Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lab 2
Hochgeladen von
Tomas Rodriguez RamirezOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab 2
Hochgeladen von
Tomas Rodriguez RamirezCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab ID: 9.9K1116A072.I4RP2.
EIGRP and Wildcard Masks
Objective
Understand wildcard masks, and use wildcard masks to specify which interfaces Enhanced Interior
Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) should use. EIGRP routers maintain a neighbor table and a topology
table. The neighbor table lists all the adjacent routers configured to run EIGRP. The topology table lists the
next hop for all the network destinations known to all the EIGRP neighbors; the next hop for a destination
represents a loop-free path to that destination. Each of these next-hop destinations is known as a
successor.
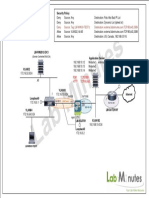
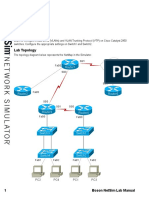
Lab Topology
The topology diagram below represents the NetMap in the Simulator. The five routers are connected
by point-to-point WAN links. Each router also has a LAN connected to its FastEthernet interface. Each
LAN has one host PC connected. This network is comparable to an actual network connecting five
geographically separate offices, each with a LAN to which desktop PCs and servers are connected.
HostB S0/1 HostC
192.168.1.2 192.168.100.5 S0/0
192.168.100.6 192.168.4.2
Fa0/0 Fa0/0
192.168.1.1 Daytona 192.168.4.1
Orlando 64K
S0/0 S0/1
192.168.100.1 192.168.100.13
HostA HostD
192.168.2.2 S0/0 192.168.3.2
S0/1
192.168.100.2 192.168.100.14
Fa0/0
512K Fa0/0
192.168.2.1 192.168.3.1
S0/1 S0/0
Tampa 192.168.100.9 192.168.100.10 Miami
Fa0/1
192.168.100.17
Fa0/1
192.168.100.18
Fa0/0 Key West
HostE 192.168.5.1
192.168.5.2
Command Summary
Command Description
configure terminal enters global configuration mode from privileged EXEC mode
enable enters privileged EXEC mode
end ends and exits configuration mode
1 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Command Description
exit exits one level in the menu structure
interface type number changes from global configuration mode to interface
configuration mode
network network-address wildcard-mask activates EIGRP on the specified network; the wildcard-mask
parameter allows for more specific configuration
ping ip-address sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo
request to the specified address
show ip eigrp interfaces displays information about interfaces configured for EIGRP
show ip interface brief displays a brief summary of interface status and configuration
show ip protocols displays information about active routing protocols
show ip route displays the IP routing table
show running-config displays the active configuration file
The IP addresses and subnet masks used in this lab are shown in the tables below:
IP Addresses
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Daytona Serial 0/0 192.168.100.6 255.255.255.252
Serial 0/1 192.168.100.13 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0
KeyWest FastEthernet 0/1 192.168.100.18 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0
Miami Serial 0/0 192.168.100.10 255.255.255.252
Serial 0/1 192.168.100.14 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/1 192.168.100.17 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
Orlando Serial 0/0 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.252
Serial 0/1 192.168.100.5 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Tampa Serial 0/0 192.168.100.2 255.255.255.252
Serial 0/1 192.168.100.9 255.255.255.252
FastEthernet 0/0 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
Device IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
HostA 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1
HostB 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
HostC 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.1
HostD 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.1
HostE 192.168.5.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.1
2 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Lab Tasks
The routers have been configured with admin as the password at console prompts, cisco as the password
at enable prompts, and sanfran as the virtual terminal (vty) password.
Task 1: Examine the Initial Network Configuration
A. Verify Routing
1. On Key West, display the contents of the routing table.
2. Refer to the network topology diagram and Key West’s routing table. Are all networks shown in the
topology diagram listed as either directly connected routes or EIGRP routes? _________________
B. Verify Connectivity
1. From HostE, attempt to ping HostA (192.168.2.2), HostB (192.168.1.2), HostC (192.168.4.2), and
HostD (192.168.3.2). Are these pings successful? ______________________________________
Task 2: Implement EIGRP Wildcard Masks
A. Examine the Current EIGRP Configuration
1. Examine the current EIGRP configuration on all five routers. How many EIGRP autonomous
systems (ASes) are present in the network? ___________________________________________
2. What is the AS number of the currently running EIGRP routing process on all five routers? _______
3. What commands should be issued on all five routers to specify the interfaces that should attempt to
form EIGRP neighbor relationships? _________________________________________________
B. Understand Wildcard Masks
1. The network commands in the router eigrp configuration of each router identify the router
interfaces that will participate in the EIGRP routing topology. In the initial configuration for this
lab, the network commands include only the classful network address. This limits the flexibility of
assigning interfaces to the EIGRP process. Briefly explain why this is so. ____________________
______________________________________________________________________________
2. Describe the main difference between wildcard masks and subnet masks.
3. Explain how EIGRP would select interfaces if it were configured with the network 192.168.100.0
0.0.0.255 command. _____________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
C. Implement EIGRP Wildcard Masks
1. Examine the configuration of each of the five routers in the topology. How many network commands
do you see listed in the EIGRP configuration of each router? ______________________________
2. Why are multiple network commands required? Briefly explain. ____________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3. Reconfigure EIGRP on each router so that a single network command can be issued to specify all
interfaces that will run EIGRP.
4. What would happen if you issued the router eigrp command with an AS number other than 100
without first removing the current EIGRP configuration? __________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Task 3: Verify EIGRP Wildcard Masks
A. Verify Routing
1. Display the Key West routing table.
2. Refer to the network topology diagram and the output of the Key West routing table. Are all networks
shown in the topology diagram either directly connected routes or EIGRP routes? _____________
3. Compare this output to the results you previously received. Has anything changed as a result of
implementing EIGRP wildcard masks? _______________________________________________
B. Verify Connectivity
1. From HostE, attempt to ping HostA (192.168.2.2), HostB (192.168.1.2), HostC (192.168.4.2), and
HostD (192.168.3.2). Are these pings successful? ______________________________________
If any of the pings fail, review and correct your configuration.
Once you have completed this lab, be sure to check your work by using the grading function.
You can do so by clicking the Grade Lab icon ( ) in the toolbar or by pressing Ctrl+G.
4 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Lab Solutions
The routers have been configured with admin as the password at console prompts, cisco as the password
at enable prompts, and sanfran as the virtual terminal (vty) password.
Task 1: Examine the Initial Network Configuration
A. Verify Routing
1. You should issue the show ip route command on the Key West router to display the contents of the
routing table.
KeyWest#show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, I - IGRP, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, * - candidate default
U - per-user static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.5.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
192.168.100.0/24 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets
C 192.168.100.16/30 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.0/24 is a summary, 00:03:37, Null0
D 192.168.100.8/30 [90/5514496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.4/30 [90/41026560] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.12/30 [90/5514496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.0/30 [90/6026496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.2.0 [90/5517056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.3.0 [90/5005056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.1.0 [90/6029056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.4.0 [90/5517056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:03:32, FastEthernet0/1
2. Yes, all networks are either directly connected routes or EIGRP routes in the Key West routing
table. Routes to networks learned by EIGRP are preceded by a D, and routes to directly connected
networks are preceded by a C in the show ip route command output.
B. Verify connectivity
1. Yes, pings from HostE to HostA (192.168.2.2), HostB (192.168.1.2), HostC (192.168.4.2), and HostD
(192.168.3.2) are successful.
C:>ping 192.168.2.2
C:>ping 192.168.1.2
C:>ping 192.168.4.2
C:>ping 192.168.3.2
5 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Task 2: Implement EIGRP Wildcard Masks
A. Examine the Current EIGRP Configuration
1. There is one EIGRP autonomous system in the simulated network. The output of the show running-
config command displays the AS number assigned to each of the five routers. Below is sample
output from the Key West router:
KeyWest#show running-config | section router eigrp
router eigrp 100
network 192.168.100.0
network 192.168.5.0
auto-summary
2. The AS number of the EIGRP routing process is 100. Output from the show running-config
command or the show ip protocols command shows that all five routers are configured with the
router eigrp 100 command. The number 100 indicates the AS number with which the EIGRP
routing process will associate. Sample output from the show ip protocols command on the Key
West router is shown below:
KeyWest#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is “eigrp 100”
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing:
Automatic network summarization is in effect
Routing for Networks:
192.168.100.0
192.168.5.0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.100.17 90 00:10:29
Distance: internal 90 external 170
3. The network command should be issued on all five routers to specify the router interfaces that will
take part in the EIGRP routing process and that will attempt to form relationships with their EIGRP
neighbors. Each router in the simulated network is configured with network commands that EIGRP
uses to determine which interfaces to use.
B. Understand Wildcard Masks
1. When the network command is configured with only a network address, EIGRP will include all
interfaces whose IP addresses fall within the classful network boundary identified by the network
command. For example, the network 192.168.1.0 command will cause EIGRP to use all interfaces
that are configured with IP addresses that fall within the 192.168.1.0/24 Class C network.
6 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
2. A wildcard mask is the inverse of a subnet mask. The mask 0.0.0.255 is an example of a classful
wildcard mask. In the binary address, the bits that are zeros must match exactly and the bits that are
ones will match any address. A wildcard mask of 0.0.0.255 would require exact matches in the first
three octets and would match anything in the fourth octet.
3. The network 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.255 command indicates that EIGRP will use all interfaces with IP
addresses that fall between 192.168.100.1 and 192.168.100.254. This particular example uses a
wildcard mask that falls on a classful network boundary.
The benefit of using wildcard masks is that they can designate a range of addresses that does not
necessarily fall on a network boundary.
To calculate the wildcard mask, begin by calculating a subnet mask that, when combined with the
network address, covers the range of IP addresses desired. Then subtract the subnet mask you
calculated from 255.255.255.255.
If you wanted to include all interfaces configured with IP addresses that fall in the range from
192.168.100.1 through 192.168.100.30, you could use regular subnetting techniques to determine
that the network 192.168.100.0 and the subnet mask 255.255.255.224 will define this range. You
could then subtract 255.255.255.224 from 255.255.255.255 to find the wildcard mask 0.0.0.31
(255.255.255.255 – 255.255.255.224 = 0.0.0.31). You would then issue the network 192.168.100.0
0.0.0.31 command to configure EIGRP to use interfaces configured with IP addresses that fall in the
range from 192.168.100.1 through 192.168.100.30.
C. Implement EIGRP Wildcard Masks
1. Each router is configured with two network commands.
2. All five routers are configured with 192.168.0.0 private Class C addresses. Each router has
interfaces that are configured with IP addresses that fall in different Class C networks in the
192.168.0.0 address space. It is therefore necessary to identify each Class C network with a
separate network command in the EIGRP configuration.
3. You should issue the following commands to reconfigure EIGRP so that a single network command
can be issued:
Tampa(config)#no router eigrp 100
Tampa(config)#router eigrp 100
Tampa(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
Orlando(config)#no router eigrp 100
Orlando(config)#router eigrp 100
Orlando(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
KeyWest(config)#no router eigrp 100
KeyWest(config)#router eigrp 100
KeyWest(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
(continued on next page)
7 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
(continued from previous page)
Daytona(config)#no router eigrp 100
Daytona(config)#router eigrp 100
Daytona(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
Miami(config)#no router eigrp 100
Miami(config)#router eigrp 100
Miami(config-router)#network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
The router eigrp 100 and network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255 commands enable EIGRP on the
routers and configure the routers to use a single network command. Note that removing the entire
EIGRP configuration by issuing the no router eigrp 100 command saves time because you do not
need to remove each network command individually. Removing the EIGRP configuration removes
all the associated network commands.
4. Issuing the router eigrp command with another AS number without first removing the current
EIGRP configuration would create a second instance of the EIGRP routing process.
Task 3: Verify EIGRP Wildcard Masks
A. Verify Routing
1. You should issue the show ip route command on the Key West router to display the routing table.
Sample output is shown below:
KeyWest#show ip route
<output omitted>
Gateway of last resort is not set
C 192.168.5.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
192.168.100.0/30 is subnetted, 5 subnets
D 192.168.100.0 [90/6026496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.4 [90/41026560] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.8 [90/5514496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.100.12 [90/5514496] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
C 192.168.100.16 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.3.0 [90/5005056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.4.0 [90/5517056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.2.0 [90/5517056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
D 192.168.1.0 [90/6029056] via 192.168.100.17, 00:05:32, FastEthernet0/1
2. Yes, all networks in the topology diagram are either directly connected routes or EIGRP routes.
3. Nothing in the EIGRP routing table on the Key West router has changed as a result of implementing
EIGRP wildcard masks.
8 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
B. Verify Connectivity
1. Yes, pings from HostE to HostA (192.168.2.2), HostB (192.168.1.2), HostC (192.168.4.2), and HostD
(192.168.3.2) are successful.
C:>ping 192.168.2.2
C:>ping 192.168.1.2
C:>ping 192.168.4.2
C:>ping 192.168.3.2
Sample Configuration Script
KeyWest KeyWest (confinued)
KeyWest#show running-config interface FastEthernet0/0
Building configuration... description KeyWestLAN
Current configuration : 908 bytes ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0
! no ip directed-broadcast
Version 12.3 !
service timestamps debug uptime interface FastEthernet0/1
service timestamps log uptime description toMiami
no service password-encryption ip address 192.168.100.18 255.255.255.252
! no ip directed-broadcast
hostname KeyWest bandwidth 512
enable secret 5 $1$lYSY$Ai2eZ8KpUCL9ptJCN1c41w !
! router eigrp 100
ip subnet-zero network 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
! !
ip cef ip classless
no ip domain-lookup no ip http server
! !
interface Serial0/0 line con 0
no ip address login
no ip directed-broadcast password admin
! line aux 0
interface Serial0/1 line vty 0 4
no ip address login
no ip directed-broadcast password sanfran
! !
no scheduler allocate
end
Copyright © 1996–2017 Boson Software, LLC. All rights reserved. NetSim software and documentation are protected by copyright law.
9 Boson NetSim Lab Manual
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsVon EverandARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityVon EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network ProjectsDokument13 SeitenNetwork ProjectsDelenzy Cino0% (1)
- CCNA 2 EIGRP Skills Based Assessment Exam AnsweredDokument4 SeitenCCNA 2 EIGRP Skills Based Assessment Exam Answeredsc_ramiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Von EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- MtcnaDokument34 SeitenMtcnaAuliyaDiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei OptiX PTN 950 Commissioning Guide (V100R005)Dokument106 SeitenHuawei OptiX PTN 950 Commissioning Guide (V100R005)Thunder-Link.com100% (1)
- Lab 3Dokument16 SeitenLab 3Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skills Mod 2 FinalDokument2 SeitenSkills Mod 2 FinalquestionsremainthesameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9.2 - OSPF Troubleshooting: ObjectiveDokument14 SeitenLab 9.2 - OSPF Troubleshooting: ObjectiveOdoch HerbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4Dokument2 Seiten15.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4marcelo tanimucaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.8.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Nat For Ipv4 PDFDokument2 Seiten6.8.1 Packet Tracer - Configure Nat For Ipv4 PDFMaría ArmijosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.8.1 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4Dokument2 Seiten6.8.1 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4Jeff HambreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ostinato UNL Lab 16 PDFDokument1 SeiteOstinato UNL Lab 16 PDFHai Pham VanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4 - ILMDokument2 Seiten15.2.2 Packet Tracer - Configure NAT For IPv4 - ILMfotcheping noubissi FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocolo de Ruteo EIGRP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaDokument4 SeitenProtocolo de Ruteo EIGRP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaerlurazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2.3.6 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP For IPv4 Swinburne V1.0Dokument9 Seiten5.2.3.6 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic EIGRP For IPv4 Swinburne V1.0Ishu GaneshaMuralidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Dokument16 Seiten11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Deux AmisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMDokument22 Seiten11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMlokuras de la vidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocolo de Ruteo RIP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaDokument4 SeitenProtocolo de Ruteo RIP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaerlurazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Certified Network Associate: Zoom TechnologiesDokument34 SeitenCisco Certified Network Associate: Zoom Technologiesamaba3d91% (11)
- Protocolo de Ruteo RIP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaDokument4 SeitenProtocolo de Ruteo RIP Configuración: Elena Tsukiko ClaudiaerlurazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDokument5 SeitenSubnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramJermyn G EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2Dokument6 Seiten10.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2Andres Carlos Rodriguez RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Policy: Deny Source: Tag (LM-WIN10-TEST1)Dokument1 SeiteSecurity Policy: Deny Source: Tag (LM-WIN10-TEST1)Petko KolevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eigrp: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing ProtocolDokument24 SeitenEigrp: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing ProtocolJorge DíazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Resource ManagerDokument9 SeitenRelative Resource ManagerYoochun SarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP SP SprouteDokument168 SeitenCCNP SP SproutewjjjxsNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Configuration Step by Step GuideDokument15 SeitenOSPF Configuration Step by Step GuideBharath VadinalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Selecting Provisioning and Cabling Routers Switches and PCs - Seite1Dokument1 SeiteCCNA Selecting Provisioning and Cabling Routers Switches and PCs - Seite1Niklas's Music ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- E2 Lab 9 6 2 InstructorDokument8 SeitenE2 Lab 9 6 2 Instructordiverron100% (1)
- 22.1.3 Lab - Troubleshoot URPF - ILMDokument6 Seiten22.1.3 Lab - Troubleshoot URPF - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationVon EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNoch keine Bewertungen
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkVon EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multicore DSP: From Algorithms to Real-time Implementation on the TMS320C66x SoCVon EverandMulticore DSP: From Algorithms to Real-time Implementation on the TMS320C66x SoCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Controller Forth For The 8051 FamilyVon EverandEmbedded Controller Forth For The 8051 FamilyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Advanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationVon EverandAdvanced Raspberry Pi: Raspbian Linux and GPIO IntegrationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementVon EverandEthernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionVon Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Profile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997Von EverandProfile of the Worldwide Semiconductor Industry - Market Prospects to 1997: Market Prospects to 1997Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3Von EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- PC Engine / TurboGrafx-16 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #16Von EverandPC Engine / TurboGrafx-16 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Connection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksVon EverandConnection-Oriented Networks: SONET/SDH, ATM, MPLS and Optical NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Token Ring Technology ReportVon EverandToken Ring Technology ReportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Von EverandMaster System Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #15Noch keine Bewertungen
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingVon EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingVon EverandSPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Von EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamVon EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- NES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1Von EverandNES Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #1Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingVon EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedVon EverandMobile Terminal Receiver Design: LTE and LTE-AdvancedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9Dokument16 SeitenLab 9Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5Dokument12 SeitenLab 5Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MikroTik Routers and Wireless - Products - hAP Ac Lite TCDokument7 SeitenMikroTik Routers and Wireless - Products - hAP Ac Lite TCTomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4Dokument6 SeitenLab 4Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument13 SeitenLab 2Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSPF Authentication II: Objective Lab TopologyDokument9 SeitenOSPF Authentication II: Objective Lab TopologyTomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument10 SeitenLab 1Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument11 SeitenLab 1Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyDokument5 SeitenIP Access Lists: Objective Lab TopologyTomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5Dokument13 SeitenLab 5Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4Dokument14 SeitenLab 4Tomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Certification Exam Voucher PricesDokument12 SeitenMicrosoft Certification Exam Voucher PricesTomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practica de LaboratorioDokument10 SeitenPractica de LaboratorioTomas Rodriguez RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLDokument69 SeitenACLr00t32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation Guide SEP12.1 PDFDokument1.049 SeitenImplementation Guide SEP12.1 PDFreanveNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Internet WorksDokument23 SeitenHow The Internet WorksAmy-Elizabeth ManlapasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics and Communication Engineering: Question Paper Code: X10366Dokument4 SeitenElectronics and Communication Engineering: Question Paper Code: X10366krithikgokul selvam100% (1)
- ID - Vantive Cliente Cidade Localidade #LP Protocolo ServiçoDokument4 SeitenID - Vantive Cliente Cidade Localidade #LP Protocolo Serviçofranciscomorais1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- IP AddressesDokument23 SeitenIP Addressesfarooq929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Palo Alto Next Generation FirewallDokument15 SeitenPalo Alto Next Generation FirewallOm PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1 Version 1.0 (ICND 1)Dokument9 SeitenInterconnecting Cisco Network Devices Part 1 Version 1.0 (ICND 1)Zain MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conntrack AttackDokument123 SeitenConntrack AttackIgnacio GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Support System 100 2019-Week4-MemoDokument6 SeitenTechnical Support System 100 2019-Week4-MemoBonginkosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Network Basics: IP AddressingDokument33 SeitenUnderstanding Network Basics: IP Addressingnishasaiyed2304Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks CSU 07412: Sub - Enabling OutcomesDokument57 SeitenComputer Networks CSU 07412: Sub - Enabling OutcomesClaus MouriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Serie 300 EjemplosDokument103 SeitenCCNP Serie 300 EjemplosFrank PortorrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netplus CheatsheetDokument15 SeitenNetplus Cheatsheetworsham9915Noch keine Bewertungen
- Avaya G700 Firmware Download InstructionsDokument20 SeitenAvaya G700 Firmware Download InstructionseadrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test and DiagnosisDokument26 SeitenTest and DiagnosisMariana Ribeiro GentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rip Version 1 (Ripv1) : Network Command. in Our Router Configuration We Have To Type Every Directly Connected NetworkDokument51 SeitenRip Version 1 (Ripv1) : Network Command. in Our Router Configuration We Have To Type Every Directly Connected NetworkPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemDokument144 SeitenStratus Ftserver System Administrator'S Guide For The Windows Operating SystemphyosithumgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec2352 Computer Networks Question BankDokument5 SeitenEc2352 Computer Networks Question BankVignesh SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Exam WebsiteDokument150 SeitenFrom Exam WebsitemohammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7000 Security Gateway DatasheetDokument5 Seiten7000 Security Gateway DatasheetAlejandro FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HC S 412 Course Outline 2019Dokument3 SeitenHC S 412 Course Outline 2019tgotora0% (1)
- U14EC509: SEMINAR: (An Autonomous Institute Under Kakatiya University, Warangal)Dokument16 SeitenU14EC509: SEMINAR: (An Autonomous Institute Under Kakatiya University, Warangal)Dadi VinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Camera User Manual - EN - FinalDokument35 SeitenIP Camera User Manual - EN - FinalMike BelandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Test-King 300-410 v2021-04-06 by Isabelle 85qDokument121 SeitenCisco Test-King 300-410 v2021-04-06 by Isabelle 85qMelroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHV-Networking Best PractisesDokument77 SeitenAHV-Networking Best PractisesVishal IdgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Route (300-101)Dokument219 SeitenCCNP Route (300-101)HareRamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comcast SFI Policy - Jan-2010Dokument2 SeitenComcast SFI Policy - Jan-2010orbitas00Noch keine Bewertungen