Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Vascular Annual Meeting, Boston, USA, 2018
Hochgeladen von
Yasmon NugrohoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Vascular Annual Meeting, Boston, USA, 2018
Hochgeladen von
Yasmon NugrohoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
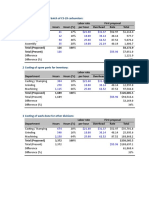
e232 Abstracts Journal of Vascular Surgery
June 2018
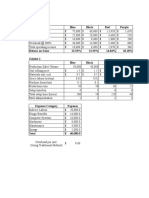
Table. Table. Continued.
Total cast of caval Total cast of caval
Value reconstruction Value reconstruction
Staffing cost Balloon catheter quantity
Nurse hourly wage Minimum 9 $19,958.64
Minimum $35.70/h $20,936.74 Maximum 13 $21,142.95
Maximum $78.02/h $20,936.74 Microcatheter cost (per unit)
Nurse time required/case Minimum $13.50 $19,308.96
Minimum 7.15 h $20,598.01 Maximum $895.00 $24,157.21
Maximum 11.5 h $20,823.60 Microcrater quality
Tech hourly wage ($/h) Minimum 3 $20,033.32
Minimum $29.29/h $20,493.39 Maximum 8 $21,364.34
Maximum $62.57/h $20,973.87 Sheath cost (per unit)
Tech time required/case Minimum $25.50 $20,478.88
Minimum 8.0 h $20,418.67 Maximum $121.50 $21,222.88
Maximum 16.2 h $20,418.67 Sheath quality
Fellow hourly wage ($/h) Minimum 5 $20,550.66
Minimum $28.81/h $20,668.81 Maximum 12 $20.927.83
Maximum $39.79/h $20,729.79 Street cost (per unit)
Fellow time required/case Minimum $985.00 $19,655.73
Minimum 5.75 h $20,686.65 Maximum $1,671.97 $26,868.92
Maximum 7.15 h $20,721.35 Street quality
Endovascular proceduralist Minimum 7 $16,933.63
attending hourly wage (s/h)
Maximum 13 $23,409,69
Minimum $72.73/h $20,781.54
Maximum $246.97/h $20,920.04
Endovascular proceduralist
attending time required/case
Minimum 5.75 h $20,631.11
Maximum 7.15 h $20,920.04 PC218.
Attending anesthesiologist
hourly wage ($/h) Correlation Among Six Single Nucleotide
Minimum $156.57/h $20,489.37 Polymorphisms Related to Cell Survival,
Maximum $272.221/h $20,882.43 Inflammation and Lipoprotein Regulation for
Attending anesthesiologist Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risk Factor
time required/case Nyityasmono T. Nugroho,1 Monika Herten,2 Nani Osada,1 Sonja
Minimum $16.00 min $20,031.53 Sielker,1 Giovanni B. Torsello3. 1University of Münster, Muenster, Ger-
Maximum 566.00 min $21,049.71
many; 2University Hospital, Essen, Germany; 3St. Franziskus Hospital,
Muenster, Germany
Certified registered nurse
Objectives: Genetic disposition plays a role in up to 20% of all abdom-
anesthetist hourly wage ($/h)
inal aortic aneurysm (AAA), with a prevalence of 13% to 19% for first-rate
Minimum $81.79/h $20,446.36 relatives. Meta-analyses of different genome association studies have
Maximum $157 58/h $20,929.20 identified various genes with high evidence for AAA. The purpose of
this study is to identify six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) corre-
Certified registered nurse anesthetist
lating with AAA to identify them as predictor of AAA with simple blood
time required per case
screening. Those functional SNPs are low density lipoprotein receptor-
Minimum 5.75 h $20,623.45 related protein 1 (LRP1, rs1466535 C/T), DAB2-interacting protein (DAB2IP,
Maximum 7.15 h $20,793.44 rs7025486 G/A; cell growth and survival), CDKN2BAS or ANRIL (rs10757278
A/G; cell proliferation and apoptosis), sortilin1 (SORT1, rs599839 A/G; LDL
Materials cost
cholesterol circulation), interleukin-6 receptor (IL6R, rs2228145 A/C), and
Guide cost (per unit) lipoprotein-A (LPA, rs3798220 T/C).
Minimum $10.38 $20,418.23 Methods: In this case-control, single-center study, patients with AAA
diagnosis or without AAA (controls) were recruited from consulting hours.
Maximum $51.65 $20,872.20
Ethical approval was obtained before patients were recruited. According
Guidewire quantity to the sample size estimation, 150 AAA and 60 control patients were
Minimum 6 $20,519.39 planned. Inclusion criteria were adult AAA and consent to the study,
exclusion criteria were known connective tissue disorders or HIV/hepatitis
Maximum 15 $20,842.39
C infection or missing consent. DNA was isolated from 8.5 ml of whole
Balloon catheter cast (per unit) blood in PAXgene Blood DNA tubes (PreAnalytiX) with the PAXgene
Minimum $160.00 $19,133.96 Blood DNA Kit. After PCR, the PCR products were detected in 1.8%
agarose gel and the relevant PCR products were purified with PeqGOLD
Maximum $425.00 $22,181.46
Microspin Cycle-Pure Kit (VWR International). Sequencing was performed
(Continued) using the Sanger method (GATC Biotech AG) and the evaluation was
Journal of Vascular Surgery Abstracts e233
Volume 67, Number 6
done by SNAPGene Viewer (GSL Biotech LLC), Clustal Omega (EMBL-EBI) PC222.
and statistics with SPSS 25 (IBM) software.
Results: Intermediate results from 52 patients (39 AAAs/13 controls) Duplex Scan and Histologic Assessment of
revealed no significant differences in the expression of the investigated
SNPs within the two groups. The P values and frequencies of heterozy- Acute Renal Injury in a Kidney-Kidney
gote and rare homozygote between AAAs and controls in LRP1, DAB2IP, Crosstalk Swine Experimental Model
CDKN2BAS, SORT1, and IL6R were 0.270 (13%/3%); 0.454 (7%/0%); 0.670 Anna Paula W. Baptista-Sincos,1 Igor Rafael Sincos,2 Felipe Coelho,3
(28.2%/15.4%); 0.709 (41%/15.4%); 1.0 (3%/1%), respectively. For LPA no poly- Nelson Wolosker,2 Ricardo Aun,1 Vitoria P. de Paula,1 Oskar G.
morphism could be detected. There was no significant correlation Kaufmann4. 1Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein, Sao Paolo, Brazil;
between those SNPs with AAA risk. 2
University of Sao Paulo Medical School, Sao Paolo, Brazil; 3Hospital
Conclusions: For the preliminary data, there is no correlation between Vascular de Londrina, Londrina, Brazil; 4Federal University of São
polymorphism of the tested SNPs with AAA. Despite of this result, larger Paulo, Sao Paolo, Brazil
sample will lead to a new perspective.
Objectives: The objective of this study was to identify the effect of two
Author Disclosures: M. Herten: Nothing to disclose; N. T. Nugroho: left renal vasculature occlusion strategies on the duplex ultrasound-
Nothing to disclose; N. Osada: Nothing to disclose; S. Sielker: Nothing assessed rheology and histology of the contralateral kidney.
to disclose; G. Torsello: Nothing to disclose. Methods: Pigs were randomly assigned to one of two groups: left renal
artery-only clamping (A group, n ¼ 8) or left renal artery and vein clamp-
ing (AV group, n ¼ 9). Bilateral renal parenchymal biopsy specimens were
PC220. taken every 10 minutes for 90 minutes. Duplex ultrasound resistive index
(RI) and pulsatility index (PI) were measured. Mixed models with normal
distribution and first-order autoregressive correlation structure and
Impaired Wound Healing in Diabetes Is Driven by generalized estimating equation models were used. Results are pre-
Epigenetic Regulation of the Cyclo-Oxygenase-2/ sented as adjusted means with standard errors, estimated proportions
PGE2 Pathway in Macrophages with standard errors, and line plots with 95% confidence intervals.
Results: RI and PI increased in the nonischemic kidney (Figs 1 and 2). In
Frank M. Davis,1 Amrita Joshi,2 Andrew Kimball,1 Matthew Schaller,2
A group animals, RI values increased significantly (P < .01) after 30
Aaron denDekker,2 Bethany Moore,2 Katherine Gallagher1. 1Univer-
minutes of ischemia and PI increased significantly (P < .04) from 30 to
sity of Michigan Medical Center, Ann Arbor, Mich; 2University of
60 minutes of ischemia. The number of histologic abnormalities was
Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich
higher in A group than in AV group biopsy specimens. The percentage
Objectives: Macrophage (M) plasticity, allowing for transition of Ms of lesions increased significantly after 10 minutes in A group nonischemic
from an inflammatory to a reparative phenotype, is critical for normal kidneys (P < .02) and between 50 and 80 minutes in AV group nonische-
wound healing. In pathologic conditions, such as type 2 diabetes mic kidneys (P < .01). Our finding that the nonischemic kidney experi-
(T2D), wounds fail to heal owing to impaired resolution of inflamma- enced acute effects stemming from contralateral ischemia may help
tion. The mechanism(s) responsible for the persistent inflammatory M surgeons prevent acute kidney injury during vascular and urologic
phenotype in T2D wounds are unclear. There is increasing evidence procedures. Moreover, simultaneous artery and vein clamping seemed
that epigenetic-based mechanisms control M function. These mecha- to affect the occurrence of renal crosstalk, which was reflected in wors-
nisms include DNA hypomethylation that leads to overexpression of ening perfusion, elevated resistive index and pulsatility index values,
genes. The cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2/prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) axis as and a tendency for thrombi to form in control kidneys. In addition, renal
well as upstream pathways including cytosolic phospholipase (c(PL) clamping protocol affected the occurrence of histologic lesions.
A2), involved in the release arachidonic acid, have been associated Conclusions: The nonischemic kidney experienced acute effects stem-
with chronic inflammation, however these pathways have not been ming from contralateral ischemia, and the hilar clamping protocol
examined in diabetic wounds. The purpose of this study was to seemed to affect the occurrence of renal crosstalk, which was reflected
investigate if epigenetic modifications alter gene expression of the in worsening perfusion, elevated RI and PI values, and a tendency for
COX-2/PGE2 and c(PL)A2 pathway leading to derangements in M thrombi to form in nonischemic kidneys. The analysis of acute histologic
inflammation in diabetes. findings and Doppler ultrasound parameters indicated that RI and PI
Methods: Using our murine model of wound healing, wound Ms were measurements may have predictive value in AKI. We believe that intrao-
isolated from control and diet-induced obese (DIO) mice (n ¼ 40/group). perative Doppler ultrasound imaging can help to guide surgeons in
Expression of miR-29B, c(PL)A2, COX2, and PGE2 were determined by determining tolerable ischemia times and the probability of AKI onset.
qPCR. TGF protein was examined by ELISA. Standard phenotyping and Nevertheless, further clinical and experimental research is required to
killing assays were used to determine M function in DIO and control fully understand ischemia- reperfusion injury and renal crosstalk.
BMDM. Statistical significance was determined between two groups us-
ing Student t tests, and differences between more than two groups
were evaluated by analysis of variance followed by Newman-Keuls post
hoc test.
Results: We demonstrate that c(PL)A2 seems to be significantly upre-
gulated in diabetic Ms and human diabetic monocytes. In addition,
TGF is significantly elevated in DIO wound Ms in comparison to control
wound Ms. Further, the increase in TGF stimulates miR-29B production,
resulting in hypomethylation of the COX-2 gene and overexpression.
Increased COX-2 in diabetic Ms significantly increased PGE2 levels in
DIO wound Ms resulting inflammatory gene expression and impaired
killing/phagocytosis.
Conclusions: In summary, these results demonstrate that the COX-2/
PGE2 pathway is increased in diabetic wound Ms by elevated TGF/miR-
29b that hypomethylate COX-2 and results in elevated PGE2 that drives
M-mediated inflammation and impaired phagocytosis preventing
wound repair.
Author Disclosures: F. M. Davis: Nothing to disclose; A. denDekker:
Nothing to disclose; K. Gallagher: Nothing to disclose; A. Joshi: Nothing
Fig 1. Resistive index (RI). Estimated means and 95% confidence
to disclose; A. Kimball: Nothing to disclose; B. Moore: Nothing to disclose;
intervals.
M. Schaller: Nothing to disclose.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 212 - Holy Cross Hospital - DRGDokument3 Seiten212 - Holy Cross Hospital - DRGswarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimasi-OO-Costs-Alat BorDokument12 SeitenEstimasi-OO-Costs-Alat Borzulfikri hakim akbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zara ReportsDokument13 SeitenZara ReportsMuskanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA PracticeDokument7 SeitenMA Practiceshilpa.1595Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jola PublishingDokument4 SeitenJola PublishingSabrina LaganàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics in Surgery Is It Worth The Investment?Dokument19 SeitenRobotics in Surgery Is It Worth The Investment?renjythNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Ball - Gentle LentilDokument25 SeitenCrystal Ball - Gentle LentilHardik SemlaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morada PHYs101L-A12 Report 4Dokument5 SeitenMorada PHYs101L-A12 Report 4Renchie MoradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Analysis and EvaluationDokument39 SeitenProject Analysis and Evaluationgabisan1087Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 10 - Curled Metal IncDokument13 SeitenGroup 10 - Curled Metal IncParikshit ModyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source 3R Medical Disposable Circumcision Staplers On PDFDokument1 SeiteSource 3R Medical Disposable Circumcision Staplers On PDFdr_hotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetricia Informe Diagnostico Fetal MexicoDokument5 SeitenObstetricia Informe Diagnostico Fetal MexicoRosa Elena CastelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMG 20170617 1 Rep OB PDFDokument5 SeitenIMG 20170617 1 Rep OB PDFCris RivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huron Automotive Company ExcelllDokument6 SeitenHuron Automotive Company Excelllmaximus0903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lelly Muridi Zham Zham - Rep - OBDokument4 SeitenLelly Muridi Zham Zham - Rep - OBPutera BrahmansaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explore: Case Processing SummaryDokument6 SeitenExplore: Case Processing SummaryKhadijah Husainy HasbullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pac 750Xl Non-Financed Costs ComparisonsDokument9 SeitenPac 750Xl Non-Financed Costs ComparisonsFatyaRizkySafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awaiting Image: 24 Opzs3000 Physical SpecificationDokument2 SeitenAwaiting Image: 24 Opzs3000 Physical SpecificationABEL JACOB SICHA HUAMANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Akuntansi Manajemen Lanjutan PROBLEM 4.32 Dan 4.35: Teuku Aldefa Angkasa Wangsa Banowo 2006623132Dokument3 SeitenTugas Akuntansi Manajemen Lanjutan PROBLEM 4.32 Dan 4.35: Teuku Aldefa Angkasa Wangsa Banowo 2006623132Teuku AldefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classic Pen ComapanyDokument5 SeitenClassic Pen Comapanyvijaya bhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dbergessssssrac D3D3D3Systems: The Challenge of Backward IntegrationDokument4 SeitenDbergessssssrac D3D3D3Systems: The Challenge of Backward IntegrationZee ShanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Destin Brass Products Co.: 1. Answer - 1Dokument5 SeitenDestin Brass Products Co.: 1. Answer - 1Chetan DasguptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Dhana Invoice For Dell Systems 106Dokument1 SeiteSri Dhana Invoice For Dell Systems 106Scv BackendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect-20 Power Plant Rating, Relative CostDokument10 SeitenLect-20 Power Plant Rating, Relative CostAwesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incandescent Bulbs LED CFL: Over 13 Inches in Length and Over 5 Inches in DiameterDokument2 SeitenIncandescent Bulbs LED CFL: Over 13 Inches in Length and Over 5 Inches in DiameterhariventanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MVV - Assignment 1 - ManyaDokument14 SeitenMVV - Assignment 1 - ManyaManya SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALLE0000Dokument3 SeitenALLE0000Ernesto LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation Cost Calculator Electric 2016Dokument4 SeitenIrrigation Cost Calculator Electric 2016BiruckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description Method of Measurement Unit CostDokument3 SeitenDescription Method of Measurement Unit CostTahjay BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Guide Line - Rule of Thumb For Estimate Electrical Usage For HotelDokument1 SeiteBasic Guide Line - Rule of Thumb For Estimate Electrical Usage For Hotelanon_923638458Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effective CNG Handling & Logistics For Industries: (An Indonesian Case Study)Dokument32 SeitenEffective CNG Handling & Logistics For Industries: (An Indonesian Case Study)Eis NovidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kreative Kasuals NewDokument11 SeitenKreative Kasuals Newdebapriya sarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel Time (Total) : Unlicensed Trial VersionDokument11 SeitenTravel Time (Total) : Unlicensed Trial VersionwulanfitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water, Wastewater, & Reclaimed Water RatesDokument3 SeitenWater, Wastewater, & Reclaimed Water RatessubitofasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuldeep DeathDokument13 SeitenKuldeep DeathLANKAPATRUDU6772Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part/Material Inputs: Injection Molding Technical Cost Model MIT - Materials Systems LaboratoryDokument13 SeitenPart/Material Inputs: Injection Molding Technical Cost Model MIT - Materials Systems LaboratoryEmba MadrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lampiran 3. Hasil Penelitian Frequencies: StatisticsDokument4 SeitenLampiran 3. Hasil Penelitian Frequencies: StatisticsTri Wahyu HidayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma CameraDokument20 SeitenGamma CameraLuis Fernando Garcia SNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEL Techfine 12V100A-Short.Dokument3 SeitenGEL Techfine 12V100A-Short.Yesibeth MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brillantes, Isabella Francesca C. Paraso, Noelle Patricia EDokument1 SeiteBrillantes, Isabella Francesca C. Paraso, Noelle Patricia EBella BrillantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 3 Body Sleep - Sample ReportDokument6 SeitenLevel 3 Body Sleep - Sample Reportjunior browNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7 Tutorial Suggested Solutions (Students, Non-Printable)Dokument8 SeitenWeek 7 Tutorial Suggested Solutions (Students, Non-Printable)Ai Tien TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadena de AbastecimientoDokument3 SeitenCadena de AbastecimientoChristian FT100% (1)
- Book 1Dokument2 SeitenBook 1Fabie EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kitcharao Cis - Calamity Repair Cis-15-2023-Asdi-ImoDokument48 SeitenKitcharao Cis - Calamity Repair Cis-15-2023-Asdi-ImoJ-red MondejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALLIED SNP Statistics Week 45 06 - 11 - 2015 PDFDokument9 SeitenALLIED SNP Statistics Week 45 06 - 11 - 2015 PDFDJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scaffold QtyDokument2 SeitenScaffold Qtyjhomel garciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Habersham Medical Center 1 1009Dokument126 SeitenHabersham Medical Center 1 1009swarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Employees at 8 Hrs Each Employee No. of Days Basic PayDokument4 Seiten3 Employees at 8 Hrs Each Employee No. of Days Basic PayShanel VillaluzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huron Automotive Company ExcelDokument6 SeitenHuron Automotive Company ExcelAnsh LuthraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 18 Standard Costing PDFDokument8 SeitenBab 18 Standard Costing PDFSandi SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traditional Costing: Activity Cost Pool Activity MeasureDokument4 SeitenTraditional Costing: Activity Cost Pool Activity Measureyola yufitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcelWorkshops (2016-2017) Exercises CompleteDokument12 SeitenExcelWorkshops (2016-2017) Exercises CompleteGreisy VillarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Study of A/C (Old Plant)Dokument2 SeitenEnergy Study of A/C (Old Plant)Viplove SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kreative Kasuals - NewDokument10 SeitenKreative Kasuals - NewDeep Gandhi100% (1)
- 1 MergedDokument17 Seiten1 MergedMahindra DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP12-18 (12V18Ah) LP Series-General Purpose: SpecificationsDokument2 SeitenLP12-18 (12V18Ah) LP Series-General Purpose: SpecificationsEduardo SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hasil SPSSDokument9 SeitenHasil SPSSalviano filmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centella Asiatica - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side Effects - ExamineDokument30 SeitenCentella Asiatica - Scientific Review On Usage, Dosage, Side Effects - ExamineMethaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pertemuan 8. TDM Atau PKODDokument43 SeitenPertemuan 8. TDM Atau PKODBudi SayogaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Unit f214 01 Communication Homeostasis and EnergyDokument20 SeitenQuestion Paper Unit f214 01 Communication Homeostasis and EnergygeorgiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male Factor InfertilityDokument53 SeitenMale Factor InfertilityMarcel MusteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infeksi Alami Virus Rabies Pada Anjing: Studi Morfopatologi Dan ImunohistokimiaDokument63 SeitenInfeksi Alami Virus Rabies Pada Anjing: Studi Morfopatologi Dan ImunohistokimiaMuhammad KikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress BustingDokument24 SeitenStress BustingMarianne ChristieNoch keine Bewertungen
- October 2018 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDokument24 SeitenOctober 2018 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelCheung PhilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTICONVULSANTSDokument1 SeiteANTICONVULSANTSPadmavathi CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomyDokument17 SeitenCorrections and Additions To Taxonomists' Glossary of Mosquito AnatomymokarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids: Chapter 8 Lehninger 5 EdDokument17 SeitenNucleotides and Nucleic Acids: Chapter 8 Lehninger 5 Edarun231187Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 DystoniaDokument23 Seiten2018 DystoniaTony NgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacificgoldenplover Microbe Mission Practice TestDokument5 SeitenPacificgoldenplover Microbe Mission Practice TestsandeeptaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avishek Roy Class12 Bio Project On ThalassemiaDokument20 SeitenAvishek Roy Class12 Bio Project On ThalassemiaDazzling DilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene Technology ...Dokument28 SeitenGene Technology ...Jelita AlviolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRK - Spring 2020 - BT502 - 2 - BC170203159Dokument11 SeitenMRK - Spring 2020 - BT502 - 2 - BC170203159Mashal WakeelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mual MuntahDokument8 SeitenMual MuntahRosalindaRezkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL1040 Lecture NotesDokument50 SeitenBIOL1040 Lecture NotesJonathanZhaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochipsDokument20 SeitenBiochipstusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Cancer - Stages and Grades - 2015-09-01Dokument7 SeitenEye Cancer - Stages and Grades - 2015-09-01Ruslan KamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of The Nurse in Health Promotion PDFDokument1 SeiteThe Role of The Nurse in Health Promotion PDFCie Ladd0% (1)
- What Are The Different Types of BiochipDokument2 SeitenWhat Are The Different Types of Biochipajrai07Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Article On MicrobalsDokument29 SeitenThe Article On Microbalsrangesh aravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchizophreniaDokument34 SeitenSchizophreniaSarasija NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Exam QuestionsDokument4 SeitenPast Exam Questionskeirob100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: G.SethuramanDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: G.SethuramanSethuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Output 8 and 9Dokument11 SeitenOutput 8 and 9Angelo ParaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Dokument170 SeitenAcute Myeloid Leukemia: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)amor letrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.panoramic Radiograph in PathologyDokument53 Seiten1.panoramic Radiograph in PathologyMIREYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Lesions and DiagnosisDokument25 SeitenSkin Lesions and DiagnosisBUCM Class 2023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trypanosoma Evansi Infection (Surra) : C H A P T E R 2 - 1 - 1 7Dokument15 SeitenTrypanosoma Evansi Infection (Surra) : C H A P T E R 2 - 1 - 1 7WormInchNoch keine Bewertungen