Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chronic Kidney Disease Management
Hochgeladen von
Angie MandeoyaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chronic Kidney Disease Management
Hochgeladen von
Angie MandeoyaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Patient’s Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Short Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) occurs when one suffers from gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function over time. With loss of kidney function, there is an
accumulation of water; waste; and toxic substances, in the body, that are normally excreted by the kidney. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), the measure of the kidney's function,
determines the severity or stage of the disease (whereas Stage 5 CKD is considered Renal Failure due to gradual loss of GFR, GFR < 15: needs dialysis). CKD often develops from 1Diabetes
(stenosis/ischemic), 2Hypertension (microvascular damage), 3Glomerulonephritis (post-infection), or 4Nephrotoxicity (medications).
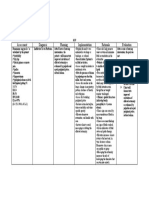
Priority Problem: (Priority 1) Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation of the Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Problem
Subjective: Ineffective Impaired GFR results into Goal: Collaborative:
Breathing Pattern fluid overload. With fluid Establish Spontaneous, non- 1. Administer humid Oxygen 1. To help patient get
Patient is not r/t impending volume excess, venous Labored Breathing (8-10Lpm) as ordered. adequate oxygen despite
able to verbalize. pulmonary pressure is more likely to of DOB.
congestion d/t cause both circulatory and Short Term: 2. Assist in Manual 2. To assist patient on
impaired GFR and pulmonary congestion. The After 4 hours of nursing Ventilation via ET Tube. respiration and to ensure
fluid retention or patient may possibly interventions, patient will be adequate tidal volume.
Objective: respiratory manifests fatigue, able to reduce labored and
> Deep, fast, noisy muscle weakness dyspnea, tachypnea, difficult breathing and
breathing d/t physical stress. muscle weakness establish a respiratory rate
of less than 30cpm. Independent:
(including diaphragm), or
> RR 33cpm 1. Monitor and record vital 1. To check and reassess
sputum production that
are related to pulmonary Long Term: signs. vital function changes
> Crackles heard
congestion. Physical stress After 5 days of nursing (Respiration).
on inspiration
also impacts pulmonary interventions, patient will be
> SaO2 99% functioning. able to demonstrate non- 2. Assess for lung sounds. 2. To identify extent of
labored and spontaneous fluid accumulation in the
> BP Diabetic, there is a breathing. respiratory system.
140/100mmhg
possibility that sugar
crystallization has occurred 3. Position on moderate high 3. To facilitate
> PR 80bpm back rest. gravitational expansion of
and leads to renal artery
stenosis or a microvascular the lungs to decrease
> T 37.0 C
complication due to inspiratory effort.
> Diaphoretic, cold viscosity.
clammy skin 4. Maintain calm and non- 4. To avoid stressors and
stimulating environment. let patient regain strength
> Unresponsive; by manipulation of
may be due to environment.
fatigue/weakness.
5. Suction secretions PRN. 5. To facilitate airway
> Increased
respiratory clearance and reduce
secretions. effort from DOB.
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S.
WUP SN’13 senior block 04
Patient’s Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
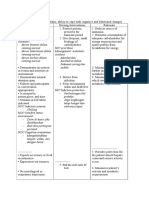
Main Problem: (Priority 2) Fluid Volume Excess
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation of the Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Problem
Subjective: Fluid Volume Renal disorder impairs Goal: Collaborative: Collaborative:
Excess R/T glomerular filtration that Reduce Fluid Volume 1. Administer loop diuretics 1. Diuretics reduce fluid
Patient is not decrease resulted to fluid overload. Excess, output more (Furosemide/Lasix) as ordered. volume by helping kidney
able to verbalize. Glomerular With fluid volume excess, than input. excrete urine and sodium.
filtration Rate and hydrostatic pressure is 2. Assist in specimen extraction for 2. To prepare patient for
sodium retention. higher than the usual Short Term: serum analysis (Serum Electrolytes/ possible lab orders..
pushing excess fluids into After 4 hours of RBS or FBS) and urine analysis
Objective: the interstitial spaces, nursing interventions, (BUN/Crea).
> Anuria causes venous return, patient will be able to 3. CBG Test as ordered. 3. To determine the
leading the patient to have avoid recurrence of efficacy of DM regimen.
> BP 140/100mahg fluid excess Independent: Independent:
edema, weight gain,
pulmonary congestion and 1. Monitor and record vital signs 1. To check and reassess
> RR 27cpm
HPN at the same time due vital function changes
> PR 80bpm to decrease GFR, nephron Long Term: (Circulation).
hypertrophied leading to After 5 days of 2. Auscultate breath sounds 2. To determine extent of
> T 37.0 C decrease ability of the nursing intervention fluid excess.
kidney to concentrate the patient will 3. Record occurrence of dyspnea 3. To check possible
> Peripheral Edema urine and impaired manifest stabilize fluid respiratory complications
excretion of fluid thus volume, I & O, normal (pulmonary congestion).
> Diaphoretic, cold
leading to oliguria/anuria. VS, stable weight,
clammy skin
and free from signs of 4. Review lab data like BUN, 4. To monitor kidney
> Unresponsive; With associated DM, there edema. Creatinine, Serum electrolyte. function and fluid
may be due to is a possibility that sugar
fatigue/weakness.
retention (electrolyte
crystallization has occurred
and leads to renal artery compensation).
> Increased stenosis or a microvascular
respiratory 5. Record I&O accurately and
complication due to 5. To determine fluid
secretions.
viscosity of blood. calculate fluid volume balance retention and kidney
> CBG 126mg/dL function (GFR).
6. Weigh client 6. Increasing weight may
indicate fluid retention.
7. Encourage quiet, restful 7. To allow patient cope
atmosphere. with stressors naturally.
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S.
WUP SN’13 senior block 04
Patient’s Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Manifestation Problem: (Priority 3) Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation of the Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Problem
Subjective: Risk for Impaired Due to fluid retention, fluid Goal: Collaborative:
Skin Integrity r/t accumulates and fluid Prevent Risks on Developing 1. Ferrous Sulfate (Iron 1. To help body regulate
Patient is not edema and shifts from intracellular Skin Breakdown. supplement) as ordered. RBC in the
able to verbalize. prolonged bed rest compartment to absence/lacking of
d/t extracellular compartment Short Term: hormone erythropoietin.
causing escape of fluid to After 4 hours of nursing 2. Update Lab Findings for 2. To evaluate efficacy of
the tissues (edema). With interventions, patient will be CBC (RBC, Hgb, Hct). treatment/prophylaxis for
Objective: associated complications of able to remove potential anemia regimen.
> Peripheral Edema anemia, skin nutrition threats that may lead to
would be crucial and may poor skin integrity. 3. CBG T.I.D. as ordered. 3. To determine
> Prolonged bed
have easily broken off. hyperglycemia that
rest
Long Term: makes blood viscous and
> Pallor DM could cause high blood After 5 days of nursing induces the risk for
sugar levels and leads to interventions, patient will be infection.
> Hgb viscosity of blood that also able to identify and avoid
impairs nutrition of skin or factors that lead to skin Independent:
> Diaphoretic, cold reduction of blood cells to breakdown. 1. Assess skin appearance 1. To determine edema or
clammy skin capillaries. (color, texture, erythema that indicates
temperature). possible bed sore.
> Unresponsive;
may be due to
fatigue/weakness. 2. Turn patient side to side 2. To make pressure
every 2 hours if possible. equal when lying to avoid
> CBG 126mg/dL unilateral skin tissue
blood insufficiency.
3. Maintain crease-free bed 3. To avoid skin irritation
linen. from crease.
4. Maintain a clean, 4. To avoid risk for skin
therapeutic environment. injury and infection.
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S.
WUP SN’13 senior block 04
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDokument4 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Dokument2 SeitenNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Impaired ComfortDokument2 SeitenNCP Impaired ComfortGia P. de VeyraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For UTIDokument3 SeitenNCP For UTIlachrymoseai100% (4)
- NCP StrokeDokument2 SeitenNCP StrokeEtienne NinxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory FailureDokument25 SeitenAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaDokument4 Seiten"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaMelissa MhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP EdemaDokument1 SeiteNCP EdemaR Hornilla ArcegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyJanina Patricia BuddleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actual NCPDokument2 SeitenActual NCPbaki0146Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Inactivity ToleranceDokument16 SeitenNCP Inactivity ToleranceChrisTine M. MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Acute Confusion 1-4Dokument2 SeitenRisk For Acute Confusion 1-4DewiRestiNazullyQiran100% (1)
- NCP DM and HCVDDokument3 SeitenNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitGenEsis CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study OverviewDokument26 SeitenDrug Study Overviewrn msnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Dokument6 SeitenIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Rationale Interventions Rationale EvaluationJobie CasipongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Electrolyte ImbalanceManuel Jacob YradNoch keine Bewertungen
- NafarinDokument2 SeitenNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Dokument3 SeitenNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDokument12 SeitenCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bladder Infection Nursing CareDokument8 SeitenBladder Infection Nursing CareJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDokument6 SeitenESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - ConstipationDokument3 SeitenNCP - ConstipationDaniel Dave KapunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Con ConstipationDokument2 SeitenNCP Con ConstipationChristine Marie Bucio OraizNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPERTENSION Health TeachingDokument3 SeitenHYPERTENSION Health TeachingPaulo JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDokument3 SeitenImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument2 SeitenNCPZmiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain NCP BillrothDokument2 SeitenPain NCP BillrotharjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diarrhea Care PlanDokument2 SeitenDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Alendronate Study on Bone LossDokument12 SeitenAlendronate Study on Bone LossTrio San LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIGOCIDDokument2 SeitenVIGOCIDKaren DamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument2 SeitenActivity IntoleranceJaney Ceniza تNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP-Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenNCP-Airway ClearanceTimi BCNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP ErDokument4 SeitenNCP ErljarseniornNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTIDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTITrida Hermano CabansagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDokument3 SeitenImpaired Urinary EliminationDenise Republika100% (1)
- Jose Rizal University: College of NursingDokument11 SeitenJose Rizal University: College of NursingDhan Mark Trinidad100% (3)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDokument3 SeitenBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPsimonjosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleeding NCPDokument13 SeitenBleeding NCPBiway Regala100% (1)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument6 SeitenNCPyupipsjamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia Concept Mapping. Group 1Dokument82 SeitenAnemia Concept Mapping. Group 1Giselle EstoquiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study TableDokument14 SeitenDrug Study TableAl-Mujib TanogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Or NCP (Impaired Elimination)Dokument1 SeiteOr NCP (Impaired Elimination)Nikki M. ArapolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenDrug StudyGrace CadawasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDokument20 SeitenAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDokument4 SeitenNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Tracheobronchial Secretions CAPLP Benoza100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument9 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas Exchange PneumoniaShanice BedecirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument10 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument10 SeitenNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationGuile RilleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care PlansDokument10 SeitenChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care Planscy belNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congestive Cardiac Failure Nursing CareDokument22 SeitenCongestive Cardiac Failure Nursing CareSampada GajbhiyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument9 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final NCPDokument13 SeitenFinal NCPBAGUIO CATSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonDokument2 SeitenConcepts in Prioritization: Speaker: Vicki RobertsonAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harri AnnaDokument57 SeitenHarri AnnaAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Dokument1 SeitePharm 1.31 SOCK Method For Learning Pharm 1Angie Mandeoya100% (1)
- PDFDokument5 SeitenPDFAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDokument9 SeitenNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- I. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerDokument2 SeitenI. Calculating IV Flow Rates: Day 2 AnswerAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slideshare - Perioperative Nursing Lecture PDFDokument9 SeitenSlideshare - Perioperative Nursing Lecture PDFAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDokument6 SeitenRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm 1.09 Medication AntidotesDokument1 SeitePharm 1.09 Medication AntidotesAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFDokument6 Seiten50 Motivational Nursing Quotes PDFAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac NCLEX Points OverviewDokument21 SeitenCardiac NCLEX Points OverviewSheena Sacha100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- Day 2 QuizDokument2 SeitenDay 2 QuizAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: 75 Yrs. OldDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: 75 Yrs. OldAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentDokument10 SeitenNursing Process Guide: St. Anthony's College Nursing DepartmentAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 000print or NCPDokument6 Seiten000print or NCPAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book DiscussionDokument4 SeitenBook DiscussionAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL - References & AppendicesDokument23 SeitenFINAL - References & AppendicesAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan and Diagnosis For MastectomyAngie Mandeoya100% (2)
- Compilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeDokument3 SeitenCompilation of Different Disasters: Erica G. Mandeoya Grade 7-JadeAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wps Media Objects 3918 4012970 NursingTools Ch52 NCP DFV 1478-1479Dokument2 SeitenWps Media Objects 3918 4012970 NursingTools Ch52 NCP DFV 1478-1479Mayls Sevilla CalizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharm 1.12 Common AntihypertensivesDokument1 SeitePharm 1.12 Common AntihypertensivesAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Gastritis: Diagnosis, Interventions & GoalsDokument16 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Gastritis: Diagnosis, Interventions & GoalsAngie Mandeoya50% (2)
- 50 Motivational Nursing QuotesDokument6 Seiten50 Motivational Nursing QuotesAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Health Agenda - Dec1 - 1 PDFDokument26 SeitenPhilippine Health Agenda - Dec1 - 1 PDFreyalene gallegosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Exam SmpleDokument18 SeitenPsychiatric Exam SmpleAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angina PectorisDokument12 SeitenAngina Pectorismardsz93% (14)
- Respondeat Superior PDFDokument1 SeiteRespondeat Superior PDFAngie MandeoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Vehicle BatteryDokument15 SeitenElectric Vehicle BatteryTotal Acess100% (1)
- Pvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Dokument2 SeitenPvpsit Department of Mechanical Engineering PVP19Satya NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteo Book Final 2014Dokument51 SeitenOsteo Book Final 2014hyanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- P1007 PPPS For Raw Milk 1AR SD3 Cheese Risk AssessmentDokument304 SeitenP1007 PPPS For Raw Milk 1AR SD3 Cheese Risk AssessmentNicholasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunDokument6 SeitenRendemen Dan Skrining Fitokimia Pada Ekstrak DaunArdya YusidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 204 (AutoRecovered)Dokument27 SeitenF 204 (AutoRecovered)safiqulislam100% (1)
- Evaluation of Personal Dust Exposure of The Rice Mill Workers in AssamDokument10 SeitenEvaluation of Personal Dust Exposure of The Rice Mill Workers in AssamIJAMTESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioreactor For Air Pollution ControlDokument6 SeitenBioreactor For Air Pollution Controlscarmathor90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastDokument7 SeitenEffects of Sucrose Concentration On Cell Respiration in YeastRachel Utomo83% (23)
- Oplan Nena (Violation of RA 10364 Expanded Anti-Trafficking in Person Act of 2012)Dokument3 SeitenOplan Nena (Violation of RA 10364 Expanded Anti-Trafficking in Person Act of 2012)Jhunary MunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD - 15. Republic of The Philippines Vs Sunlife Assurance of CanadaDokument2 SeitenCD - 15. Republic of The Philippines Vs Sunlife Assurance of CanadaAlyssa Alee Angeles JacintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracking SARDO StudentsDokument2 SeitenTracking SARDO StudentsLean ABNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas Tool Specs SummaryDokument3 SeitenAtlas Tool Specs SummaryWaleed Barakat MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kluge 2004 MetabolaDokument42 SeitenKluge 2004 MetabolaBlah BlahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section III - Topic 3Dokument7 SeitenSection III - Topic 3KARINE HOVSEPYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transpo Printable Lecture4Dokument10 SeitenTranspo Printable Lecture4Jabin Sta. TeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two-day workshop budgetDokument2 SeitenTwo-day workshop budgetVishwanath BaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Archives of Oral Biology 100 (2019) 42-48Dokument7 SeitenArchives of Oral Biology 100 (2019) 42-48pedro cuellar proNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics of Design Error in The Process IndustriesDokument13 SeitenStatistics of Design Error in The Process IndustriesEmmanuel Osorno CaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rorschach y SuicidioDokument17 SeitenRorschach y SuicidioLaura SierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesDokument9 SeitenDesign AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesTELKOMNIKANoch keine Bewertungen
- PPC Production PlantDokument106 SeitenPPC Production PlantAljay Neeson Imperial100% (1)
- A Text Book On Nursing Management AccordDokument790 SeitenA Text Book On Nursing Management AccordMohammed AfzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caregiving Learning Activity SheetDokument7 SeitenCaregiving Learning Activity SheetJuvy Lyn Conda100% (5)
- Working at Height ProcedureDokument11 SeitenWorking at Height ProcedureAniekan AkpaidiokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Inlet Centrifugal FanDokument43 SeitenSingle Inlet Centrifugal Fan4uengineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiration PHYSIODokument23 SeitenRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Employment Document TitleDokument1 SeiteCertificate of Employment Document TitleAyni ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFDokument75 SeitenCivil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFVEERKUMAR GNDEC100% (1)
- Strategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsDokument9 SeitenStrategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsAkii WingNoch keine Bewertungen