Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Resource 3 Resource 1: Population Dynamics
Hochgeladen von
Kazuma SatouOriginaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenResource 3 Resource 1: Population Dynamics
Hochgeladen von
Kazuma SatouAnthony Martin P.
Navarez
Resource 1 Resource 3
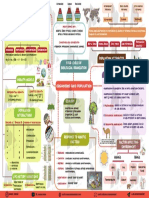
CONCEPTS DEMOGRAPHY IMPORTANCE TYPES OF POPULATIONS
* Population Birth Conservation FACTORS SEMELPAROUS ITEROPAROUS
* Population Immigration Control REPRODUCTIVE PERIOD ONCE SEVERAL
Dynamics Emigration Maintaining
Death AGE STRUCTURE ABSENT PRESENT
OFFSPRING COUNT LARGE AT MOST 10
EXAMPLES RICE MAMMALS
ECOLOGICAL PERIODS MEASURES AGAINST OVERPOPULATION
(cause: Biotic potential) (cause: Environmental resistance) Pre-reproductive (0-14 yrs) raising the reproductive period to 25 yrs
Carrying capacity Reproductive (14-49 yrs) lowering the Total Fertility Rate through
Post-reproductive (<49 yrs) economic development and reproductive
death THE PHILIPPINE POPULATION health programs
log
stationary approx. 106M (2016) aim for Zero Population Growth
high population growth affects
lag economic and ecologic
exponential growth logistic growth development
POPULATION
DYNAMICS
LIFE TABLES
SURVIVOR MORTALITY DENSITY-DEPENDENT FACTORS DENSITY-INDEPENDENT FACTORS
AGE DEATH - affects the per capita growth rates - affects the per capita growth rates
COUNT RATE
as population changes; biotic in regardless of its population
0-3 yrs 1000 15 0.015 nature - may lead to erratic, abrupt changes
- may lead to a logistic pattern of in population
3-5 YRS 985 48 0.49
growth Example:
Examples: natural disasters
SURVIVORSHIP CURVES AGE-SEX PYRAMID
predation
type I age disease and parasites (cyclical oscillations)
type II
survivors
population
CONCEPTS
type III * Population Fluctuations
* Population Cycles
life expectancy
time
Resource 2 Resource 4
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Genetic Drift Simulation AnalysisDokument6 SeitenGenetic Drift Simulation AnalysisTiffanie100% (3)
- Virtual Simulation Natural SelectionDokument6 SeitenVirtual Simulation Natural Selectionapi-38237256480% (5)
- Geofile Stage 5Dokument4 SeitenGeofile Stage 5reservoirgeogsNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 5 Human Ecology and SucessionDokument28 SeitenGROUP 5 Human Ecology and SucessionDeniebev'z OrillosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Don't Panic: The Truth about World Population GrowthDokument5 SeitenDon't Panic: The Truth about World Population GrowthKRISTINEIVY CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roland Berger Trend - Compendium - 2050 - enDokument62 SeitenRoland Berger Trend - Compendium - 2050 - enFredyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEE REVDokument7 SeitenPEE REVAeiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer BiologyDokument25 SeitenReviewer Biologyyumi timtimNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Transisi EpidemiologyDokument78 SeitenA Transisi EpidemiologyVasthu Broto Ariyo100% (1)
- Global population trends and food securityDokument4 SeitenGlobal population trends and food securityRenz VizcondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 5 PopulationsDokument52 SeitenBiology Chapter 5 PopulationsLesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Relation With Other DisciplinesDokument2 SeitenPopulation Relation With Other DisciplinesGuang ZuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mind Mapping Population Dynamics ConceptDokument1 SeiteMind Mapping Population Dynamics ConceptQUEEN OF QUEENSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Longevity Among Hunter-GatherersDokument46 SeitenLongevity Among Hunter-GatherersTomasz IgnasiakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - CPH LectureDokument4 SeitenChapter 4 - CPH LectureMarichris CabanitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20171114161157topic 3 Biotic Factors - Population Dynamics and Behavioral AdaptationsDokument42 Seiten20171114161157topic 3 Biotic Factors - Population Dynamics and Behavioral AdaptationsMizsarah Siti SarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCW NotesDokument7 SeitenTCW NotesCatherine AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population ecology and community structureDokument82 SeitenPopulation ecology and community structureRizky Achmad KurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 Population Properties and Dynamics BWDokument69 SeitenLecture 7 Population Properties and Dynamics BWPeter JimenezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Populations: More Free Powerpoints atDokument18 SeitenPopulations: More Free Powerpoints atmisterbrowner@yahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population and Migration - Revision PlacematDokument1 SeitePopulation and Migration - Revision PlacematGaming TriadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 1 - Ecology Slide 2Dokument23 SeitenBio 1 - Ecology Slide 2Matthew LimboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2.2 Population EcologyDokument6 SeitenChapter 2.2 Population EcologyNur HananiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd AssignmentDokument2 Seiten2nd AssignmentRabab IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 PopulationsDokument2 SeitenUnit 6 Populationsapi-332813379Noch keine Bewertungen
- Population and Migration Patterns PDFDokument1 SeitePopulation and Migration Patterns PDFRuryk KowaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B13 Organisms and Population.Dokument1 SeiteB13 Organisms and Population.lakshya singhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bocquet-AppelScience When The World's Population Took OffDokument3 SeitenBocquet-AppelScience When The World's Population Took OffagnesrodolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Biological PopulationsDokument9 SeitenDynamics of Biological Populationsits mitziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tel 2b-The Human Population and The EnvironmentDokument6 SeitenTel 2b-The Human Population and The EnvironmentJaymel ZamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 - Population - Ecology - Pyramids - 2020 PDFDokument20 SeitenG10 - Population - Ecology - Pyramids - 2020 PDFmr____stuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 19 PopulationsDokument12 SeitenTopic 19 PopulationsareenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Population iGCSEDokument5 Seiten1 - Population iGCSEAndy FunnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asas Dan Konsep Ekosistem - Kuliah 1Dokument20 SeitenAsas Dan Konsep Ekosistem - Kuliah 1DwiMariaUlfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Population Growth & Exponential GrowthDokument9 SeitenFactors Affecting Population Growth & Exponential GrowthTrenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Ecology 52Dokument59 SeitenPopulation Ecology 52rosalyn sugayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rai - 2003. Minimum Sizes For Viable Population and Conservation BiologyDokument7 SeitenRai - 2003. Minimum Sizes For Viable Population and Conservation BiologyELIANA VANESA CASTAÑO DOMINGUEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do Populations Change In: Size?Dokument1 SeiteDo Populations Change In: Size?Muh HaidirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demographic Transition Model: Presented by Arpita KaushikDokument11 SeitenDemographic Transition Model: Presented by Arpita KaushikArpita KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology of Populations Population PropertiesDokument21 SeitenEcology of Populations Population PropertiesM PilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSCI 111 Explores Human Population Growth in AfricaDokument7 SeitenNSCI 111 Explores Human Population Growth in AfricaHiroshi MatsushimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Patterns and ProcessesDokument15 SeitenPopulation Patterns and ProcessesStephanie Gregorio ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Explosion Rabab SinghDokument14 SeitenPopulation Explosion Rabab SinghREHEB SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological annihilation via ongoing sixth mass extinctionDokument8 SeitenBiological annihilation via ongoing sixth mass extinctionArthur FilipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology of Populations: PopulationDokument23 SeitenEcology of Populations: PopulationJÜnn BatacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demography: Basic PrinciplesDokument45 SeitenDemography: Basic PrinciplesSharmila HemalathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - DTM Animation (Old)Dokument4 Seiten4 - DTM Animation (Old)Adam ProctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population DynamicDokument19 SeitenPopulation DynamicDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review: Ecological PyramidDokument63 SeitenReview: Ecological PyramidDarryl Faith RuinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson TwoDokument22 SeitenLesson TwoPaulo Victor SazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ScienceDokument2 SeitenEnvironmental Sciencegatuslao micaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical study of human population trends and demographicsDokument32 SeitenStatistical study of human population trends and demographicskaren marie dela pasionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breu 10.2 Extinciones IIDokument36 SeitenBreu 10.2 Extinciones IIEloysa LechowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FFB-311-L3,4 & 6 (Popl - GCurve)Dokument16 SeitenFFB-311-L3,4 & 6 (Popl - GCurve)joshigautaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3 ENVI SCIDokument24 SeitenGroup 3 ENVI SCIJose mar m. RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Populationecology 131014045901 Phpapp02Dokument32 SeitenPopulationecology 131014045901 Phpapp02rkskrrskrrsol15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 DemographicsDokument6 SeitenLesson 1 DemographicsKrixie Lagundi100% (1)
- HUMAN POPULATION and THE ENVIRONMENTDokument4 SeitenHUMAN POPULATION and THE ENVIRONMENTRonan FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demographics - Census and Its FeaturesDokument71 SeitenDemographics - Census and Its Featuresmnadimbashir13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2 Report in Science Module 7Dokument37 SeitenGroup 2 Report in Science Module 7johnrichcapiloyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative EcologyDokument123 SeitenQuantitative EcologyKrishnan JeevanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Master: Life SciencesDokument8 SeitenStudy Master: Life SciencesKeana AprilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources and Methods of Historical Demography: Studies in Social DiscontinuityVon EverandSources and Methods of Historical Demography: Studies in Social DiscontinuityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative GeneticsDokument27 SeitenQuantitative GeneticsCapitán NemoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Spatial Development and Land Use in Beijing Implications From London's ExperiencesDokument16 SeitenUrban Spatial Development and Land Use in Beijing Implications From London's ExperiencesChandra Egy SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Potential Transit-Oriented Development Stations Along Addis Ababa's LRTDokument17 SeitenDetermining Potential Transit-Oriented Development Stations Along Addis Ababa's LRTHerland MalauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecological Footprint and Climate Change The Role of Gas Consumption in Five African Macro EconomiesDokument8 SeitenEcological Footprint and Climate Change The Role of Gas Consumption in Five African Macro EconomiesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimating Grasshopper Populations with Capture-RecaptureDokument7 SeitenEstimating Grasshopper Populations with Capture-RecaptureEmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilocos Norte Quickstat January 2015Dokument5 SeitenIlocos Norte Quickstat January 2015redNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Society: Salient Features, Diversity, Women, Population, Poverty, UrbanizationDokument5 SeitenIndian Society: Salient Features, Diversity, Women, Population, Poverty, Urbanizationpradyu1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Human SettlementDokument23 SeitenHuman Settlementapi-349709677Noch keine Bewertungen
- RSU Environmental Science SyllabusDokument8 SeitenRSU Environmental Science SyllabusMelch Champion RufonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 5 UNIT 1 Global Cities, MODULE 5 UNIT 2 Global Demography, and MODULE 5 UNIT 3 Global Migration-GonzagaDokument6 SeitenMODULE 5 UNIT 1 Global Cities, MODULE 5 UNIT 2 Global Demography, and MODULE 5 UNIT 3 Global Migration-GonzagaBSDS - 12 Gonzaga Aron J.Noch keine Bewertungen
- World Urbanization Prospects UN 2014 Full ReportDokument517 SeitenWorld Urbanization Prospects UN 2014 Full ReportotaviosbarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerPoint Maps Template by SlideLizardDokument13 SeitenPowerPoint Maps Template by SlideLizardpradeep311085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Breathing Easier in SW Detroit: Mitigating Fugitive Dust With VegetationDokument121 SeitenBreathing Easier in SW Detroit: Mitigating Fugitive Dust With VegetationStephen Boyle100% (1)
- Biology Ecology Questions (With Answer)Dokument3 SeitenBiology Ecology Questions (With Answer)Vanessa AlexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group: 3 Members: 1. Regine E. Julian 2. Riselyn Jane Jabla 3. Rhona Jane Lontayao 4. Marie Conney Lagunay 5. Silvestre DionelaDokument2 SeitenGroup: 3 Members: 1. Regine E. Julian 2. Riselyn Jane Jabla 3. Rhona Jane Lontayao 4. Marie Conney Lagunay 5. Silvestre DionelaRegine Estrada JulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wongchuig Et Al. 2016 1Dokument15 SeitenWongchuig Et Al. 2016 1huili hansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blueprint For Survival-Ecologist-1972-01Dokument48 SeitenBlueprint For Survival-Ecologist-1972-01Oscar WindsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arbler: in This Issue..Dokument12 SeitenArbler: in This Issue..Portland Audubon SocietyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resumo Texto InglesDokument18 SeitenResumo Texto InglesGiselda100% (10)
- Ernesto Serote - Dynamics of Urban Development PDFDokument30 SeitenErnesto Serote - Dynamics of Urban Development PDFsmol adlawan-margate100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDokument2 SeitenDaftar PustakaBramantiyo MarjukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al Gore, Agenda 21 and Population ControlDokument8 SeitenAl Gore, Agenda 21 and Population ControlParain100% (1)
- Hashem Al GhailiDokument5 SeitenHashem Al GhailiAmirul AsyrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 6 PopulationDokument15 SeitenChapter - 6 Populationrizwanaabegum88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impacts of Human-Wildlife Conflict in Developing C PDFDokument6 SeitenImpacts of Human-Wildlife Conflict in Developing C PDFJunaid JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measures of MigrationDokument11 SeitenMeasures of MigrationAbdisamed AllaaleNoch keine Bewertungen