Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
COMMED 0503C Leptospirosis PDF
Hochgeladen von
Gabby ElardoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
COMMED 0503C Leptospirosis PDF
Hochgeladen von
Gabby ElardoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LEPTOSPIROSIS
5
RUBILYN C. NUEVA ESPANA, MD
LEPTOSPIROSIS CLINICAL COURSE
• Acute systemic zoonotic infection, caused by pathogenic
leptospires, caused by spirochetes of the genus
Leptospira, is primarily a disease of domesticated and
wild animals.
o This can occur when mucus membrane and skin
are contaminated by the urine of the infected
animals.
• The main carriers of leptospires are animals such as
rodents, dogs, cats and livestock.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
• This occurs worldwide but it is most common in tropical
and subtropical areas with high rainfall. Figure 2. Phases of Leptospirosis
• Highly endemic in the Philippines, found in flood-prone 1. Incubation period is usually 7-10 days, with a range of 2-
areas like Metro Manila especially during typhoon season 30 days.
(July-October) and in areas with poor housing and 2. After the incubation period, septicemic stage is
sanitation conditions. characterized by acute systemic infection (high grade
• This is 53% higher compared to the same time period last fever, headache, nausea and muscle pain). Leptospires
year. can be isolated in the blood, CSF and tissue
• Most of the cases were from REGION VI, CARAGA, 3. Interphase: 1-3 days resolution of symptoms
REGION X, REGION XI and NCR. 4. Immune phase/Second Stage is characterized by the
presence of circulating antibody and is associated with
TRANSMISSION recurrence of fever, severe headache jaundice,
• Transmitted directly or indirectly from animals to hemorrhage, Meningitis, Renal manifestations
humans (Hematuria, oliguria) and Weil’s Syndrome
o Direct contact with the urine or reproductive fluids
from infected animals. Weil’s Syndrome = Jaundice, Renal dysfunction, hemorrhagic
o Contact with urine-contaminated water (floodwater, diathesis and pulmonary dysfunction
rivers, streams, sewage) and wet soil.
o Ingestion of floodwater or water contaminated by Note: The typical course of leptospirosis starts with acute
urine. septicemic phase followed by the immune phase
o Transmission occurs through mucous membranes,
conjunctiva, and skin cuts or abrasions. ** The clinical course of leptospirosis varies but is generally
predicable and can be divided into 2:
• Anicteric leptospirosis (mild)
o Patient can present with fever, chills, persistent
headache, severe myalgias, abdominal pain and
nausea and vomiting.
o Flu-like syndrome
• Icteric leptospirosis (severe)
o Weil’s syndrome, impaired renal and hepatic
function, hemorrhage, vascular collapse, severe
alterations in consciousness.
Figure 3. Clinical course of Leptospirosis. See at the end of the trans
Figure 1. The different means of leptospirosis transmission.
Leptospirosis (October 25, 2018) 1
Dr. Nueva Espana
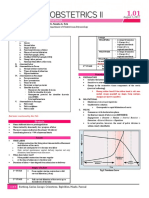
CLASSIFICATION OF LEPTOSPIROSIS Table 3. Criteria for Hospital Admission
Table 1. Classification of Leptospirosis. See table at the end of the CRITERIA FOR HOSPITAL ADMISSION
trans
MILD LEPTOSPIROSIS MODERATE TO SEVERE
DIAGNOSIS LEPTOSPIROSIS
• Early recognition and treatment is important to prevent Out-Patient Setting Healthcare/Hospital Setting
complications of the disease
Stable vital signs Unstable vital signs
• Diagnosis can be based on the clinical assessment and
Anicteric sclerae Jaundice/Icteric sclerae
epidemiological history
Good urine output Oliguria/Anuria
• Antibiotic therapy should be started as soon as the
diagnosis of leptospirosis is suspected regardless of the No evidence of sepsis/septic Sepsis/Septic shock
phase of the disease or duration of symptoms shock
• Generally, it is not necessary to confirm the diagnosis or No evidence of Meningismus/Meningeal
wait for the result of the tests before starting treatment meningismus/meningeal Irritation
irritation
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS No difficulty of breathing Difficulty of breathing
DIRECT METHOD No Jaundice Abdominal Pain
• Culture and Isolation – GOLD STANDARD Can take oral medication Nausea, Vomiting, and
• Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) has the advantage of Diarrhea
early confirmation of the diagnosis especially during Altered Mental Status
acute leptospiremic phase (first week of illness) before Hemoptysis
the appearance of antibodies
PREVENTION AND CONTROL
INDIRECT METHOD PRIMARY PREVENTION
• Microagglutination Test (MAT) – a four-fold rise of the • The most effective preventive measure is avoidance of
titer from acute to convalescent sera is confirmatory of high risk exposure (i.e. wading in floods and
the diagnosis. In endemic areas like the Philippines, a contaminated water, contact with animal’s body fluid)
single titer of at least 1:1600 in symptomatic patients is o If avoidance is not possible, use protective clothing
indicative of leptospirosis such as gloves and boots
• Specific IgM Rapid Diagnostic Test like LeptoDipstick, • Avoidance of exposure to urine and tissues from infected
Leptospira IgM ELISA (PanBio), MCAT and Dridot false animals such as wading in flooded areas
negative results can be a problem if the tests are • Vaccination of animals
performed during early stage of the illness. A second • Rodent control
sample should be obtained for suspected cases with the • Chemoprophylaxis
initial negative or doubtful results.
PRE-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
TREATMENT Table 4. Recommended pre-exposure prophylaxis for adults and
pediatrics for Leptospirosis
Table 2. Dosages of Antibiotics Recommended for Leptospirosis
1,2 3,4
MILD LEPSTOSPIROSIS MODERATE-SEVERE ADULTS PEDIA
LEPTOSPIROSIS 200mg capsule taken >45kg <45kg
Antibiotics Dosage Antibiotics Dosage orally OD once a 100mg OD 4mg/kg/day OD
First Line Agent week once a week once a week
(i.e. two 100mg
Doxycycline 100mg BID PO Penicillin G 1.5mu q6-8h
(for 1 week) capsules taken as
Alternative Agents single oral dose)
1 For all adults including children 12 years of age
Amoxicillin 500mg q6 or Ampicillin IV 0.5-1g q6h
2 Excluding pregnant and breastfeeding mothers
1g q8 PO
Azithromycin 1g initially, Azithromycin 500mg OD for 5 3 For children between 8-12 years old
followed by days 4 Doxycycline is contraindicated for children <8 years old
500mg OD Ceftriaxone 1g q24h
for 2 more * Should be given 1-2 days prior to exposure and continued
Cefotaxime 1g q6h
days PO throughout the period of exposure
***Antibiotic therapy should be completed for 7 days, except
for azithromycin dehydrate which could be given for 3 days • Not routinely recommended
o Recommended in high-risk areas and for those
who are likely to be infected
o E.g. for rescuers, health care providers, soldiers
people residing in flooded areas or those engaged in
Leptospirosis 2
Dr. Nueva Espana
water-related recreational and occupational
activities
• Short-term exposures
• However, Doxycycline is not available as syrup so
alternatives (i.e. amoxicillin or azithromycin) are given
to pediatric patients
o Doxycyline is available as 100mg capsules
POST-EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
• For individuals with history of exposure to contaminated
water, soil and tissue
• Doxycycline (hydrochloride and hyclate) is the
recommended post exposure chemoprophylactic agent
for leptospirosis
• The duration of prophylaxis depends on the degree of
exposure and the presence of wounds.
• Not 100% effective: monitor for any untoward signs and
symptoms
• Individuals should continue to monitor themselves for
fever and other flu-like symptoms and should continue to Figure 4. Post-exposure Prophylaxis for Leptospirosis
wear personal protective measures since antibiotic
prophylaxis is not 100% effective Table 5. Post exposure prophylaxis Adult
DRUG OF CHOICE ALTERNATIVE
DEGREE OF RISK EXPOSURE Low Risk Exposure Doxycycline 200 mg single
1. LOW RISK EXPOSURE dose within 24-72 hours from
• Those individuals with a single history of wading in exposure
flood or contaminated water without wounds, cuts, Moderate Risk Exposure Doxycycline 200 mg once
or open lesions of the skin daily for 3-5 days within 24-
2. MODERATE RISK EXPOSURE 72 hours from exposure
• Those individuals with a single history of wading in High Risk Exposure Doxycycline 200 mg once
flood or contaminated water and the presence of weekly until the end of
wounds, cuts, or open lesions of the skin, OR exposure
accidental ingestion of contaminated water
3. HIGH RISK EXPOSURE Table 6. Post-exposure Prophylaxis for Pediatrics
• Those individuals with continuous exposure (those DRUG OF CHOICE ALTERNATIVE
having more than a single exposure or several days Doxycycline 4mg/kg as Azithromycin 10mg/kg as
such as those residing in flooded areas, rescuers, and single dose single dose
relief workers) of wading in flood or contaminated Max dose: 200mg Max dose: 500mg
water with or without wounds, cuts, or open lesions Amoxicillin 50mg/kg q6 for 3-
of the skins. 5 days
• Swimming in flooded waters especially in urban Max dose: 500mg q6
areas infested with domestic/sewer rats and If children are exposed for more than 7 days, the dose should
ingestion of contaminated water are also be repeated after 1 week
considered high risk exposure.
Table 4. Summary of Degree of Risk Exposure **Doxycycline is usually given in children 8 years old and
RISK EXPOSURE DEFINITION above. Usually in children less than 8 years old, the
LOW Single history (-) wounds or lesions in alternative drugs such as Amoxicillin and Azithromycin are
skin given.
MODERATE Single history (+) wounds; OR
(+) accidental ingestion of REFERENCES
contaminated water 1. Powerpoint
HIGH Continuous (+/-) wounds 2. Lecture Notes
exposure Swimming in 3. Recordings
contaminated flooded TRANSCRIBERS
waters especially in urban 1. TRANS GROUP: 4A
areas 2. SUBTRANSHEAD: Lance Cua
Ingestion of contaminated
water
Leptospirosis 3
Dr. Nueva Espana
Figure 3. Clinical course of Leptospirosis
Table 1. Classification of Leptospirosis.
Leptospirosis 4
Dr. Nueva Espana
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Family Life CycleDokument34 SeitenFamily Life CycleKathrina AbastarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineDokument6 Seiten107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineGiel Margareth LindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advocacy For The Magna Carta For Students BillDokument14 SeitenAdvocacy For The Magna Carta For Students BillvankroydzordicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging and Reemerging Infectious DiseasesDokument25 SeitenEmerging and Reemerging Infectious DiseasesNorberto Francisco BaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFDokument2 SeitenTopnotch Waiver Oath and Checklist April 2015 PDFRalph JuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CyclosporineDokument3 SeitenCyclosporineraki9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Obgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingDokument96 SeitenObgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingMon Ordona De Guzman100% (2)
- Mucinous Cystadenoma 0708Dokument12 SeitenMucinous Cystadenoma 0708eosfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB Gyne ReviewerDokument52 SeitenOB Gyne ReviewerRaffy Lucmans100% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDokument27 SeitenAbnormal Uterine BleedingMari ArcenganNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Pcap 2012 PDFDokument54 SeitenCPG Pcap 2012 PDFroshmae67% (3)
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in AdultsDokument10 SeitenChronic Suppurative Otitis Media in AdultsRstadam TagalogNoch keine Bewertungen
- PulmoconDokument64 SeitenPulmoconapi-3704562100% (1)
- Portal Hypertension - A Case ReportDokument65 SeitenPortal Hypertension - A Case ReportTEAM K 1920Noch keine Bewertungen
- 002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFDokument11 Seiten002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFale_fearNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutVon EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Dokument117 SeitenSexually Transmitte D Infections: Keeshia Anna Zerrudo Clinical Clerk Iloilo Doctors' Hospital Inc. August 18, 2020Angela SaldajenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine OB History and PE TemplateDokument9 SeitenMedicine OB History and PE TemplateJanella SuerteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome in PregnancyDokument7 SeitenAntiphospholipid Syndrome in PregnancyDara Dasawulansari SyamsuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Clinical Practice Guidelines For Acute Otitis Media 2016 LectureDokument53 SeitenPhilippine Clinical Practice Guidelines For Acute Otitis Media 2016 LecturePrincess Noreen SavellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Labor and Delivery 2015Dokument78 SeitenCPG Labor and Delivery 2015TintalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concept On Toxicology PDFDokument40 SeitenBasic Concept On Toxicology PDFmefav7778520Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Acute Infectious DiarrheaDokument10 SeitenCPG Acute Infectious DiarrheaKristine Jade OdtujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAFP Clinical Pathway For The Diagnosis and Management of Patients With COVID 19 in Family Practice PDFDokument35 SeitenPAFP Clinical Pathway For The Diagnosis and Management of Patients With COVID 19 in Family Practice PDFZaqueo Gutierrez FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics/Cord Prolapse: Clinical Practice GuidelinesDokument3 SeitenObstetrics/Cord Prolapse: Clinical Practice Guidelines69x4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesDokument32 SeitenPhilippine Pediatric Society in Cooperation With The Society of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, PhilippinesShari TernolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Family Oriented Medical RecordDokument4 Seiten02 Family Oriented Medical RecordFernandez-De Ala NicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesth BarashDokument6 SeitenAnesth BarashIAN GABRIELLE MERCADO CUYNONoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For The Integrated Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in and Out Patient Treatment 12.2011Dokument182 SeitenGuidelines For The Integrated Management of Severe Acute Malnutrition in and Out Patient Treatment 12.2011Jonathan Renier VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spontaneous Abortion - Risk Factors, Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnostic Evaluation - UpToDate PDFDokument23 SeitenSpontaneous Abortion - Risk Factors, Etiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnostic Evaluation - UpToDate PDFPaula Grtrs WstrmrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 29 - Fetal Growth Restriction-IUGR CPG FinalDokument26 Seiten29 - Fetal Growth Restriction-IUGR CPG FinalkukadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beta Lactams: Drugs of Choice and First Line AgentsDokument3 SeitenBeta Lactams: Drugs of Choice and First Line AgentsKeisha Dela CernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications Paper1 of "Changing Unethical Organizational Behavior" by NielsenDokument2 SeitenApplications Paper1 of "Changing Unethical Organizational Behavior" by NielsenMingLi JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG AID - Full VersionDokument120 SeitenCPG AID - Full VersionJoniee SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedia QuizesDokument19 SeitenPedia QuizesPraneeth PaletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 57 74Dokument5 Seiten57 74Lisa Puspadewi SusantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Gyne) 2.06 Aub - Dr. Quillamor (Final)Dokument8 Seiten(Gyne) 2.06 Aub - Dr. Quillamor (Final)Rj PolvorosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gyne - Torsion of Dermoid CystDokument4 SeitenGyne - Torsion of Dermoid CystroshmaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio Placentae: Insert or Drag & Drop Your PhotoDokument42 SeitenAbruptio Placentae: Insert or Drag & Drop Your PhotoClareen JuanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Uti PDFDokument7 SeitenCPG Uti PDFhellokathyyyyyy100% (1)
- Protein Energy MalnutritionDokument16 SeitenProtein Energy MalnutritionAisha Abdullah ManzurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Peer Assessment PAP SmearDokument5 Seiten2015 Peer Assessment PAP SmearRichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- OB 1.01 DystociaDokument9 SeitenOB 1.01 DystociaRaquel Reyes100% (1)
- Family Medicine COPCDokument20 SeitenFamily Medicine COPCrachellesliedeleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leopando Hospice-Palliative3Dokument2 SeitenLeopando Hospice-Palliative3Judy Ignacio EclarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mccod NotesDokument7 SeitenMccod NotesMaui GamutanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finals QuestionsDokument10 SeitenFinals QuestionsBobet ReñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Practice Guidelines: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in AdultsDokument28 SeitenClinical Practice Guidelines: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in Adultsnanu-jenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Presentation: NeurologyDokument19 SeitenCase Presentation: NeurologySydrex SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO - Haemoglobin Level For Anemia 2011Dokument6 SeitenWHO - Haemoglobin Level For Anemia 2011Adhi SanjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RISE REVIEW - Female Reproductive SystemDokument9 SeitenRISE REVIEW - Female Reproductive SystemGerben Villanueva100% (1)
- Causes of Fetal DeathDokument3 SeitenCauses of Fetal DeathRene Cordova InapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hap VapDokument18 SeitenHap VapAgita GintingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulvovaginal Hematoma With ComplicationsDokument83 SeitenVulvovaginal Hematoma With ComplicationsAR CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFDokument82 SeitenPhilippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFVirginia AbalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- P 04-LeptospirosisDokument2 SeitenP 04-LeptospirosisRaymund AldabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leptospira: H. Dele Davies Dan Kari A. SimonsenDokument3 SeitenLeptospira: H. Dele Davies Dan Kari A. SimonsenKharisma Wildan FuadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leptospirosis - Ferri's Clinical AdvisorDokument2 SeitenLeptospirosis - Ferri's Clinical AdvisorAndika GhifariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clio Prosecutor Resolution FinalDokument4 SeitenClio Prosecutor Resolution FinalGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice of Profession Samahan NG Optometrists Sa Pilipinas v. Acebedo International Corporation G.R. No. 117097. March 21, 1997. FactsDokument1 SeitePractice of Profession Samahan NG Optometrists Sa Pilipinas v. Acebedo International Corporation G.R. No. 117097. March 21, 1997. FactsGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLOCK 2 GROUP D (For The Wife) S.Y. 2020-2021 Mercader, Aiza A. Oarde, Anthea Margarita R. Ocampo, Clio Marie Bernadette CDokument4 SeitenBLOCK 2 GROUP D (For The Wife) S.Y. 2020-2021 Mercader, Aiza A. Oarde, Anthea Margarita R. Ocampo, Clio Marie Bernadette CGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clio Prosecutor Resolution ExamDokument3 SeitenClio Prosecutor Resolution ExamGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Church of Christ in The Philippines Vs Bradford - ElardoDokument1 SeiteUnited Church of Christ in The Philippines Vs Bradford - ElardoGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIR Vs Filinvest Development CorpoDokument18 SeitenCIR Vs Filinvest Development CorpoGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales Agreement Draft (Oven)Dokument2 SeitenSales Agreement Draft (Oven)Gabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Outline in AgencyDokument6 SeitenReview Outline in AgencyGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 123 CMC ACE Vs LaguesmaDokument1 SeiteCase 123 CMC ACE Vs LaguesmaGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amorito V. Canete For Petitioner. Pablo R. Cruz For Private RespondentDokument5 SeitenAmorito V. Canete For Petitioner. Pablo R. Cruz For Private RespondentGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atty. Viviana M. PaguiriganDokument1 SeiteAtty. Viviana M. PaguiriganGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 34 Amendment by RA 8042Dokument4 SeitenArticle 34 Amendment by RA 8042Gabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELARDO, SEBASTIAN GABRIEL M. (Illegal Recruitment)Dokument7 SeitenELARDO, SEBASTIAN GABRIEL M. (Illegal Recruitment)Gabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natres Digest Pool 2Dokument11 SeitenNatres Digest Pool 2Gabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELARDO, SEBASTIAN GABRIEL M. (Illegal Recruitment)Dokument23 SeitenELARDO, SEBASTIAN GABRIEL M. (Illegal Recruitment)Gabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merida vs. PeopleDokument2 SeitenMerida vs. PeopleGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Martin B. Laurea and Associates For Petitioner-Appellee. Office of The Solicitor General For Respondents-AppellantsDokument5 SeitenMartin B. Laurea and Associates For Petitioner-Appellee. Office of The Solicitor General For Respondents-AppellantsGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abe-Abe Vs MantaDokument4 SeitenAbe-Abe Vs MantaGabby ElardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrea Elizabeth Shaw - The Embodiment of Disobedience - Fat Black Women's Unruly Political Bodies-Lexington Books (2006)Dokument162 SeitenAndrea Elizabeth Shaw - The Embodiment of Disobedience - Fat Black Women's Unruly Political Bodies-Lexington Books (2006)Mirani Barros100% (1)
- Onechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideDokument83 SeitenOnechanbara - Bikini Samurai Squad Game GuideStefan RoscaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jobsheet PMDokument49 SeitenJobsheet PMwindhy fitrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robot Structural Analysis 2017 Help - Push Over Analysis ParametersDokument3 SeitenRobot Structural Analysis 2017 Help - Push Over Analysis ParametersJustin MusopoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For Financial Institutions Week 1Dokument4 SeitenAccounting For Financial Institutions Week 1emadhamdy2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- B2 UNIT 4 Test StandardDokument6 SeitenB2 UNIT 4 Test StandardВладимир РанцовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Delhi Project Scientist Project Associate Posts Advt Details Efa5f6Dokument1 SeiteIit Delhi Project Scientist Project Associate Posts Advt Details Efa5f6SadanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionDokument10 SeitenCase of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionRHEANoch keine Bewertungen
- CodeDokument47 SeitenCodeNadia KhurshidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument7 SeitenLiterature Reviewapi-353923446Noch keine Bewertungen
- 35.ravi Gupta Writs (CLE)Dokument22 Seiten35.ravi Gupta Writs (CLE)Ravi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fellowship 2nd Edition Book 2 - Inverse Fellowship (Playbooks)Dokument44 SeitenFellowship 2nd Edition Book 2 - Inverse Fellowship (Playbooks)AleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effectives of e Wallets NewDokument15 SeitenEffectives of e Wallets NewRicardo SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Gas DistributionDokument46 SeitenNatural Gas DistributionscribdmisraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Camera Obscura Was Increasingly Used by ArtistsDokument4 SeitenThe Camera Obscura Was Increasingly Used by Artistsapi-284704512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reflective Journal 4Dokument3 SeitenReflective Journal 4api-550030025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation One Complete Updated (Atty. Mickey Ingles)Dokument116 SeitenTaxation One Complete Updated (Atty. Mickey Ingles)Patty Salas - Padua100% (11)
- Tutorial 2 - Financial EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenTutorial 2 - Financial EnvironmentShi ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Media and Media ConvergenceDokument70 SeitenTypes of Media and Media ConvergenceYsmile De LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionDokument32 Seiten1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionashwiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- BArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDokument3 SeitenBArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDevkalpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Physician V CIRDokument24 SeitenUniversity of Physician V CIROlivia JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Feasibility/Project Study OnDokument14 SeitenA Feasibility/Project Study OnWilson Domingo LazarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- End-Of-Chapter Questions: CambridgeDokument17 SeitenEnd-Of-Chapter Questions: CambridgeMido MidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Gandhari Version of The Rhinoceros Sutra - Salomon.thieuDokument29 SeitenA Gandhari Version of The Rhinoceros Sutra - Salomon.thieuTRAN NGOCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance SheetDokument6 SeitenBajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance Sheetsarathkumarreddy855081Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agmt - Spa Schedule HDokument20 SeitenAgmt - Spa Schedule Hapi-340431954Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ra 9293 Amending Ra 7836Dokument2 SeitenRa 9293 Amending Ra 7836vonoblesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talking SwedishDokument32 SeitenTalking Swedishdiana jimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reich 0001 PDFDokument87 SeitenReich 0001 PDFYordys Domínguez RodríguezNoch keine Bewertungen