Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
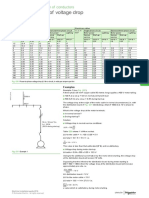
Table 3: Voltage Drop: Example
Hochgeladen von
taufiqishak09Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Table 3: Voltage Drop: Example
Hochgeladen von
taufiqishak09Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Table 3: Voltage Drop
Nominal DC- Single-phase Three-phase
cross-sectional System AC-System AC-System
area
(mm²) (mV/A/m) (mV/A/m) (mV/A/m)
1.5 24.2 27.9 24.1
2.5 14.3 17.1 14.8
4 9.0 10.7 9.3
6 6.0 7.2 6.2
10 3.6 4.3 3.7
16 2.3 2.8 2.4
25 1.5 1.8 1.5
35 1.1 1.3 1.1
50 0.8 0.96 0.85
70 0.6 0.70 0.60
95 0.4 0.55 0.45
120 0.3 0.45 0.35
150 0.25 0.35 0.31
185 0.20 0.30 0.26
240 0.15 0.25 0.22
300 0.12 0.22 0.19
400 0.10 0.19 0.17
The voltage drop in a circuit, of which the cable forms a part, should not exceed 3 - 5% of the nominal voltage; e.g. 20.0 volts
(5%) for a three-phase 400 volts supply. The above mentioned voltage drop is tabulated for a current of 1 ampere for a
1 metre run. For any cable length, the values need to be multiplied by the length of the cable (in metres) and by the current
(in amperes).
Example:
Formula for the calculated voltage drop in mV/A/m:
permissible voltage drop (e) x 1000
ecal =
current (I) x length (l)
Installation length (l): 300 m
Current (I) to carry: 80 A
Nominal voltage (U): 400 V (Three-phase AC)
Permissible voltage drop (e): 20.0 V (5% of 400 V)
20.0 V x 1000
ecal = = 0.83 mV/A/m
80 A x 300 m
Select a cross-section, such that the voltage drop is equal to or less than 0.83 mV/A/m from table 3. It has to be ensured that
the selected cross-section will carry the current (see pages H5 up to H7).
The corresponding cross-section will be 50 mm².
H4 KERPEN GmbH & Co. KG • 07.2005 • Printing errors excepted. Subject to alteration
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Government Publications: Key PapersVon EverandGovernment Publications: Key PapersBernard M. FryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop CalculatorxlsDokument4 SeitenVoltage Drop CalculatorxlsTTaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsVon EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- UPM PHY3401 Mini Project Assignment Info and QuestionsDokument9 SeitenUPM PHY3401 Mini Project Assignment Info and QuestionsMohd Amiruddin Abd RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsVon EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- PART B: Measure Voltage and Current in Circuit ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenPART B: Measure Voltage and Current in Circuit ObjectivesYap Yu XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Voltage Drop CalcDokument12 SeitenDC Voltage Drop CalcJonathan Brylle CardinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injection Table (CITY)Dokument1 SeiteInjection Table (CITY)Hasilwan ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SE Compact NS Circuit Breaker Heat LossDokument2 SeitenSE Compact NS Circuit Breaker Heat LossibrahimulusamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velocidad de InfiltracionDokument3 SeitenVelocidad de InfiltracionWillington MoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac10cfiip.c18158 002Dokument2 SeitenAc10cfiip.c18158 002anon_116727886Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop CalculationsDokument8 SeitenVoltage Drop CalculationsYousif_AbdalhalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop CalculationsDokument8 SeitenVoltage Drop CalculationsYousif_AbdalhalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Check ACS880-04-585A-3: Network and Transformer Data Supply Unit DataDokument2 SeitenNetwork Check ACS880-04-585A-3: Network and Transformer Data Supply Unit DataKrishna JashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic of PNP Tranistor in CE Configuration: Object: Apparatus UsedDokument7 SeitenCharacteristic of PNP Tranistor in CE Configuration: Object: Apparatus UsedVasursharpNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 20-TableDokument1 SeiteC 20-Tablebill_allen_33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curva Granuometrica12121Dokument5 SeitenCurva Granuometrica12121MEGA FLASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet: Equipment Wire Equipment Wire Equipment Wire Equipment WireDokument3 SeitenData Sheet: Equipment Wire Equipment Wire Equipment Wire Equipment Wireamro emadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FT 200 AaDokument1 SeiteFT 200 AaFranklin J Talero BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magmeter Accuracy Graph: Column CDokument1 SeiteMagmeter Accuracy Graph: Column CFranklin J Talero BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios Cinética EnzimáticaDokument6 SeitenEjercicios Cinética EnzimáticaDenis PavasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Dia 0.75 (M/S) Around 2.5 (M/S) Around 1.5 (M/S) Rise (MM) Slope (Minimum) (%) Slope (Maximum) (%) Slope (Maximum) (%)Dokument2 SeitenPipe Dia 0.75 (M/S) Around 2.5 (M/S) Around 1.5 (M/S) Rise (MM) Slope (Minimum) (%) Slope (Maximum) (%) Slope (Maximum) (%)mazzam75Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11kV or 33kV Cable Sizing CalculationDokument1 Seite11kV or 33kV Cable Sizing Calculationanamulk-183% (18)
- Tutorial MaterialDokument12 SeitenTutorial MaterialYamada Takeshi100% (2)
- Study of LVDT and Precision RectifierDokument10 SeitenStudy of LVDT and Precision RectifierDivyam Gupta 1373 -12th BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Current Rating Chart: For Full Load AmpsDokument2 SeitenMotor Current Rating Chart: For Full Load AmpsMuhammad UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Volts Fla Charts 1Dokument2 SeitenHP Volts Fla Charts 1Vivekyathi BowanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Volts Fla ChartsDokument2 SeitenHP Volts Fla ChartsRaj Goud VailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Load Limits For SlingsDokument11 SeitenWorking Load Limits For Slingstolis-gefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Datas Voltage Drop For Low Voltage CablesDokument14 SeitenTechnical Datas Voltage Drop For Low Voltage CablesFelipe GustavoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Cable 2023Dokument5 SeitenSolar Cable 2023H. NurzeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1: ApparatusDokument7 SeitenExperiment 1: ApparatusMaria MeharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop Calculation in CableDokument3 SeitenVoltage Drop Calculation in Cablekrajeev2802Noch keine Bewertungen
- P-N Junction Practical Class 12Dokument3 SeitenP-N Junction Practical Class 12Swapnil Sahu67% (6)
- Motor Branch Circuit.Dokument2 SeitenMotor Branch Circuit.perezjubert27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop - ARD - TameplateDokument6 SeitenVoltage Drop - ARD - TameplateJian RoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sysnchronous Generator Transient Analysis2Dokument18 SeitenSysnchronous Generator Transient Analysis2mnsatyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- OverloadrelayDokument7 SeitenOverloadrelayvaranasianilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix 2 - Lab Report For DC-DC Converter ExperimentDokument7 SeitenAppendix 2 - Lab Report For DC-DC Converter ExperimentAlfred LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 9.1: 2 Traffic Level-of-Service Two-Lane Highways in Class IDokument23 SeitenTable 9.1: 2 Traffic Level-of-Service Two-Lane Highways in Class IAnthony AnglubenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ohms Law and Resistance Virtual Lab PHET Lesson 9 and 10Dokument5 SeitenOhms Law and Resistance Virtual Lab PHET Lesson 9 and 10Ghala AlHarmoodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengujian UCS Sampel 1Dokument2 SeitenPengujian UCS Sampel 1SyafiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic of PNP Tranistor in CB Configuration: Object: Apparatus UsedDokument7 SeitenCharacteristic of PNP Tranistor in CB Configuration: Object: Apparatus UsedDhiman AlianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Guidelines For HydroPlast U-PVC FittingsDokument20 SeitenTechnical Guidelines For HydroPlast U-PVC FittingsOsama AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Roughness Conversion ChartDokument1 SeiteSurface Roughness Conversion ChartShobhith DevadigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Machines Lab ReportDokument11 SeitenHydraulic Machines Lab ReportBaran ShafqatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Media 15.1.2015Dokument17 SeitenFilter Media 15.1.2015Prashant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toaz - Info Ieee 30 Bus System Data PRDokument4 SeitenToaz - Info Ieee 30 Bus System Data PRMerera TaresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valoare Maxima Numar Intervale Oi: (Frecventa Obs.)Dokument3 SeitenValoare Maxima Numar Intervale Oi: (Frecventa Obs.)SebastianCosminAlecuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabla de FrecuenciasDokument14 SeitenTabla de FrecuenciasAiner ShuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wabco Mechanical LSVDokument8 SeitenWabco Mechanical LSVmarranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Probit ExcelDokument6 SeitenProbit ExcelVina EccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of ConductorsDokument1 Seite3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of Conductorsashraf atefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combine CalculationDokument3 SeitenCombine CalculationKamran JUTTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage DropDokument5 SeitenVoltage Dropahmed alhassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tema Laborator 2-Stoica OfeliaDokument3 SeitenTema Laborator 2-Stoica OfeliaOfelia StoicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20 - Technical Data & FormulationsDokument11 Seiten20 - Technical Data & FormulationsSnzy DelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 1. Data Collected From The ExperimentDokument3 SeitenTable 1. Data Collected From The ExperimentKarim AbdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab8 UrmilDokument12 SeitenLab8 UrmilKADALI SRI AKASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Across Pro DS EN 80774703 - CDokument2 SeitenAcross Pro DS EN 80774703 - CZoimar iseaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanfluid SurafacntDokument11 SeitenNanfluid Surafacnttaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEP3623 Sem I 20202021 Test 2Dokument6 SeitenEEP3623 Sem I 20202021 Test 2taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ibersensor 141Dokument6 SeitenIbersensor 141taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECM Assignment 1 - 2020-2021Dokument1 SeiteECM Assignment 1 - 2020-2021taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- EET308 Chapter 4 Lecture 1 - Updated 13 March 2016 - 0Dokument30 SeitenEET308 Chapter 4 Lecture 1 - Updated 13 March 2016 - 0taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rotor Dynamics and The Swing EquationDokument11 SeitenRotor Dynamics and The Swing Equationtaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric For Assessing Technical Report Advanced Power System (Eep 3623)Dokument2 SeitenRubric For Assessing Technical Report Advanced Power System (Eep 3623)taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - PQ - Voltage SagDokument20 SeitenChapter 6 - PQ - Voltage Sagtaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - PQ - HarmonicsDokument51 SeitenChapter 6 - PQ - Harmonicstaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fault Calculation ExamplesDokument28 SeitenFault Calculation Examplestaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Electrical Conductivity of Nanoparticle-Enhanced FluidsDokument22 SeitenA Review On Electrical Conductivity of Nanoparticle-Enhanced Fluidstaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 EEP5252Dokument80 SeitenChapter 4 EEP5252taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Issa Batarseh, Ahmad Harb - Power Electronics - Circuit Analysis and Design (2018, Springer) PDFDokument689 SeitenIssa Batarseh, Ahmad Harb - Power Electronics - Circuit Analysis and Design (2018, Springer) PDFtaufiqishak09100% (4)
- Research Proposal RaufDokument10 SeitenResearch Proposal Rauftaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - EEP5252 - Voltage DropDokument84 SeitenChapter 3 - EEP5252 - Voltage Droptaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - EEP5252 - Voltage DropDokument84 SeitenChapter 3 - EEP5252 - Voltage Droptaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Turn Your Thesis Into An ArticleDokument18 SeitenHow To Turn Your Thesis Into An Articletaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fault in Power SystemsDokument75 SeitenFault in Power Systemstaufiqishak090% (1)
- Power Cable Failure Modes and Fault Loca PDFDokument5 SeitenPower Cable Failure Modes and Fault Loca PDFtaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics: DC-DC Converters (Choppers)Dokument22 SeitenPower Electronics: DC-DC Converters (Choppers)taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer of Test Paper of Advanced Power Electronics 2015 (Benny Yeung)Dokument3 SeitenAnswer of Test Paper of Advanced Power Electronics 2015 (Benny Yeung)taufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- EEE20005-week 4 5Dokument103 SeitenEEE20005-week 4 5ShelbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erosion Control Training Confirmed Participants - 4 (1) (1) 2Dokument4 SeitenErosion Control Training Confirmed Participants - 4 (1) (1) 2Kitozay94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton Dilm750Dokument12 SeitenEaton Dilm750tecnicohugogarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB C208 Stall WarningDokument14 SeitenSB C208 Stall WarningrobertobrouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton Hhi HHJ in Line Fuse Holder Data SheetDokument1 SeiteEaton Hhi HHJ in Line Fuse Holder Data SheetVaibhav DafaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOUCH CURRENT Measurement Showing How It WorksDokument18 SeitenTOUCH CURRENT Measurement Showing How It WorksshrikrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- JBL Hdi Series: Premium Home Loudspeaker SystemsDokument13 SeitenJBL Hdi Series: Premium Home Loudspeaker SystemsEnrique RangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CapacitanceDokument8 SeitenCapacitancePhilip MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog STV 25k Series Surge Protective Devices Solahd en Us 163760Dokument2 SeitenCatalog STV 25k Series Surge Protective Devices Solahd en Us 163760Jorge Dario Jarrin VivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isometric View For Reference Only Isometric View For Reference OnlyDokument8 SeitenIsometric View For Reference Only Isometric View For Reference Onlyanibal cruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Sensor Light Dependent ResistorDokument2 SeitenDatasheet Sensor Light Dependent ResistorWendo Bijaksono67% (3)
- Eel 5245 Power Electronics I Lecture #2: Chapter 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDokument27 SeitenEel 5245 Power Electronics I Lecture #2: Chapter 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsalbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Voltage DTS 60D DatasheetDokument2 SeitenHigh Voltage DTS 60D Datasheetbetho_96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hy m900 Hy Lm900 SeriesDokument7 SeitenHy m900 Hy Lm900 SeriesCao ChinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Series Suresight Service & RepairDokument14 Seiten14 Series Suresight Service & RepairgersonbartoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVDC 60years PDFDokument10 SeitenHVDC 60years PDFAdrian FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: DCDokument19 SeitenGovernment Polytechnic Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: DCTapobroto ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBM211 0 To 20 Ma Input ModuleDokument16 SeitenFBM211 0 To 20 Ma Input ModuleMiguel Angel Gómez PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toshiba KRE1012030Dokument2 SeitenToshiba KRE1012030ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making A Touch SensorDokument11 SeitenMaking A Touch Sensorsaj7689Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASIC by Sebastian SmithDokument506 SeitenASIC by Sebastian SmithKiberleab TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6129861652239090030Dokument164 Seiten5 6129861652239090030ManimegalaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drainage Pumps: Catalogue Drainage and SewageDokument90 SeitenDrainage Pumps: Catalogue Drainage and SewageИбрагим НурмамедовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton's SPD Series (Integrated Versions)Dokument16 SeitenEaton's SPD Series (Integrated Versions)solomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submittal: 5 Ton Convertible Air Handler TEM4A0C60S51SADokument8 SeitenSubmittal: 5 Ton Convertible Air Handler TEM4A0C60S51SASantiago Del Rio RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Inspection Sheet (Fis) : Design As Built Qyt Qyt Items No. Uom MSP Check Description of ItemDokument1 SeiteField Inspection Sheet (Fis) : Design As Built Qyt Qyt Items No. Uom MSP Check Description of ItemshaukatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designed: JfetsDokument1 SeiteDesigned: JfetsLuis Carlos OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klipsch ForteDokument2 SeitenKlipsch ForteKenny SharpensteenNoch keine Bewertungen
- R2 SuperDuct Four-Wire Duct Smoke Detector Technical BulletinDokument16 SeitenR2 SuperDuct Four-Wire Duct Smoke Detector Technical BulletinAKITA DRILLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Hydro-Power PlantDokument17 SeitenDesign of Hydro-Power PlantRoy SwaidanNoch keine Bewertungen