Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment 4 Geochemistry (Semester Genap 18/19)
Hochgeladen von
Stefany P0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 SeitenThis document outlines an assignment on radioactivity and geochemistry. It contains 5 questions assessing understanding of radioactive decay types and equations, applications of stable and unstable isotopes, using isotope data to determine the age of rocks via half-life calculations, and using linear regression to calculate rock ages from isotope ratio data. Students are asked to define terms, write decay equations, fill in charts with isotope percentages over time, and perform age calculations using isotope dating methods. The assignment is due in 1 week and should be submitted as a hard copy.
Originalbeschreibung:
Radio
Originaltitel
Radioactivity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document outlines an assignment on radioactivity and geochemistry. It contains 5 questions assessing understanding of radioactive decay types and equations, applications of stable and unstable isotopes, using isotope data to determine the age of rocks via half-life calculations, and using linear regression to calculate rock ages from isotope ratio data. Students are asked to define terms, write decay equations, fill in charts with isotope percentages over time, and perform age calculations using isotope dating methods. The assignment is due in 1 week and should be submitted as a hard copy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
16 Ansichten2 SeitenAssignment 4 Geochemistry (Semester Genap 18/19)
Hochgeladen von
Stefany PThis document outlines an assignment on radioactivity and geochemistry. It contains 5 questions assessing understanding of radioactive decay types and equations, applications of stable and unstable isotopes, using isotope data to determine the age of rocks via half-life calculations, and using linear regression to calculate rock ages from isotope ratio data. Students are asked to define terms, write decay equations, fill in charts with isotope percentages over time, and perform age calculations using isotope dating methods. The assignment is due in 1 week and should be submitted as a hard copy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Assignment 4 Geochemistry (Semester Genap 18/19)
Material: Radioactivity
Format: hard copy on A4 paper
Due date: + 1 WEEK
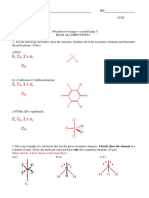
Q1. (30 points)
a. Define the difference between unstable and stable isotope.
b. Mention 1 application each of unstable and stable isotope.
c. Explain 3 decay type and write down the reaction for each decay type.
d. Define parent and daughter nuclides. Draw the graph if necessary.
e. Explain briefly why carbon dating has limited application in rock-dating.
f. Explain 2 decay systems that you know and the application on rock-dating.
Q2. (15 points)
Hint: see periodic table to help with your answer.
a. Plutonium-239 decays via alpha decay. Write out the decay equation for Plutonium-239!
%&#
#$𝑃𝑢
b. Scandium-46 decays via the beta-minus process. Write out the decay equation for scadium-
46.
$*
%)𝑆𝑐
c. A certain isotope decays via the beta-plus process to neon-22. Write out the complete decay
equation.
%%
)-𝑁𝑒
Q3. (15 points)
A rock sample was examine to determine the %age of the parent and daughter nuclide.
a. Fill in the table below
Number of half- 0 1 2 3 4 5
life
% Parent
Nuclide
% Daughter
Nuclide
b. Using the above chart, estimate the percentage of parent and daughter material that
should be present if 5 half-lives have passed. If the length of the half-life is 1 million
years. How old is the rock?
c. What is the age of a basaltic lava flow which has isotopic abundances D=87.5% and
P=12.5% and isotopic half-life of 10 million years?
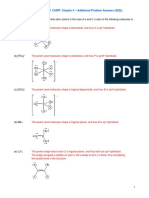
Q4. (25 points)
Let it be known there were samples measured on phlogopites (P) from a kimberlite obtained in
Canada. Using simple linear regression and based on the table below, determine:
a. The age of the rock
b. The initial 87Sr/86Sr ratio
Q5 (15 points)
The following data were analysed from lava flow retrieved in Mt. St Helens. Using simple linear
regressions, calculate the age of the rock.
Supplementary
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryVon EverandThe Principles of Heterocyclic ChemistryBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Geochemistry Assignment - Week 07 PDFDokument1 SeiteGeochemistry Assignment - Week 07 PDFfarhan syariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photochemistry – 6: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Sixth International Symposium on Photochemistry, Aix-En-Provence, France, 19-23 July, 1976Von EverandPhotochemistry – 6: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Sixth International Symposium on Photochemistry, Aix-En-Provence, France, 19-23 July, 1976A. GilbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19 - The Nucleus: A Chemist's View: Answer: BDokument24 SeitenChapter 19 - The Nucleus: A Chemist's View: Answer: B鄭子玄0% (1)
- XI Chemistry Full PortionDokument2 SeitenXI Chemistry Full PortionPadmanabhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding - Part 2Dokument2 SeitenChemical Bonding - Part 2Om TipsetwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 November 1st Term Test 2019Dokument13 SeitenGrade 12 November 1st Term Test 2019Piyumi ObeyesekeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Geotechnical Engg Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)Dokument2 SeitenBasic Geotechnical Engg Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)Akash PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 5825482654320954404Dokument32 Seiten4 5825482654320954404Anil KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 11Dokument3 SeitenChemistry 11RAGHAV JINDALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam1 121 KeyDokument5 SeitenExam1 121 KeyAl 12Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIME262MidtermWinter2018 SolutionsUploadVersionDokument8 SeitenMIME262MidtermWinter2018 SolutionsUploadVersionNoor JethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycbseguide: Class 11Th ChemistryDokument5 SeitenMycbseguide: Class 11Th ChemistryloduuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KV Sci Model PapDokument5 SeitenKV Sci Model PapMukundan PolurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cblechpu 09Dokument7 SeitenCblechpu 09anushdonkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Paper Syllabus 2020-21: ClassDokument2 SeitenSample Paper Syllabus 2020-21: ClassBalachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Dokument14 Seiten12 Chemistry23 24 sp10Babur HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI CHEMISTRYMCQsDokument13 SeitenXI CHEMISTRYMCQsjj545rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry PQDokument15 SeitenChemistry PQKrishna Mani100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding Sample PaperDokument5 SeitenChemical Bonding Sample PaperUditaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Review2013Dokument4 SeitenTest Review2013Riri AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19: The Nucleus: A Chemist's ViewDokument13 SeitenChapter 19: The Nucleus: A Chemist's ViewIron ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vimp Question Chem: A) 8,8 B) 4,4 C) 6,6 D) 8,4Dokument3 SeitenVimp Question Chem: A) 8,8 B) 4,4 C) 6,6 D) 8,4Ankit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy A Ba - BSC Sem6 2017Dokument3 SeitenPhy A Ba - BSC Sem6 2017Sahil ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF DownloadDokument40 SeitenNEET Sample (Model-5) Question Paper With Answer Keys - Free PDF Downloadt.nishar61258Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 11 - 7.3Dokument4 SeitenPhysics 11 - 7.3danaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FY Radio MCQDokument3 SeitenFY Radio MCQNeelam KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chemistry23 24 sp07Dokument13 Seiten12 Chemistry23 24 sp07anikettiwari386Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Nuclear Reactions Review WorksheetDokument5 SeitenChemistry: Nuclear Reactions Review WorksheetMichelle Oquindo TucongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 17 Feb 2024Dokument8 SeitenAdobe Scan 17 Feb 2024TanishqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page of Paper Trick-4-ScienceDokument2 SeitenPage of Paper Trick-4-ScienceKirti SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM (1st) May19Dokument1 SeiteCHEM (1st) May19Hitakshi VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Government Model Question Paper With Answer Key EMDokument16 SeitenNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Government Model Question Paper With Answer Key EMPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Government Model Question Paper With Answer Key EM PDFDokument16 SeitenNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Government Model Question Paper With Answer Key EM PDFPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactive Dating Game LabDokument5 SeitenRadioactive Dating Game LabtariniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Pastpaper For Aqa Oxford ChemsitryDokument25 SeitenBest Pastpaper For Aqa Oxford Chemsitryemandurranix09Noch keine Bewertungen
- CUNJCSSP 4 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF June 2012 Chemical ScienceDokument43 SeitenCUNJCSSP 4 1 Question Paper CSIR UGC NET JRF June 2012 Chemical Sciencehojibox903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Additional Problem Answers 2022Dokument12 SeitenChapter 9 Additional Problem Answers 2022Marta TogatoropNoch keine Bewertungen
- + 2 Chemistry 1 Mark Repeated Qs EM Upto Sept - 2016Dokument38 Seiten+ 2 Chemistry 1 Mark Repeated Qs EM Upto Sept - 2016Raison ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2024 Set 2Dokument23 Seiten2024 Set 2Manab GhoshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 - HHDokument74 SeitenClass 12 - HHgujjarvikram123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry PQDokument13 SeitenChemistry PQAman SilayachNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS 12 Chemistry-PQDokument24 SeitenCLASS 12 Chemistry-PQJeremiah ShibuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio-1 1ST QTR PDFDokument2 SeitenBio-1 1ST QTR PDFJunaid Ahmed MuazzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Selection Examination For The 2004 Australian Chemistry Olympiad TeamDokument6 SeitenFinal Selection Examination For The 2004 Australian Chemistry Olympiad Teamrajeswar royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure QPDokument25 SeitenAtomic Structure QPsatyendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monthly Tests For Federal 1st Year FinalDokument10 SeitenMonthly Tests For Federal 1st Year FinalAtif RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pixl Independence:: Chemistry - Student Booklet Ks5Dokument19 SeitenPixl Independence:: Chemistry - Student Booklet Ks5saadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Test Sample Paper Grade 12 ChemistryDokument6 SeitenUnit Test Sample Paper Grade 12 Chemistrymilonee lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uni/Tersity The Pui/Jab: Llo :'J ' 'J:'JDokument21 SeitenUni/Tersity The Pui/Jab: Llo :'J ' 'J:'JJhon EstwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbjescpu 16Dokument13 SeitenCbjescpu 16Tapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-xi-To Xii PCB Nacst-22 QPDokument9 SeitenClass-xi-To Xii PCB Nacst-22 QPBhavana RangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding O1 1-40Dokument20 SeitenChemical Bonding O1 1-40Mahesh choudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50Q - NucleiDokument8 Seiten50Q - NucleiAkash SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannDokument10 SeitenOxo AQA16 P7uu T801 CsaannemailusageNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemDokument145 SeitenChemPriyanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Chemistry-IDokument7 SeitenHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2011 Chemistry-IKaushikBoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 713 12 Chemistry March 2016 Public Exam Key Answer emDokument18 Seiten713 12 Chemistry March 2016 Public Exam Key Answer emSathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inbo2013 QDokument40 SeitenInbo2013 QanisusantimalerolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 Module 1Dokument7 SeitenQ2 Module 1Aellayh LucienneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jcy 0281 PDFDokument5 SeitenJcy 0281 PDFStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jcy 0281 PDFDokument5 SeitenJcy 0281 PDFStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmaraDokument4 SeitenAmaraStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0393 Firstpage PDFDokument1 Seite0393 Firstpage PDFStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Marine AcquisitionDokument28 Seiten02 Marine AcquisitionStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Equivalence and Compound InterestDokument2 SeitenLatihan Equivalence and Compound InterestRifky FayuzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects in Contemporary OrganizationsDokument29 SeitenProjects in Contemporary OrganizationsTalha Bin SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGSCE19 Abstract Submission (First Name) .Dokument4 SeitenAGSCE19 Abstract Submission (First Name) .Stefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM LogDokument1 SeiteMM LogStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Form Staff Recruitment SPE UI SC 2019Dokument9 SeitenApplication Form Staff Recruitment SPE UI SC 2019Stefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4 Geochemistry (Semester Genap 18/19)Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 4 Geochemistry (Semester Genap 18/19)Stefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- P11 04 Nomin-ErdeneDokument4 SeitenP11 04 Nomin-ErdeneStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content: Elastic ModuliDokument3 SeitenContent: Elastic ModuliStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15281-Article Text-58848-1-10-20150524Dokument6 Seiten15281-Article Text-58848-1-10-20150524Stefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Form ProgramDokument14 SeitenApplication Form ProgramboygembelNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormatJournal TBM1Dokument6 SeitenFormatJournal TBM1Stefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focal Mechanism PrimerDokument14 SeitenFocal Mechanism PrimerRodrigo Muñoz ValderramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- V LawDokument3 SeitenV LawStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- (I) Geodynamics IntroductionDokument42 Seiten(I) Geodynamics IntroductionStefany PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Overview of Rock and Fluid Factors That Impact Seismic Velocity and ImpedanceDokument40 SeitenConceptual Overview of Rock and Fluid Factors That Impact Seismic Velocity and ImpedanceFerrando NañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Form ProgramDokument14 SeitenApplication Form ProgramboygembelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabela de Correlação de Normas PDFDokument5 SeitenTabela de Correlação de Normas PDFFABRICIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Buffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyDokument14 SeitenBuffers Complete Handout 2020 With Answer KeyRadhika RaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA - Chemistry - Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - KnowIT - GCSEDokument86 SeitenAQA - Chemistry - Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - KnowIT - GCSEAlwayne SappletonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Sachin - Anand - PaperDokument11 Seiten5 - Sachin - Anand - PaperTAPAS CHAKRABORTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReactionsDokument8 SeitenReactionsmhdahodwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State13thDokument19 SeitenSolid State13thRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry 2nd Edition (Housecroft) - Copy - 1Dokument169 SeitenInorganic Chemistry 2nd Edition (Housecroft) - Copy - 1firda noer ainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument7 SeitenChemistryVic Rizenn Isidore BobilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abhinav Prabhakar Chemistry Project CLASS 12FDokument20 SeitenAbhinav Prabhakar Chemistry Project CLASS 12FSumedhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP 11B Important Organic Substances (2023) Solution-8-9Dokument2 SeitenPP 11B Important Organic Substances (2023) Solution-8-9friedricepersonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of The Transition Elements The Inner Transition Elements Highlights of Selected Transition Elements Coordination Compounds Theoretical Basis For The Bonding and Properties of ComplexesDokument91 SeitenProperties of The Transition Elements The Inner Transition Elements Highlights of Selected Transition Elements Coordination Compounds Theoretical Basis For The Bonding and Properties of ComplexesLuis VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesDokument9 SeitenBenedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesRica NorcioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particles and Atoms MCQ TestDokument5 SeitenParticles and Atoms MCQ TestVgyggNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mole ConceptDokument16 SeitenThe Mole ConceptKamilo Vuciri ManyimanyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTexas 8 Moles and Empirical Formulas-ProblemsDokument4 SeitenUTexas 8 Moles and Empirical Formulas-ProblemsTutor AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biuret TestDokument7 SeitenBiuret TestBoaz OngaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Dokument9 Seiten2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Prasad C M100% (2)
- 20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDokument4 Seiten20-Inorganic Pharmaceutical ChemistrythucinorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ammonia Solubility in SaltsDokument1 SeiteAmmonia Solubility in Saltsivan estevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Unknown SugarDokument3 SeitenAnalysis of Unknown SugarsasmithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS 2001 Local PDFDokument9 SeitenACS 2001 Local PDFleo leoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex IVDokument13 SeitenAnnex IVJosé BarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryDokument2 SeitenAnswers To Eocqs: Cambridge International As Level ChemistryArevik Meliqyan100% (1)
- General Chemistry CHE 101: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokument60 SeitenGeneral Chemistry CHE 101: Atoms, Molecules and IonsDavid MaranzhyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P3Dokument11 Seiten2013 YJC H2 Chem Prelim P3Chow Kim WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Che CP CASS NEET-UG (Sol) ENG 2PDokument4 SeitenS Che CP CASS NEET-UG (Sol) ENG 2PRaktim FactoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hints & Solutions: INJSO (STAGE-II) - 2017Dokument10 SeitenHints & Solutions: INJSO (STAGE-II) - 2017Sandeep JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1 TitrationDokument2 SeitenExp 1 TitrationAbhay ManwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Basic Concepts of Chem Prac QnsDokument9 SeitenSome Basic Concepts of Chem Prac QnsShobi ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 6 Chemistry (SEM 1) - Intermolecular ForcesDokument2 SeitenForm 6 Chemistry (SEM 1) - Intermolecular ForcesimclaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionVon EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityVon EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Von EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- STEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Von EverandSTEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (6)
- Interactive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookVon EverandInteractive Science Notebook: The Human Body WorkbookBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsVon EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningVon EverandNature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- How Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksVon EverandHow Do Cell Phones Work? Technology Book for Kids | Children's How Things Work BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetVon EverandNature-Based Learning for Young Children: Anytime, Anywhere, on Any BudgetBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookVon EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingVon EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- Interactive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8Von EverandInteractive Notebook: Life Science, Grades 5 - 8Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)