Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
EEE 4273 Slide 1
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad Wazed UllahCopyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenEEE 4273 Slide 1
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad Wazed UllahEEE 4273
Mobile Cellular Communication
3 Credits 3 hours/week
MD. AMINUL ISLAM
Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, AUST
Introduction:
Concept, evolution and fundamentals, analog and digital cellular systems.
Cellular Radio System:
Frequency reuse, co-channel interference, cell splitting and components.
Mobile Radio Propagation:
Propagation characteristics, models for radio propagation, antenna at cell
site and mobile antenna.
Frequency Management and Channel Assignment:
Fundamentals, spectrum utilization, fundamentals of channel assignment,
traffic and channel assignment.
Handoffs and Dropped Calls:
Reasons and types, forced handoffs, mobile assisted handoffs and dropped call rate.
Diversity Techniques:
Concept of diversity branch and signal paths, carrier to noise and carrier to
interference ratio performance.
Digital Cellular Systems:
Global system for mobile, time division multiple access and code division multiple
access. GSM, AMPS, GPRS, EDGE, W-CDMA, 3rd generation of mobile
communication, Packet switching and data communication
Reference books
Wireless communications : principles and
practice
By- Theodore S. Rappaport
Wireless and Cellular Telecommunications
By- William C. Y. Lee
History of mobile
communications
Before 1946, half-duplex push-to-talk telephone system with 120 KHz RF
bandwidth (per channel) was used
In 1946, first public mobile telephone was introduced in 25 major
American cities (a single high power Tx is used to cover 50 km)
In 1950, FCC (Federal Communication Commission) double the number of
channels per area with channel BW 60 KHz
By the mid 1960 FM BW of voice transmission was cut to 30 KHz
By 1976, the Bell Mobile phone service for NY city market (10,000,000
people) had only 12 channels and could serve 543 customers
There was a waiting list of 3,700 people
Service was poor due to call blocking and usage over the few channels
History of mobile
communications
During 1950 to 1960, AT&T Bell Laboratories and other telephone
companies developed the theory and techniques of cellular radiotelephony
The idea is a subscriber will carry a small-sized Tx-Rx with an assigned RF
channel through which PSTN subscriber can call mobile subscriber and vice-
versa
In 1973 17th October, Dr. Martin Cooper patent to Motorola for radio
telephone system. Today this cell phone is the enlarge version of this
technology and he is the father of cell phone.
In 1st May of 1974 FCC took a step to establish spectrum of 115 MHz
wavelengths (2300 channels used for cellular phone service)
History of mobile
communications
Following table can give clear conception on cellular Ph. Initialization:
Year Events
May 1978 First cellular phone was marketed in Bahrain
July 1978 Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) start in NA by AT&T and
Bell system joint venture
December, Started in Tokyo, Japan and within 5 years whole country
1979
1983 Aurora 400 system introduced instead of AMPS . Next NMT
(Nordic Mobile Telephone) tech. was introduced
Later TACS (Total Access Comm. Sys.) C-Netz, Radicom-2000,
RTMI, RTMS technologies were used for mobile comm. Now
more sophisticated technology is used throughout the whole
world.
EEE 4273
Mobile Cellular Communication
Lecture 1
Classification of mobile cellular communication system
o 1G (1st generation,analog,1982+)
AMPS,NMT,TACS.
o 2G (2nd generation, digital,1992+,9.6-14.4kbps)
GSM, D-AMPS(IS-136),CDMA 1x(IS-95A).
o 2.5G (Intermediate multimedia, 2001+,57.6-171kbps)
HSCSD, IS-95B, GPRS
o 2.75 ( Intermediate multimedia+, packet switched network for data,2003+,384-553Kbps)
EDGE(E-GPRS),CDMA 2000 1x RTT(144kbps)
o 3G (Multimedia, 2004+, 2Mbps)
UMTS (WCDMA), CDMA 2000 3x RTT, CDMA 1x EV/DO/DV.
o 3.5G+(High speed Multimedia, all IP network 2006+, 10mbps+)
HSDPA,HSUPA,HSPA,UMB
o 4G (Ultimate multimedia, 2010+,1Gbps)
LTE(Long Term Evolution)
Evolution path for different technology
Evolution of GSM
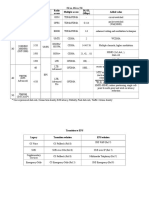
Comparative study of various cellular technologies
Features Spectrum
Channel/ Carrier
Voice per FDMA
Up Down
Channel Band
Channel(slot)
No. of FDMA
Modulation
Technology
Gen. Link Link
Additional
width(Hz)
Data rate
Remarks
Example
(MHz) (MHz)
Time/
Place
1G AMPS 1982 FDMA FM 824- 869-894 30K 25M/30 1 N/A Ckt switching
/US /FDD 849 K =833
2G GSM 1992/ FDMA GMSK 890- 935- 200K 125 8 9.6K Ckt switching
Europe +TDMA 915 960
/FDD
2G IS-95A 1992 FDMA OQPSK 824- 869-894 1.25M 20 64 14.4k Ckt switching
/US +CDMA 849
/FDD
2.5G HSCSD 2001/ FDMA GMSK 890- 935- 200K 125 8 57.6K 1.Ckt switching.
Europe +TDMA 915 960 (=14.4k 2.GSM+ new SW
/FDD /slotX at BTS only.
4slot) 3.Requires new
Handset
2.5G GPRS 2001/ FDMA GMSK 890- 935- 200K 125 8 171.2K 1. Ckt + Pkt
Europe +TDMA 915 960 (=21.4k switching.
/FDD /slot X 2. GSM+ new
8slot) SW +new
Hardware for
packet data.
3.Requires new
Handset
2.75G EDGE 2003/ FDMA 8PSK 890- 935- 200K 125 8 553K 1. Ckt + Pkt
Europe +TDMA 915 960 (=69.2k switching.
/FDD /slot X 2. GSM+ new
8slot) SW +new
Hardware for
packet data.
3.Requires new
Handset
3G UMTS 2004+/ FDMA+ QPSK 880- 925- 5M 7 128 2 Mbps 1. Ckt + Pkt
Europe WCDMA 915 960 switching.
/FDD 2. Completely
new setup+ new
SW +new
Hardware for
packet data.
3.Requires new
Handset
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Wireless Communications Systems OverviewDokument101 SeitenWireless Communications Systems OverviewAnushka PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC-CDMA Technology and ApplicationsDokument71 SeitenMC-CDMA Technology and ApplicationsNaresh TeresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Wireless Mobile Communication: 3G 3.9G (High Speed Data) 4G (Very High Speed Data)Dokument20 SeitenEvolution of Wireless Mobile Communication: 3G 3.9G (High Speed Data) 4G (Very High Speed Data)malli gaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument77 SeitenMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsBenin06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksDokument53 SeitenSoft Handover For 3G WCMDA NetworksNoilalam100% (2)
- Mobile phone subscribers worldwide development and GSM overviewDokument13 SeitenMobile phone subscribers worldwide development and GSM overviewYugandhara RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOBILE TELECOM SYSTEMDokument76 SeitenMOBILE TELECOM SYSTEMRethina Sabapathi PandiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksDokument102 SeitenEEE 264-5: 3G Wireless NetworksSundus AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument91 SeitenMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsgskaswinthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture2 Intro Mobiel Generations UMS 2021 Last v3Dokument81 SeitenLecture2 Intro Mobiel Generations UMS 2021 Last v3بليغ عبدالله صبريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sysc5608 CellularEvolution 2Dokument1 SeiteSysc5608 CellularEvolution 2Shubham VarshneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To GSMDokument52 SeitenIntroduction To GSMapi-3717973100% (2)
- WCDMADokument2 SeitenWCDMAshayan_2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- All About: Ferdinand AguilarDokument32 SeitenAll About: Ferdinand AguilarBong AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System of Mobile Communications (GSM)Dokument24 SeitenGlobal System of Mobile Communications (GSM)Sunny SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPL476 Mobile Networks Fall 2009: Cellular Telephony Architectures Instructor: Dr. Vasos VassiliouDokument71 SeitenEPL476 Mobile Networks Fall 2009: Cellular Telephony Architectures Instructor: Dr. Vasos Vassiliourtamrakar53Noch keine Bewertungen
- LTEDokument6 SeitenLTEDereje FelekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTEDokument6 SeitenLTEDereje FelekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Iii Wireless Telecommunication Systems: GSM, GPRS, Umts, Satellite Systems, GPS, Lte/Wimax 2G, 3G, 4GDokument93 SeitenUnit-Iii Wireless Telecommunication Systems: GSM, GPRS, Umts, Satellite Systems, GPS, Lte/Wimax 2G, 3G, 4GMerlin Linda GNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMO Antenna System EvolutionDokument57 SeitenMIMO Antenna System EvolutionArshwin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to 3G-WCDMA: Evolution and ConceptsDokument58 SeitenIntroduction to 3G-WCDMA: Evolution and ConceptssmineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G TutorialDokument126 Seiten3G TutorialRajaRajan ManickamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (Wcdma) For Umts: Kari Aho Senior Research Scientist Kari - Aho@magister - FiDokument74 SeitenWideband Code Division Multiple Access (Wcdma) For Umts: Kari Aho Senior Research Scientist Kari - Aho@magister - FiIman El HilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome TO GSM OverviewDokument50 SeitenWelcome TO GSM OverviewphaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS Quick GuideDokument53 SeitenUMTS Quick GuideHashem AllahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMOS - Power - Amplfiers (Gray&Niknejad)Dokument110 SeitenCMOS - Power - Amplfiers (Gray&Niknejad)Ahmed KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Tutorial1Dokument74 Seiten3G Tutorial1asdg95919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument74 SeitenMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsRAJESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument74 SeitenMobile Communications Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsUma TamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G 3GDokument6 Seiten2G 3GrogertehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5G Wireless Network Planning Introduction - KSDokument37 Seiten5G Wireless Network Planning Introduction - KStizmail100% (1)
- Wireless Communications and NetworksDokument201 SeitenWireless Communications and Networksrasool5711Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument108 SeitenMobile Communications: Chapter 4: Wireless Telecommunication Systemsradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RFIC Design Guide: LNA TopologiesDokument71 SeitenRFIC Design Guide: LNA TopologiesPascole MkobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umts Overview Eğitimi PDFDokument77 SeitenUmts Overview Eğitimi PDFYahya Hasan Uğur YazganNoch keine Bewertungen
- LactureDokument39 SeitenLactureapi-3831940Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To GSM: Cellular MobileDokument52 SeitenIntroduction To GSM: Cellular MobileShylaja HalageriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konsep Kanal Fisik Dan Logik Pada GSM PDFDokument34 SeitenKonsep Kanal Fisik Dan Logik Pada GSM PDFWaluyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G Basics: GSM Fundamentals ExplainedDokument192 Seiten2G Basics: GSM Fundamentals ExplainedbisibamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Wireless and Mobile Communication?Dokument21 SeitenWhat Is Wireless and Mobile Communication?nabilahnazromNoch keine Bewertungen
- C04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemsDokument98 SeitenC04-Wireless Telecommunication SystemsGrace KaslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications: Lecturer: Michael O'GradyDokument54 SeitenMobile Communications: Lecturer: Michael O'GradyNayansi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Po MobilfunkDokument1 SeitePo MobilfunkwagnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3gseminar Omcekm PDFDokument162 Seiten3gseminar Omcekm PDFAnoop K JayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G 4G 5G: A Guide to Mobile Network GenerationsDokument2 Seiten3G 4G 5G: A Guide to Mobile Network GenerationsipapathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Third Generation" Redirects Here. For Third-Generation Immigrants, SeeDokument9 Seiten"Third Generation" Redirects Here. For Third-Generation Immigrants, SeeMayank BanthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument72 SeitenUnit 1Hdks VajshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Tips On WCDMA Measurements: MT8222A MS272xBDokument6 SeitenPractical Tips On WCDMA Measurements: MT8222A MS272xBarcimagNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc OrangeDokument126 Seiten3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc Orangesrinivm50Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc OrangeDokument126 Seiten3G Tutorial: Brough Turner & Marc OrangeWaheed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4G Lte: Vivek Datar, Anand Jayaraman, David MindelDokument84 Seiten4G Lte: Vivek Datar, Anand Jayaraman, David MindelAlemseged HabtamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communications GuideDokument33 SeitenMobile Communications Guidekarlo_stuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Kaydian Johnson MIS Yr 1/ STR 2Dokument6 SeitenName: Kaydian Johnson MIS Yr 1/ STR 2clintionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile telecom system development historyDokument2 SeitenMobile telecom system development historyradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ora000004 Cdma2000 Principle Issue4.0Dokument106 SeitenOra000004 Cdma2000 Principle Issue4.0wael kubbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSMDokument186 SeitenGSMriboy77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayVon EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksVon EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Thesis ContentsDokument11 SeitenThesis ContentsMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus3 Bus1 01Dokument3 SeitenBus3 Bus1 01Muhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Muhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WordsDokument2 SeitenWordsMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus3 Bus1 01Dokument3 SeitenBus3 Bus1 01Muhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greco Buddhism WikipediaDokument80 SeitenGreco Buddhism WikipediaMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi Sultanate - WikipediaDokument101 SeitenDelhi Sultanate - WikipediaMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Constant For RC CircuitsDokument3 SeitenTime Constant For RC CircuitsMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument64 SeitenSyllabusMuhammad Wazed UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP Airtel TDD LTE 2355 2376895 AMD568 BSNL UMTS 2100 BBReport PDFDokument9 SeitenSP Airtel TDD LTE 2355 2376895 AMD568 BSNL UMTS 2100 BBReport PDFRavi ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Glazings: Standard Test Method ForDokument8 SeitenElectromagnetic Shielding Effectiveness of Glazings: Standard Test Method ForAlevj DbNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF TXDokument15 SeitenHF TXMuhammad Sharif JanjuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sajid Khan RF Field Optimizer CCS InternationalDokument38 SeitenSajid Khan RF Field Optimizer CCS InternationalFakhar Muhammad Hussain NaqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G 3G Interview QuestionsDokument10 Seiten2G 3G Interview Questionsmohnish1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3GPP TS 38.215Dokument15 Seiten3GPP TS 38.215AhmedMa'moonNoch keine Bewertungen
- FYP Thesis LastDokument48 SeitenFYP Thesis LastImtiaz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antena FA2BA Minimacro FW2PCDokument3 SeitenAntena FA2BA Minimacro FW2PCMatias FabroniNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Radio Frequency Allocation ChartDokument1 SeiteUnited States Radio Frequency Allocation ChartJason Bentley100% (2)
- Random Tales Mobile HackerDokument58 SeitenRandom Tales Mobile HackerJonel Kay HowardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vista 128 FBP PDFDokument4 SeitenVista 128 FBP PDFGustavo CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAN Power Control Feature DescriptionDokument76 SeitenRAN Power Control Feature DescriptionAnonymous g8YR8b9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bluetooth Basics ExplainedDokument4 SeitenBluetooth Basics ExplainedRaj VenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mimosa by Airspan B11 Datasheet DS 0007 04Dokument2 SeitenMimosa by Airspan B11 Datasheet DS 0007 04Jeferson TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furuno VHF Radio Telephone External PhotosDokument109 SeitenFuruno VHF Radio Telephone External PhotosRafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kirisun PT8100-Service-ManualDokument35 SeitenKirisun PT8100-Service-ManualRobertino100% (1)
- BlakeDokument5 SeitenBlakeRiza May BaisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajebush Tikuye PDFDokument64 SeitenAjebush Tikuye PDFgebreyesusweldegebrialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Massive Mimo and Beamforming The Signal Processing Behind The 5g BuzzwordsDokument5 SeitenMassive Mimo and Beamforming The Signal Processing Behind The 5g BuzzwordsEduardo JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keysight X-Series RELEASE NOTESDokument107 SeitenKeysight X-Series RELEASE NOTESlauguicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50mW BH1417 Stereo PLL FM TransmitterDokument5 Seiten50mW BH1417 Stereo PLL FM TransmitterMaster SajithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems 5G IndiaDokument5 SeitenProblems 5G IndiaRajendra DulalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The SAR Handbook Chp2ContentDokument24 SeitenThe SAR Handbook Chp2ContentCentro GeomaticaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en 13757-4 PDFDokument41 SeitenBS en 13757-4 PDFdbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microwave Radio Link Design GuideDokument8 SeitenMicrowave Radio Link Design GuideTejas RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- R3 AIS Vessel Transponder For Universal AIS: Universal Ship-Borne Automatic Identification System - Universal AISDokument2 SeitenR3 AIS Vessel Transponder For Universal AIS: Universal Ship-Borne Automatic Identification System - Universal AISJerry LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipefinder1 PDFDokument1 SeitePipefinder1 PDFhawggy60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bridgemaster E Radar Fault Reporting and First Line Servicing Ship'S ManualDokument240 SeitenBridgemaster E Radar Fault Reporting and First Line Servicing Ship'S ManualqwpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Broadband MIMO-OFDM Wireless CommunicationsDokument10 SeitenProject Report On Broadband MIMO-OFDM Wireless CommunicationsPreetam PolakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2P 2L C1 Product SpecificationsDokument4 Seiten2P 2L C1 Product SpecificationsAbi Agung EnjiniaNoch keine Bewertungen