Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fuel System
Hochgeladen von
Jamil AhmedCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fuel System
Hochgeladen von
Jamil AhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jenbacher 5.1.
6
Documentation Fuel Gas System
1. General description:
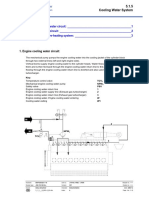
Fuel gas enters the air-gas mixer vertically, where it is mixed with air and then passed on through a pipe
to the exhaust gas turbochargers.
Behind the exhaust gas turbocharger the compressed gas/air mixture flows through the mixture cooler
(heat exchanger mixture / water).
The gas/air mixture is then fed through the throttle valve. Depending on its position, this valve controls the
flow into the intake lines. From the intake lines the mixture is distributed to the all the separate cylinders.
2. Exhaust gas turbocharger bypass:
The exhaust gas turbocharger bypass connects the pressure side and the suction side of the intake
pressure charging system (exhaust gas turbocharger). Throughput is controlled by electrically operated
valves.
The exhaust gas turbocharger bypass has two functions. Firstly, it is designed to protect the exhaust gas
turbocharger against the effects of pumping, and secondly it is used to control the power output during
operation, as a result of which the level of control can be significantly improved.
3. Schematic diagram – fuel gas system:
Key:
Actuator Actuator
Heat exchanger (mixture/water) NCG
Intake air filter NFV
Exhaust gas turbocharger NSG
Electrical control valve NVA
Air-gas mixer NVD3
Throttle valve NVG
Differential-pressure manometer PDI D
Fuel gas entering D
Air-intake lines 1
M
NVD3
NFV
NVA
NVG
Actuator NCG
NSG
Keyword: ENI Pakistan 1-10 Unit no.: J F516/ J F662 - J F670 Module no.: ------
Module type : JGS 312 GS-N.L. Version: C01 Engine no.: ------
Issued: Doku./Schartner Checked: Dokumentation Date: 2004-12
EN 5_1_6___B_BR2+3_EN.doc Index: b Page - No.: 1 / 1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Component OverviewDokument20 SeitenComponent OverviewAndronic Cosmin0% (1)
- Jenbacher: 1. Key To Module Diagrams and Technical Schema: - 1Dokument14 SeitenJenbacher: 1. Key To Module Diagrams and Technical Schema: - 1Jamil Ahmed100% (1)
- GE Type 3 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF THE CONTROLDokument24 SeitenGE Type 3 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION OF THE CONTROLSerg MarushkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas MixerDokument38 SeitenGas Mixershahzad67% (3)
- JMS 612 GS-N.L: Jenbacher Gas EnginesDokument4 SeitenJMS 612 GS-N.L: Jenbacher Gas EngineshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher Combustion Air CoolingDokument10 SeitenJenbacher Combustion Air CoolingAli AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Diagram enDokument4 SeitenTechnical Diagram enJamil Ahmed100% (2)
- Amjad Textile JH827 - 2196246 - 258Dokument279 SeitenAmjad Textile JH827 - 2196246 - 258Shahzad AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher Start UpDokument3 SeitenJenbacher Start UpJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Bulletin: GE PowerDokument4 SeitenService Bulletin: GE PowerPopa Mihai100% (1)
- Jenbacher: DocumentationDokument11 SeitenJenbacher: DocumentationArîf100% (1)
- Extended DIA - Ne XT - AccessDokument2 SeitenExtended DIA - Ne XT - Accesslaiquz zaman33% (3)
- Jenbacher: 1100-0110 Boundary Conditions For GE Jenbacher Gas EnginesDokument12 SeitenJenbacher: 1100-0110 Boundary Conditions For GE Jenbacher Gas EnginesArîfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher: 1902-0228E Screwing and Tightening Torque J 6..GS-EDokument6 SeitenJenbacher: 1902-0228E Screwing and Tightening Torque J 6..GS-EArîf100% (2)
- Jenbacher: 1. Ignition System: - 1Dokument2 SeitenJenbacher: 1. Ignition System: - 1ArîfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specifiaction of Control SystemDokument34 SeitenTechnical Specifiaction of Control SystemLidef SellenrofNoch keine Bewertungen
- 320Dokument61 Seiten320Rashid Mahmood JaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 1 1 B J320C enDokument12 Seiten5 1 1 B J320C enAdnan Yousaf67% (3)
- GE - 200802 - Technical Specs Jenbacher Type 6 PDFDokument2 SeitenGE - 200802 - Technical Specs Jenbacher Type 6 PDFsakthivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- J624 G01 6300VDokument5 SeitenJ624 G01 6300VJajap TanudjajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- X20CM0985 1 Eng - V1.42Dokument72 SeitenX20CM0985 1 Eng - V1.42rushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE Jenbacher DIA NE XT System InformationDokument87 SeitenGE Jenbacher DIA NE XT System InformationSerg Marushko100% (1)
- J320V21 enDokument4 SeitenJ320V21 enMartin KratkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TA 1400-0100 Procedura de Rodaj A Motoarelor (TIMPI) PDFDokument10 SeitenTA 1400-0100 Procedura de Rodaj A Motoarelor (TIMPI) PDFPopa MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Technician Instruction: Dia - Ne Xt4 HmiDokument7 SeitenService Technician Instruction: Dia - Ne Xt4 HmiAhad Khalil100% (3)
- CG 170-16K - Data Sheet PDFDokument1 SeiteCG 170-16K - Data Sheet PDFShah Newaz Kabir100% (1)
- Tem Evolution Systems Manual1Dokument24 SeitenTem Evolution Systems Manual1wramadhani65Noch keine Bewertungen
- JMS 616 GS-N.L: Technical SpecificationDokument4 SeitenJMS 616 GS-N.L: Technical SpecificationMartin KratkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TTEM AGS CG170 Cg260 MWM CATERPILLARDokument51 SeitenTTEM AGS CG170 Cg260 MWM CATERPILLARR TONYNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAD1343GEDokument8 SeitenTAD1343GEGeorge BarsoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- PandarosDokument9 SeitenPandarosTempest_LNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST-124 New Gear Train PDFDokument21 SeitenST-124 New Gear Train PDFPopa MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specific Trip Event 'Knocking Failure A3339Dokument4 SeitenSpecific Trip Event 'Knocking Failure A3339msavoymaggi100% (3)
- ManualDokument4 SeitenManualmuhammad arif67% (3)
- Boundary Conditions Engines Installation 1100-0110 enDokument19 SeitenBoundary Conditions Engines Installation 1100-0110 enAndronic Cosmin50% (2)
- J 312Dokument4 SeitenJ 312shahzad 28390% (1)
- Limit Value 2020 2.50.13 CPU-PDokument30 SeitenLimit Value 2020 2.50.13 CPU-PRaul Montoya100% (3)
- JGS 420 B05 - 1500 KW (Nox - 500)Dokument11 SeitenJGS 420 B05 - 1500 KW (Nox - 500)Ibrahim Ahmed FarrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- J616V21 enDokument4 SeitenJ616V21 enMartin KratkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Control Systems & IgnitionDokument44 SeitenGas Control Systems & Ignitionaaakengyahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Lehe0124-00) RTD Module - Emcp 4Dokument4 Seiten(Lehe0124-00) RTD Module - Emcp 4victor.ciprianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Electronic Technician 2019A v1.0 Product Status ReportDokument32 SeitenCat Electronic Technician 2019A v1.0 Product Status ReportMohamed Mohamed100% (1)
- MWM TCG 2020Dokument4 SeitenMWM TCG 2020MohammadFaisalAmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schaltplan JGS420 - SO#36824 JY108 - 7458609 - 258Dokument249 SeitenSchaltplan JGS420 - SO#36824 JY108 - 7458609 - 258Muhammad Mujtaba TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- TBG616K PDFDokument4 SeitenTBG616K PDFTyler GoodwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easygen 3400 3500 Technical Manual PDFDokument838 SeitenEasygen 3400 3500 Technical Manual PDFRodrigo Santibañez100% (2)
- Diane WinDokument15 SeitenDiane Winimranbseee100% (2)
- JENBACHERDokument457 SeitenJENBACHERRaymundo Jimenez Herrera100% (1)
- Jenbacher: 4.1 Checklist For Alarm MessagesDokument32 SeitenJenbacher: 4.1 Checklist For Alarm MessagesAqeel Ahmad100% (3)
- Emcp II Sensor CheckDokument14 SeitenEmcp II Sensor CheckAbdul Khaliq100% (1)
- MWM TCG2032 Tem I/o CG260Dokument61 SeitenMWM TCG2032 Tem I/o CG260R TONYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher: 5.1.1 DescriptionDokument12 SeitenJenbacher: 5.1.1 DescriptionJamil Ahmed100% (1)
- Leanox ControllerDokument32 SeitenLeanox ControllerShahzad Ahmad94% (18)
- CDVR General InformationDokument6 SeitenCDVR General InformationTTIBCCANoch keine Bewertungen
- TEM Evo Wiring DiagramDokument40 SeitenTEM Evo Wiring DiagramAnonymous yugocxn100% (1)
- Jenbacher: 1. General DescriptionDokument3 SeitenJenbacher: 1. General DescriptionArîfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Train DrawingDokument1 SeiteGas Train DrawingJamil Ahmed100% (2)
- 5 2 3 B BRa-spez ENDokument2 Seiten5 2 3 B BRa-spez ENArîfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Water SystemDokument3 SeitenCooling Water SystemJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGVon EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- TI-1000-1109 - Lubricating Oil For Type 2,3,4 and 6Dokument5 SeitenTI-1000-1109 - Lubricating Oil For Type 2,3,4 and 6Jamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation & Maintenance Best Practice O&MBestPracticesDokument169 SeitenOperation & Maintenance Best Practice O&MBestPracticesevrimkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry Gas Seals and Support Systems: Benefits and Options: Plant Safety and EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenDry Gas Seals and Support Systems: Benefits and Options: Plant Safety and EnvironmentMuzammil SaleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Cvcs / Mvcs of The Punjab: SR Districts Tehsil Name of CVC / MVC Vaccination Center Type (CVC/MVC)Dokument9 SeitenFunctional Cvcs / Mvcs of The Punjab: SR Districts Tehsil Name of CVC / MVC Vaccination Center Type (CVC/MVC)alihassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical DiagramDokument2 SeitenTechnical DiagramJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training AesealDokument8 SeitenTraining AesealJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Strokes, 2 Rotations: Intake Valve OpensDokument1 Seite4 Strokes, 2 Rotations: Intake Valve OpensJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Diagram enDokument4 SeitenTechnical Diagram enJamil Ahmed100% (2)
- Ti 1000 0206 - enDokument2 SeitenTi 1000 0206 - enJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ti 1000 0200 - enDokument2 SeitenTi 1000 0200 - enJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Water CircuitDokument3 SeitenCooling Water CircuitJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher: 1. Key To Engine DiagramsDokument1 SeiteJenbacher: 1. Key To Engine DiagramsJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher: 5.1.1 DescriptionDokument12 SeitenJenbacher: 5.1.1 DescriptionJamil Ahmed100% (1)
- Jenbacher: Build Data: Operational DataDokument1 SeiteJenbacher: Build Data: Operational DataJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Water SystemDokument3 SeitenCooling Water SystemJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher: 1. Engine Oil System: - 1Dokument1 SeiteJenbacher: 1. Engine Oil System: - 1Jamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel SystemDokument1 SeiteFuel SystemJamil Ahmed100% (1)
- 3.1 Technical Specification of The ControlDokument1 Seite3.1 Technical Specification of The ControlJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jenbacher Start UpDokument3 SeitenJenbacher Start UpJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenox Ge-JenbacharDokument6 SeitenLenox Ge-JenbacharJamil Ahmed100% (2)
- Gas Train DrawingDokument1 SeiteGas Train DrawingJamil Ahmed100% (2)
- G3600 Schematic PDFDokument1 SeiteG3600 Schematic PDFJamil AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working With The Seagull FrameworkDokument48 SeitenWorking With The Seagull Frameworkbantana100% (2)
- An Introduction To Software Engineering: ©ian Sommerville 2004 Slide 1Dokument31 SeitenAn Introduction To Software Engineering: ©ian Sommerville 2004 Slide 1Rohit KshirsagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python by WiproDokument48 SeitenPython by WiproPratik SanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insem PPLDokument28 SeitenInsem PPLhi vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exception HandlingDokument7 SeitenException HandlingRakesh SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test CH 06Dokument2 SeitenTest CH 06dinosour CuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SEDokument2 SeitenTutorial SESmiti LohaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISSP Exam SimulationDokument145 SeitenCISSP Exam SimulationMac Joy100% (2)
- Ecu ApplauseDokument3 SeitenEcu ApplauseJamsyare MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Fault Injection TechniquesDokument16 SeitenA Survey On Fault Injection TechniquesMustafamna Al SalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT 103 Presentation 1 Lesson1Dokument31 SeitenIT 103 Presentation 1 Lesson1Zed DeguzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVCon Europe 2015 T01 PresentationDokument152 SeitenDVCon Europe 2015 T01 PresentationJon DCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vsphere Esxi Vcenter 802 Availability GuideDokument92 SeitenVsphere Esxi Vcenter 802 Availability GuidegenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copy of PLC EXPERIMENT 6Dokument10 SeitenCopy of PLC EXPERIMENT 6Anonymous DtXw1wNoch keine Bewertungen
- New ResumeDokument5 SeitenNew Resumear vigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security in Red Hat Enterprise Linux Other Than SelinuxDokument10 SeitenSecurity in Red Hat Enterprise Linux Other Than Selinuxal teNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRITON V - Cylinder - Pressure - Monitoring - eDokument6 SeitenTRITON V - Cylinder - Pressure - Monitoring - eSyed UmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1151ec117 - Eosdd - Unit1 - Question - Bank PDFDokument15 Seiten1151ec117 - Eosdd - Unit1 - Question - Bank PDFLordwin CecilNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPS PumpsDokument4 SeitenCPS PumpsJovenal TuplanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroservicesDokument12 SeitenMicroservicesgauravgupta005100% (1)
- Caterpillar C32Dokument10 SeitenCaterpillar C32Carlos BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xjtag Product List enDokument2 SeitenXjtag Product List enkmrchetan94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project ReportDokument29 SeitenFinal Project ReportKrishna SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank ManagementDokument58 SeitenBank ManagementPushpendra Singh100% (1)
- SCADA OverviewDokument38 SeitenSCADA Overviewameet_ngangomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solidity Part 2Dokument103 SeitenSolidity Part 2Muhammad Zahid FaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tester Interview Questions and Answers Are Completely Based On The Interview I and My Friends Attended During Last Years of Working Experience As Quality Assurance TestersDokument10 SeitenTester Interview Questions and Answers Are Completely Based On The Interview I and My Friends Attended During Last Years of Working Experience As Quality Assurance TestersedubharathNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLID Properties PDFDokument26 SeitenSOLID Properties PDFNandita HansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahrain Approach PlateDokument31 SeitenBahrain Approach PlateAshish AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Project Management HandbookDokument443 SeitenAerospace Project Management HandbookJiri Dokulil100% (1)