloud for the enterprise.
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 4 Charles D. Gnanesh
Community Clouds – Google Gov Cloud is a good example of a community
cloud, where several organizations come together to offer their resources in
order to establish a service for a community cause. Since the users are less in
this type of a cloud, the cost of using this cloud is usually higher than that of the
public clouds.
Advantages of using the cloud
Scalability – You can expect to have more virtual PC’s to be added for your
usage in a matter of seconds (120 secs to bring up another XP/Linux machine).
Imaging a scenario when you have to ramp up a team with 30-40 people but
need to do this in a couple of days or lose the project. Cloud computing will solve
this problem, all you need to do is place a request for 30-40 virtual machines and
they will all be available for you in a couple of hours maximum. That is called
elastic or dynamic or on-demand scaling, which was not economically or
chronologically feasible before.
Cost effective – A perfect example that is always used to prove the cost
effectiveness of cloud computing is about an online greeting card company
handling valentine’s day traffic. They will expect almost 400 times the traffic to
their sites on Valentine’s Day, than on most of the days in the year. So do they
plan and procure infrastructure for peak performance or ramp up before
Valentine’s day and ramp down again after its over? Cloud computing solves this
problem in a jiffy, they can order extra servers as the traffic grows on valentine’s
day and still be back to normal the next day by asking the provider to take off
those machines that they ordered on valentine’s day. Its all virtual, so it will be
ordered and removed in a click, thus saving huge costs to the company and also
helping them service high traffic on a particular day, making them enjoy higher
profits for that day.
Reliability – Most of the cloud-computing providers have redundancy built in to all
of their storage services. So anything you store will be durable and available for
operations at all times guaranteed. This will save our efforts on Disaster
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 5 Charles D. Gnanesh
recovery, backup etc. Amazon claims all data would be durable 99.999999% in a
given year, meaning it’s very unlikely that you will lose your data unless it’s the
end of the world!
Multi-tenancy – Server consolidation can happen in any enterprise by using multi
tenancy and virtualization of the resources available on servers, thus enabling a
pool of users to use the servers and utilize its computing power to the maximum.
This will also improve centralization of servers and thereby a reduction on the
real estate and electricity consumption.
Maintenance – Users no longer need to upgrade/install service packs, antivirus
on their systems, since the cloud provider will take care of upgrading and
maintaining the machines with the latest available OS patch or security measure.
This will decrease to a great extent the required number of IT personal in any
enterprise to a bare minimum, as everything will be managed in the cloud itself
and not on a per user or per machine basis.
Many of the advantages of a Cloud circulate around the reduction of initial
expenditure incurred for setting up the infrastructure (CAPEX) and in economies
of scale with minimal cost.
Issues to be addressed by the cloud
Security – Everyone is concerned about security of their data in the cloud. For ex,
the data pertaining to an enterprise could be residing in different servers located
across different countries that are governed by their own laws. Here are a few
issues with the security of data on a cloud
1. How does one ensure physical access is restricted if the data does not
reside on a server on our premises, but is somewhere in the world that we
don’t even know?
2. What is the guarantee that the data is not being copied without proper
authentication from the actual owner of the data?
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 6 Charles D. Gnanesh
3. What is the proof for deletion of the data once the contract is over with the
said provider?
Amazon has come out with an excellent white paper1 on addressing these
concerns and how Amazon is tackling the security issues for their customers.
Availability and Performance – Since our entire business will now rest upon the
service provider to ensure 100% availability, what are the various methods by
which he would ensure we are live always? What if there is a breach or a
shutdown; will they bring up our business sites from a different data center?
Legal Contractual issues – Ownership of the computed data, managing the IPR
are some of the legal and contractual issues that need to be sorted out between
the provider and the enterprise. Working out of different countries will also pose
more legal issues w.r.t to the data storage and physical access.
Conclusion
The majority of technology experts expect that by 2020 most people will access
software applications online and share and access information through the use of
remote server networks, rather than depending primarily on tools and information
housed on their individual, personal computers. This was concluded in a survey
on Internet usage by pewresearch center. They say that cloud computing will
become more dominant than the desktop in the next decade. In other words,
most users will perform most computing and communicating activities through
connections to servers operated by outside firms.
Among the most popular cloud services now are
Social networking sites (Facebook is in the cloud),
Webmail services like Gmail and Yahoo mail,
Microblogging and blogging services such as Twitter and WordPress,
Video-sharing sites like YouTube,
Picture-sharing sites such as Flickr,
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 7 Charles D. Gnanesh
Document and applications sites like Google Docs,
Social-bookmarking sites like Delicious,
Business sites like eBay,
Ranking, rating and commenting sites such as Yelp and TripAdvisor.
This does not mean, however, that most of these experts think the desktop
computer will disappear soon. The majority sees a hybrid life in the next decade,
as some computing functions move towards the cloud and others remain based
on personal computers.
References
1. Frost.com
2. Amazon
3. PewResearch
4. Virtualization for Dummies – Bernard Golden
5. 1AWS – Overview of Security Process White paper by C.Moses of
Amazon
6. Open Source and Cloud Computing – A White paper from Sun
Microsystems
Cloud Computing – An Exploration 8 Charles D. Gnanesh
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDVon EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading 2Dokument23 SeitenReading 2FisalAmarShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect #1 Audio Crash Course Guide To Master Exams, Practice Test Questions, Cloud Practitioner and SecurityVon EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect #1 Audio Crash Course Guide To Master Exams, Practice Test Questions, Cloud Practitioner and SecurityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing QuestionsDokument7 SeitenCloud Computing Questionstejinder kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionVon EverandCloud Computing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing1Dokument32 SeitenCloud Computing1NiharikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureVon EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Assignment 3Dokument6 SeitenCloud Computing Assignment 3Dipesh KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud CompuingDokument5 SeitenCloud CompuingMuppalla PravallikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing NotsDokument42 SeitenCloud Computing Notssutsav81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument85 SeitenUnit 123mz02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Security White PaperDokument5 SeitenCloud Security White Paperzrdhn2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing NotesDokument35 SeitenCloud Computing NotesFeisal MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4:: Professor William HefleyDokument12 SeitenAssignment 4:: Professor William Hefleyapi-315444897Noch keine Bewertungen
- Demistifying The Cloud A Cloud Computing GuideDokument10 SeitenDemistifying The Cloud A Cloud Computing GuidePemmasaniSrinivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Cloud ComputingDokument4 SeitenApplications of Cloud ComputingAkshat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 NotesDokument24 SeitenChapter 1 NotesAnekket DharaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Unit-1 - Introduction To Cloud TechnologiesDokument78 SeitenCloud Computing: Unit-1 - Introduction To Cloud TechnologiesSarika80% (5)
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDokument38 SeitenCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Chapter Capstone CaseDokument8 SeitenChapter Capstone CaseShaira SalandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Technical Seminar Report OnDokument13 SeitenCloud Computing: Technical Seminar Report OnRajesh KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rsa SecurityDokument6 SeitenRsa SecuritySumana SikdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing JUNE 2022Dokument12 SeitenCloud Computing JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azure FundamentalsDokument38 SeitenAzure Fundamentalsumakant bhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing AUDokument11 SeitenCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview QuestionsDokument4 SeitenInterview QuestionsEswari DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS3551 Distributed Computing Unit5Dokument31 SeitenCS3551 Distributed Computing Unit5smitcse2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Assignment Questions 1st April 2021Dokument5 SeitenCloud Computing Assignment Questions 1st April 2021Kiran Sk100% (1)
- Unit 1Dokument13 SeitenUnit 1Bnod MsraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing - Lecture MaterialDokument14 SeitenCloud Computing - Lecture Materialchirayush chakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDokument11 SeitenCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanDokument10 SeitenAssignment On: by Pragya Chakshoo (4067) To Prof. Narender Singh ChauhanPragya ChakshooNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLoud ComputingDokument10 SeitenCLoud ComputingSelma SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR On CloudDokument2 SeitenDR On CloudvinodkalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distributed and Cloud Computing Homework SolutionsDokument6 SeitenDistributed and Cloud Computing Homework Solutionsg3z7texa100% (1)
- Keywords: Computing Technology Data Storge Deployment ComponentDokument18 SeitenKeywords: Computing Technology Data Storge Deployment ComponentlekanNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Group-13) Data Storage in Cloud Platform and Its Disaster Recovery (Group - 7 Nadira Khan - IMB2020034 & Aqdam Aslam - IMB2020003)Dokument6 Seiten(Group-13) Data Storage in Cloud Platform and Its Disaster Recovery (Group - 7 Nadira Khan - IMB2020034 & Aqdam Aslam - IMB2020003)Nadira KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.introduction To Cloud ComputingDokument24 Seiten1.introduction To Cloud ComputingTeja MylavarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDokument27 SeitenAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud NotesDokument45 SeitenCloud Notesmala100% (1)
- Unit 1Dokument20 SeitenUnit 1Sarika KondekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing ArticleDokument6 SeitenCloud Computing ArticleTaaha BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Cloud ComputingDokument12 SeitenFeatures of Cloud Computinggenerey de pazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument37 SeitenUnit 1yashika sarodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2 Cloud ComputingDokument23 SeitenUnit-2 Cloud ComputingDr.Ramesh Babu PittalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Ibm CloudDokument91 SeitenIntroduction To Ibm CloudlijamannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview PrepDokument131 SeitenInterview PrepStudy CircleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Cloud ComputingDokument28 SeitenTypes of Cloud Computingneela madheswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CloudDokument96 SeitenCloudAshu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Cloud Computing - 10 Major Characteristics of Cloud ComputingDokument12 SeitenFeatures of Cloud Computing - 10 Major Characteristics of Cloud Computinggenerey de pazNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLOUD COMPUTING (WWW - Ebookmaterials.blogspot - Com)Dokument7 SeitenCLOUD COMPUTING (WWW - Ebookmaterials.blogspot - Com)Mis MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Cloud Computing?: ComputersDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Cloud Computing?: ComputersNaidu SwethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument16 SeitenModule 2Alhatmi AlhatmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing DocumentationDokument11 SeitenCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Recovery Using Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenDisaster Recovery Using Cloud Computingrajesh laddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Interview QuestionDokument12 SeitenCloud Computing Interview QuestionAkshay MahtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDokument16 SeitenCloud Computing IntroductionVicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingDokument17 SeitenUnit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingManya JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, RoparDokument16 SeitenCloud Computing Section-1: Prepared by Manish Kumar Aery. IET Bhaddal Technical Campus, Roparjuanestudia12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - Cloud ComputingDokument26 SeitenAssignment - Cloud ComputingBiju PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10gen Big Data White PaperDokument16 Seiten10gen Big Data White Paperwellington7martillo7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 03 P8 IBM Power Systems For SugarCRM 18april FINALDokument11 Seiten03 P8 IBM Power Systems For SugarCRM 18april FINALdanielvp21Noch keine Bewertungen
- ArcSight Product Brief LoggerDokument3 SeitenArcSight Product Brief Loggernduc_181273Noch keine Bewertungen
- AWS2Dokument37 SeitenAWS2Luis Fernando Bomfim100% (1)
- Water Distribution SystemDokument6 SeitenWater Distribution SystemHarish BapkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVI InfrastructureDokument23 SeitenAVI InfrastructurewalexmueeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forrester Top 10 Facts Every Infrastructure and Operations Pro Should Know About Cloud EconomicsDokument12 SeitenForrester Top 10 Facts Every Infrastructure and Operations Pro Should Know About Cloud Economicsapi-388173202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Azure Resiliency - Business Continuity - Disaster Rec PDFDokument31 SeitenAzure Resiliency - Business Continuity - Disaster Rec PDFDavid F MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scalable Web ArchitectureDokument20 SeitenScalable Web ArchitecturePramavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opentext Archive Server 10 5 Functional PaperDokument22 SeitenOpentext Archive Server 10 5 Functional PaperRoshan Parvez67% (3)
- Introduction To CassandraDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Cassandraanon_888776202Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Load BalancingDokument17 SeitenNetwork Load BalancingAga ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Data DesignDokument4 SeitenData DesignManuel BandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethereum 2.0 Staking Ecosystem ReportDokument40 SeitenEthereum 2.0 Staking Ecosystem ReportPedro HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDU - DATASHEET - Vsphere Optimize and Scale V6.7Dokument2 SeitenEDU - DATASHEET - Vsphere Optimize and Scale V6.7Denno Guara Labukti AY.Noch keine Bewertungen
- TSPDokument10 SeitenTSPwreed226Noch keine Bewertungen
- OceanStor Dorado 3000 V6, Dorado 5000 V6, and Dorado 6000 V6 6.0.1 Product DescriptionDokument233 SeitenOceanStor Dorado 3000 V6, Dorado 5000 V6, and Dorado 6000 V6 6.0.1 Product DescriptionLuis FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.AutoScaling-Elastic Load BalancingDokument53 Seiten4.AutoScaling-Elastic Load BalancingBiplab ParidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ODSEEDokument2 SeitenODSEENandan AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open RAN ORAN Seminar ReportDokument22 SeitenOpen RAN ORAN Seminar ReportVirag Patil0% (1)
- VTVCable Solution Description 20-10-22Dokument26 SeitenVTVCable Solution Description 20-10-22RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Management FundamentalsDokument39 SeitenNetwork Management FundamentalsMichael AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Architecture: Challenges and Opportunities For The Next DecadeDokument13 SeitenComputer Architecture: Challenges and Opportunities For The Next DecadePranju GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nosql DatabaseDokument8 SeitenNosql Databaseapi-300210076Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nano: A Feeless Distributed Cryptocurrency NetworkDokument8 SeitenNano: A Feeless Distributed Cryptocurrency NetworkAleksandar AngelovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vast Data Comparing File Systems White PaperDokument5 SeitenVast Data Comparing File Systems White PaperNs sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing For The Internet of ThingsDokument6 SeitenDesigning For The Internet of ThingsLaura PetrilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IDokument88 SeitenCS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IvdsrihariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBD-C sp13Dokument6 SeitenMBD-C sp13matrix_33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityVon EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldVon EverandThe Dark Net: Inside the Digital UnderworldBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (104)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationVon EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleVon EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (16)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyVon EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (421)
- Practical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTVon EverandPractical Industrial Cybersecurity: ICS, Industry 4.0, and IIoTNoch keine Bewertungen
- More Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingVon EverandMore Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (24)
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellVon EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersVon EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowVon EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (388)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerVon EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (34)
- CISM Certified Information Security Manager Study GuideVon EverandCISM Certified Information Security Manager Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTML5 and CSS3 Masterclass: In-depth Web Design Training with Geolocation, the HTML5 Canvas, 2D and 3D CSS Transformations, Flexbox, CSS Grid, and More (English Edition)Von EverandHTML5 and CSS3 Masterclass: In-depth Web Design Training with Geolocation, the HTML5 Canvas, 2D and 3D CSS Transformations, Flexbox, CSS Grid, and More (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldVon EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineVon EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineNoch keine Bewertungen
- React.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)Von EverandReact.js Design Patterns: Learn how to build scalable React apps with ease (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design That Scales: Creating a Sustainable Design System PracticeVon EverandDesign That Scales: Creating a Sustainable Design System PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineVon EverandHow to Start a Blog with WordPress: Beginner's Guide to Make Money by Writing OnlineBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)