Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is A Magnet
Hochgeladen von
Mariam BurhanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is A Magnet
Hochgeladen von
Mariam BurhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is A Magnet?
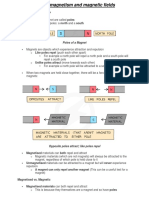
Magnets are objects (made out of magnetic materials) that produce a magnetic field. Magnets
pull other objects made of magnetic materials towards them. They will either attract or repel other
magnets. Magnets always have two poles: a north pole and a south pole. Each pole of a magnet
is attracted to the opposite pole of another magnet (e.g. the north pole of one magnet will be
attracted to the south pole of another magnet, and vice versa). If you put the north pole of one
magnet near the south pole of another magnet you will be able to feel them pulling towards each
other. However, if you put the north pole of one magnet to the north pole of another, or the south
pole of one magnet to the south pole of another, then you will be able to feel them pushing away
from each other. The two sides of a magnet are called north and south poles because if a
magnet is able to spin freely, the north pole of the magnet will always end up pointing towards
the Earth’s North Pole.In fact, the magnet will point at the Earth’s Magnetic North Pole, which is
near to – but not the same as – the Geographic North Pole.That’s because the world is like one
big magnet, with its own magnetic north and magnetic south poles. The Earth’s core is made of
iron, which is what causes its magnetism and produces its magnetic field. Some materials are
naturally highly magnetic, and can be made into magnets. These materials are ‘ferromagnetic’.
Ferromagnetic materials include iron, nickel, cobalt and (most of) their alloys (an alloy is a
mixture of a metal and another element), such as steel.
Types Of Magnets
Permanent Magnets
After being ‘magnetized’ (made into magnets), some ferromagnetic materials don’t lose their
magnetic power. This is the property of being magnetically ‘hard’. Other materials are
magnetically ‘soft’, and do not retain their magnetism. Magnets that keep their magnetism are
known as ‘permanent magnets’. Two common types of permanent magnets are the bar magnet
and the horseshoe magnet. Bar magnets are narrow rectangular in shape, and their north and
south poles are at opposite ends of the bar.Horseshoe magnets are like bar magnets that have
been bent round into a thin ‘U’ shape. One of the tips is the north pole, the other the south
pole.All substances have a degree of magnetism, but those least affected by a magnetic field are
known as ‘non-magnetic’ substances. These include plastics, copper, and gases.
Another type of magnet is an electromagnet.
Electromagnets work because an electric current produces a magnetic field.Electromagnetism
was discovered in 1820 by Hans Christian Ørsted, a Danish scientist. He noticed that a freely
hanging compass needle moved when brought close to a wire carrying an electric current.Unlike
a permanent magnet, an electromagnet’s magnetism disappears when the current is turned off.If
the wire carrying the electric current is coiled, the magnetic affect is stronger. If the wire is coiled
around a piece of iron then the effect is stronger still.The first electromagnet was invented by
British scientist William Sturgeon in 1824, who wrapped wire around a horseshoe-shaped iron
bar.A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of a magnet. It is invisible, but can be detected with a
compass or another magnet.If you could see the magnetic field of a magnet, it would look like a
series of curved lines going between the north and south poles.If you sprinkle iron filings on a
sheet of paper, and place a magnet under the sheet of paper, the iron filings will arrange
themselves into ‘lines of force’, showing the magnet’s magnetic field.
Uses Of Magnets:Magnets and electromagnets have many uses in the
modern world. From the simplest fridge magnets, to advanced computer data storage
systems, we rely on magnets and magnetism to perform a wide range of tasks.
Compasses :One of the first uses of magnetism was to make compasses.
Because the needle of a compass is a magnet, it will always spin round to align itself with
the Earth’s magnetic field. Using a compass, an explorer will always know which way is
north, and therefore the direction in which he is headed.
Computer Hard Drives: A computer’s hard drive is used to store data such
as emails, pictures and movies. At the heart of a computer hard drive is a spinning disc
with a magnetic surface. The data is stored on the disc in the form of magnetic patterns.
Speakers:Speakers use magnetism to
convert electrical sound information into sound
waves. The electrical signal is passed through a
coil that is attached to the speaker cone. The coil is
hung between the poles of a permanent magnet.
The coil becomes an electromagnet and is forced to
move by the magnet, which in turn vibrates the
speaker cone and produces sound.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Magnetism Part 1Dokument8 SeitenMagnetism Part 1AnonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch.13 Fun With Magnets Class 6Dokument4 SeitenCh.13 Fun With Magnets Class 6Verma Sheela100% (1)
- What Is MagnetDokument9 SeitenWhat Is Magnetarsc123Noch keine Bewertungen
- More Free Powerpoints at HTTPDokument56 SeitenMore Free Powerpoints at HTTPhamang khullafah100% (1)
- Science PPT MagnetsDokument8 SeitenScience PPT Magnetsapi-313062442Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Dokument21 SeitenElectric and Magnetic Fields (2) - Lecture 1 Spring 2021-2022Ahmed tarek gaballahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceVon EverandThe Attractive Story of Magnetism with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form5 Unit1 Magnetism NotesDokument10 SeitenForm5 Unit1 Magnetism NotesJus BetikNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetismDokument12 SeitenMagnetismtshiamo.dintweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism - Summary - 084650Dokument50 SeitenMagnetism - Summary - 084650Maricar Faraon100% (1)
- Earth MagnetismDokument7 SeitenEarth Magnetismisa_diogo8170Noch keine Bewertungen
- The MagnetsDokument6 SeitenThe Magnetsromethsunsuka678Noch keine Bewertungen
- What are Magnets? A Child's Guide to Understanding Magnets - Science Book for Elementary School | Children's How Things Work BooksVon EverandWhat are Magnets? A Child's Guide to Understanding Magnets - Science Book for Elementary School | Children's How Things Work BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3Dokument9 SeitenLesson 3Anonymous 0gBzy7uMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Magnets WorksheetsDokument2 SeitenScience Magnets WorksheetselmalynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compass For OOW Class IIIDokument260 SeitenCompass For OOW Class IIIKyaw Mya OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Magnets WorksheetsDokument2 SeitenScience Magnets WorksheetselmalynNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismDokument6 Seiten4.1 Simple Phenomena of MagnetismAbdul Hadi TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectromagneticDokument2 SeitenElectromagneticAiman Zylle MosotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other. For Example, Pair of North Poles Repel Each Other and A Pair of South Poles Repel EachDokument1 SeiteOther. For Example, Pair of North Poles Repel Each Other and A Pair of South Poles Repel EachatkindsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Magnets WorkDokument37 SeitenHow Magnets WorkShamim AhmmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument10 SeitenPhysics ProjectMandeep TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 MagnetismDokument17 Seiten14 Magnetismapi-235269401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machines Lab No. 1Dokument7 SeitenMachines Lab No. 1Marvin Lucero FiscalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetismDokument20 SeitenMagnetismmadhumitharajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism 1Dokument13 SeitenMagnetism 1Vina PardedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Electromagnetic MeilanyDokument23 SeitenLaporan Electromagnetic MeilanyMyunieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)Dokument3 SeitenMagnetism: (South-Seeking Pole)ChathunikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDokument82 SeitenMagnetism and ElectromagnetismschlemielzNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAGNETISMDokument5 SeitenMAGNETISMJim Agcaoili LindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah MagnetDokument29 SeitenMakalah MagnetAinur RokhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Written Report Physics 4 Characterize Magnetic ForceDokument3 SeitenWritten Report Physics 4 Characterize Magnetic Forceellamaecariaga2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism: TH THDokument8 SeitenMagnetism and Electromagnetism: TH THapi-27085921Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13.1 Magnets and Magnetic MaterialsDokument4 Seiten13.1 Magnets and Magnetic MaterialscindyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is MagnetDokument14 SeitenWhat Is MagnetTapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnets Class6Dokument34 SeitenMagnets Class6Moumita DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCEDokument7 SeitenSCIENCEJheiah UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Concepts About MagnetsDokument2 SeitenMain Concepts About MagnetschethansharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism Notes FinalDokument29 SeitenMagnetism Notes FinalMuryum SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsDokument9 Seiten4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsIshraque MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics - MagnetismDokument5 SeitenCSEC Physics - MagnetismCornflakes ToastedNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 3Dokument15 SeitenApril 3Kim CarandangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAGNETISM Notes PDFDokument10 SeitenMAGNETISM Notes PDFChisha Mwewa100% (2)
- Chap10no1 PDFDokument2 SeitenChap10no1 PDFTajiriMollel23% (13)
- Magnetism: A Strangely Attractive TopicDokument28 SeitenMagnetism: A Strangely Attractive TopicYo100% (1)
- What Is A Magnet 1Dokument20 SeitenWhat Is A Magnet 1Rosi Jimenez100% (1)
- Magnetism IGCSE PhysicsDokument44 SeitenMagnetism IGCSE PhysicsKavya KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - ElectromagnetismDokument26 SeitenLesson 1 - ElectromagnetismAN - 12BM 795510 Harold M Brathwaite SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - MagnetismDokument12 SeitenTopic - Magnetismsom277342Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism G10 ScienceDokument16 SeitenMagnetism G10 ScienceVianca Rein MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- In A Flash: Magnets and ElectricityDokument20 SeitenIn A Flash: Magnets and ElectricityJohn Paul BaquiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magn Tis LíthosDokument10 SeitenMagn Tis Líthosgritchard4Noch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetsDokument3 SeitenMagnetsvijayap71Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 MagnetismDokument4 SeitenTopic 4 MagnetismKelly Fresco100% (1)
- MagnetismDokument29 SeitenMagnetismYoshiro YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1 MagnetismDokument44 SeitenQuestion 1 MagnetismRanjit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Magnets WorkDokument6 SeitenHow Magnets WorkSharmini AmbalaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Unemployment Refers To A Mismatch Between The Jobs Available and The SkillDokument2 SeitenStructural Unemployment Refers To A Mismatch Between The Jobs Available and The SkillMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The City School: Figurative Language - Idiom, Simile, MetaphorDokument2 SeitenThe City School: Figurative Language - Idiom, Simile, MetaphorMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terms and Conditions CAIEDokument3 SeitenTerms and Conditions CAIEMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Term Report: GDP and InflationDokument8 SeitenMacroeconomics Term Report: GDP and InflationMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creative StrategiesDokument13 SeitenCreative StrategiesMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Industries Include TheDokument2 SeitenMajor Industries Include TheMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ke2 Pages Deleted PDFDokument2 SeitenKe2 Pages Deleted PDFMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ke2 Pages Deleted PDFDokument2 SeitenKe2 Pages Deleted PDFMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color MeaningDokument5 SeitenColor MeaningMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEDIA - A Source of Information or DisinformationDokument12 SeitenMEDIA - A Source of Information or DisinformationMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinepdf PDFDokument6 SeitenCombinepdf PDFMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEDIA - A Source of Information or DisinformationDokument12 SeitenMEDIA - A Source of Information or DisinformationMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mis 303Dokument7 SeitenMis 303Mariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEGMENTATIONDokument1 SeiteSEGMENTATIONMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food and Fun Together: Mcdonalds PakistanDokument5 SeitenFood and Fun Together: Mcdonalds PakistanMariam BurhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Science Exemplar Chapter 13Dokument6 Seiten6 Science Exemplar Chapter 13ALKA RANINoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - Science 3 - Q3 - W5Dokument3 SeitenDLL - Science 3 - Q3 - W5Melissa Joyce SunicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Field Mapper DocumentationDokument19 SeitenMagnetic Field Mapper DocumentationJuan Ignacio Guerrero HenríquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP-Sept.30-facts About MagnetismDokument7 SeitenLP-Sept.30-facts About MagnetismDiona Bangga - ModestoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionsDokument17 SeitenMagnetism and Electromagnetism QuestionseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Us 20040070299Dokument3 SeitenUs 20040070299Victor Von Doom100% (1)
- How Can I Build A Powerful Electromagnet Using A Nine Volt Battery and Easily Available Material - Yahoo! AnswersDokument2 SeitenHow Can I Build A Powerful Electromagnet Using A Nine Volt Battery and Easily Available Material - Yahoo! AnswersDayal SaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-729-Pt2 Iss2Dokument23 Seiten02-729-Pt2 Iss2br1ggsy100% (1)
- Lowrie GeomagnetismDokument11 SeitenLowrie GeomagnetismLucas Schtargloff OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- g-10 Activity Unit2Dokument10 Seiteng-10 Activity Unit2marjja millanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vanda 1405Dokument7 SeitenVanda 1405Khanh ChiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS5000-MS-20-150 Spec v0 1Dokument7 SeitenAS5000-MS-20-150 Spec v0 1Victor ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Material ScienceDokument10 SeitenElectrical Material SciencesushinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Dynamo As Electric Generator": Jet Llewellyn N. Lastimosa Glywys Claude Igoy Edlyn Joy FrondozoDokument11 Seiten"Dynamo As Electric Generator": Jet Llewellyn N. Lastimosa Glywys Claude Igoy Edlyn Joy FrondozoQu33n ZyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument79 SeitenModule 3KetanRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Raihan Sunaryo - Magnetic ForceDokument11 SeitenM Raihan Sunaryo - Magnetic ForceMuhammadRaihan sunaryoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Yokes: Mobile Crack Detection UnitsDokument4 SeitenHand Yokes: Mobile Crack Detection UnitsizmitlimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Finishing ProcessesDokument15 SeitenAdvanced Finishing ProcessesADWAITH G SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil I 6868Dokument23 SeitenMil I 6868Miguel BordasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 30 Assignment 8 1 PDFDokument8 SeitenPhysics 30 Assignment 8 1 PDFSami AlmuallimNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS PROJECT NETURAL POINT OF A MAGNE Pages Deleted Edited EditedDokument14 SeitenPHYSICS PROJECT NETURAL POINT OF A MAGNE Pages Deleted Edited EditedAnand KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0625 s17 QP 23 PDFDokument20 Seiten0625 s17 QP 23 PDFarif asgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MR Fin Action Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenMR Fin Action Lesson PlanCielito GumbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class VI Science Annual Sample PaperDokument6 SeitenClass VI Science Annual Sample PapermkbbhawanipatnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes of CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Elect' Currentl Class 10th ScienceDokument17 SeitenNotes of CH 13 Magnetic Effects of Elect' Currentl Class 10th SciencetusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turning Effect of A Current-Carrying Coil in A Magnetic FieldDokument0 SeitenTurning Effect of A Current-Carrying Coil in A Magnetic FieldRizal SalasiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Potter and CarpenterDokument53 SeitenThe Potter and CarpenterMizaa ÖöNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is MagnetDokument14 SeitenWhat Is MagnetTapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8J Magnets and ElectromagnetsDokument29 Seiten8J Magnets and ElectromagnetsPoornimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIVS Overview and Some Instructions: The Most Recent Events Concerning The FIVS Gen VDokument4 SeitenFIVS Overview and Some Instructions: The Most Recent Events Concerning The FIVS Gen VDavid ReasterNoch keine Bewertungen