Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous 4ADs7sW8Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Hochgeladen von
Anonymous 4ADs7sW8Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Belt Speed (V) = (PD) (rpm)
Drive Design 3.82
Where: V = Belt speed, ft/min
Speed Ratio = rpm (faster) = PD = N
rpm (slower) pd n PD = Pitch diameter, in.
Where: rpm = Revolutions per minute rpm = Revolutions per minute of same pulley
PD = Larger pitch diameter
pd = Smaller pitch diameter The exact belt pitch length, in inches, can be found as follows:
N = Larger sprocket grooves
n = Smaller sprocket grooves Pitch Length = 2(CD)(Cos q) + p(PD + pd) + q (PD - pd)
2 180
q = Sin-1 PD – pd
( )
2CD
Horsepower = (Q) (rpm) Where: CD = Drive center distance, in.
63025
PD = Large pitch diameter, in.
Where: Q = Torque, lb-in
pd = Small pitch diameter, in.
rpm = Revolutions per minute
Be sure to use torque and rpm values at the same shaft; do not mix
torque and rpm values from different shafts.
The approximate center distance in inches can be found as follows:
Center Distance = K + K 2 - 32(PD - pd)2
Horsepower = (Te)(V)
33,000 16
Where: Te = Effective tension, lb. K = 4PL - 6.28 (PD + pd)
V = Belt speed, ft/min Where: PD = Large pitch diameter, in.
pd = Small pitch diameter, in.
PL = Belt pitch length, in.
Design Horsepower = hp x SF
Where: hp = Horsepower
SF = Service Factor The exact center distance can be calculated using an iterative process between
the center distance and belt length equations above. The exact center distance
has been found when the two equations converge.
2
Torque (lb-in) = 63025 (hp) Span Length = CD2 - (PD - pd)
rpm 4
Where: hp = Horsepower Where: PD = Large pitch diameter, in.
rpm = Revolutions per minute pd = Small pitch diameter, in.
CD = Drive center distance, in.
Design Torque = Q x SF
Where: T = Torque load The arc of contact on the smaller pulley in degrees can be found as follows:
SF = Service factor
Arc of Contact = 180 - 60 (PD - pd)
( )
CD
Where: PD = Large pitch diameter, in.
Service Factor = Rated Ta pd = Small pitch diameter, in.
(Te + Tc) CD = Drive center distance, in.
Where: Ta = Rated belt working tension, lb.
Te = Effective tension, lb.
Tc = Centrifugal tension, lb.
®
103
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Drive Design – Continued Synchronous Belt Tension
Effective Pull
The number of teeth in mesh on the smaller sprocket can be found as follows: Te = TT - TS = 2(Q)
pd
Teeth in Mesh = (Arc) (n) Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
360 TS = Slack side tension, lb.
Where: Arc = Arc of contact; small sprocket, degrees Q = Torque Load, lb-in
n = number of grooves, small sprocket pd = Pitch diameter, in.
Te = Effective tension, lb.
Drop any fractional part and use only the whole number as any tooth not fully Total Tension (8:1)
engaged cannot be considered a working tooth.
TT + TS = 2.571(Q)
If the teeth in mesh is less than 6, correct the belt torque rating with the
pd
following multiplication factors: Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
5 Teeth in Mesh – Multiply by 0.8 TS = Slack side tension, lb.
4 Teeth in Mesh – Multiply by 0.6 Q = Torque load, lb-in
3 Teeth in Mesh – Multiply by 0.4 pd = Pitch diameter, in
2 Teeth in Mesh – Suggest Redesign
1 Tooth in Mesh – Suggest Redesign Tight Side Tension (8:1)
TT = 2.286(Q)
pd
Torque loading due to flywheel effect (acceleration or deceleration) can be Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
calculated as follows: Q = Torque load, lb-in
pd = Pitch diameter, in.
Torque (lb-in) = 0.039(RPM - rpm) (WR2)
t Slack Side Tension (8:1)
Where: RPM = Final revolutions per minute TS = 0.285(Q)
pd
rpm = Initial revolutions per minute
Where: TS = Slack side tension, lb.
WR2 = Flywheel effect, pound-feet2 Q = Torque load, lb-in
(lb-ft2) (1 ft-lb-sec2 is equivalent to 32.2 lb-ft2) pd = Pitch diameter, in.
t = time, seconds
Working Tension Belt Section Belt Width M
Tw = (Te + Tc) (SF) 2MGT GT3 4mm 0.026
Where: Tw = Working tension, lb. 6mm 0.039
The flywheel effect of a sprocket can be estimated as follows: 9mm 0.059
Te = Effective tension, lb.
4 4 12mm 0.078
WR 2 (lb-ft 2) = (F) (Z) (D - d ) Tc = Centrifugal tension, lb. 3MGT GT3 6mm 0.078
1467 SF = Service Factor 9mm 0.117
Where: F = Face width of rim, in. 12mm 0.156
Centrifugal Belt Tension 15mm 0.195
Z = Material density, lb/in3 Tc = (M) (PD)2 (rpm)2 5MGT GT3 9mm 0.172
D = Outside rim diameter, in. 12mm 0.229
16.2 x 106 15mm 0.286
d = Inside rim diameter, in. Where: Tc = Centrifugal tension, lb. 25mm 0.476
M = Belt mass constant
Typical Values: 2024 Aluminum - 0.100 lb/in3 PD = Smaller pitch diameter, in. Belt Section Belt Width M
3M HTD 6mm 0.067
6061 Aluminum - 0.098 lb/in3 rpm = Smaller sprocket 9mm 0.100
revolutions per minute 15mm 0.167
Iron - 0.284 lb/in3
5M HTD 9mm 0.163
15mm 0.272
25mm 0.453
MXL 1/8” 0.019
3/16” 0.029
1/4” 0.038
XL 1/4” 0.071
3/8” 0.106
104 ®
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Polyflex® JB® Belt Tension Micro-V® Belt Tension
Effective Pull Effective Pull
TT - TS = 33,000 hp = Te
( ) TT - TS = 33,000 hp = Te
( )
V V
Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb. Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
TS = Slack side tension, lb. TS = Slack side tension, lb.
hp = Horsepower hp = Horsepower
V = Belt speed, ft/min V = Belt speed, ft/min
Te = Effective tension, lb. Te = Effective tension, lb.
Total Tension (5:1) Total Tension (4:1)
TT + TS = 33,000 (2.5 - G) hp ( ) TT + TS = 33,000 (2.67 - G) hp ( )
GV GV
Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb. Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
TS = Slack side tension, lb. TS = Slack side tension, lb.
hp = Horsepower hp = Horsepower
V = Belt speed, ft/min V = Belt speed, ft/min
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86) G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86)
Tension Ratio Tension Ratio
TT / TS = 1 (Also, TT / TS = eK e ) TT / TS = 1 (Also, TT / TS = eK e )
1 - 0.8G 1 - 0.75G
Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb. Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
TS = Slack side tension, lb. TS = Slack side tension, lb.
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86) G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86)
e = Base of natural logarithms e = Base of natural logarithms
K = .51230, a constant for V-belt drive design K = .44127, a constant for Micro-V drive design
u = Arc of contact in radians u = Arc of contact in radians
Tight Side Tension (5:1) Tight Side Tension (4:1)
TT = 41,250 hp
( ) TT = 44,000 hp( )
GV GV
Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
Where: TT = Tight side tension, lb.
hp = Horsepower
hp = Horsepower
V = Belt speed, ft/min
V = Belt speed, ft/min
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86)
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86)
Slack Side Tension (5:1) Slack Side Tension (4:1)
TS = 33,000 (1.25 - G) hp( ) TS = 33,000 (1.33 - G) hp
(GV)
GV
Where: TS = Slack side tension, lb.
hp = Horsepower Where: TS = Slack side tension, lb.
V = Belt speed, ft/min hp = Horsepower
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86) V = Belt speed, ft/min
G = Arc of contact correction factor (Table 34, Page 86)
®
105
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Power Transmission Conversions
Torque Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric Metric to Metric
Newton Meters x 141.6119 = Ounce Inches Ounce Inches x 0.0071 = Newton Meters Newton Meters x 10.1972 = Kilogram
Newton Meters x 8.8508 = Pound Inches Pound Inches x 0.1130 = Newton Meters Centimeters
Newton Meters x 0.7376 = Pound Feet Pound Feet x 1.3558 = Newton Meters Kilogram Centimeters x 0.0981 = Newton Meters
Newton Meters x 0.1020 = Kilogram Meters
Kilogram Meters x 9.8067 = Newton Meters
Power Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric
Kilowatt x 1.3410 = Horsepower Horsepower x 745.6999 = Watt
Watt x 0.0013 = Horsepower Horsepower x 0.7457 = Kilowatt
Velocity Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric Metric to Metric
Meters/Second x 196.8504 = Feet/Minute Feet/Minute x 0.0051 = Meters/Second Meters/Second x 3.6000 = Kilometers/Hour
Other Conversions
Force Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric Metric to Metric
Newtons x 3.5969 = Ounces Ounces x 0.2780 = Newtons Kilograms x 9.8067 = Newtons
Newtons x 0.2248 = Pounds Pounds x 4.4482 = Newtons Newtons x 0.1020 = Kilograms
Kilograms x 2.2046 = Pounds Pounds x 0.4536 = Kilograms
Length Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric
Millimeters x 0.0394 = Inches Inches x 25.4000 = Millimeters
Meters x 39.3701 = Inches Inches x 0.0254 = Meters
Meters x 3.2808 = Feet Feet x 0.3048 = Meters
Meters x 1.0936 = Yards Yards x 0.9144 = Meters
Kilometers x 3280.84 = Feet Feet x 0.0003048 = Kilometers
Kilometers x 0.6214 = Statute Miles Statute Miles x 1.6093 = Kilometers
Kilometers x 0.5396 = Nautical Miles Nautical Miles x 1.8532 = Kilometers
Area Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S. U.S. to Metric
Square Millimeters x 0.0016 = Square Inches Square Inches x 645.160 = Square Millimeters
Square Centimeters x 0.1550 = Square Inches Square Inches x 6.4516 = Square Centimeters
Square Meters x 10.7639 = Square Feet Square Feet x 0.0929 = Square Meters
Square Meters x 1.1960 = Square Yards Square Yards x 0.8361 = Square Meters
Hectares x 2.4711 = Acres Acres x 0.4047 = Hectares
Square Kilometers x 247.105 = Acres Acres x 0.004047 = Square Kilometers
Square Kilometers x 0.3861 = Square Miles Square Miles x 2.5900 = Square Kilometers
Weight Conversion Constants
Metric to U.S.
Grams x 15.4324 = Grains Kilograms x 35.2740 = Ounces (Avd.) Metric Tons (1000 Kg) x 1.1023 = Net Ton (2000 lb)
Grams x 0.0353 = Ounces (Avd.) Kilograms x 2.2046 = Pounds (Avd.) Metric Tons (1000 Kg) x 0.9842 = Gross Ton (2240 lb)
Grams x 0.0338 = Fluid Ounces (water)
106 ®
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Useful Formulas and Calculations
Other Conversions – Continued
Weight Conversion Constants – continued
U.S. to Metric
Grains x 0.0648 = Grams Pounds (Avd.) x 0.4536 = Kilograms
Ounces (Avd.) x 28.3495 = Grams Net Ton (2000 lb) x 0.9072 = Metric Tons (1000 Kg)
Fluid Ounces (water) x 29.5735 = Grams Gross Ton (2240 lb) x 1.0160 = Metric Tons (1000 Kg)
Ounces (Avd.) x 0.0283 = Kilograms
Measures of Pressure
= 144 pounds per square foot = 62.35 pounds per square foot
1 foot of water at 62°F
= 0.068 atmosphere = 0.433 pounds per square inch
1 pound per square inch = 2.042 inches of mercury at 62°F
= 1.132 feet of water at 62°F
= 27.7 inches of water at 62°F
1 inch of mercury at 62°F = 13.58 inches of water
= 2.31 feet of water at 62°F
= 0.491 pounds per square inch
= 30 inches of mercury at 62°F
Column of water 12 inches high, 1 inch in diameter = 0.341 lb.
= 14.7 pounds per square inch
1 atmosphere
= 2116.3 pounds per square foot
= 33.95 feet of water at 62°F
Decimal and Millimeter Equivalents of Fractions
Inches Inches
Fractions Decimals Millimeters Fractions Decimals Millimeters
1/64 .015625 .397 33/64 .515625 13.097
1/32 .03125 .794 17/32 .53125 13.494
3/64 .046875 1.191 35/64 .546875 13.891
1/16 .0625 1.588 9/16 .5625 14.288
5/64 .078125 1.984 37/64 .578125 14.684
3/32 .09375 2.381 19/32 .59375 15.081
7/64 .109375 2.778 39/64 .609375 15.478
1/8 .125 3.175 5/8 .625 15.875
9/64 .140625 3.572 41/64 .640625 16.272
5/32 .15625 3.969 21/32 .65625 16.669
11/64 .171875 4.366 43/64 .671875 17.066
3/16 .1875 4.763 11/16 .6875 17.463
13/64 .203125 5.159 45/64 .703125 17.859
7/32 .21875 5.556 23/32 .71875 18.256
15/64 .234375 5.953 47/64 .734375 18.653
1/4 .250 6.350 3/4 .750 19.050
17/64 .265625 6.747 49/64 .765625 19.447
9/32 .28125 7.144 25/32 .78125 19.844
19/64 .296875 7.541 51/64 .796875 20.241
5/16 .3125 7.938 13/16 .8125 20.638
21/64 .328125 8.334 53/64 .828125 21.034
11/32 .34375 8.731 27/32 .84375 21.431
23/64 .359375 9.128 55/64 .859375 21.828
3/8 .375 9.525 7/8 .875 22.225
25/64 .390625 9.922 57/64 .890625 22.622
13/32 .40625 10.319 29/32 .90625 23.019
27/64 .421875 10.716 59/64 .921875 23.416
7/16 .4375 11.113 15/16 .9375 23.813
29/64 .453125 11.509 61/64 .953125 24.209
15/32 .46875 11.906 31/32 .96875 24.606
31/64 .484375 12.303 63/64 .984375 25.003
1/2 .500 12.700 1 1.000 25.400
®
107
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Useful Formulas and Calculations
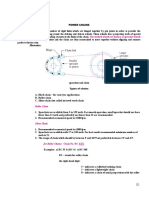
Power To or From A.C. Machinery D.C. Machinery
Machinery Kilowatts = (volts) (amps) (p.f.) Kilowatts = (volts) (amps)
Y 1000
In the absence of accurate data on horsepower
requirements for a drive, it is sometimes possible Where: p.f. = Power factor
to calculate the power output from a driveR
machine or the required power input to a driveN Y = 1000 (Single phase) Power required for generator
machine. In each formula below, efficiency must be Y = 577 (Three phase)
known or estimated. For checking a drive which is Horsepower = (volts) (amps)
providing power to a pump or generator, it is more (746)(eff)
conservative to estimate a low efficiency for the Power required for generator (alternator)
Where: eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic
driveN machine. For power input to a drive from a
efficiency.
motor or turbine, is more conservative to estimate Horsepower = (volts) (amps) (p.f.)
high efficiency for the driveR machine. Efficiency is (Z) (eff)
used as a decimal in the formulas. For example, if a
Where: eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic Power from motor
pump is 70% efficient, use .70 in the formula.
efficiency.
Horsepower = (volts) (amps) (eff)
p.f. = Power factor 746
Hydraulic Machinery Z = 746 (Single phase) Where: eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic
Power required by pumps Z = 431 (Three phase) efficiency.
Horsepower = (F) (p)
(1714) (eff) Power from motor
Where: F = Flow rate, gallons per minute
Horsepower = (volts) (amps) (p.f.) (EFF)
P = Discharge pressure for pumps, inlet (Z)
pressure for turbines, pounds/square
Where: eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic
inch
efficiency.
eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic
p.f. = Power factor
efficiency.
Z = 746 (Single phase)
Z = 431 (Three phase)
Power from water wheel or turbine
Horsepower = (F) (p) (eff)
(1714)
Where: F = Flow rate, gallons per minute
P = Discharge pressure for pumps, inlet
pressure for turbines, pounds/square
inch
eff = Overall mechanical and hydraulic
efficiency.
108 ®
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Gates Application Data Worksheet
Company: ___________________________________________________ Contact: ____________________________________________
Address: ____________________________________________________ Title: ______________________________________________
____________________________________________________ Phone: ____________________ Fax: ___________________
____________________________________________________ Email: _____________________________________________
Application Summary
General Description: ____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Product Type: __________________________________________________________ Estimated Production Volume: ____________________
Prototype Time Schedule: _________________________________________________ Production Time Schedule: ______________________
Function: Motion Transfer Reversing Light Loads Moderate Loads Heavy Loads
On/Off Cycle Continuous Operation Cycle Description: ___________________________________________
Design Parameters
DriveR
Motor Type & Description (Servo, Stepper, D.C., A.C., etc.): ________________________________________________________________________
Nominal Motor Torque/Power Output: __________________________________ RPM:________________________________________________
Max/Peak Motor Torque/Power Output: _________________________________ RPM:________________________________________________
Motor Stall Torque (If Applicable): __________________________________________________________________________________________
DriveN
Description of DriveN Component:: _________________________________________________________________________________________
Required Operating RPM: _____________________ Speed Ratio: ______________________ Speed Up/Down: __________________________
Additional Details: _____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Geometry
Two Point Drive Multi-Point Drive If Multi-Point: Are Layout Prints Available? Yes No
Center Distance Range: ___________________________ To _________________________ Fixed Design Adjustable Design
Type of Adjustment: ____________________________________________________________________________________________________
Tensioner Idler: None Inside Outside Slack Side Tight Side Diameter: _______________________
DriveR: Max O.D. ______________ Max Width _________________________ DriveN: Max O.D. __________ Max Width __________
Special Requirements
Product Design Life: ________________ Belt Design Life: _______________ Usage: Hours/Day: _______________ Hours/Year: _______________
Shafts: DriveR ________________ DriveN _________________ Pulley Materials: Prototype ________________Production ________________
Environmental Conditions:
Temperature _____________ Moisture _____________ Oil ____________ Abrasives ______________ Static Conductivity _______________
Special Requirements (Registration, Motion Control, Speed Control, Etc.) ______________________________________________________________
®
109
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
GATES CORPORATION For Power Transmission drive design assistance,
800.777.6363 contact Gates Product Application at 303-744-5080
©2015 Gates Corporation
or 17183 1/2015
Polígono Indutrial O Rebullón s/n. 36416 - Mos - España - rodavigo@rodavigo.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Handouts MD Day 5Dokument7 SeitenHandouts MD Day 5James Ivan AnoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meshing Spur GearsDokument25 SeitenMeshing Spur GearsCherrydhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE ME 8 SEM-Design For Flat Belt Drive Centrifugal Tension Max. Tension Max. Power - Khemraj Berag 2239301Dokument11 SeitenBE ME 8 SEM-Design For Flat Belt Drive Centrifugal Tension Max. Tension Max. Power - Khemraj Berag 2239301Ankan BeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 5B Rheology & HydraulicsDokument10 SeitenSection 5B Rheology & HydraulicsLazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of A Crankshaft National InstitutDokument12 SeitenDesign of A Crankshaft National Institutozofereh jesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejemplo de Engranajes HelicoidalesDokument2 SeitenEjemplo de Engranajes HelicoidalesMijhael Anatholi Romero MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation FD Fan PowerDokument7 SeitenCalculation FD Fan PowerIrwansyah MuchtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV Ahmad Rizal FawziDokument10 SeitenPV Ahmad Rizal FawziAji Putra PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering and Development Corporation of The Philippines: H P H PDokument2 SeitenEngineering and Development Corporation of The Philippines: H P H Pmark ignacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts MD Day 2Dokument7 SeitenHandouts MD Day 2Cantera, Cris Bryan E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design Formula ListDokument7 SeitenMachine Design Formula ListHarpreet Randhawa100% (3)
- The Toothed Wheels Are Known As Sprocket Wheels or Simply SprocketsDokument5 SeitenThe Toothed Wheels Are Known As Sprocket Wheels or Simply SprocketsLanugan, Jenkhen B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tedata: Programm Benutzer Datum Kunde Proj. NRDokument3 SeitenTedata: Programm Benutzer Datum Kunde Proj. NRJason CanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tedata: Programm Benutzer Datum Kunde Proj. NRDokument3 SeitenTedata: Programm Benutzer Datum Kunde Proj. NRJason CanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine DesignDokument15 SeitenMachine DesignYaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flange Analysis For Internal Pressure - ASME Section VIII, Division 1, Appendices 2 and S - 2004 EditionDokument1 SeiteFlange Analysis For Internal Pressure - ASME Section VIII, Division 1, Appendices 2 and S - 2004 Editionגרבר פליקסNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design 2 FinalDokument64 SeitenMachine Design 2 FinalbacalsojvahronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Escuela Politécnica Nacional: Facultad de Ingeniería MecánicaDokument16 SeitenEscuela Politécnica Nacional: Facultad de Ingeniería MecánicaAly HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 452 ContentDokument63 SeitenM 452 ContentprasannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRESSING CALCULATIONS - Malbogon BridgeDokument1 SeiteSTRESSING CALCULATIONS - Malbogon BridgeRay Vincent Agorita FriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEATER (H-01) : LMTD (-T) - (T - T) LN - T - TDokument8 SeitenHEATER (H-01) : LMTD (-T) - (T - T) LN - T - TJofanny Ferdian RahmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenSample Formula Sheetjessica castilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helical Gears: Free Body DiagramDokument9 SeitenHelical Gears: Free Body Diagramterrence miguel balitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belts and Pulleys Chains and Sprockets Bolts and Screws December 19 2019Dokument13 SeitenBelts and Pulleys Chains and Sprockets Bolts and Screws December 19 2019peter grimmieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming FormulasDokument2 SeitenProgramming FormulasYashNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssdDokument12 SeitenAssdjoe leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turan Ijaz - (18-CLE-53)Dokument5 SeitenTuran Ijaz - (18-CLE-53)56-2k18 Muhammad Abdullah100% (1)
- Length of ReactorDokument5 SeitenLength of ReactorLily Antonette AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of Pulley Belt DriveDokument8 SeitenDesign Calculation of Pulley Belt Driveأحمد دعبس80% (5)
- ShaftDokument5 SeitenShaftWendel EjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lampiran Perhitungan Menggunakan Data Aktual 1. Menghitung Heat Balance (Q)Dokument8 SeitenLampiran Perhitungan Menggunakan Data Aktual 1. Menghitung Heat Balance (Q)Mas BagusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShaftDokument15 SeitenShaftFamela GadNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Power Requirement/Design Horsepower A. Force Required: ComputationDokument8 SeitenI. Power Requirement/Design Horsepower A. Force Required: Computationjaynard_alejandrinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Service Welding Calculation (Confidential)Dokument1 SeiteIn Service Welding Calculation (Confidential)Rudi DaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JavaProp Users GuideDokument69 SeitenJavaProp Users GuideNurhayyan Halim RosidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satellite Link Design Analog & DigitalDokument12 SeitenSatellite Link Design Analog & Digitalavi.avi.90457Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanische WellenDokument62 SeitenMechanische WellenScribdTranslationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocating+Compressors+ +3.+Useful+CorrelationsDokument17 SeitenReciprocating+Compressors+ +3.+Useful+CorrelationsChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stern Tube NewDokument1.154 SeitenStern Tube NewMuchammatAlvinurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project-7 Design of A Connecting RodDokument9 SeitenProject-7 Design of A Connecting Rodhitesh reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FWEFJLNIY4QKLQXDokument13 SeitenFWEFJLNIY4QKLQXSoldan MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation RCP T-BridgeDokument5 SeitenCalculation RCP T-BridgeAndreas SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handouts MD Day 2Dokument7 SeitenHandouts MD Day 2Obane Ordnael P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compressors Efficiency Calculations5Dokument11 SeitenCompressors Efficiency Calculations5Ahmed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of DavitDokument2 SeitenCalculation of DavitpiziyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perhitungan FatgueDokument6 SeitenPerhitungan FatgueArianta RianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation Coconut Dehusking and Decorticating MachineDokument10 SeitenCalculation Coconut Dehusking and Decorticating MachineJakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Truss Malika Ali BSCE-5ADokument78 SeitenDesign of Truss Malika Ali BSCE-5AUdat Hakeem Malang AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Selection According "Warman Slurry Pumping Handbook"Dokument12 SeitenPump Selection According "Warman Slurry Pumping Handbook"yoel cueva arquinigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 1Dokument2 SeitenLesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 1Dokument2 SeitenLesson 1 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- Project Gear Design TemplateDokument38 SeitenProject Gear Design Templatenofal AdreesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaft DesignDokument13 SeitenShaft DesignKarthikeyan SankarrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reducer GearDokument2 SeitenReducer GearAditya DarmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface-Stress Analysis of A Spur-Gear Train: EXAMPLE 12-6Dokument4 SeitenSurface-Stress Analysis of A Spur-Gear Train: EXAMPLE 12-6Jesus 'JsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trunnion Check Calculation (Onsite) : Page No: Contract No: System NoDokument2 SeitenTrunnion Check Calculation (Onsite) : Page No: Contract No: System NoJ A S JAS0% (1)
- Joint Check 1Dokument9 SeitenJoint Check 1abin100% (1)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsVon EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 29Dokument22 SeitenLesson 29jake maramotNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Dictionary of Units of MeasurementDokument3 SeitenA Dictionary of Units of MeasurementkapilnexusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vixen r130s Users Manual 458559Dokument1 SeiteVixen r130s Users Manual 458559Gandhi PalominoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm - e 220Dokument12 SeitenAstm - e 220Prima SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 2metrologyDokument6 SeitenEx 2metrologyPiyush ChaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academy of Sciences, 112 (11), 3173-3175Dokument3 SeitenAcademy of Sciences, 112 (11), 3173-3175Venesse Aulga Abellanosa100% (2)
- Chapter 1-Part 1Dokument36 SeitenChapter 1-Part 1Ammar FitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astro 245gw Rajasekharuni Vamsi Mohan 20171024.17516.8478Dokument3 SeitenAstro 245gw Rajasekharuni Vamsi Mohan 20171024.17516.8478Mike VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mine Surveying CompileDokument31 SeitenMine Surveying Compilenuno pereira0% (1)
- Pt. Muria Sumba Manis Rindi Majangga Estate (RME) : Peta Rencana RidgerDokument1 SeitePt. Muria Sumba Manis Rindi Majangga Estate (RME) : Peta Rencana RidgerSyahrul KamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp-Error-by-Azimuth-of-the-Sun Allistair BallileDokument4 SeitenComp-Error-by-Azimuth-of-the-Sun Allistair BallileAnoopNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetrologyDokument25 SeitenMetrologyThanga PrakasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Weights and MeasurementsDokument5 SeitenBible Weights and MeasurementspalharjeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce F213Dokument1 SeiteCe F213Vinayaka RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Material Code Creation (21.08.2021)Dokument9 SeitenSap Material Code Creation (21.08.2021)CwsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physic Laboratory Report: Measurement of Basic Constant:Length and WeightDokument9 SeitenPhysic Laboratory Report: Measurement of Basic Constant:Length and Weightpchek_s100% (1)
- The Michelson InterferometerDokument13 SeitenThe Michelson InterferometerVũ BìnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab #4 SpectrophotometryDokument10 SeitenLab #4 Spectrophotometrythamizh555Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 1 B A LinearmeasurementusDokument4 Seiten3 1 B A Linearmeasurementusapi-312666393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1Dokument7 SeitenExp 1Hafiz SallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flu InstruDokument21 SeitenFlu InstruAshok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problems From Hibbelers Book Engineering Mechanics - SECTIONS 12-9 AND 12-10Dokument21 SeitenSolved Problems From Hibbelers Book Engineering Mechanics - SECTIONS 12-9 AND 12-10Sai PavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Calibration03112015Dokument29 SeitenAntenna Calibration03112015daveNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNR - VS - Ber - Sanabria-CifuentesDokument3 SeitenSNR - VS - Ber - Sanabria-CifuentesCamilo Andres SanabriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Changes in Magnitude, Direction, or BothDokument4 SeitenChanges in Magnitude, Direction, or BothTrixia MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- B47AA-Process Industries A Student GuideDokument159 SeitenB47AA-Process Industries A Student GuideSaif RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liebmann - Testing Temperature Uniformity On A Flat-Plate Infrared CalibratorDokument6 SeitenLiebmann - Testing Temperature Uniformity On A Flat-Plate Infrared CalibratorCristian MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Xi Practical (Slide Callipers)Dokument11 SeitenClass Xi Practical (Slide Callipers)Spandan NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUG532 - Advanced Geodesy Final ReportDokument13 SeitenSUG532 - Advanced Geodesy Final Reportmruzainimf67% (3)
- List of Measuring Devices - WikipediaDokument8 SeitenList of Measuring Devices - WikipediaVeer EducationNoch keine Bewertungen