Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
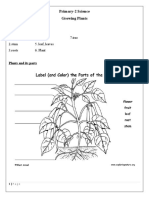
Plants and Their Uses
Hochgeladen von
ARIF AHAMMED POriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plants and Their Uses
Hochgeladen von
ARIF AHAMMED PCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GEMS United Indian School, Abu Dhabi
EVS Grade2
Plants and its uses. Notebook work
Vocabulary:
Stem herbs
Leaf shrubs
Flower trees
Fruit creepers
Root climbers
Water desert plants
Air trunk
Sunlight bark
Soil perennial plants
Biennial plants annual plants
Draw a plant and label the parts.( In the left blank page)
Answer the following:
1. Define the following and state 2 examples for each:
Tree- a big plant with a large hard and strong stem.
eg: coconut tree, mango tree
herb- a small plant with a soft, green stem.
eg: tomato and chillie
Shrub- a bushy plant with many hard stems.
eg: tea plant, rose
Climber- a plant that climbs on nearby objects.
eg: pepper, grape
Creeper- a plant with a weak stem that grows along the ground.
eg: watermelon, pumpkin.
2. Write two examples for the following:
1. Drinks from plants- tea, coffee
2. Roots of plants which we eat- carrot, turnip
3. Leaves of plants which we eat- cabbage, spinach
4. Nuts from plants which we eat- walnut, cashewnut
5. Flowers of plant which we eat- cauliflower, broccoli,
6. Food grains from plants- rice, wheat
7. Fibres from plants- cotton, jute
8. Oil from plants- groundnut, coconut
9. Spices from plants- pepper, turmeric
10. Medicinal plants- aloe. tulsi
11. Perfumes from plants- rose, jasmine
12. Seeds of plants which we eat- pea, seasame
13. Stems of plants which we eat- potato, ginger
3. List two uses of wood.
A. wood is used to make furniture, paper.
4. Name a seed used for obtaining oil.
A. Neem seeds are used to make oil.
Value based question: ( given as HW)
Write in your own words, how animals will be affected if many trees are cut.
5 .Write the functions of the following:
Stem – gives support to the plant. Carries food and water to different parts of plant.
Roots- absorbs water and minerals from the soil
Leaves- food factory of plant.
Fruit – edible part of plant
Flower- attractive part of plant which becomes fruit
6. What are the parts of seed?
A. There are three parts of seed.
1. Seed coat
2. Food
3. Baby plant
7. Define the following:
Perennial, biennial, annual plants
Perennial plants- live for a long time. Eg Neem, Coconut
Biennial plants- live for two seasons. Eg. Carrot, Radish
Annual plants- live for one season. Eg. Wheat, Maize
_____________________________
Task sheets(AFL), Catchup, level descriptors, students profile.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Plant Paradox: The Hidden Dangers in "Healthy" Foods That Cause Disease and Weight Gain - Dr. Steven R Gundry MDDokument5 SeitenThe Plant Paradox: The Hidden Dangers in "Healthy" Foods That Cause Disease and Weight Gain - Dr. Steven R Gundry MDrugywine15% (13)
- How To Eat For MassDokument8 SeitenHow To Eat For MassIvan Vasilev100% (6)
- Major Classification of Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsDokument19 SeitenMajor Classification of Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsJhoy Angeles PinlacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Process Skills Activity IDokument5 SeitenScience Process Skills Activity IAshneiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElecsyyysDokument45 SeitenElecsyyysARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slimming WorldDokument5 SeitenSlimming WorldAmber McDonald100% (4)
- Seed FormationDokument11 SeitenSeed FormationMufida Rizqi Agustina100% (2)
- Lesson Plan For Parts of A PlantDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan For Parts of A PlantStephen Akins75% (4)
- Sim Science Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsDokument17 SeitenSim Science Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsMichelle Alejo Cortez100% (3)
- Sci Mod3 1Dokument11 SeitenSci Mod3 1Pauline Jane FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-4 Q2 Week-3Dokument8 SeitenScience-4 Q2 Week-3Jhon Mark BalansagNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRIMARY SIX LESSON NOTES FOR TERM II 2018 TERM II ScienceDokument61 SeitenPRIMARY SIX LESSON NOTES FOR TERM II 2018 TERM II ScienceShamim Omulangira50% (2)
- Validation SOP ChecklistDokument5 SeitenValidation SOP ChecklistARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument183 SeitenUntitledMaximiliano TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksVon EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pintong Gubat Elementary School's TLE Agriculture Table of SpecificationDokument4 SeitenPintong Gubat Elementary School's TLE Agriculture Table of SpecificationMirage M. Montero100% (1)
- PreciControl ClinChem Multi 2.05117224001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenPreciControl ClinChem Multi 2.05117224001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED P29% (7)
- Alternative Learning System (Als) : Learning Strand 2: Scientific Literacy and Critical ThinkingDokument10 SeitenAlternative Learning System (Als) : Learning Strand 2: Scientific Literacy and Critical ThinkingJocelene Zamora ParungaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class: 2 Subject: Evs Topic: PlantsDokument7 SeitenClass: 2 Subject: Evs Topic: PlantsSumaira SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 The Plant WorldDokument5 Seiten15 The Plant WorldnishantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plants Around YouDokument6 SeitenPlants Around YouJovilyn JardielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 02Dokument9 SeitenExp SC 3 - Chapter 02megamind publicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science ExamDokument15 SeitenScience ExamAmapola Zane PalamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plants: Key Stage: 1 Year: 1Dokument2 SeitenPlants: Key Stage: 1 Year: 1abc abcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indira National School Wakad, Pune (A.Y. 2021 - 22) STD: III EVS Worksheet Answers Ls 2-Parts of A PlantDokument4 SeitenIndira National School Wakad, Pune (A.Y. 2021 - 22) STD: III EVS Worksheet Answers Ls 2-Parts of A PlantUPANSH SETHNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Dokument18 SeitenCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4shinu goyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growing Plants Parts and FunctionsDokument5 SeitenGrowing Plants Parts and FunctionsMay Nyein ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVS - Plants Around UsDokument16 SeitenEVS - Plants Around UsRenu SyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - 6 - Getting To Know Plants - T - 1 PDFDokument9 SeitenClass - 6 - Getting To Know Plants - T - 1 PDFParul GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 2 Subject EVS Chapter 5 Growing PlantsDokument2 SeitenClass 2 Subject EVS Chapter 5 Growing Plantspinkikaushik4719Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of PlantsDokument24 SeitenClassification of PlantsJaphet BagsitNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCEDokument10 SeitenSCIENCESomen SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp SC 6 - Chapter 09Dokument17 SeitenExp SC 6 - Chapter 09megamind publicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sim Science Flowering and Non-Flowering PlantsDokument20 SeitenSim Science Flowering and Non-Flowering Plantsjigs michelle pasamonte100% (1)
- CBSE EVS Notes on Roots and FlowersDokument4 SeitenCBSE EVS Notes on Roots and FlowersK LohithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term 1 Revision W-S Answer KeyDokument3 SeitenTerm 1 Revision W-S Answer Keyabdulrahimabdulahad974Noch keine Bewertungen
- p.4 Science Lesson NotesDokument115 Seitenp.4 Science Lesson NotesEcungu George williamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plants NewDokument1 SeitePlants Newnidhi mohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP 7 EVS More About PlantsDokument3 SeitenLP 7 EVS More About PlantsarunradNoch keine Bewertungen
- PlantsDokument6 SeitenPlantsDeepak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Root: Parts of PlantDokument3 SeitenThe Root: Parts of PlantOurschoolhouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDokument3 SeitenSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013E.C Grade 2 Environment ScinceDokument2 Seiten2013E.C Grade 2 Environment Scincenatan makuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Non-Living Things Plants AnimalsDokument10 SeitenLiving Non-Living Things Plants AnimalsEstherJimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting To Know PlantsDokument4 SeitenGetting To Know PlantsSonam BaghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2. Adaptations in Plants QADokument6 SeitenC2. Adaptations in Plants QAZohraQureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLANT ADAPTATIONS IN DIFFERENT AREASDokument3 SeitenPLANT ADAPTATIONS IN DIFFERENT AREASRAJ STUDY WIZARDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Getting To Know PlantsDokument17 SeitenModule 1 - Getting To Know PlantsKhanakNoch keine Bewertungen
- By: Ramonita RodriguezDokument12 SeitenBy: Ramonita RodriguezPotato ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seeds and PlantsDokument12 SeitenSeeds and PlantsANTONETTE MERCADERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise For Science Mid TestDokument3 SeitenExercise For Science Mid Testfaizal rizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- p4 Science Lesson Notes All TermsDokument116 Seitenp4 Science Lesson Notes All Termsrabsonmasereka7Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE DikonversiDokument3 SeitenSCIENCE Dikonversiannisa husniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 - W6 Science 5Dokument45 SeitenQ2 - W6 Science 5Mac RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Dokument4 SeitenFlowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Anchal ChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusDokument2 SeitenLycopersicum Esculentum Antocarpus HeterophyllusAbegail Bantilan ConiendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Plant Parts and Their FunctionsDokument38 SeitenIdentify Plant Parts and Their FunctionsMa Jovi Zamora AbusoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Plant Fairy: These Notes Are For Learning and Not To Be Written in NotebookDokument4 SeitenThe Plant Fairy: These Notes Are For Learning and Not To Be Written in NotebookStepping PebblesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioDokument6 SeitenBioJulie Jean ToloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting To Know Plants Class 6Dokument21 SeitenGetting To Know Plants Class 6Shahnaaz ParveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts and Needs of A PlantDokument8 SeitenParts and Needs of A PlantDong Phan Thi AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationDokument7 SeitenI. Objectives:: 4. Appreciate The Purpose and Importance of ClassificationBethymay EspinosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saving Life: A Summary of Theme 1Dokument11 SeitenSaving Life: A Summary of Theme 1Anthoneta M. Samoy100% (1)
- Lesson 12.1Dokument13 SeitenLesson 12.1Chrise RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angeospermic Plant MorphologyDokument60 SeitenAngeospermic Plant MorphologyMr. Balwant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Science Summary Unit 41Dokument18 SeitenNatural Science Summary Unit 41VirgiLópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Higher Plants - 2020Dokument109 SeitenChapter 9 Higher Plants - 2020SARA LIM YEN ZI MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Dokument17 SeitenCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Aswani PokuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- GK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54Dokument7 SeitenGK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54عبیرہ کیانیNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nafi QuizDokument14 SeitenNafi QuizARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estab QC RNG - Use of CVDokument6 SeitenEstab QC RNG - Use of CVARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notebook Work: Wonders in The Water: GEMS United Indian School - LP - Rev 2: April 2018Dokument3 SeitenNotebook Work: Wonders in The Water: GEMS United Indian School - LP - Rev 2: April 2018ARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arabic Letters ةَّيب َرَعلا فرحلأا: j th t b aDokument10 Seiten Arabic Letters ةَّيب َرَعلا فرحلأا: j th t b aARIF AHAMMED P100% (1)
- Ckklst-Qual Meth VLDDokument3 SeitenCkklst-Qual Meth VLDARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHKLST Intr QCDokument3 SeitenCHKLST Intr QCARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Laboratory Deficiencies Across Accreditation Agencies PDFDokument7 SeitenTop Laboratory Deficiencies Across Accreditation Agencies PDFARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- IcDokument1 SeiteIcARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smile Linearity Worksheet: Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable AcceptableDokument3 SeitenSmile Linearity Worksheet: Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable Acceptable AcceptableARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Direct and Indirect Ion Selective Electrode Results Conflict PDFDokument3 SeitenWhen Direct and Indirect Ion Selective Electrode Results Conflict PDFARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- RangeeeDokument43 SeitenRangeeeARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- July 2018 A1cDokument1 SeiteJuly 2018 A1cARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap CompDokument12 SeitenCap CompARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total MPA Controls.05885442001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenTotal MPA Controls.05885442001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stand by Bottle ThresholdDokument1 SeiteStand by Bottle ThresholdARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joint Commission Top 10 Deficiencies in 2016 PDFDokument1 SeiteJoint Commission Top 10 Deficiencies in 2016 PDFARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- STFR Control Set.12178206001.V6.EnDokument2 SeitenSTFR Control Set.12178206001.V6.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreciControl HbA1c Norm.05975115001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenPreciControl HbA1c Norm.05975115001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- PreciControl HbA1c Path.05854237001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenPreciControl HbA1c Path.05854237001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precipath L.12174685001.V8.en PDFDokument2 SeitenPrecipath L.12174685001.V8.en PDFARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precipath U Plus.12173697001.V12.EnDokument2 SeitenPrecipath U Plus.12173697001.V12.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDM Control Set.04714768001.V6.EnDokument2 SeitenTDM Control Set.04714768001.V6.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- TPLA Control Set.04955188001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenTPLA Control Set.04955188001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Control Set.03005526001.V6.enDokument2 SeitenRF Control Set.03005526001.V6.enARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precinorm - Precipath Fructosamine.11934589001.V9.en PDFDokument2 SeitenPrecinorm - Precipath Fructosamine.11934589001.V9.en PDFARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPR Control Set.04955196001.V4.EnDokument2 SeitenRPR Control Set.04955196001.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotesDokument68 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Revision NotespranjaylakshitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hibiscus TiliaceusDokument30 SeitenHibiscus TiliaceusAgustina Sekar PuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory Project PDFDokument16 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project PDFStuthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delicious homemade recipesDokument20 SeitenDelicious homemade recipesLaboratory Plant 7Noch keine Bewertungen
- A History of Beer and BrewingDokument729 SeitenA History of Beer and BrewingAnn SteengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lackberries: Texas Fruit and Nut ProductionDokument8 SeitenLackberries: Texas Fruit and Nut ProductionGina FelyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Potassium Foods EsrdDokument4 SeitenLow Potassium Foods EsrdM EbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menu Ingles ColombiaDokument22 SeitenMenu Ingles ColombiaCarlos NaranjoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day2Session4 - Organic ConcoctionsDokument73 SeitenDay2Session4 - Organic ConcoctionsFlorinda GagasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to make a fruit salad step-by-stepDokument2 SeitenHow to make a fruit salad step-by-stepNithya SweetieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Repaso s1Dokument5 SeitenIngles Repaso s1Nagel ChNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOMOLECULESDokument54 SeitenBIOMOLECULESTanmayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science p4 Revision Unit 5Dokument6 SeitenScience p4 Revision Unit 5starsschooljktNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrate in vegetables risk assessmentDokument79 SeitenNitrate in vegetables risk assessmentAna LaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aposto Wine MenuDokument3 SeitenAposto Wine MenuDRCNoch keine Bewertungen
- GGMucusFormingFoods PDFDokument8 SeitenGGMucusFormingFoods PDFIrina AokiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megafol Biotic Extract Natural Enzimes Foliar FertDokument2 SeitenMegafol Biotic Extract Natural Enzimes Foliar FertraulestradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Writing Fresh FruitsDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Writing Fresh FruitsNurul Ain IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3: Lessons 11-15: MatchDokument2 SeitenTest 3: Lessons 11-15: MatchstellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edible Coatings For Fruits and VegetablesDokument16 SeitenEdible Coatings For Fruits and VegetablesHƯƠNG NGUYỄN LÊ NGỌCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health and Illness: Worksheet 3.1Dokument4 SeitenHealth and Illness: Worksheet 3.1Davis PindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotation Diet PlanDokument2 SeitenRotation Diet PlanSethNoch keine Bewertungen
- 36 - ch2 - Reproduction in PlantsDokument21 Seiten36 - ch2 - Reproduction in PlantsAnonymous Azxx3Kp9100% (1)
- Storage Guidelines For Fruits & VegetablesDokument4 SeitenStorage Guidelines For Fruits & VegetablesShruti JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen