Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1.1 Construction of Response Spectra
Hochgeladen von
AHMADOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.1 Construction of Response Spectra
Hochgeladen von
AHMADCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
1 Lecture 9: Construction of Response Spectra
1.1 Construction of Response Spectra
The response spectrum for a given ground motion component (e.g., a (t)) is developed using the following
steps:
(1) Obtain the ground motion (a (t)) for an earthquake. Typically the acceleration values should be defined
at time steps of 0.02 second, or less.
(2) Select the natural vibration period, 𝑇𝑛 , and damping ratio, 𝜉 , for SDOF system. (Usually 5 percent
damping is selected.)
(3) Determine the maximum displacement response for a SDOF structure with the selected percent
damping for a given period or frequency of vibration.
To do this, we must solve the following differential equation
𝑚𝑥̈ + 𝑐𝑥̇ + 𝑘𝑥 = 𝐹(𝑡)
Solution of above equation can be
(a) Closed form solution (linear systems)
Solution is only valid for initial conditions at rest
(b) Duhamel’s integral (linear systems)
Based on treating the periodic motion as a series of short impulses
(c) Frequency Domain method (linear systems)
Fourier transform
Inverse Fourier transform
(d) Numerical methods (linear and nonlinear systems)
Numerical time stepping methods (Newmark’s β method, Wilson-θ method etc.)
(4) Repeat step 3 and vary the fundamental period of the structure by changing the mass (m), the stiffness
(k), or both. Plot the new results.
CE-445N Elements of Earthquake and Wind Engineering Dr. Moonis Zaheer
2
(5) Calculate the other pseudo spectral velocity values using:
𝑉 = 𝜔𝐷
(6) Calculate the pseudo acceleration response values from:
Maximum Pseudo Acceleration (g)
𝐴 = 𝜔2 𝐷
It is common to express 𝐴 in units of𝑔, thus:
𝐴(𝑖𝑛 𝑔) = 𝜔2 𝐷⁄𝑔
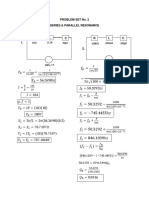
Example: To create a displacement response spectrum from Earthquake record of Imperial Valley El
Centro earthquake
First linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 100 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.32 s, f = 3.13 Hz, w = 19.65 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 0.700 inches
Second linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 50 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.45 s, f = 2.21 Hz, w = 13.89 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 1.677 inches
Third linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 25 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.64 s, f = 1.56 Hz, w = 9.82 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 3.051 inches
Fourth linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 200 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
CE-445N Elements of Earthquake and Wind Engineering Dr. Moonis Zaheer
3
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.23 s, f = 4.42 Hz, w = 27.79 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 0.359 inches
Fifth linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 400 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.16 s, f = 6.25 Hz, w = 39.30 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 0.135 inches
Sixth linear analysis
m = 100 kips; k = 1000 kips / in; c = 5 percent of critical damping
Earthquake record is Imperial Valley El Centro Record; Period = 0.10 s, f =0.259 Hz, w = 62.14 rad/s
Maximum displacement = 0.056 inches
CE-445N Elements of Earthquake and Wind Engineering Dr. Moonis Zaheer
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportVon EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vabrition DataDokument20 SeitenVabrition Datamilan44Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental of VrsDokument20 SeitenFundamental of VrsgirisanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesVon Everand3D Modeling of Nonlinear Wave Phenomena on Shallow Water SurfacesNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Practical ReportDokument11 SeitenMy Practical Reportironmyan18Noch keine Bewertungen
- High-Speed Imaging of Dynamic Shock Wave Reflection PhenomenaDokument11 SeitenHigh-Speed Imaging of Dynamic Shock Wave Reflection Phenomenaahajiali2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Damping Lab 1Dokument60 SeitenDamping Lab 1Robert Lau Yik SiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seakeeping ExercisesDokument26 SeitenSeakeeping ExercisesRaniero FalzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES Chapter 1 AC FundamentalsDokument23 SeitenNOTES Chapter 1 AC FundamentalsShaina MabborangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Sheet 1 Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation Due Date On or Before 16/09/2014 Problems Based On Chap 3 - DynamiccharactersticsDokument3 SeitenAssignment Sheet 1 Mechanical Measurements and Instrumentation Due Date On or Before 16/09/2014 Problems Based On Chap 3 - DynamiccharactersticsJim HarrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Engineering Activity 3Dokument3 SeitenVibration Engineering Activity 3Ace Heart Rosendo AmanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 13 Simple Harmonic MotionDokument78 SeitenLesson 13 Simple Harmonic MotionGLoria, Danica Joy A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Time Domain Simulation of Jack-Up Dynamics Witli The Extremes of A Gaussian ProcessDokument5 SeitenTime Domain Simulation of Jack-Up Dynamics Witli The Extremes of A Gaussian ProcessAndyNgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Midterm 2012Dokument2 SeitenVibration Midterm 2012Aravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Investigation of The PlungeDokument22 SeitenExperimental Investigation of The PlungePrakash Duraisamy CITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Midterm 2012Dokument2 SeitenVibration Midterm 2012Aravind KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of Design Response Spectrum - The Chilean Way: EPS 256 Rodrigo MusicDokument25 SeitenConstruction of Design Response Spectrum - The Chilean Way: EPS 256 Rodrigo MusicShrishail SambanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computation of Earthquake Response SpectrumDokument33 SeitenComputation of Earthquake Response SpectrumAngela100% (1)
- Chapter 14 SlidesDokument40 SeitenChapter 14 SlidessuperwebonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Gravity: The Universal Electrogravitational Quantum Frequency of The UniverseDokument15 SeitenQuantum Gravity: The Universal Electrogravitational Quantum Frequency of The UniverseAJ AbracosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Department Mechanical Vibration (Met-351) Tutorial 1Dokument15 SeitenMechanical Engineering Department Mechanical Vibration (Met-351) Tutorial 1Aakash SinglaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.5 Rating Power Systems For Earthquake Safety: 4.5.1 General PrinciplesDokument14 Seiten4.5 Rating Power Systems For Earthquake Safety: 4.5.1 General PrinciplesNur FajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument10 SeitenLab Reportajay shresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics Department B.E-Sem.-Vi - Earthquake Engineering (160605) ASSIGNMENT - 3: Structural Dynamics (Module I)Dokument3 SeitenApplied Mechanics Department B.E-Sem.-Vi - Earthquake Engineering (160605) ASSIGNMENT - 3: Structural Dynamics (Module I)archan_daveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units: Basic MathematicsDokument38 SeitenUnits: Basic MathematicsGraham MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Response SpectrumDokument29 SeitenResponse SpectrumKhalid WaziraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Design Equipment SupportsDokument7 SeitenEarthquake Design Equipment Supportsmseif1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sdan 0025-0158 CDokument134 SeitenSdan 0025-0158 CGis7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 06bDokument2 SeitenAssignment 06bDhiraj NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getaran Lec1Dokument23 SeitenGetaran Lec1AzrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 H2 Physics Prelim Exams (9745) Suggested SolutionsDokument4 Seiten2009 H2 Physics Prelim Exams (9745) Suggested SolutionsnasyrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 222 Spring 2009 PDFDokument363 Seiten222 Spring 2009 PDFcombatps1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises Seismic Methods: 1 Elements of Seismic SurveyingDokument6 SeitenExercises Seismic Methods: 1 Elements of Seismic SurveyingAltin KarriqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 105 Waves and Oscillation PDFDokument147 SeitenPHY 105 Waves and Oscillation PDFGlitchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floating Wind Turbine Motion Assessment: Numerical Simulation Results Compared To Model Test MeasurementsDokument10 SeitenFloating Wind Turbine Motion Assessment: Numerical Simulation Results Compared To Model Test MeasurementsRahil KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics Laboratory: Project ReportDokument10 SeitenStructural Mechanics Laboratory: Project ReportJayanth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-1 Single-Degree-Of-Freedom Linear Systems: Part - B (Long Answer Questions)Dokument6 SeitenUNIT-1 Single-Degree-Of-Freedom Linear Systems: Part - B (Long Answer Questions)USERANoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch6 Statics 2014Dokument10 SeitenCh6 Statics 2014tarek mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Fluid MechanicsDokument12 SeitenHeat Transfer Fluid MechanicsKieran YeowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SheetsDokument11 SeitenTutorial SheetsKAMARAJU SAI VAMSHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Hwa 2Dokument10 SeitenHwa 2imryuk19Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Review QuestionsDokument49 SeitenAnswers To Review QuestionsAfzalZubir85% (13)
- Time Domain Simulation of Jack-Up Dynamics Witli The Extremes of A Gaussian ProcessDokument5 SeitenTime Domain Simulation of Jack-Up Dynamics Witli The Extremes of A Gaussian ProcessMoe LattNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 19Dokument18 SeitenCH 19Dr. Rama Raju KunadharajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerometer PrinciplesDokument5 SeitenAccelerometer PrinciplesJosé ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 3 07102010 Answers.257Dokument7 SeitenExercise 3 07102010 Answers.257Emmanuel PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 14Dokument13 SeitenLec 14RUCHIRA KUMAR PRADHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Vibration Is Defined As A Temporarily Sustained Vibration of ADokument6 SeitenTransient Vibration Is Defined As A Temporarily Sustained Vibration of AsdfohfsioHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Post Stack InversionDokument174 Seiten2 Post Stack Inversionsantosmonetta2100% (2)
- MIT Aircraft Stability and Control 02 - AssignmentsDokument14 SeitenMIT Aircraft Stability and Control 02 - AssignmentsAndré Da Luz MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 Computing The Planck FunctionDokument4 Seiten00 Computing The Planck FunctionClaudio TesserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 CE532Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 CE532kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Nov Dec 2018Dokument32 SeitenQuestion Paper Nov Dec 2018VICTORYSUBIKSHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Class XI Notes - Ch-14 and CH - 15Dokument11 SeitenPhysics Class XI Notes - Ch-14 and CH - 15workforadynamichamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- FILE0032Dokument85 SeitenFILE0032MEOW41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forced Oscillations Lab Report Draft 1Dokument13 SeitenForced Oscillations Lab Report Draft 1Praveen Dennis XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Eective Number of Cycles of Earthquake Ground Motion: Jonathan Hancock and Julian J. BommerDokument28 SeitenThe Eective Number of Cycles of Earthquake Ground Motion: Jonathan Hancock and Julian J. Bommerjuan muneraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limitation Imposed On Structural DesignerDokument2 SeitenLimitation Imposed On Structural DesignerdvarsastryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems 1Dokument11 SeitenProblems 1LogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSNL Summer Traning ReportDokument39 SeitenBSNL Summer Traning ReportMohd MunzirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Manual: REJ09B0261-0100Dokument1.692 SeitenHardware Manual: REJ09B0261-0100Ferdinand KlautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Browserstack Test PDFDokument2 SeitenBrowserstack Test PDFnavinkumargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me2 Installation Guide PDFDokument4 SeitenMe2 Installation Guide PDFJojo LeaonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIS AssignmentDokument3 SeitenMIS Assignmentsparepaper7455Noch keine Bewertungen
- SSA TrainingDokument48 SeitenSSA TrainingStats TutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duckademy LFI-RFI How LFI and RFI WorkDokument42 SeitenDuckademy LFI-RFI How LFI and RFI WorkKlentiB.ÇukariNoch keine Bewertungen
- bc817, bc818 FairchildDokument6 Seitenbc817, bc818 FairchildCarlos EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poly Matla BBDokument2 SeitenPoly Matla BBdandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niladri - Ganguly New BioDokument3 SeitenNiladri - Ganguly New Biohresab_banerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP Sound Conexant 14062 DriversDokument242 SeitenDP Sound Conexant 14062 DriversRamesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set No.2 SolutionDokument9 SeitenProblem Set No.2 SolutionAshley Quinn MorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 5Dokument6 SeitenLab Manual 5Nasr UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 174872-Report On Voice Enabled Enterprise ChatbotDokument61 Seiten174872-Report On Voice Enabled Enterprise ChatbotBalaji GrandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RobotStudio Simulation of Industrial PDFDokument140 SeitenRobotStudio Simulation of Industrial PDFcabecavil100% (1)
- Upload 1 Document To Download: Kill Team 2021 - Core BookDokument4 SeitenUpload 1 Document To Download: Kill Team 2021 - Core BookgoneoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Threat Analysis ReportDokument18 SeitenThreat Analysis Reporttodo nothingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Quarter Exam in Math9Dokument3 Seiten1st Quarter Exam in Math9Robert Jay Mejorada100% (4)
- Industrial Hygiene Air SamplingDokument8 SeitenIndustrial Hygiene Air SamplingMiguel Gonzalez SaborioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Go HackersDokument23 SeitenPython Go HackersAdaAdaAjeChanel33% (3)
- Design and Analysis of Manually Operated Floor Cleaning MachineDokument4 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Manually Operated Floor Cleaning MachineAnonymous L9fB0XUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feature Evaluation For Web Crawler Detection With Data Mining TechniquesDokument11 SeitenFeature Evaluation For Web Crawler Detection With Data Mining TechniquesSlava ShkolyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CsoundDokument238 SeitenCsoundorchestration100% (1)
- MATLAB and Simulink: Prof. Dr. Ottmar BeucherDokument71 SeitenMATLAB and Simulink: Prof. Dr. Ottmar BeucherShubham ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Apple Watch Series 9 and Apple Watch Ultra 2Dokument9 SeitenIntroducing Apple Watch Series 9 and Apple Watch Ultra 2soniarivera6036Noch keine Bewertungen
- m4s BrochureDokument8 Seitenm4s BrochureAnderson José Carrillo NárvaezNoch keine Bewertungen
- WoodwardCatalog PDFDokument48 SeitenWoodwardCatalog PDFJul Cesar100% (1)
- AcanDokument36 SeitenAcanAlberto Ramon EspinolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors 09 07431 PDFDokument14 SeitenSensors 09 07431 PDFFamiloni LayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDokument2 SeitenComputer Integrated ManufacturingDhiren Patel100% (1)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (812)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsVon EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldVon EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (595)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutVon EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (142)
- The Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Von EverandThe Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildVon EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (44)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsVon EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (65)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeVon EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (19)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (35)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogVon EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsVon EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (223)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorVon EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (137)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishVon EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (30)
- Microscopy of Numerology: Numerology SimplifiedVon EverandMicroscopy of Numerology: Numerology SimplifiedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateVon EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1003)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceVon EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)