Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology - March 2016
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biology - March 2016
Hochgeladen von
Rahique ShuaibCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
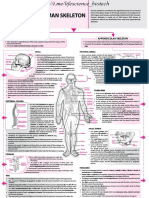
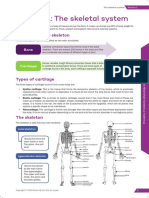
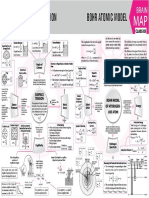
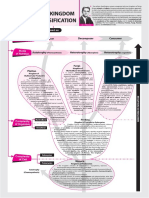
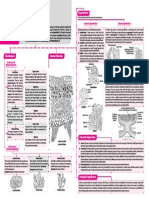
Human skeleton constitutes the rigid framework of connected
CONCEPT HUMAN SKELETON
bones that gives shape to the body, protects and supports its
soft organs and tissues and provides attachments for muscles.
MAP
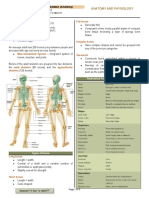
Human skeleton is made up of 206 bones (300 bones in
newborns) which are distributed into axial and appendicular
skeleton.
AXIAL SKELETON APPENDICULAR SKELETON
· It lies along the longitudinal axis of the body; supports and protects the organs of the · It is situated at the lateral sides which actually extend outwards from the principal axis.
head, neck and trunk. · It consists of two girdles, the pectoral and pelvic girdles and the bones of arms and
· It includes skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs . legs.
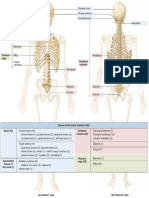
SKULL PECTORAL GIRDLE
Parietal Manubrium of sternum Coracoid
Frontal bone bone · Skull is the bony framework of the head. · Each pectoral girdle consists of two bones : 1 Clavicle process
· It consists of 29 bones, separated by sutures. These bones clavicle and 1 scapula. The scapula (shoulder
Nasal bone are cranial bones (8 flattened bones forming the brain blade) consists of a sharp ridge, the spine and a Pectoral Girdle
triangular body. The end of the spine projects as a (Shoulder Girdle)
Zygomatic box or cranium), facial bones (14 bones forming the front
bone part of the skull), hyoid bone (single bone forming floor of flattened and expanded process called acromion.
Maxilla the buccal cavity) and bones of middle ear (3 small bones This process articulates with the clavicle. Acromion
Scapula
in each ear, namely malleus, incus and stapes). · At the lateral end of the superior of the scapula is a process
Occipital
bone · The bones of cranium are : 1 frontal bone, 2 parietal bones, projection of the anterior surface called the coracoid
Mandible Temporal
Mastoid 2 temporal bones, 1 occipital bone, 1 sphenoid bone and process, to which the tendons of the muscles
bone
process
1 ethmoid bone. attach. At the point where the superior and
· Temporal bone has a projection called mastoid lateral borders of the scapula meet there is the lateral angle which
process. Cranium presents a shallow articular surface termed as glenoid cavity into
which the head of the humerus is articulated.
· The cranium has two small protuberances at the Skull
· The primary function of the pectoral girdle is to provide an
posterior end called occipital condyles, that articulate with the first vertebra (atlas
Facial bones attachment point for the numerous muscles that allow the shoulder
vertebra), thus, human skull is dicondylic.
and elbow joints to move.
· 14 bones form the skeleton of face viz. 2 zygomatic, 2 maxilla, 2 nasal, 2 Clavicle
mandible
lacrimal, 1 vomer, 2 palatine, 2 inferior nasal conchae and 1 mandible.
Ribs
· Hyoid is a u-shaped bone which attaches tongue with the floor of buccal Cervical
cavity. It does not articulate with any other bone. vertebra
· A large hole called foramen magnum at the base of skull allows the
FORELIMBS
brain to continue into the spinal cord located in the backbone. Scapula
· Each arm has 30 bones, which constitute 1 humerus (upper arm), 1
· Skull protects our brain; it bears jaws which help in mastication of food, Sternum radius and 1 ulna (lower arm), 8 carpals (wrist),
etc. 5 metacarpals (palm) and 14 phalanges (digits).
Humerus · The humerus is the longest bone in the upper extremity.
VERTEBRAL COLUMN Xiphoid · At the bottom of the humerus, are two depressions where it
process of connects to the ulna and radius of the forearm.
7 Cervical vertebrae · It is also called backbone or spine. It sternum · Together, the humerus and the ulna make up the elbow, ulna is
(neck backbones) is curved, vertical rod, about 70 cm
longer than the radius. Radius, however, contributes more to the
long, in the mid-dorsal line of the Radius movement of the wrist and hand than the ulna.
neck and trunk. It consists of 33
12 Thoracic vertebrae Ulna · Each wrist is composed of eight carpals which are
(chest backbones) vertebrae. However it consists of 26
Coccyx arranged in two rows : scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum and
bones, because five sacral vertebrae
Pubis pisiform in proximal row and trapezium, trapezoid,
are fused to form one sacrum and
four coccygeal vertebrae are fused to capitate and hamate in distal row.
Intervertebral disc
form one coccyx. Carpals · The forelimbs give support to the shoulders by articulating
Ischium Metacarpals the head of the humerus with the glenoid cavity of the
5 Lumbar vertebrae · A typical vertebra has a large, disc-like
(lower backbones) anterior, flattened portion, the Phalanges pectoral girdle.
Sacrum (5 fused
centrum or body and a posterior Femur
pelvis backbones) portion, the neural arch.. The latter
Coccyx encloses the spinal cord. The hole formed Ilium PELVIC GIRDLE
by the neural arch is the vertebral
foramen.. The vertebral foramina of all Lumbar · The pelvic girdle
girdle, also
twenty four vertebrae form the vertebral canal or neural canal. vertebra Patella called the hip girdle, is
Sacrum
· Vertebrae are categorised into five groups: cervical (7), thoracic (12), (12) composed of two coxal
lumbar (5), sacral (5) and coccygeal (4). (hip) bones. Ilium
· Vertebral column displays four curves to enhance balancing powers and firmness for · The coxal bones are also
called the ossa coxae or Coccyx
upright posture of the body. These curvatures are cervical, thoracic, lumbar and pelvic Fibula Pubis Acetabulum
(=sacral). innominate bones. Ischium
· Each coxal bone consists Pubic
· Between the centre of adjacent vertebrae there are elastic pads of fibrocartilage, the Tibia Pubic arch symphysis
intervertebral discs which provide mobility to the vertebrae, check undue frictions and of three separate parts :
take up shocks. the ilium (short and
Tarsals
· Vertebral column carries the weight of the body in motion and when the organism is standing. straight bone), the ischium (lower elongated bone, running parallel to
Metatarsals vertebral column) and the pubis (inner, smaller bone).
STERNUM Phalanges · On its outer surface it has a deep depression called the acetabulum which,
Clavicular
with almost spherical head of the femur, forms the hip joint.
· This is a flat bone which is present just under the
notch · It supports the weight of the body from the vertebral column. It also protects
Manubrium skin in the middle of the front of the chest. It is about
and supports the lower organs, including the urinary bladder, the
Sternal 15 cm long.
angle reproductive organs, and the developing foetus in case of a pregnant
Facets for · Its shape is like a dagger and consists of three parts—the woman.
attachment
Body of ribs 1-7 manubrium is the uppermost part, the body is the middle portion
and the xiphoid process is the tip of the bone.
· The true ribs (7 pairs) are attached to the sternum. HINDLIMBS
Xiphoid
process · It protects the internal organs in the thoracic region and helps in the · Each leg has 30 bones which constitute 1 femur, 1 patella, 1 tibia, 1 fibula, 7 tarsals, 5
respiratory mechanism. metatarsals and 14 phalanges.
· Femur, tibia and fibula bones together support the shank of the leg. The tarsals form the
RIBS ankle, metatarsals form the sole and phalanges form the digits of the foot.
· The ribs are thin, flat, curved bones that form a protective cage around the organs in the upper body. · The femur is the longest, largest, and strongest bone in the body whose head fits into the
· Ribs comprise of 24 bones arranged in 12 pairs. Each rib remains attached to the respective thoracic acetabulum of hip girdle.
vertebra. · The tibia connects to the femur to form the knee joint and with the talus, a foot bone, to
· The first seven pairs of ribs are attached directly with the sternum and are called true ribs. The 8th, 9th and allow the ankle to flex and extend.
10th pairs of ribs do not articulate directly with sternum, but join the seventh rib by hyaline cartilage. These · The tibia is larger than the fibula because it bears most of the weight, while the fibula
are called vertebrochondral ribs or false ribs. The last two (11th and 12th) pairs of ribs remain free serves as an area for muscle attachment.
anteriorly and are not attached either to sternum or cartilage of another rib, and are called floating ribs. · Fibula is shorter, thinner and slender.
· A typical rib consists of 2 parts : vertebral and sternal. The vertebral part is long and bony. It articulates with · Each ankle is composed of seven tarsals which are calcaneum, talus, cuboid, navicular
the thoracic vertebrae. and first, second, third cuneiforms.
· The sternal part is short and cartilaginous. It articulates with the sternum or sternal part of its upper rib. · The leg bones carry the weight of the body and are involved in propulsion and support.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Human Skeleton Concept MapDokument1 SeiteHuman Skeleton Concept MapSalil ShauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument10 SeitenSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy LecDokument2 SeitenAnaphy LecEdrea Aquino MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System Information BookDokument15 SeitenSkeletal System Information BookMartin SujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy From The DoctorDokument208 SeitenAnatomy From The DoctorSweet manNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Skely AnatomyDokument3 Seiten7 - Skely AnatomyGel Austin PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument17 SeitenSkeletal SystemRachell AvecillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Skeleton F3 NoradinDokument5 SeitenHuman Skeleton F3 NoradinIbnu RaxaabNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skeletal System: Bones and FunctionsDokument15 SeitenThe Skeletal System: Bones and FunctionsJUNAID KHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle and Skeletal FunctionDokument23 SeitenMuscle and Skeletal FunctionLuan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human body systems overviewDokument23 SeitenHuman body systems overviewBismitha NazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code 802Dokument8 SeitenCode 802Steph CaronanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Dokument39 SeitenSports Science Study (Topics 1 - 6)Jayden OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDokument3 SeitenSkeletal System Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument4 SeitenSkeletal SystemHenry BuñagNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDokument59 Seiten2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsFauziah Abu Bakar100% (1)
- Skeletal System Bones GuideDokument4 SeitenSkeletal System Bones Guideydnic alykPNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDokument59 Seiten2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliefeng81100% (8)
- Skeletal SystemDokument37 SeitenSkeletal Systemchiamaka anthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.2 Skeletal SystemDokument11 Seiten6.2 Skeletal SystemEly FructuosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Permas Jaya: Prepared By:-Azam SenseiDokument59 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Permas Jaya: Prepared By:-Azam SenseiazamsenseiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemDokument10 Seiten11 Axial Division of The Skeletal SystemMira Chariza Therese A. - BSN 1- CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axial Skeleton SummaryDokument1 SeiteAxial Skeleton SummaryKathy Yu100% (1)
- The Skeletal SystemDokument10 SeitenThe Skeletal SystemAarchi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDokument7 Seiten(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skeletal System 1Dokument6 SeitenThe Skeletal System 1tffnllrnt1215Noch keine Bewertungen
- Skeleton & LocomotionDokument10 SeitenSkeleton & Locomotionali mtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Lesson 8Dokument22 SeitenAnaphy Lesson 8Richee LunnayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skeletal System ExplainedDokument6 SeitenThe Skeletal System Explainedstar fireNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human SkeletonDokument23 SeitenThe Human SkeletonZia UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDokument8 SeitenAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Axial SkeletonDokument7 SeitenAxial SkeletonArmileo C AuxteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal SystemDokument5 SeitenSkeletal SystemIra George ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2 Reading 1Dokument62 SeitenL2 Reading 1Milena RohenkohlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Dokument3 SeitenAnatomy - Physiology of Animals - Skeletal System.Erica MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Dokument13 SeitenAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Skeletal System OfficialDokument14 SeitenHuman Skeletal System Officialconirv1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebral or Spinal Column or Spine: Science Skeletal SystemDokument4 SeitenVertebral or Spinal Column or Spine: Science Skeletal SystemChristine Joy DañosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers To Review 3RDDokument7 SeitenPointers To Review 3RDClarissa MontoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skeletal System-Ch.7 TortoraDerrickson 15th EdDokument5 SeitenThe Skeletal System-Ch.7 TortoraDerrickson 15th EdislahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEMDokument126 SeitenTopic 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEMIreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal System Part 2Dokument9 SeitenSkeletal System Part 2mariam miladNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skeletal SystemDokument35 SeitenThe Skeletal SystemSamantha EllaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Veterinary OsteologyDokument279 SeitenVeterinary OsteologyTatenda Mageja100% (2)
- Bones and skeletal system overviewDokument2 SeitenBones and skeletal system overviewStephanie DimaculamganNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemDokument7 SeitenARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemJohanna Marie GantalaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Midterm 2Dokument92 SeitenAnatomy Midterm 2Cassandra DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 Skeletal SystemDokument3 SeitenAssignment 1 Skeletal Systemjodi_clark_8100% (2)
- 2.osteology FormattedDokument45 Seiten2.osteology FormattedSling100% (1)
- Skeletal SystemDokument51 SeitenSkeletal SystemkrhimkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form5 - Locomotion and SupportDokument40 SeitenBiology Form5 - Locomotion and SupportHeon100% (3)
- Presented By: Directed By:: Department of Tashreeh-UL-Badan (Anatomy)Dokument38 SeitenPresented By: Directed By:: Department of Tashreeh-UL-Badan (Anatomy)QC quadcoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology MidtermsDokument14 SeitenZoology MidtermsJULIANNE ANACTANoch keine Bewertungen
- All About Skull PDFDokument28 SeitenAll About Skull PDFJoel SeradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal System For BMDokument13 SeitenMusculoskeletal System For BMNepimuga OliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body SystemsDokument27 SeitenHuman Body SystemsKrushna devsarkar100% (2)
- Skeletal SystemDokument73 SeitenSkeletal SystemDEEPANKAR SAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nums FLPDokument27 SeitenNums FLPRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkDokument28 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkDokument28 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction To The TrunkRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - April 2018Dokument1 SeitePhysics - April 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - October 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2016Rahique Shuaib0% (1)
- Biology - November 2016Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - October 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - September 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - September 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2014Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2014Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESSENTIALS OF CHEMISTRYDokument1 SeiteESSENTIALS OF CHEMISTRYRahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - November 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - October 2015Dokument1 SeiteBiology - October 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alicyclic Hydrocarbons + Solid StatesDokument1 SeiteAlicyclic Hydrocarbons + Solid StatesSantanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - May 2017Dokument1 SeiteBiology - May 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - March 2018Dokument1 SeiteBiology - March 2018Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - May 2016Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - May 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - November 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - November 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - July 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - July 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - November 2017Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - November 2017Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - March 2016Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - March 2016Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - June 2015Dokument1 SeiteChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Thigh CompartmentDokument20 SeitenGross Anatomy of Posterior Thigh CompartmentOnah ArinzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elbow JointDokument12 SeitenElbow Jointbpt2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy MnemonicsDokument7 SeitenAnatomy MnemonicsUlfatul UlyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Systematic Approach To Adult Hip PainDokument12 SeitenA Systematic Approach To Adult Hip Pain69016Noch keine Bewertungen
- Australian Iron Man - Bodybuilder's Bible Part 2 2016 PDFDokument124 SeitenAustralian Iron Man - Bodybuilder's Bible Part 2 2016 PDFJun JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimate 10 X 10 Mass Work OutDokument45 SeitenUltimate 10 X 10 Mass Work OutWacharin Cheepsaritdiphong92% (13)
- 1 PBDokument7 Seiten1 PBAfifah Nur FauzaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD Package For Electromagnetic and Thermal Analysis Using Finite ElementsDokument62 SeitenCAD Package For Electromagnetic and Thermal Analysis Using Finite ElementsEnmel Martínez BejaranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentDokument16 SeitenModule 6 - Muscular System Part A StudentLaw HacksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocations: A Narrative ReviewDokument8 SeitenManagement of Primary Anterior Shoulder Dislocations: A Narrative Reviewamal.fathullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest, Shoulder, Back, Leg, Arm & Forearm WorkoutDokument2 SeitenChest, Shoulder, Back, Leg, Arm & Forearm WorkoutUnni KuttanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUHS - BPT - 2016 - 4 - Summer - B.P.TH - 51411 Musculoskeletal PhysiotherapyDokument2 SeitenMUHS - BPT - 2016 - 4 - Summer - B.P.TH - 51411 Musculoskeletal PhysiotherapyYuvraj AtholeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Muscular System Gross AnatomyDokument50 Seiten10 Muscular System Gross Anatomyvladu2004100% (1)
- A Test Battery For Return To Play in FootballDokument11 SeitenA Test Battery For Return To Play in FootballGustavo Javier Caraballo PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Proper DrapingDokument15 SeitenApplication of Proper DrapingCharls John Ercillo67% (6)
- Chapter 7: Skeletal SystemDokument22 SeitenChapter 7: Skeletal SystemArjohnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Postural Reeducation in The TreatmentDokument5 SeitenGlobal Postural Reeducation in The TreatmentEduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRCR Part 1 - Radiological Anatomy - New For 2013 - Set 02 PDFDokument109 SeitenFRCR Part 1 - Radiological Anatomy - New For 2013 - Set 02 PDFmohamed100% (3)
- Physical Assessment: The Breast and AxillaeDokument13 SeitenPhysical Assessment: The Breast and Axillaemalyn1218Noch keine Bewertungen
- MAKALAH Artikel Asi EksklusifDokument4 SeitenMAKALAH Artikel Asi EksklusifMegumiaisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery of Hand Grasp in Hemiparesis StrokeDokument37 SeitenRecovery of Hand Grasp in Hemiparesis StrokeIrna SulemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 FracturesDokument9 Seiten14 FracturesJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Knee System - Knee Surgical Procedure 2 PDFDokument15 SeitenKnee System - Knee Surgical Procedure 2 PDFJigar PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix: 1. Limp 8. Prolonged Sitting With The Knees FlexedDokument1 SeiteAppendix: 1. Limp 8. Prolonged Sitting With The Knees Flexedkrissh20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Veterinary OniometerDokument2 SeitenVeterinary OniometerAmarnath MuthukrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Squat Exercise Benefits and Muscles TargetedDokument15 SeitenSquat Exercise Benefits and Muscles TargetedRodjan Moscoso50% (2)
- 4th Jakarta PMR Scientific Forum Clubfoot ManagementDokument31 Seiten4th Jakarta PMR Scientific Forum Clubfoot ManagementrachmadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Crossed Syndrome - 6 Steps To Fix Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Swayback PostureDokument46 SeitenLower Crossed Syndrome - 6 Steps To Fix Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Swayback Posturepujarze2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Nutritional Status and Presence of MalnutritionDokument13 SeitenAssessment of Nutritional Status and Presence of MalnutritionFT YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icse Specimen QP - Physical EducationDokument13 SeitenIcse Specimen QP - Physical EducationVedNoch keine Bewertungen