Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C S (L 14) P 1 5: Ommunication Ystem Ecture AGE OF
Hochgeladen von
Mubashir GhaffarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenC S (L 14) P 1 5: Ommunication Ystem Ecture AGE OF
Hochgeladen von
Mubashir GhaffarCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (LECTURE 14) PAGE 1 OF 5
TELEVISION
A system used to transmit and recevie motion pictures (frame by frame) and
sound over guided or unguided channels, is called Television System.
The message transmitted by a television is two-dimensional image with motion,
and therefore a function of two variables, spatial as well as time.
The only difference between picture and sound is their structures, that is, picture
distributed on two dimensions and voice over one dimension.
Persistence of vision is how long an image sensation retain in the eye or brain
whose value is17Hz.
Normally in TV, picture are send via amplitude modulation (AM) while voice
over frequency modulation (FM).
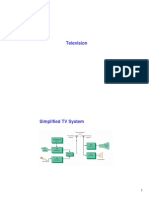
Generalized Transmit and Recevie TV system is given below.
UIT FROM THE DESK OF ENGR. DR. JAWWAD AHMAD
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM (LECTURE 14) PAGE 2 OF 5
Camera converts light signal into electrical signal while mic converts sound signal
into electrical signal thus both are behaving like transducer.
Charge Couple Device (CCD), is the recently known approch, which is used in
modern cameras.
There are several types of television systems with numerous variations found in
different countries like for analog TV, National Television System Committee
(NTSC), Squentiel Couleurmmoire (SECAM) having 60Hz, used in USA, Russia,
Korea, etc. While International Radio Consultative Committee (CCIR), Phase
Alternating Line (PAL) having 50Hz, used in European countries as well as in
Pakistan and India also.
For the digital system, High-Definition Television (HDTV) system is employed.
IMAGE
An image can be considered as a still frame subdivided into several small squares
or picture elements known as “Pixels”.
Actually, image is a distribution of light-intensities, so to “read/undertand image”
is to read light intensities.
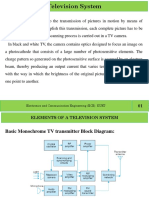
In monochromatic TV system, the information of the entire picture is transmitted
by transmitting an electrical signal proportional to the brightness level of the
picture elements / pixels taken in a certain sequence.
Conversion of light energy into electrical energy is done by means of Photo-
Electrical Effect.
Normally, the term “Reproduce” is used when electrical signal transform into light
signal, and for the transformation of light signal into electrical signal “Generation”
word is used.
Electrical reproduces
Light Light Electrical
generation
UIT FROM THE DESK OF ENGR. DR. JAWWAD AHMAD
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM (LECTURE 14) PAGE 3 OF 5
Consider a mosaic as shown in a 5 by 5 cell as fixed frame, which is a part of any
video. For the simplicity, only two levels are considered out of infinite intensity
levels.
Now this generated signal, is need to be reproduced at receiver.
RASTER/SCANNING SYSTEMS
The image at transmitter-end, furnishes by the television camera tube by means
optically generated charged image as target mosaic. This charged image on target
mosaic acquires a positive electric charge proportional to the brightness of the
image. Thus, instead of a light image, a charge image is formed.
An electron gun that generate electron beam when supplied with high voltages
known as high tension (HT) voltages, at receiver-end, now scans the target-mosaic
surface with an electron beam in the manner as shown.
The beam is controlled by a set of voltages (periodic sawtooth signals) across
horizontal and vertical deflection plates. Horizontal oscillator or relaxation
oscillator generate sawtooth signals for scanning.
Start from upper left-hand corner with 1st pixel and scan the first row (trace) in
53.5μsec, the raster/scanning beam quickly flies back (retrace) in 10μsec, to the
start of the second row horizontally, and continue this way until finishes to the last
row, and then back to 1st pixel for next frame.
The scanning lines are not perfectly horizontal but have a small downward slope,
because during the horizontal deflection the beam is also continuously deflected
downward due to a slower vertical deflection signal, as shown.
UIT FROM THE DESK OF ENGR. DR. JAWWAD AHMAD
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM (LECTURE 14) PAGE 4 OF 5
There are basically, three types of scanning techniques: (i) Flickers, (ii) Interlased
Scanning, and (iii) Frame Grabbing Reproduction.
In Flickers, the screen left blank for certain period, while in Interlased, odd and
even field scanning introduce that decreases flicker effect. Frame Grabbing
Reproduction, is even better technique than these scanning methods, as it first
store image and then reproduces frame with higher frequency rate. In Pakistan,
Siemens was the first company to lanuch TV set with employing Frame Grabbing
Reproduction Scanning technique having 100 Frames per second reproduction
rate.
Remember, field frequency is double of frame frequency because number of lines
divides on the screen.
Scanning is continuous at a rate of 50/60 picture frames per second, generating a
video signal having Bandwidth of 6MHz, using VSB-modulation.
While the voice message is 4.5MHz ahead from video signal.
SCAN-SYNCHRONIZATION & BLANKING PULSES
When the electron beam flies back horizontally after completing each horizontal
line that are control by Automatic Frequency Controller (AFC), it will leave an
unwanted flyback trace on the screen. To avoid this, a blanking pulse, known as
the horizontal blanking pulse (HBP), is added during the flyback interval, which
occurs at the end of each horizontal sweep.
UIT FROM THE DESK OF ENGR. DR. JAWWAD AHMAD
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM (LECTURE 14) PAGE 5 OF 5
Similarly, a vertical blanking pulse is added at the end of each vertical sweep to
eliminate the unwanted vertical retrace. These blanking pulses are added at the
transmitter.
To synchronize rows in transmitter and recevier, scan-synchronization
information is added at transmitter, known as synch pulses. This is done by
adding a large pulse to each blanking pulse, which tells the scanning beam about
end of the row. If this information is missing then distortion is the result.
Clipper circuit clipps the synch pulses and sent them to the synch processor.
Differentiator (High Pass Filter) seperates horizontal synch pulse and integrator
(Low Pass Filter) seperates vertical synch pulse. These pulses are then fed to the
respected sweep generator.
UIT FROM THE DESK OF ENGR. DR. JAWWAD AHMAD
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter6 VIDEO MultimediaDokument35 SeitenChapter6 VIDEO Multimediaqwertyuiopasd123xNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Static Deflection in CRTDokument43 SeitenElectro Static Deflection in CRTutadaneelimadeviutadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Phasor & Line SpectraDokument20 SeitenCommunication Systems: Phasor & Line SpectraMubashir Ghaffar100% (1)
- Ec1011 Television Video EngineeringDokument21 SeitenEc1011 Television Video Engineeringyesyouareesh100% (3)
- Cta-861-F Final Revised 2017Dokument188 SeitenCta-861-F Final Revised 2017yinning zengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of TVDokument9 SeitenFundamentals of TVMOHAN MRIDULNoch keine Bewertungen
- T.V Engineering. Learning Outcome:: 1. Basic of Television Scanning and SynchronizingDokument7 SeitenT.V Engineering. Learning Outcome:: 1. Basic of Television Scanning and SynchronizingRuhulamin SiddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level-2 Review Question and AnswerDokument40 SeitenLevel-2 Review Question and AnswerThs TeekoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Television Simplified TV SystemDokument18 SeitenTelevision Simplified TV Systememmanuel wambuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TV PricipalsDokument38 SeitenTV PricipalsDK White LionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes TVEDokument9 SeitenNotes TVETushar MuratkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Television System ExplainedDokument15 SeitenTelevision System ExplainedNAIMUR RAHAMAN ANIK 1802104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenConsumer ElectronicsBrijesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 3Dokument17 SeitenSelvam College of Technology, Namakkal - 3Nithindev GuttikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscilloscope AssDokument10 SeitenOscilloscope Assfandu889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gyan TVEDokument7 SeitenGyan TVEGyan AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of TV (Scanning, Synchronization, Video Signals Etc.)Dokument23 SeitenFundamentals of TV (Scanning, Synchronization, Video Signals Etc.)subrata sarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Television EngineeringDokument19 SeitenTelevision Engineeringvivek186Noch keine Bewertungen
- Television and Video Engineering EC345Dokument20 SeitenTelevision and Video Engineering EC345Sreejith KunjachanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Oscilloscopes - An OverviewDokument6 SeitenSpecial Oscilloscopes - An OverviewShane LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Television & Video Engineering: by S. R. GanarDokument80 SeitenTelevision & Video Engineering: by S. R. GanarJustino Quispe RemuzgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black and White Pictures: Modern Television PracticeDokument158 SeitenBlack and White Pictures: Modern Television Practicechayan_m_shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO NotesDokument9 SeitenCRO NotesAnantha Krishnan VenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathod Ray Oscilloscopes - NotesDokument22 SeitenCathod Ray Oscilloscopes - NotesVineela ThonduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii Oscilloscopes: Department of Ece Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDokument16 SeitenUnit Ii Oscilloscopes: Department of Ece Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationNaga HimanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TV 2 Marks1Dokument13 SeitenTV 2 Marks1vlsivirusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopeDokument40 SeitenPrinciples of Measurement and Instrumentation EKT 112: OscilloscopesambavaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gmail - Cathode-Ray OscilloscopeDokument4 SeitenGmail - Cathode-Ray OscilloscopeMalaya RoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makerere University: School of EngineeringDokument5 SeitenMakerere University: School of EngineeringKasamba DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Peak, P-P Values & Frequency Using an OscilloscopeDokument4 SeitenMeasure Peak, P-P Values & Frequency Using an OscilloscopealizaranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Video Display Unit (VDU) Is One of The Two Principal Interfaces Between The UserDokument29 SeitenThe Video Display Unit (VDU) Is One of The Two Principal Interfaces Between The Userlordjebus2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - DevitracesDokument14 Seiten2 - Devitracespraveen kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Video SignalDokument17 SeitenComposite Video SignalKashyap MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medc 0503 2022-2023 Lab 2 - CroDokument10 SeitenMedc 0503 2022-2023 Lab 2 - CroLance ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASIC TV GUIDEDokument4 SeitenBASIC TV GUIDEJanielle Joy Saavedra Gregorio100% (1)
- The OscilloscopeDokument6 SeitenThe Oscilloscopesumith8550% (2)
- PartDokument12 SeitenPartsameergrover04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Systems and DevicesDokument18 SeitenElectronic Systems and DevicesSSP_BikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RGB Primaries and CCD Sensors ExplainedDokument5 SeitenRGB Primaries and CCD Sensors Explainedmhd77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Display DevicesDokument7 SeitenDisplay DevicesPramod Theghost RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication SystemsDokument16 SeitenCommunication SystemsLakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Project Topic: Function of Cro (Cathod Ray Osciiloscope) & Application of Function GeneratorDokument5 SeitenTerm Project Topic: Function of Cro (Cathod Ray Osciiloscope) & Application of Function Generatorshailesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO For First YearDokument2 SeitenCRO For First YearStudent HelperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray TubeDokument13 SeitenCathode Ray Tubehema eswaramoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit6 APDokument28 SeitenUnit6 APbikesh032Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3965 Electronic Instruments IIIT-BhDokument34 Seiten3965 Electronic Instruments IIIT-BhMani Kumar AmarlapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODERN TVDokument5 SeitenMODERN TVNurul Syafiqah Jaafar SidekNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Transmitter System: in Order To Activate The Nuclei So That They Emit A UsefulDokument8 SeitenRF Transmitter System: in Order To Activate The Nuclei So That They Emit A UsefulNoor AyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRO Bs-3rdDokument44 SeitenCRO Bs-3rdAbdur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDokument4 SeitenConstruction of Cathode Ray Oscilloscopearwin0% (1)
- Micro-Scope (Microcontrolle R Oscilloscope) : Thebeast Inc. Philippines User ManualDokument10 SeitenMicro-Scope (Microcontrolle R Oscilloscope) : Thebeast Inc. Philippines User ManualRina EllaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cro ModifiedDokument34 SeitenCro Modifiedsatya_vanapalli3422Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monochrome TV TransmissionDokument2 SeitenMonochrome TV TransmissionSam DyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sync pulse generators (SPG) explainedDokument5 SeitenSync pulse generators (SPG) explainedMcAfee UrcheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope - For TeachersDokument31 SeitenCathode Ray Oscilloscope - For TeachersRaja Inayat docsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsVon EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12Dokument12 SeitenLecture 12Mubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Pulse ModulationDokument39 SeitenCommunication Systems: Pulse ModulationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Shannon's EquationDokument9 SeitenCommunication Systems: Shannon's EquationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 25 NoiseDokument19 SeitenLecture 25 NoiseMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Random ProcessDokument40 SeitenCommunication Systems: Random ProcessMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 19 PdeDokument15 SeitenLecture 19 PdeMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Pulse Code ModulationDokument44 SeitenCommunication Systems: Pulse Code ModulationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Angle ModulationDokument14 SeitenCommunication Systems: Angle ModulationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 21 Link BuDokument17 SeitenLecture 21 Link BuMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Modulation & Its TypesDokument32 SeitenCommunication Systems: Modulation & Its TypesMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Fourier AnalysisDokument11 SeitenCommunication Systems: Fourier AnalysisMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: TelevisionDokument20 SeitenCommunication Systems: TelevisionMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Modulation & Its TypesDokument32 SeitenCommunication Systems: Modulation & Its TypesMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 B - Distortion & EqualizationDokument31 SeitenLecture 12 B - Distortion & EqualizationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Fourier SeriesDokument13 SeitenCommunication Systems: Fourier SeriesMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 13 AM DemodulationDokument6 SeitenLecture 13 AM DemodulationMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument23 SeitenLecture 1Mubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Types of SignalsDokument19 SeitenCommunication Systems: Types of SignalsMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument23 SeitenLecture 1Mubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Fourier AnalysisDokument14 SeitenCommunication Systems: Fourier AnalysisMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Complex Fourier TransformDokument10 SeitenCommunication Systems: Complex Fourier TransformMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems: Basic of SignalsDokument18 SeitenCommunication Systems: Basic of SignalsMubashir GhaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBI DCH 5200pDokument4 SeitenPBI DCH 5200pRobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- AV ConnectionsDokument21 SeitenAV ConnectionsjoewillnotbetakenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino and chipKit Universal TFT display library supported modulesDokument2 SeitenArduino and chipKit Universal TFT display library supported modulesdavid reyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Multimedia CommunicationsDokument12 SeitenIntroduction of Multimedia CommunicationshimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benq MX532Dokument1 SeiteBenq MX532Diogo RodasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCH-5200EC Professional H.264 SD/HD EncoderDokument4 SeitenDCH-5200EC Professional H.264 SD/HD Encoderdanny0702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fujifilm MX 500 FolletoDokument3 SeitenFujifilm MX 500 FolletoaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elber DataSheets CLEBER (ES)Dokument2 SeitenElber DataSheets CLEBER (ES)Alejandro Rojas SeverianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLIXDokument9 SeitenFLIXCjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- PixelDokument3 SeitenPixelSopno GhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuals For Toshiba Televisions PDFDokument2 SeitenManuals For Toshiba Televisions PDFMichael DavenportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imagine Selenio 6800 Processing and 63Dokument3 SeitenImagine Selenio 6800 Processing and 63Javier Sanchez SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDokument14 SeitenHDR10+ System Whitepaper: September 4, 2019 HDR10+ Technologies, LLCDragomir ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thinkvision T2224Da User Guide: Machine Types: 60ebDokument36 SeitenThinkvision T2224Da User Guide: Machine Types: 60ebEugene AñonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVD Player Philips DVP3260 Dvp3260 - 12 - Dfu - EngDokument47 SeitenDVD Player Philips DVP3260 Dvp3260 - 12 - Dfu - Engcostin5Noch keine Bewertungen
- HDZ408LIKVDokument3 SeitenHDZ408LIKVabderrahmane.bahakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sony x300 ManualDokument8 SeitenSony x300 ManualMarcosCanforaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farenheit 2014 Catalog LowResDokument32 SeitenFarenheit 2014 Catalog LowResJhonne TJ (TJ)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Log performSetActiveMode callsDokument3 SeitenLog performSetActiveMode callsAngela CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- JVC GD v425pzwDokument52 SeitenJVC GD v425pzwShelke DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCD TV: User ManualDokument87 SeitenLCD TV: User ManualJacq97Noch keine Bewertungen
- 24MP55HQDokument5 Seiten24MP55HQbanditman2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eaglecctv Shortform6 2012Dokument40 SeitenEaglecctv Shortform6 2012fouad althourNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCTV CameraDokument3 SeitenCCTV CameraRuchit SankhesaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claudia Lucia Cruz Torres - Ie Santa Juana de LestonacDokument22 SeitenClaudia Lucia Cruz Torres - Ie Santa Juana de LestonacAnonymous XxRSClNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kenwood KVT 910dvd, 920dvd, 930dvd, 940dvd, 960dvdDokument100 SeitenKenwood KVT 910dvd, 920dvd, 930dvd, 940dvd, 960dvdМихаил ЛапченковNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40-inch 4K LED TV with Android OSDokument1 Seite40-inch 4K LED TV with Android OSlabelelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idsb TDokument27 SeitenIdsb TAmante Rivera JrNoch keine Bewertungen