Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
TOS 02 Student's
Hochgeladen von
Ced CalzadoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TOS 02 Student's
Hochgeladen von
Ced CalzadoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
THEORY OF STRUCTURES
Lecture 02
November 25, 2017 01:00pm to 05:00pm
Name:
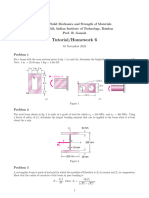
Situation 01: For the truss shown in the figure below, draw the
influence lines for the stresses in the members CD,cD,Dd, and Reference: Example 14.3 Arreola
EF. Determine the values of the maximum stresses in these Situation 06: Solve the figure shown in situation 03 by
members due to a uniform live load of 12kN/m. cantilever method.
Reference: Example 14.4 Arreola
Situation 07: Classify the following structures as statically
determinate, statically indeterminate or unstable.
Reference: Example 9.1 Arreola
Situation 02: For the Warren truss with verticals shown in the a. indeterminate 4° c. indeterminate 2°
figure below draw the influence lines for the stresses in b. indeterminate 3° d. indeterminate 1°
members L2L3, U2U3, L2U3 and U3L3. Determine the maximum
stresses in these members due to a uniform live load of 16
kN/m.
a. unstable c. statically determinate
b. indeterminate 1° d. indeterminate 2°
Situation 08: For the beam supporting the loads shown in the
Reference: Example 9.9 Arreola figure below, determine the slope and deflection of the free end.
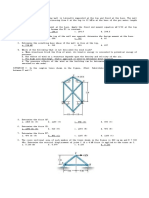
Situation 03: In order to determine the maximum force in each E=200,000 MPa and I= 80 x 106 mm4.
member of the Warren truss, shown in the photo, we must first
draw the influence lines for each of its members. If we consider
a similar truss as shown in the figure below, determine the
largest force that can be developed in member BC due to a
moving force of 25 k and a moving distributed load of 0.6 Reference: Example 15.1 Arreola
k/ft.The loading is applied at the top cord. Situation 09: For the beam shown in the figure, determine
θC, θB and θmax.
Reference: Example 15.6 Arreola
Reference: Example 6.17 Hibbeler Situation 10: For the beam shown in the figure below
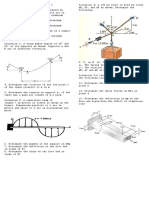
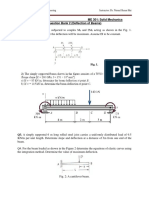
Situation 04: The steel framework is used to support the determine the slope and deflection at the free end C. E =
reinforced concrete slab that is used as an office. The slab is
200,000 MPa, I = 7.5 x 106 mm4.
150mm thick, Residential live load = 1.90kpa and unit weight of
concrete = 24kN/m3. if a = 4m and b = 6m.
Reference: Example 15.4 Arreola
Situation 11: For the cantilever beam shown in fig the figure
below supporting a triangular load which varies from zero at the
free end to 20kN/m at the support, determine the slope and
deflection at the free end. E = 200,000 MPa, I = 250 x 166 mm4.
a. Determine the type of tributary area for beam BE.
a. triangular c. rectangular
b. hexagonal d. trapezoidal
b. Determine the maximum intensity of the varying triangular
load for beam FD. Reference: Example 15.3 Arreola
a. 15 kN/m c. 22 kN/m Situation 12: Determine the deflection at points B and C of the
b. 8 kN/m d. 11 kN/m beam shown in the figure below. Values for the moment of
c. Determine the maximum positive moment carried by beam inertia of each segment are indicated in the figure. Take E =
BE. Assume supports at the ends of beam BE as simple 200 GPa
support
a. 99 kN-m c. 49.6 kN-m
b. 84.33 kN-m d. 36 kN-m
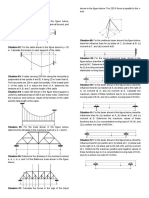
Situation 05: By the portal Method analyze the building frame
shown in the figure below. Draw the moment diagram. Reference: Example 8.7 Hibbeler
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TOS 06 Student's PDFDokument1 SeiteTOS 06 Student's PDFCed Calzado0% (1)
- Structural Theory 2 Problem Set 2Dokument1 SeiteStructural Theory 2 Problem Set 2charlotte jongcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOS 06 Student'sDokument1 SeiteTOS 06 Student'sCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Chapter2 3552Dokument5 SeitenExercise Chapter2 3552Khuon RatanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBVLDokument5 SeitenSBVLvuong100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Buckling of ColumnsDokument8 SeitenChapter 9 - Buckling of ColumnswinzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Struc Const 1 1Dokument23 SeitenStruc Const 1 1Marichu Davillo Garbiles100% (1)
- PSAD Refresher October 9 2023Dokument4 SeitenPSAD Refresher October 9 2023Joshua CopianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 KN 20 KN-M B: Assignment #1Dokument19 Seiten15 KN 20 KN-M B: Assignment #1Rajan SigdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tos1 MidtermDokument2 SeitenTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mom Ssignment Final 2016Dokument3 SeitenMom Ssignment Final 2016das2Noch keine Bewertungen
- OU - Coe OU - Coe: Faculty of EngineeringDokument2 SeitenOU - Coe OU - Coe: Faculty of EngineeringPrashanth PinnojiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Structures PDFDokument4 SeitenTheory of Structures PDFfrancis dimakilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Strength of Materials IIDokument2 SeitenAdvanced Strength of Materials IISohan RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Theory Refresher SetDokument6 SeitenStructural Theory Refresher SetLa BeamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Third Semester (C.B.S.)Dokument26 SeitenStrength of Materials: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Third Semester (C.B.S.)JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question Paper-EMDokument4 SeitenModel Question Paper-EMAgnes RituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preboard 2 SECDokument14 SeitenPreboard 2 SECJae Han100% (1)
- BP (Finals)Dokument5 SeitenBP (Finals)Jaden MoniezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Official Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDokument7 SeitenOfficial Preboard Structural Engineering and ConstructionDexter Dote0% (2)
- CE8602 Structural Analysis II Dec 2021Dokument3 SeitenCE8602 Structural Analysis II Dec 2021dhivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple StrainDokument36 SeitenSimple StrainMartina CelsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ae2254 QBDokument13 SeitenAe2254 QBMahesh J RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review CenterDokument4 SeitenRefresher - Structural Design and Construction: Inhinyero Review Centermichael SonuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce Board May 2011Dokument3 SeitenCe Board May 2011DHANYL KHRISSNA MIJARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuitorial 2Dokument8 SeitenTuitorial 2TMSHAROLDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam (Sec)Dokument15 SeitenFinal Exam (Sec)Sherwin ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEC ERyRM I PDFDokument11 SeitenPEC ERyRM I PDFAlejandro serrano pozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - Load Combinations - QuestionsDokument6 SeitenAssignment 1 - Load Combinations - QuestionsImran SaikatNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB ARM401Dokument6 SeitenQB ARM401Mahi PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1.8 - Cables and ArchesDokument10 SeitenLesson 1.8 - Cables and ArchesAnthony Jerome BellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExercisesDokument4 SeitenExercisesStudent555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Som Model QPDokument2 SeitenSom Model QPkarthick VijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- At Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)Dokument2 SeitenAt Least TWO Questions From Each Part.: (06 Marks)nvnrevNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSAD 4 May 5 2023Dokument19 SeitenPSAD 4 May 5 2023Renne Jude Rollorata100% (1)
- April-2023 DelacruzDokument2 SeitenApril-2023 Delacruzmiabuenafe27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of MaterialsDokument7 SeitenStrength of MaterialsKanakath Ajith0% (1)
- Anna University Exams Nov/Dec 2016 - Regulation 2013 CE6501 Structural Analysis I Unit-I-Indeterminate Frames Part - BDokument6 SeitenAnna University Exams Nov/Dec 2016 - Regulation 2013 CE6501 Structural Analysis I Unit-I-Indeterminate Frames Part - BA.s. MahasreerajhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME223 Tut6Dokument6 SeitenME223 Tut6Lily MaronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Task MergedDokument15 SeitenPractice Task MergedMiyuki IslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce 603 Set DDokument12 SeitenCe 603 Set DJade Paul D. BesanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Theory Refresher Set PDFDokument6 SeitenStructural Theory Refresher Set PDFezer joseph bacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics & FluidsDokument9 SeitenStatics & FluidsShu RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiDokument3 SeitenDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiSatyajit SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFDokument15 SeitenCivil and Mechnical Finalkey PDFNAVEEN BUDDARAPUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Som-Mos-I 205Dokument4 SeitenSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoM Practice QuestionDokument15 SeitenMoM Practice QuestionVallabh MehtreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Report - Pipe ClampDokument30 SeitenSample Report - Pipe ClampgaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralDokument4 Seiten(Join AICTE Telegram Group) 22303 (MOS) Mechanics of StructuralVivek Sharma0% (1)
- Psad November 2022Dokument33 SeitenPsad November 2022paisa baba100% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDokument13 SeitenStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyDokument6 SeitenB.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Week 8 Cables and ArchesDokument3 SeitenTutorial Week 8 Cables and ArchesChin Tiong LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structuralanalysis 1Dokument56 SeitenStructuralanalysis 1sravankumar116Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityhemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM 18ME73 AssignmentsDokument10 SeitenFEM 18ME73 AssignmentsFOODIE USNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesVon EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersVon EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Table of ContentsDokument1 Seite2 - Table of ContentsCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acitivities Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May. Jun. Jul. AugDokument2 SeitenAcitivities Sept. Oct. Nov. Dec. Jan. Feb. Mar. Apr. May. Jun. Jul. AugCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMPM Plate 10Dokument3 SeitenCMPM Plate 10Ced CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMPM Plate 7Dokument4 SeitenCMPM Plate 7Ced CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 27, 2018 Student's PDFDokument1 SeiteJanuary 27, 2018 Student's PDFCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 27, 2018 Student'sDokument19 SeitenJanuary 27, 2018 Student'sCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- January 27, 2018 Student's PDFDokument1 SeiteJanuary 27, 2018 Student's PDFCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete EstimatesDokument13 SeitenConcrete EstimatesCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOS 01 Student'sDokument1 SeiteTOS 01 Student'sCed CalzadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation of Air PreheaterDokument8 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of Air PreheaterAndria MatthewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RW6Dokument19 SeitenRW6devesh singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3Dokument88 SeitenCS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3sushinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein and Planck On Mass-EnergyDokument16 SeitenEinstein and Planck On Mass-EnergyLuis GPNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChapterDokument47 SeitenChapterIsmail ibrahim100% (2)
- HW3 SolutionDokument3 SeitenHW3 Solutioniam0204Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1001 PDFDokument22 Seiten1001 PDFMhmdmohmdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting Sling Load EquationsDokument2 SeitenLifting Sling Load EquationsFabio Okamoto100% (1)
- Chem Ch4 NIE Premium NOtesDokument19 SeitenChem Ch4 NIE Premium NOtesAadil ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Two Stage Reduction Gearbox For All Terrain VehiclesDokument6 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Two Stage Reduction Gearbox For All Terrain VehiclesKunal KoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- System, Law of ThermodynamicDokument31 SeitenSystem, Law of ThermodynamicsamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETA 계산Dokument20 SeitenETA 계산Paing Myint Zaw OoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration Analysis WhitepaperDokument11 SeitenVibration Analysis WhitepaperLorenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Physics Test Series 1 PDFDokument21 SeitenJEE Physics Test Series 1 PDFAkil kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMDokument6 SeitenGRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMWendell CapiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2Dokument38 SeitenLec 2Nathaniel CruelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teknologi Bahan - 2 Analisis Kegagalan Material - HermanDokument40 SeitenTeknologi Bahan - 2 Analisis Kegagalan Material - HermanWiwi Wulan SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Performance Assessment of Non-Compliant SMRF Reinforced Concrete Frame: Shake-Table Test StudyDokument42 SeitenSeismic Performance Assessment of Non-Compliant SMRF Reinforced Concrete Frame: Shake-Table Test StudyR T.INoch keine Bewertungen
- FLUENT13 Workshop XX RAE AirfoilDokument47 SeitenFLUENT13 Workshop XX RAE AirfoilJosé Javier Salinas ZavalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 204 Lecture Chapter 1 1Dokument6 SeitenCE 204 Lecture Chapter 1 1JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Dynamic Behaviour of Saddle Form Nets Under Uniform Harmonic loading-ES-GantesDokument10 SeitenNonlinear Dynamic Behaviour of Saddle Form Nets Under Uniform Harmonic loading-ES-Ganteskostas formulagrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqa MM1B W QP Jun07Dokument8 SeitenAqa MM1B W QP Jun07jfarrell_ie5767Noch keine Bewertungen
- Castigliano'S Theorem: U P U P U P WDokument4 SeitenCastigliano'S Theorem: U P U P U P WTania Rubilar GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center of Rigidity For Semi-Rigid Diaphragm - ETABS - CSI PDFDokument1 SeiteCenter of Rigidity For Semi-Rigid Diaphragm - ETABS - CSI PDFAboalmaaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP 51863Dokument9 SeitenNP 51863Teresa CarterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Forces and EnergyDokument173 SeitenUnit 3 Forces and EnergyBlopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Development of Vortex Blade Less Wind TurbineDokument3 SeitenDesign and Development of Vortex Blade Less Wind TurbineEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Shear Moment DiagramsDokument23 SeitenShear Moment DiagramsmoisesramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Strain Curve ExampleDokument8 SeitenStress Strain Curve ExampleRayhan saiaf binNoch keine Bewertungen