Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
12.13. Force Analysis SS Rattan - Torque - Force
Hochgeladen von
JithumonOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
12.13. Force Analysis SS Rattan - Torque - Force
Hochgeladen von
JithumonCopyright:
3/26/2019 12.13.
Force Analysis SS Rattan | Torque | Force
1 of 67 Search document
410 Theory of Machines
STATIC FO
12 ANALYSIS
Introduction
In all types of machinery, forces are transmitted from one component to the other such as f
a brake drum to a brake shoe, from a gear to shaft. In the design of machine mechanisms,
magnitudes as well as the directions of forces transmitted from the input to the output. The
proper sizes of the machine components to withstand the stresses developed in them. If pr
the components may fail during the machine operations. On the other hand, if the mem
more strength than required, the machine may not be able to compete with others due t
etc.
If the components of a machine accelerate, inertia forces are produced due to thei
magnitudes of these forces are small compared to the externally applied loads, they can be
the mechanism. Such an analysis is known as static-force analysis. For example, in lifting c
the static weight loads may be quite high relative to any dynamic loads due to acceleratin
force analysis is justified.
When the inertia effect due to the mass of the components is also considered, it is cal
which will be dealt in the next chapter.
12.1 CONSTRAINT AND APPLIED FORCES
A pair of action and reaction forces which constrain two connected bodies to beha
depending upon the nature of connection are known as constraint forces whereas fo
on a system of bodies are called applied forces.
Constraint forces As the constraint forces at a mechanical contact occur in pair
effect on the system of bodies. However, for an individual body isolated from the
pair of constraint forces has to be considered.
https://www.scribd.com/document/369669883/12-13-Force-Analysis-SS-Rattan 1/1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Robotics & Automation Society: A Proposal For EstabilishingDokument7 SeitenRobotics & Automation Society: A Proposal For EstabilishingAbdela Aman MtechNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Important QuestionDokument2 SeitenMCQ Important QuestionAmit MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ For Welding ShopDokument6 SeitenMCQ For Welding Shopsudhir guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Tool Engineering DesignDokument34 SeitenMachine Tool Engineering DesignAshok Kumar UppariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Material - SyllabusDokument2 SeitenMechanics of Material - SyllabusRahul PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology OptimizationDokument40 SeitenTopology OptimizationjeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass PropertiesDokument17 SeitenMass Propertiespalaniappan_pandianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Machines Lab ManualDokument56 SeitenDynamics of Machines Lab ManualSavan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Materials and Metallurgy QBDokument13 SeitenEngineering Materials and Metallurgy QBAnand Jayakumar ArumughamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis FEMDokument9 SeitenDynamic Analysis FEMbhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics PDFDokument16 SeitenEngineering Mechanics PDFSasikumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOM Content Beyond SyllabusDokument11 SeitenSOM Content Beyond SyllabusVignesh VickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction AutoDokument24 SeitenFriction AutoSayyadh Rahamath BabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lamis Theorem Gate Notes 21Dokument4 SeitenLamis Theorem Gate Notes 21Shashikant kumar 21ME15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersDokument23 SeitenEngineering Physics - I - PH6151 Important 2 Marks With AnswersZaffu Zealy100% (4)
- CAD CAM Unit - 3 PPT-ilovepdf-compressedDokument66 SeitenCAD CAM Unit - 3 PPT-ilovepdf-compressedTaha SakriwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Marks With AnswersDokument16 Seiten2 Marks With AnswersKarthik SoundarrajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Crankshaft With Different CompositeDokument9 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Crankshaft With Different CompositeSAI CHARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Vibrations PDFDokument223 SeitenMechanical Vibrations PDFmark mutimushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.kinematic SynthesisDokument13 Seiten11.kinematic SynthesisSatyam AhirwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs On SCBDokument9 SeitenMCQs On SCBjigardesai100% (1)
- Previous Year Question Paper With AnswersDokument108 SeitenPrevious Year Question Paper With AnswersTejasPatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brakes & Dynamometers - Machine Dynamics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDokument7 SeitenBrakes & Dynamometers - Machine Dynamics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryINFO TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Drafting Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenDesign & Drafting Lab ManualKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 84 TOP MOST Strength of Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument24 Seiten84 TOP MOST Strength of Materials - Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Mechanical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsJagadish MekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 - Static Force AnalysisDokument36 SeitenUnit-1 - Static Force AnalysisHareesha N GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Unit II Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenDom Unit II Imp QuestionsSree MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Test On 4 Stroke Diesel EngineDokument4 SeitenLoad Test On 4 Stroke Diesel EngineRanjit DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Unit 1Dokument41 SeitenDom Unit 1Martin SudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beam Analysis Using Singularity FunctionDokument16 SeitenBeam Analysis Using Singularity FunctionSire MkubwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibration LabDokument38 SeitenVibration Labtinkusk24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design Unit 1 Design PhilosophyDokument12 SeitenMachine Design Unit 1 Design PhilosophyAnand Babu100% (3)
- Cidm NotesDokument23 SeitenCidm NotesPrajwal Jaiswal100% (1)
- PPC Loading and SchedulingDokument11 SeitenPPC Loading and SchedulingHarshwardhan PhatakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 8594 Dynamics of Machinery Unit 1 Online Video LectureDokument42 SeitenMe 8594 Dynamics of Machinery Unit 1 Online Video LecturesankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing of I C Engines VTUDokument31 SeitenTesting of I C Engines VTUPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4-Computer Aided DesignDokument15 SeitenUnit-4-Computer Aided DesignMuthuvel M100% (2)
- ME7327 MECHANICAL VIBRATION Question PaperDokument2 SeitenME7327 MECHANICAL VIBRATION Question PaperFaisal RahmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming, Design A Spring (Helical) Under Given Static and Fluctuating Load For A Given Spring Index So That The Spring Design Lie Within Safe Limit.Dokument12 SeitenC Programming, Design A Spring (Helical) Under Given Static and Fluctuating Load For A Given Spring Index So That The Spring Design Lie Within Safe Limit.Manoj Kumar GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity of MechanismDokument10 SeitenVelocity of Mechanismرعد العكيليNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoM Summary PointsDokument39 SeitenMoM Summary PointsAmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- QT - Unit 1Dokument14 SeitenQT - Unit 1aakanksha2693Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms With Lower PairsDokument43 SeitenMechanisms With Lower PairsVincentius NikimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOME-I Unit 1 - Lec 2Dokument21 SeitenDOME-I Unit 1 - Lec 2Gautam Gunjan100% (1)
- GE6253 Engineering Mechanics 2 Mark With Answers R2013Dokument13 SeitenGE6253 Engineering Mechanics 2 Mark With Answers R2013vsanthanam100% (2)
- Shape Function GeneratioDokument34 SeitenShape Function Generatiodtr17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrations 2dofDokument29 SeitenVibrations 2dofbhukthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 2354 Automobile Engineering 2009 6th Semester Anna UniversityDokument2 SeitenME 2354 Automobile Engineering 2009 6th Semester Anna UniversityParanthaman GanapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 - Computer Assisted Part Programming - Motion StatementsDokument40 SeitenLecture 7 - Computer Assisted Part Programming - Motion StatementsRakibul HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela B. Tech. (6 Semester), Mechanical Engineering, Mid-Semester, Spring (2021-22)Dokument9 SeitenNational Institute of Technology, Rourkela B. Tech. (6 Semester), Mechanical Engineering, Mid-Semester, Spring (2021-22)Md. Tariqul Islam MunnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 One Marks QuestionsDokument6 SeitenUnit 3 One Marks QuestionsRahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOM Unit 1Dokument100 SeitenKOM Unit 1dpksobs100% (1)
- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY: UNIT 2: VELOCITY & ACCELARATION: Objective Questions From Gate With SolutionsDokument7 SeitenKINEMATICS OF MACHINERY: UNIT 2: VELOCITY & ACCELARATION: Objective Questions From Gate With SolutionsVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTU Report FormatDokument33 SeitenVTU Report Formatstorage05046Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Vibrations QuizzDokument16 SeitenMechanical Vibrations QuizzSagan PreetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.13. Force Analysis SS Rattan - Torque - ForceDokument1 Seite12.13. Force Analysis SS Rattan - Torque - ForceroshensmauelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of Per Cent Failures From Stress/Strength InterferenceDokument20 SeitenPrediction of Per Cent Failures From Stress/Strength InterferenceNohora Alejandra Jimenez AbrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom 2 MarkDokument34 SeitenDom 2 MarkJaya RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and Analysis of The Dynamics of Mechanical StructuresDokument51 SeitenMeasurement and Analysis of The Dynamics of Mechanical StructuresOscar Daga CaravantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seat No.: 3 Hours/100 MarksDokument7 SeitenSeat No.: 3 Hours/100 MarksomNoch keine Bewertungen
- snc1p Electricity Summative LabDokument3 Seitensnc1p Electricity Summative Labapi-504985945Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of Motion 5.48 MBDokument56 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motion 5.48 MBLakshyaNoch keine Bewertungen
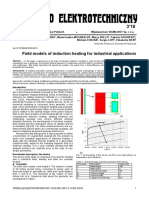
- Field Models of Induction Heating For Industrial ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenField Models of Induction Heating For Industrial ApplicationsLuckyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.0amp Schottky Barrier Rectifiers: Voltage Range FeaturesDokument2 Seiten5.0amp Schottky Barrier Rectifiers: Voltage Range Featuresيوكي آنى سانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe Simulation and Experiment of A Self Excited Synrel Generator Based On Comsol SoftwareDokument7 SeitenFe Simulation and Experiment of A Self Excited Synrel Generator Based On Comsol SoftwareboucharebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brushless DC MotorsDokument7 SeitenBrushless DC MotorsRonald LugwireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Fall: Nattanon VeerakulDokument9 SeitenFree Fall: Nattanon Veerakulapi-327824456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Branch Circuits and FeedersDokument28 SeitenBranch Circuits and FeedersgteklayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Practicals 1 and 2Dokument184 SeitenPhysics Practicals 1 and 2Zahid ArainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merlin Gerin Medium VoltageDokument10 SeitenMerlin Gerin Medium VoltagekjfenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Locking Systems: 490 Vehicle Security Systems Central Locking Systems, Locking SystemsDokument20 SeitenLocking Systems: 490 Vehicle Security Systems Central Locking Systems, Locking SystemsJulio MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Dokument27 Seiten4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Eleazar Tami-ingNoch keine Bewertungen
- MST 2Dokument4 SeitenMST 2Neha Prashant VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gek ManualDokument36 SeitenGek Manualicaro100% (1)
- Jntuk Cse r13 SyllabusDokument142 SeitenJntuk Cse r13 SyllabusJaya Tangirala100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Center of Gravity, Center of Mass andDokument28 SeitenChapter 9 Center of Gravity, Center of Mass andAnonymous uVgybS8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trickle Bed Reactor ScaleupDokument15 SeitenTrickle Bed Reactor ScaleupAks KasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 37D Metal Gearmotors: Performance Summary and Table of ContentsDokument18 Seiten37D Metal Gearmotors: Performance Summary and Table of ContentsDavid Castillo UribeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4Dokument13 SeitenLab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4api-439639600Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Calculation Summary and ExamplesDokument12 SeitenPower Calculation Summary and ExamplesHernán RodarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOL 5 Pulse GeneratorsDokument755 SeitenVOL 5 Pulse Generatorsgorods5rtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of An AUTOMATIC BLACK BOARD CleanerDokument21 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of An AUTOMATIC BLACK BOARD CleanerNAGARAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compactador Neumatico CaterpillarDokument2 SeitenCompactador Neumatico CaterpillarAnonymous KOtSfT6qNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 412291Dokument8 SeitenQuestion 412291Nikhil PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science q4 Slm4Dokument12 SeitenPhysical Science q4 Slm4Jorek MasinaringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Closed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorDokument27 SeitenClosed Loop Speed Control of 3-Phase Induction MotorRajesh kumar yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOTOR SOFT STARTERS - Air Core ReactorsDokument3 SeitenMOTOR SOFT STARTERS - Air Core Reactorsmv_mallikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet PDFDokument3 SeitenDatasheet PDFAnonymous aPgW0atTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems in Physics For PracticeDokument3 SeitenProblems in Physics For PracticeAshwinNoch keine Bewertungen