Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Audit Sampling
Hochgeladen von
FarCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Audit Sampling
Hochgeladen von
FarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
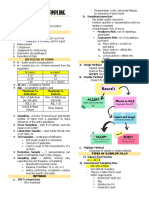
application of audit procedures to less than 1.
100% Testing
3
AUDIT SAMPLING 100% of the sample population; sample
selected is a representation of the population
Reasons: 1. Small population with large value items
2. computer performs 100% examination
cost effective
Sampling Risks – risks that a conclusions based on a sample would be different from conclusion
3. RMM are high, no sufficient evidence
based on 100% testing TERMS 2. Selecting specific items
- can be eliminated by 100% testing Population – entire set of data High value or key items
- ↑SS = ↓SR Sample – portion of population subject
All items over a certain amount
to audit testing
Items to obtain information
A lpha Risk B eta Risk
Sampling Unit – individual items
Items to test control activities
Risk of Underreliance TOC Risk of Overreliance SAMPLING TECHNIQUES
↑CR than actual CR ↓CR than actual CR Audit Procedures
1. RAP – “research” sampling 1. Random Number sampling
Risk of Incorrect Rejection ST Risk of Incorrect Acceptance 2. TOC – w/ docs sampling -assign # to every item in the population
materially misstated when not not materially misstated when it is w/o docs sampling -generate numbers
3. ST – TOD sampling
AURcy Efficiency
vs BOAness Effectiveness Sampling w/ replacement → multiple chances
AP sampling “Re-place”
additional work less audit procedures
w/o replacement → only one chance
To reduce: increase sample size 2. Systematic Sampling / Selection
use appropriate method of selecting sample items from the population -select samples based on an interval
(pattern on the population size)
Non-sampling Risks – risks of incorrect conclusion due to causes not related to SS Pop
100
every 5th item =
- cannot be eliminated SS
20
- can only be controlled by proper planning & instruction 3. Haphazard Sampling
- “conduct peer review” -select samples w/o regard for any
Human Errors particular characteristics
Inappropriate application of audit procedures -there must be proper supervision
Failure to recognize the errors 4. Block/Cluster Sampling
Misinterpretation of audit evidence -least desirable sampling technique
-select samples based on particular
SAMPLING APPROACHES Consistent characteristic
1. Statistical Sampling
↑EstPopDeviationRate = ↑SS
-uses probability theory in selecting samples + prof. judgment
-can quantify sampling risk Special Items in Sampling
-↑cost Sampling Risk ±3% a. Voided Documents (cancelled)
100 SS *if properly voided – replace w/ another
= 1000
Confidence
PopLevel ±97% sample
*if NOT properly voided – consider as
deviation
2. Non-statistical Sampling
b. Missing Documents
-uses prof. judgment only
-treat as deviations
-cannot qualify sampling risk(↑or↓ only)
AUDIT PROCEDURE (use sampling)
1. TOC – effectiveness of control
characteristic / attribute of ctrl → effective
results
missing / ineffective ctrl → not effective
violations→deviations
2. ST – detect material misstatement
fairly stated
results
materially stated
errors→misstatement
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Techniques in Wildlife Investigations: Design and Analysis of Capture DataVon EverandTechniques in Wildlife Investigations: Design and Analysis of Capture DataBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chapter 11 - Determining The Extent of TestingDokument3 SeitenChapter 11 - Determining The Extent of TestingJean GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Research 2: Sampling Size and Sampling TechniquesDokument7 SeitenPractical Research 2: Sampling Size and Sampling TechniquesJohnJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT NotesDokument4 SeitenAT NotesMei Leen DanielesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 009Dokument49 SeitenChap 009monneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample 1Dokument7 SeitenSample 1smisolesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT 211 Handout Determining The Extent of TestingDokument13 SeitenAT 211 Handout Determining The Extent of TestingJai BacalsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection and SamplingDokument13 SeitenInspection and SamplingBryan Paul50% (2)
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDokument11 SeitenLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoMae Angiela TansecoNoch keine Bewertungen
- At.3212 - Determining The Extent of TestingDokument12 SeitenAt.3212 - Determining The Extent of TestingDenny June CraususNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 FinalDokument45 SeitenChapter 7 FinalMahesh JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Sampling: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokument49 SeitenAudit Sampling: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinJulius Antonio GopitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- At114 Audit Sampling PDF FreeDokument8 SeitenAt114 Audit Sampling PDF FreeKaila SalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 10 NotesDokument3 SeitenLec 10 NotesNehal SalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scan 0116Dokument2 SeitenScan 0116Hazem El SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acceptance SamplingDokument22 SeitenAcceptance SamplingAby MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 05 Statistical Quality Control: Prof N D Sadaphal Mechanical Engg. DepartmentDokument42 SeitenUnit 05 Statistical Quality Control: Prof N D Sadaphal Mechanical Engg. DepartmentAbhijeet RandhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- APP006 REVIEWER HotdogDokument6 SeitenAPP006 REVIEWER HotdoglopezorateangelitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling 1Dokument59 SeitenSampling 1Anonymous mzuRnewGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roque Quick Auditing Theory Chapter 8 PDFDokument47 SeitenRoque Quick Auditing Theory Chapter 8 PDFSherene Faith Carampatan100% (2)
- Sampling Techniques: Dr. MadhumithaaDokument59 SeitenSampling Techniques: Dr. MadhumithaaPraveen Kumar MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisa NotesDokument2 SeitenCisa Notesesskae59mNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT - Chapter 10-Notes - Part 1Dokument3 SeitenAT - Chapter 10-Notes - Part 1hoxhiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection and SamplingDokument2 SeitenInspection and SamplingPrecious MagpaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Techniques: Dr. Shilpi GuptaDokument59 SeitenSampling Techniques: Dr. Shilpi GuptaTashi WangmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Auditing: Modern AuditingDokument24 SeitenModern Auditing: Modern AuditingHaileNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Sampling Design and ProceduresDokument21 Seiten11 Sampling Design and ProceduresAhanafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The POPULATION For Audit SamplingDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding The POPULATION For Audit SamplingAnthony Koko CarlobosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 14 Audit SamplingDokument9 SeitenLesson 14 Audit SamplingMark TaysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 4Dokument2 SeitenAT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 4hoxhiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 Audit-SamplingDokument24 Seiten07 Audit-Samplingfrancis albaracinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing Notes - Chapter 5Dokument14 SeitenAuditing Notes - Chapter 5Future CPA75% (4)
- Practical Research 2 Participants of The StudyDokument3 SeitenPractical Research 2 Participants of The StudyAbegail Decasa100% (7)
- Ana ChemDokument1 SeiteAna ChemElizer Robles Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Audit Sampling: Assurance, Principles, Professional Ethics & Good Governance SUMMER (MTH 5:00-9:00PM)Dokument32 SeitenAudit Sampling: Assurance, Principles, Professional Ethics & Good Governance SUMMER (MTH 5:00-9:00PM)Hannaj May De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biostatistics Laboratory SAMPLINGDokument6 SeitenBiostatistics Laboratory SAMPLINGTrisha Joy SicatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specificity 100 X No - of Dse Individual WithDokument4 SeitenSpecificity 100 X No - of Dse Individual WithmarianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auditing II-Ch-OneDokument13 SeitenAuditing II-Ch-OnebanteamlakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Method: Census Vs SamplingDokument8 SeitenBusiness Research Method: Census Vs SamplingPulkit AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- C GEMTH MidtermsDokument4 SeitenC GEMTH MidtermsKarl LintanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter OneDokument12 SeitenChapter OneTesfaye Megiso BegajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringDokument5 SeitenStatistics (Mid-Terms!) : Steps in Data GatheringLaila Joshbeth SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 CalibrationsDokument7 Seiten5 CalibrationsJonathan MusongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliability and Validity IBRDokument2 SeitenReliability and Validity IBRpaulien.beekerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Sampling: Concepts-Types of Sampling - Probability Sampling - Simple Random SamplingDokument10 SeitenSampling Sampling: Concepts-Types of Sampling - Probability Sampling - Simple Random SamplingUday GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 3Dokument3 SeitenAT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 3hoxhiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF 20230427 073408 0000 PDFDokument32 SeitenPDF 20230427 073408 0000 PDFShiela ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH-7 Audit SamplingDokument13 SeitenCH-7 Audit SamplingHarsh DaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT.2813 - Determining The Extent of Testing PDFDokument7 SeitenAT.2813 - Determining The Extent of Testing PDFMaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SamplingDokument34 SeitenSamplingPulkit Sharma100% (1)
- L2 Procedures Are Common For Both Categories of SamplingDokument2 SeitenL2 Procedures Are Common For Both Categories of SamplingBethelhemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probability Sampling and Non Probability Sampling ComparisionDokument1 SeiteProbability Sampling and Non Probability Sampling ComparisionNgo Chi Thien (K17CT)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research ReviewerDokument8 SeitenResearch Reviewerelecgabrielr.123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: 1. Audit SamplingDokument6 SeitenChapter One: 1. Audit SamplingZelalem HassenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SamplingDokument24 SeitenSamplingAdithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Details of Study: Sampling DesignDokument29 SeitenDetails of Study: Sampling DesignharsimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPSTONEDokument3 SeitenCAPSTONEAlen Joy CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Audit Sampling For Test of Controls - ppt2068956617Dokument34 SeitenChapter 18 Audit Sampling For Test of Controls - ppt2068956617Clar Aaron BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Science for Beginners: Tips and Tricks for Effective Machine Learning/ Part 4Von EverandData Science for Beginners: Tips and Tricks for Effective Machine Learning/ Part 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7: Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsDokument3 SeitenChapter 7: Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 1-5: Task No. 6 Process QuestionsDokument4 SeitenChapters 1-5: Task No. 6 Process QuestionsFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10-11Dokument12 SeitenChapter 10-11FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 1-5: Task No. 6 Process QuestionsDokument4 SeitenChapters 1-5: Task No. 6 Process QuestionsFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDokument17 SeitenChapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Application: International Trade: 9.1 The Determinants of TradeDokument5 SeitenChapter 9: Application: International Trade: 9.1 The Determinants of TradeFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Application: International Trade: 9.1 The Determinants of TradeDokument5 SeitenChapter 9: Application: International Trade: 9.1 The Determinants of TradeFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16-17Dokument15 SeitenChapter 16-17FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Thinking Like An Economist: 2-1 The Economist As ScientistDokument3 SeitenChapter 2: Thinking Like An Economist: 2-1 The Economist As ScientistFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16-17Dokument15 SeitenChapter 16-17FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10-11Dokument12 SeitenChapter 10-11FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary NotesDokument2 SeitenSummary NotesFar100% (1)
- Chapter 7: Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsDokument3 SeitenChapter 7: Consumers, Producers, and The Efficiency of MarketsFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10-11Dokument12 SeitenChapter 10-11FarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary at Pre-EngagementDokument1 SeiteSummary at Pre-EngagementFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandDokument17 SeitenChapter 4: The Market Forces of Supply and DemandFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Thinking Like An Economist: 2-1 The Economist As ScientistDokument3 SeitenChapter 2: Thinking Like An Economist: 2-1 The Economist As ScientistFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit ReportDokument1 SeiteAudit ReportFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tax Reform For Acceleraction and INclusion LawDokument1 SeiteTax Reform For Acceleraction and INclusion LawFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit ReportDokument1 SeiteAudit ReportFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced Scorecard: The BS PhilosophyDokument6 SeitenBalanced Scorecard: The BS PhilosophyFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk AssessmentDokument1 SeiteRisk AssessmentFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lancaf Banda - SCARY and Amazing." Yes, at First, We Still Get To Joke About It. We Never ReallyDokument2 SeitenLancaf Banda - SCARY and Amazing." Yes, at First, We Still Get To Joke About It. We Never ReallyFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fraudulent Financial ReportingDokument3 SeitenFraudulent Financial ReportingFarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Soaps of HUL, P& G, Godrej, Nirma and Johnson & JohnsonDokument71 SeitenComparative Study of Soaps of HUL, P& G, Godrej, Nirma and Johnson & JohnsonKshitiz Gupta83% (12)
- Chapter 8 Tella and OgunkanDokument14 SeitenChapter 8 Tella and OgunkanOgunkan Gbenga DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business StatisticsDokument229 SeitenBusiness StatisticsEjaz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Ed Research Project FullDokument96 SeitenB. Ed Research Project Fullsaharsaeed100% (2)
- 18MBA23 Research Methods Full Notes With Question BankDokument87 Seiten18MBA23 Research Methods Full Notes With Question BankNeena86% (7)
- Statistical AssignmentDokument26 SeitenStatistical Assignmentsuma.v PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Work Stress On Employee Performance in The Public Sector in Kenya: A Case of The National TreasuryDokument21 SeitenEffect of Work Stress On Employee Performance in The Public Sector in Kenya: A Case of The National TreasuryABDUL KARIM ASLAMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Fisher, R. A. (1925) Statistical Methods For Research WorkersDokument145 SeitenFisher, R. A. (1925) Statistical Methods For Research Workersberorakun75% (4)
- Practical Research 1Dokument7 SeitenPractical Research 1Ron Marc MarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheets GynesisDokument9 SeitenWorksheets GynesisGynesis Lim Roquero100% (1)
- Statistical Analysis With Software Application (Stats 20053) Module AnswersDokument48 SeitenStatistical Analysis With Software Application (Stats 20053) Module AnswersJayson ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 6Dokument2 SeitenMod 6Pierce ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing SyllabusDokument186 SeitenNursing Syllabuspramod kumawat100% (1)
- Assessment of Budgetary PerformanceDokument44 SeitenAssessment of Budgetary Performancepadm100% (1)
- QA Acceptance CriteriaDokument19 SeitenQA Acceptance CriteriaLouisAucampNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling, Standardization and Calibration: Topic 7Dokument77 SeitenSampling, Standardization and Calibration: Topic 7A/P SUPAYA SHALININoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment MultisectorDokument92 SeitenAssessment MultisectorEngkhalid AlghaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Share Trading SynopsisDokument11 SeitenOnline Share Trading Synopsisneeraj_sharma18320100% (1)
- Summary of Freedman - Pisani - Purves, Statistics - 4e - 2007 - With SolutionsDokument15 SeitenSummary of Freedman - Pisani - Purves, Statistics - 4e - 2007 - With SolutionstchungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broken FamilyDokument15 SeitenBroken FamilyGabriel VillaveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Goldpine Lemon Masti and Jeera Masti Soft DrinksDokument102 SeitenProject Report On Consumer Behaviour Towards Goldpine Lemon Masti and Jeera Masti Soft DrinksAmritraj D.BangeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Level ResultsDokument2 SeitenPerformance Level ResultsSarrah May S. MendivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Working Capital Management On The Manufacturing Firms' ProfitabilityDokument20 SeitenThe Effect of Working Capital Management On The Manufacturing Firms' ProfitabilityAbdii DhufeeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polling & Survey Methods PDFDokument673 SeitenPolling & Survey Methods PDFMaksym KopylovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Quiz For SBI PO 2015Dokument7 SeitenMarketing Quiz For SBI PO 2015Bhowanisankar Charati Ias HunterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Manual For PQWT-S150/S400/S500 Geophysical Prospecting InstrumentDokument35 SeitenOperation Manual For PQWT-S150/S400/S500 Geophysical Prospecting InstrumentRamon ducci torrealba100% (1)
- Itc Sip Report-1Dokument64 SeitenItc Sip Report-1ADARSH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Instruments Thesis SampleDokument5 SeitenResearch Instruments Thesis Samplelisakennedyfargo100% (1)
- Market ResearchDokument5 SeitenMarket ResearchHellen KahuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 2Dokument73 SeitenDocument 2Pooja75% (4)