Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mental Illness Types, Risk Factors, and Treatment
Hochgeladen von
MediBuddyCopyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Mental Illness Types, Risk Factors, and Treatment
Hochgeladen von
MediBuddyCopyright:
MIND
VER
MATTER: THE ANATOMY OF MENTAL ILLNESSES
Mental health is important at all stages in life. It affects how we act, think,
and feel and is comprised of psychological, social, and emotional
well-being. In this infographic, we perform a post-mortem
on mental illnesses, the common types, the diagnosis, treatment, and more.
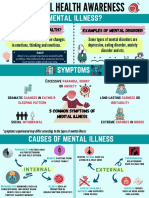
MENTAL HEALTH
NEURODEVELOPMENTAL
DISORDERS
PSYCHOTIC
DISORDERS
DISORDERS:
Abnormal brain development or damage Paranoia, delusions, and hallucinations
Examples: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Example: Schizophrenia
(ADHD),
Autism spectrum disorder, and learning disorders.
BIPOLAR AND RELATED DEPRESSIVE ELIMINATION SLEEP-WAKE
DISORDERS DISORDERS DISORDERS DISORDERS
Excessive excitement and depression. Alternating Emotional feelings of sadness and happiness
Inappropriate elimination of stool and urine — Sleep disorders that require clinical attention
periods of mania. Examples: Depressive and premenstrual
accidental or on purpose Examples: Insomnia, restless legs syndrome,
Example: Mania and hypomania dysphoric disorders
Example: Bedwetting (enuresis) sleep apnea
OBSESSIVE-COMPULSIVE AND ANXIETY GENDER DISRUPTIVE, IMPULSE-CONTROL
RELATED DISORDERS DISORDERS DYSPHORIA AND CONDUCT DISORDERS
Repetitive thoughts and actions, It’s an umbrella term for different types Distress attached to a person's desire to be Behavioural self-control and emotional problems
preoccupations, obsessions of conditions another gender Examples: Intermittent explosive disorder
Examples: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), Examples: Anxiety disorder, phobias, Example: Preference to dress, or Kleptomania
trichotillomania and panic disorder develop mannerisms, grow, and live as the
opposite gender
TRAUMA AND STRESSOR-RELATED DISSOCIATIVE SUBSTANCE-RELATED AND NEUROCOGNITIVE DISORDERS
DISORDERS DISORDERS ADDICTIVE DISORDERS
Adjustment disorders, trouble coping after Escape from reality and detachment Risk of psychological and physiological Inability to think and reason.
or during a stressful life event from memory, thoughts, harm due to misuse of Examples: Delirium, and disorders caused by or
Examples: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) consciousness, and identity. drugs and alcohol Alzheimer's disease or traumatic brain injury.
and acute stress disorder Examples: Disrup Example: Alcohol, caffeine, tobacco and drug abuse.
Also includes gambling disorder
SOMATIC SYMPTOM AND PERSONALITY PARAPHILIC
FEEDING AND EATING
RELATED DISORDERS DISORDERS DISORDERS
DISORDERS
Physical symptoms with no clear medical cause, Disturbances associated with eating Unhealthy behaviour, emotional instability Sexual interest -> causes distress -> leads to actual
associated with significant Examples: Binge-eating disorder —> Hamper life and relationships. or potential harm to another person.
impairment and distress and Anorexia nervosa Examples: Borderline personality and Examples: Sexual sadism, pedophilic disorder,
Examples: Somatic Symptom Disorder antisocial personality disorders. and voyeuristic disorder.
( hypochondriasis)
and factitious disorder
INHERITED TRAITS
ADDITIONAL Heritable mental illnesses
RISK
Risk factor: Genes
COMPLICATIONS DEVELOPMENTAL
Exposure to toxins at a developmental stage.
Risk factor: Exposure to alcohol, drugs, viruses,
Untreated mental illness causes disability, severe emotional,
physical, behavioural and health problems.
Also causes legal and financial problems.
FACTORS:
In general, mental illnesses understood to
toxins, while in the womb
BRAIN CHEMISTRY
be caused by: Developmental & Genetic factors.
Chemical changes in the brain.
Weakened immunity Risk factor: Biochemical changes in the brain,
brain chemicals (neurotransmitters), and
Unhappiness, relationship difficulties, family conflicts,
hormonal imbalances
poverty and homelessness
Social isolation problems
Alcohol, tobacco, and drug abuse
Problems related to work or school
SYMPTOMS
Suicidal/Homicidal thoughts Feeling down or sad
Other medical conditions including heart disease Reduced ability to concentrate or confused thinking
Extreme feeling of guilt, excessive worries or fears
Extreme high and low mood swings
Withdrawal from activities and friends
Low energy, problems sleeping, significant tiredness
Delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia
Inability to cope with stress or daily problems
Trouble relating to/understanding situations/people
Alcohol or drug abuse
Significant changes in eating habits and sex drive
Excessive hostility, violence, anger
Suicidal thoughts
Physical problems: headache, stomach pain, back pain
TREATMENT
MEDICATIONS PSYCHOTHERAPY
Recommended when: Condition, feelings, moods, behaviour and thoughts
Antidepressants
are to assessed.
For anxiety, and depression
Recommended when: Patient exhibits anxiety, depression, sadness,
Comprised of: Stress management skills, talk therapy with a mental health provider.
hopelessness, difficulty concentrating, lack of energy, disinterest in activities.
Anti-anxiety medications
For panics and generalized anxiety disorder.
Recommended when: Patient exhibits panics and generalized anxiety disorder.
BRAIN-STIMULATION
TREATMENTS
Mood-stabilizing medications
Recommended when: medications and psychotherapy fail.
For bipolar disorder with alternating episodes of mania and depression.
Recommended when: Patient exhibits bipolar disorder with alternating episodes Comprised of: transcranial magnetic stimulation, electroconvulsive therapy,
of mania and depression. vagus nerve stimulation, deep brain stimulation.
Make sure you understand all the risks and benefits of any recommended treatment.
Antipsychotic medications
For schizophrenia, bipolar disorders and depression.
Recommended when: Patient exhibits psychotic disorders like schizophrenia,
bipolar disorders, and depression.
SUBSTANCE ABUSE
TREATMENT
RESIDENTIAL AND HOSPITAL
Recommended when: Drugs, alcohol, and tobacco interferes with treatment
TREATMENT PROGRAMS and worsens mental illness.
Recommended when: mental illness severe (can’t care for yourself, danger Comprised of:
of harming oneself/someone) Medications (for withdrawal/stem cravings)
Inpatient treatment (withdrawal/detox programme)
Comprised of: Partial or day hospitalization, residential treatment, Outpatient treatment programs
24-hour inpatient care, intensive outpatient treatment. Support groups (eg., Alcoholics Anonymous (A.A.))
STAY ACTIVE-EXERCISE
REGULARLY
AVOID ALCOHOL/ DETERMINE
DRUG/TOBACCO PRIORITIES/GOALS
STICK TO
STAY POSITIVE,
TREATMENT PLAN
ACCEPT CHANGES
SELF-CARE
Self-treatment: doesn’t work in most cases. Requires professional help.
TAKE BIG DECISIONS
SKIP WHEN SYMPTOMS SEVERE
MEDICATION
SKIP THERAPY IGNORE YOUR
SESSIONS TREATING DOCTOR
www.medibuddy.in
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Relapse Prevention WorkbookDokument129 SeitenRelapse Prevention WorkbookDanielle Russell Maskell100% (1)
- Summary of Mental IllnessDokument6 SeitenSummary of Mental IllnessNelsie Duhilag100% (2)
- SchizophreniaDokument58 SeitenSchizophreniaArpit AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Terms - PsychDokument13 SeitenSummary of Terms - Psychapi-642709499Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status Exam: Component Elements To Assess Potential Illnesses Sample QuestionsDokument8 SeitenMental Status Exam: Component Elements To Assess Potential Illnesses Sample QuestionsLa LangNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Psychology Module 66+67Dokument5 SeitenAP Psychology Module 66+67kyuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types and Symptoms of Common Psychiatric DisordersDokument6 SeitenTypes and Symptoms of Common Psychiatric DisordersRanusha AnushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Psychological DisordersDokument39 SeitenIntro Psychological DisordersMary Jo LegaspiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Living Recovery True Stories of Addiction RecoveryDokument8 SeitenLiving Recovery True Stories of Addiction RecoveryIulian MitranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health AwarenessDokument2 SeitenMental Health Awarenessfarhatulhanimzulkifl100% (2)
- PSYCH 1.1A Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDokument28 SeitenPSYCH 1.1A Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderZaza100% (1)
- Major Depression With Psychotic FeaturesDokument12 SeitenMajor Depression With Psychotic FeaturesNICOLE BASENoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20Dokument47 SeitenNursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20nidhi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing ReportDokument43 SeitenMental Health and Psychiatric Nursing ReportvernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Health AwarenessDokument53 SeitenMental Health AwarenessSairah Faith TablatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To The Judicious Use of Lab Tests in PsychiatryDokument8 SeitenA Guide To The Judicious Use of Lab Tests in Psychiatrykoyote73100% (1)
- Psychological DisordersDokument46 SeitenPsychological DisordersanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological DisordersDokument52 SeitenPsychological Disordersember_memoriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Assignment - Substance AbuseDokument19 SeitenGroup Assignment - Substance AbuseDukkana Bariisaa100% (1)
- FSH QB Wid Ans TieDokument16 SeitenFSH QB Wid Ans TieAnanya PkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apometria (English) 58 Pages Apometria A New Cured ArtDokument57 SeitenApometria (English) 58 Pages Apometria A New Cured Artyannick100% (1)
- Bipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Dokument19 SeitenBipolar Disorder: Presented By: Group 2Pao DelossantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete - Gordon's Functional Health Pattern - Group 4Dokument7 SeitenComplete - Gordon's Functional Health Pattern - Group 4TaanzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABPG1103 - Topic 12 - Psychological Disorder - 222Dokument21 SeitenABPG1103 - Topic 12 - Psychological Disorder - 222nureryani bathowiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abpsych Chapter 1Dokument4 SeitenAbpsych Chapter 1Renz ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Disorders 2Dokument36 SeitenMental Disorders 2Iraide GarcésNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Disorder: Cretoiu StefanDokument8 SeitenMental Disorder: Cretoiu StefanStefanCretoiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Dokument7 SeitenEducational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Leonardo YsaiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Introudction For Abnormal PsychologyDokument40 SeitenModule 1 Introudction For Abnormal PsychologyKeven James PaclejanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Categories of PsychopathologyDokument1 SeiteMajor Categories of PsychopathologyCandice LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- NotesDokument2 SeitenNotesPsyche AbierasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Bags For The HomelessDokument1 SeiteLove Bags For The HomelessTroy CabrillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Disorders: Hapter 14Dokument14 SeitenPsychological Disorders: Hapter 14Di XuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychopathology MSE NotesDokument5 SeitenPsychopathology MSE Noteszubair.19cbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideDokument65 SeitenChapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideRainier Moreno-LacalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personality Development Weeks 5-6 LectureDokument7 SeitenPersonality Development Weeks 5-6 LectureCzarina Ciara AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417Dokument44 SeitenMood Disorders: Mental Health Nursing-NUR 417preeti vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personality Development Weeks 5-6 LectureDokument6 SeitenPersonality Development Weeks 5-6 LectureCzarina Ciara AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13Dokument7 SeitenChapter 13Chin SilverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psy Chapter 13Dokument7 SeitenPsy Chapter 13MichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification in DSM-5Dokument7 SeitenClassification in DSM-5RintuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Neurosis and PsychosisDokument4 SeitenDifference Between Neurosis and PsychosisShaheen Khan Warsi100% (1)
- Gen Psyc 15 Psych Disorders A BB 1Dokument38 SeitenGen Psyc 15 Psych Disorders A BB 1Mauricio Carl Acosta PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modifiable Factors Non-Modifiable FactorsDokument8 SeitenModifiable Factors Non-Modifiable Factorskim cortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Michael D. Jibson, M.D., Ph.D. Ira D. Glick, M.D. Rajiv Tandon, M.DDokument14 SeitenSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: Michael D. Jibson, M.D., Ph.D. Ira D. Glick, M.D. Rajiv Tandon, M.Dserene_tha067746Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gambaran Umum Gangguan JiwaDokument85 SeitenGambaran Umum Gangguan Jiwaindah pebriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateDokument55 SeitenGreen Monochromatic Simple The Minimalist Presentation TemplateInnen BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages 522-527 Pages 527-529 Pages 532-534 536-539Dokument2 SeitenPages 522-527 Pages 527-529 Pages 532-534 536-539LaibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scenario: Hallucinations and Delusions Are Often Taken As Signs of A Failure of RealityDokument5 SeitenScenario: Hallucinations and Delusions Are Often Taken As Signs of A Failure of RealityJoshua TercenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSYCHIATRYDokument12 SeitenPSYCHIATRYSavanthi Carmaline de SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP20 PSY381 Examples and DefinitionsDokument75 SeitenSP20 PSY381 Examples and Definitionsvasudha_kurugantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis OcdDokument3 SeitenCase Analysis OcdAjay SupanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture9 (Chapter15) Psychological DisordersDokument50 SeitenLecture9 (Chapter15) Psychological DisordersEDA SEYDINoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychiatryDokument18 SeitenPsychiatryWorld MedclickzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pt10603 Personality and Individual DifferencesDokument45 SeitenPt10603 Personality and Individual DifferencesMuhammad Firdaus RamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Mood DisordersDokument7 Seiten1.3 Mood DisordersDomalaon, Princess Sophia B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human Behavior 1Dokument55 SeitenHuman Behavior 1Noe HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia (Draft)Dokument8 SeitenSchizophrenia (Draft)ag.carismaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental DisordersDokument12 SeitenMental DisordersCiara C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Psychodynamic and Psychopathology (Compatibility Mode) PDFDokument27 SeitenPsychodynamic and Psychopathology (Compatibility Mode) PDFMade Satria PawitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rit Aec26 Unit 1 Lecture 2Dokument56 SeitenRit Aec26 Unit 1 Lecture 2pshashank138Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13 - InTRODUCTION To PSYCHOPATHOLOGY - Psychological Disorders and TreatmentsDokument50 Seiten13 - InTRODUCTION To PSYCHOPATHOLOGY - Psychological Disorders and Treatmentsareeshakashif21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deteksi Dini Gangguan JiwaDokument47 SeitenDeteksi Dini Gangguan JiwaDillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psyh 118 Presentation HestonDokument12 SeitenPsyh 118 Presentation HestonGde KayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obessive-Compulsive Disorder: Avila Gomez Erandi Nayeli Ramos Valencia Mariana Segura Salmerón AldahirDokument14 SeitenObessive-Compulsive Disorder: Avila Gomez Erandi Nayeli Ramos Valencia Mariana Segura Salmerón AldahirNayeli AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim ReviewerDokument8 SeitenPrelim ReviewerAGNER JASMIN ROSE L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bailey Et Al (2011)Dokument8 SeitenBailey Et Al (2011)Alkistis MarinakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatry PDFDokument101 SeitenPsychiatry PDFUltimategoal DeathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delirium TremensDokument15 SeitenDelirium Tremensgiseladelarosa2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs by Ingrid Marianne D. Ognita Submitted To: Dr. SB. Cahiwat, RGC StimulantsDokument6 SeitenDrugs by Ingrid Marianne D. Ognita Submitted To: Dr. SB. Cahiwat, RGC StimulantsDex Lunzaga OgnitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akron ManualDokument19 SeitenAkron ManualMichael GriffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PsychopathologyDokument8 SeitenPsychopathologySmerylGoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- College News Spring 2016Dokument32 SeitenCollege News Spring 2016AripinSyarifudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019Dokument50 SeitenSubstance Use and Abuse For Students 2018-2019ZauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Education Chapter 10Dokument3 SeitenPhysical Education Chapter 10hanjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis. Rehabilitation Center. Meta Project Fot The BlindDokument126 SeitenThesis. Rehabilitation Center. Meta Project Fot The Blindshikha chugh0% (1)
- Hepatitis C SlidesDokument51 SeitenHepatitis C SlidesChukwu NedumNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVDokument5 SeitenTVShahid RazwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KIT TalensDokument161 SeitenKIT TalensVinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Anxiety DisordersDokument10 Seiten6 Anxiety DisordersAndrés Camilo Ramírez AarónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Disorders in Self-CuttingDokument4 SeitenMental Disorders in Self-CuttingWilson Javier Dominguez PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- DraDokument19 SeitenDrapennarasi pennarasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineDokument23 SeitenDextroamphetamine: Brand Name: DexedrineSharry Fe OasayNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On The Indian LiquorDokument7 SeitenA Case Study On The Indian LiquorManish Singh100% (1)
- Antisocial Personality Disorder: Understanding NICE GuidanceDokument12 SeitenAntisocial Personality Disorder: Understanding NICE Guidanceaina_bilhahNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAPP Finals Thesis StatementDokument19 SeitenEAPP Finals Thesis StatementUriel MapatacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subhankar BiologyDokument21 SeitenSubhankar BiologyvvdgkyezyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flight - Movie AnalysisDokument2 SeitenFlight - Movie AnalysisBryan JanierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin For Skin by Gerald M. SiderDokument44 SeitenSkin For Skin by Gerald M. SiderDuke University Press100% (1)