Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fiitjee Gravitation
Hochgeladen von
Rhombi50%(6)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (6 Abstimmungen)
931 Ansichten42 SeitenClassroom package FIITJEE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden50%(6)50% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (6 Abstimmungen)
931 Ansichten42 SeitenFiitjee Gravitation
Hochgeladen von
RhombiSie sind auf Seite 1von 42
JEE Syllabus
Newton’s Law of gravitation
Gravitational Field and Intensity
Variation of Acceleration Due to Gravity (g)
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -1
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential
Binding Energy
Escape Velocity
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -2
Motion of Planets
Motion of Satellites
Kepler’s Second Law
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -3
Answers to Exercise
Concepts and formula a glance
Assignments
Section-|
Section-II
Answers to Assignments
JEE Syllabus
Newton’s Law of gravitation
Gravitational Field and Intensity
Variation of Acceleration Due to Gravity (g)
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -1
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential
Binding Energy
Escape Velocity
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -2
Motion of Planets
Motion of Satellites
Kepler’s Second Law
Solved Problems
Subjective
Objective
Exercise -3
Answers to Exercise
Concepts and formula a glance
Assignments
Section-|
Section-II
Answers to Assignments
GRAVITATION
Syllabus ERASE REA =
Universal law of gravitation, Gravitational field,
Gravitational potential energy and Gravitational potential,
Acceleration due to gravity, Motion of planets and
Satellites in circular orbit.
SENSES
Newton's Law of Gravitation states that “Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a
{force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of
the distance between them’,
Consider two bodies A and B of masses m, and ms, ma me
attracting each other with forces Fx, (force on A due to B) ae, a8
‘and Faq (force on B due to A), respectively.
Then, Fa =~ Fan
and
Fas =|Fas| = magnitude of the attractive force
=¢ Mame
=o Mame
&
where d is the distance between them. G is a universal constant known as Universal Gravitational
Constant. Its value was first measured by Cavendish and is now known to be:
G = 6.6726 « 10°" N-m*kg?
If F,, Fo, Fs,... are the gravitational forces acting on the particle A due to particles P;, P2, Ps,
respectively, then net gravitational force on a particle A due to particles P;, P,..., Pxis given by:
PaR eh tothe,
This is called principle of superposition.
Important points
> The gravitational force is an attractive force,
> The gravitational force between two particles does not depend on the medium
> The gravitational force between two particles is along the straight line joining the particles (called
line of centers).
IMlustration 1: Three identical particles,
equilateral triangle of side
mass m placed at
(2) the mid-point of a side
(0) the centre ofthe triangle,
h of mass m, are placed at the three comers of an
Find the force exerted by this system on another particle of
Solution: (a) Using the principle of superposition
Fm Fur Pye Pe
When the particle is placed at the mid point of a side (at P), Fe
each other.
SSS —
~ Fs, and they cance!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Quartic FormulaDokument3 SeitenQuartic FormulaShubham SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5Dokument1 Seite5RhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOTA Inorganic1Dokument1 SeiteKOTA Inorganic1RhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kota InorganicaDokument1 SeiteKota InorganicaRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kote Inorganic JEEDokument1 SeiteKote Inorganic JEERhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOTA IIT JINorganicaDokument1 SeiteKOTA IIT JINorganicaRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
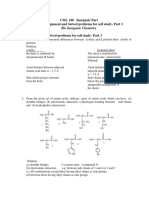
- CML 100 Inorganic Part Home Assignment and Solved Problems For Self Study-Part 3Dokument1 SeiteCML 100 Inorganic Part Home Assignment and Solved Problems For Self Study-Part 3RhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Organic Framework (MOF) : CH-103 B.Tech. Chemistry Course Indian Institute of Technology IndoreDokument37 SeitenMetal Organic Framework (MOF) : CH-103 B.Tech. Chemistry Course Indian Institute of Technology IndoreRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IstrumDokument1 SeiteIstrumRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- cIIT KoTachemmDokument3 SeitencIIT KoTachemmRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIt Kota ChemmistrreeDokument2 SeitenIIt Kota ChemmistrreeRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
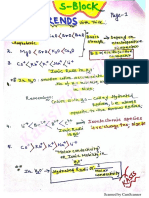
- aIIT Kota NotesDokument5 SeitenaIIT Kota NotesRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JEE 2014 Paper 2 UnsolvedDokument40 SeitenIIT JEE 2014 Paper 2 UnsolvedRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT Lota ChemioquwbsaDokument5 SeitenIIT Lota ChemioquwbsaRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide by Christian WoodsDokument4 SeitenA Guide by Christian WoodsSamuel Jade RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
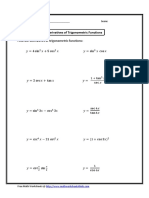
- 03 - Chain Rule With Trig PDFDokument2 Seiten03 - Chain Rule With Trig PDFRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LinkDokument1 SeiteLinkRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Name: - ScoreDokument2 SeitenStudent Name: - ScoreRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6224496450538045652 PDFDokument6 Seiten5 6224496450538045652 PDFRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020Dokument5 SeitenQuick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020RhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 GasesDokument7 Seiten10 GasesKkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6224496450538045652 PDFDokument6 Seiten5 6224496450538045652 PDFRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- %T S 5× (w3 (N S@T!H% 9) F) 6 M (& D@PDokument14 Seiten%T S 5× (w3 (N S@T!H% 9) F) 6 M (& D@PRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyperzDokument5 SeitenHyperzRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyperzDokument4 SeitenHyperzRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths DPP1Dokument1 SeiteMaths DPP1Nibha PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lens Pow Formula RLDokument1 SeiteLens Pow Formula RLHimanshu SethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- K N$T'B 2g Z) F Y#d%y$t d%6v:g Q¿ Pl¡o M/X"Dokument6 SeitenK N$T'B 2g Z) F Y#d%y$t d%6v:g Q¿ Pl¡o M/X"RhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- %T S 5× (w3 (N S@T!H% 9) F) 6 M (& D@PDokument14 Seiten%T S 5× (w3 (N S@T!H% 9) F) 6 M (& D@PRhombiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2aiits Adv 2020Dokument2 Seiten2aiits Adv 2020KeshavNoch keine Bewertungen