Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology - December 2015
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biology - December 2015
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
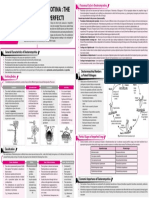
Inflorescence is the arrangement and distribution of flowers on the
CONCEPT INFLORESCENCE
shoot system of a plant. The axis of the inflorescence is called
peduncle, whereas the stalk of individual flower is called pedicel. A
flattened peduncle is known as receptacle. Inflorescence is of five
MAP types- solitary, racemose, cymose, mixed and special.
Compound
racemose
Compound racemose inflorescence is an
indefinite or indeterminate inflorescence in
which the peduncle is branched repeatedly once
Solitary or twice in a racemose fashion. It is of following
terminal types–
Single flower occurs on Solitary (a) Compound raceme or panicle, e.g., goldmohur,
the terminal part of a Flowers occur singly or are Cassia fistula, Yucca.
branch, e.g., poppy. separated from other flowers (b) Compound spike or spike of spikelets, e.g., wheat.
of the same plant by (c) Compound spadix, e.g., coconut, date, banana.
vegetative regions. (d) Compound corymb, e.g., Pyrus, cauliflower.
(e) Compound umbel, e.g., Daucus carota,
fennel, Coriandrum sativum.
Solitary (f ) Compound capitulum, e.g.,
axillary Echinops.
Single flower occurs in
the axil of a leaf, e.g.,
Petunia, China rose.
Solitary
axillary
Racemose
It is an indeterminate inflorescence
which shows indefinite growth. The Catkin
arrangement of flowers is either
Dichasial
acropetal (vertical orientation of
cyme Polychasial cyme axis) or centripetal
(horizontal orientation
Cymose of axis).
A determinate inflore - Spike
scence in which the tip of main Raceme
axis terminates in a flower and further Umbel
Helicoid growth continues by one or more lateral
cyme Cymose branches. The arrange-ment of flowers is
head
either basipetal (vertical orientation Simple
of axis) or centrifugal Raceme
(horizontal orientation of
racemose Peduncle is elongated having
Simple racemose inflore- pedicellate flowers in an acropetal
axis).
Cymose scence is an indefinite fashion, e.g., Lupinus, Raphanus,
inflorescence in which Linaria.
head the peduncle is
Sessile or subsessile flowers unbranched.
are borne centrifugally Spike
around a receptacle, e.g., An elongated peduncle bears sessile
Albizzia, Anthocephalus Scapigerous flowers in an acropetal fashion, e.g.,
Umbel
cadamba, Acacia. Head All the pedicellate flowers arise from a single Achyranthes, Callistemon, Adhatoda
The leafless flowering axis point in a centripetal fashion. The peduncle is vasica.
known as scape bears clusters very much reduced, e.g., Hydrocotyle, Prunus.
of flowers that form a head
which is covered by spaths, Spikelet
With long peduncle
With short peduncle
Biparous or e.g., Allium cepa. Corymb Spikelets are small and few flowered
Dichasial cyme The main axis is comparatively short, and the spikes which are surrounded at the
A terminal flower is subtended lower flowers have much longer pedicels than base by two scales or glumes, e.g.,
by two lateral branches which the upper ones so that all the flowers are brought rice, bamboo, oat, etc.
also end in flowers. The process is more or less to the same level, e.g., Iberis amara .
repeated. Inflorescence axis is Catkin
multipodial, e.g., Spergula, Multiparous Corymbose raceme Pendulous spike which bears naked
Stellaria media, The young flowers appear to be arranged like a
Clerodendrum.
or Polychasial cyme pistillate or staminate flowers, (but
More than two lateral branches corymb but in mature state the longer pedicels not both) e.g., mulberry, poplar, Salix,
continue the growth of of the lower flowers do not bring them to the Quercus.
inflorescence when the parent level of upper ones, e.g., mustard.
axis ends in a flower, e.g.,
Spadix
With flattened
Uniparous or Hamelia, Calotropis, Capitulum
peduncle
Asclepias. The flattened receptacle bears numerous sessile Spike with fleshy peduncle and
Monochasial cyme and small florets (ray florets and disc florets) in a having both male and female flowers.
A single lateral branch arises from the centripetal manner, e.g., Zinnia, Sunflower, Cosmos. It is surrounded by a large green or
peduncle of old flower which terminates coloured bract called spathe, e.g.,
in a flower. The lateral branch also palm, Colocasia, Musa.
terminates in a flower. It is of two types:
(a) Helicoid cyme – All the flowers are borne Cyathium
on the same side forming a sort of helix, e.g., The inflorescence looks like a
Drosera, Begonia, Myosotis. flower. The bracts or the involucre
(b) Scorpioid cyme - Flowers are become fused to form a cup shaped
Hypanthodium
alternately borne on both the sides, structure. The inflorescence contains It has a flask-shaped fleshy
e.g., Tecoma, Ranunculus, pedicellate, achlamydeous, unisexual receptacle which possesses a
Heliotropium. flowers of both the types, male and narrow apical opening guarded by
female. The cup encloses a single hairy structure. The receptacle bears
female flower surrounded by a male flowers towards the pore and
large number of male flowers. female flowers towards the
E.g., Euphorbia Hypanthodium base. E.g., Ficus religiosa,
Mixed pulcherrima. Ficus carica.
Two or more t ypes of
inflorescences get mixed up to
form a mixed inflorescences. It is of
following types:
(a) Panicle of spikelets, e.g., oat, rice. Cyathium Verticillaster
(b) Corymb of capitula, e.g., Ageratum Verticillaster
conyzoides. Two dichasial cyme inflore-
(c) U m b e l o f c a p i t u l a , scences develop from axil of
raceme of capitula. opposite leaves. They together
(d) Thyrsus, e.g., Special form a false whorl around the
grapevine. node, e.g., Ocimum, Leucus.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nums FLPDokument27 SeitenNums FLPRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - June 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - December 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - December 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - February 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - February 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Colocasia GiganteaDokument5 SeitenColocasia GiganteaRonald Deck YamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Iread g8 Hummingbirds Nonfiction Reading TestDokument1 Seite3rd Iread g8 Hummingbirds Nonfiction Reading TestPauline Diane PresenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Reproduction QuestionsDokument3 SeitenPlant Reproduction QuestionsBenjamin YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction Part 2Dokument6 SeitenReproduction Part 2KELVIN CHIBINDANoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 04 - Pollination and FertilizationDokument9 SeitenCHP 04 - Pollination and FertilizationKartavya Jhunjhunwala 9ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Sexual - Reproduction - in - Flowering - PlantsDokument12 Seiten2 Sexual - Reproduction - in - Flowering - PlantsNishtha JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2b. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument5 Seiten2b. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsshobhitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orchid Pollination Biology: Haleigh Ray and Wagner VendrameDokument6 SeitenOrchid Pollination Biology: Haleigh Ray and Wagner VendrameSue OrangesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi BijiDokument16 SeitenAnatomi BijiMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pollen Viability and in Vitro Pollen Germination Studies in Momordica Species and Their Intra and Interspecific HybridsDokument10 SeitenPollen Viability and in Vitro Pollen Germination Studies in Momordica Species and Their Intra and Interspecific HybridsJagatha RaasmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life History of AngiospermDokument45 SeitenLife History of AngiospermgbgbkrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPDokument10 SeitenExperiment 4 Gymnosperms and Angiosperms: Hibiscus SPMirahmad FadzlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Vitro Pollination and in Vitro Fertilization": An Assignment OnDokument13 SeitenIn Vitro Pollination and in Vitro Fertilization": An Assignment OnJagrit KhanalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision of WrightiaDokument22 SeitenRevision of WrightiaRaine BugayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2022-PollinationFlowerFruitDokument6 SeitenAssignment 2022-PollinationFlowerFruitjaveriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embriologi Tumbuhan - Materi 2Dokument21 SeitenEmbriologi Tumbuhan - Materi 2gahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solitaire Flower: Author Frank Nic. Bazsika ©2003Dokument2 SeitenSolitaire Flower: Author Frank Nic. Bazsika ©2003Frank Nic. Bazsika0% (1)
- Program CodingDokument24 SeitenProgram CodingAniket BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument8 SeitenBiology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsYasir SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table FinalDokument3 SeitenTable Finallegendsac2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cotton Breeding: Prof. Dr. Farhatullah SirDokument6 SeitenCotton Breeding: Prof. Dr. Farhatullah SirMuhammad AnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSDokument18 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSAnshika AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PollinationDokument18 SeitenPollinationapi-233236478Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIO PRACTICAL For Class 12Dokument2 SeitenBIO PRACTICAL For Class 12Tushar PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDokument23 SeitenSexual Reproduction in PlantsStephen AreriNoch keine Bewertungen
- FlowersDokument31 SeitenFlowersAleczandra QuesadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Worksheet 9 Updated FlowerDokument2 SeitenLab Worksheet 9 Updated FlowerEnrique F. OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Part 2Dokument3 SeitenSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Part 2HarpreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 Biology AssignmentDokument4 SeitenCH 2 Biology Assignment502 Jainul ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDokument11 SeitenSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsAjayNoch keine Bewertungen