Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Histology World Histology Testbank
Hochgeladen von
Ralp BarriosCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Histology World Histology Testbank
Hochgeladen von
Ralp BarriosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Histology-World!
Histology
Testbank
1.
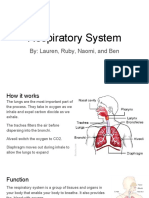
What part of the respiratory tree is the functional unit where gas
exchange occurs?
a. Alveolar duct
b. Alveoli
c. Alveolar sac
d. Respiratory bronchiole
e. Terminal bronchiole
Answer: b
The respiratory tract is made of branching structures, much like the
branches of a tree. The trachea branches into two bronchi which
branch into smaller bronchi. The bronchi ultimately branch into smaller
bronchioles. Bronchioles are distinguished from bronchi in that they do
not have cartilage and submucosal glands. The terminal bronchioles
are the last part of the airway in which gas exchange does not occur.
Terminal bronchioles lead to the respiratory bronchioles. The
respiratory bronchioles are the first section of the respiratory tree that
gas exchange can occur. The alveoli duct is analogous to a
thoroughfare with many cul-du-sacs branching off of it. At the end of
the alveoli duct is an alveoli sac. An alveoli sac is a cluster of alveoli,
much like a cluster of grapes. Alveoli are individual sacs where gas
exchange occurs.
2.
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 1 of 6
Which cell type is involved in general sensation of the olfactory
mucosa?
a. Basal cells
b. Brush cells
c. Olfactory cells
d. Sustentacular cells
e. All of the above
Answer: b
Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal
cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory
cells and sustentacular cells.
Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved
with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are
bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells
are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type
in the olfactory epithelium.
3.
What type of cells are found in the olfactory mucosa?
a. Basal cells
b. Brush cells
c. Olfactory cells
d. Sustentacular cells
e. All of the above
Answer: e
Olfactory mucosa lines the roof and portions of the walls of the nasal
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 2 of 6
cavity. It contains several cell types: basal cells, brush cells, olfactory
cells and sustentacular cells.
Basal cells are located in the basal lamina. Brush cells are involved
with general sensation of the olfactory mucosa. Olfactory cells are
bipolar neurons that are the receptors for smell. Sustentacular cells
are supporting cells. Sustentacular cells are most numerous cell type
in the olfactory epithelium.
4.
What type of tissue makes up the rings of the trachea?
a. Compact bone
b. Spongy bone
c. Hyaline cartilage
d. Fibrocartilage
e. Elastic cartilage
Answer: c
The rings of the trachea are composed of hyaline cartilage.
5.
Which cell is a squamous pulmonary epithelial cell?
a. Clara cell
b. Type I pneumocyte
c. Type II pneumocyte
d. Dust cell
e. Brush cell
Answer: b
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 3 of 6
The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I
pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface
of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The
type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the
alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the
alveolar epithelium.
6.
Which cell is also called an alveolar phagocyte?
a. Clara cell
b. Type I pneumocyte
c. Type II pneumocyte
d. Dust cell
e. Brush cell
Answer: d
The Clara cell is found in the terminal bronchioles. The type I
pneumocyte is a squamous epithelial cell. It covers most of the surface
of the alveoli. The type II pneumocyte is also called a septal cell. The
type II pneumocyte secretes surfactant. The dust cell is also called the
alveolar phagocyte. Brush cells are occasionally, but rarely, seen in the
alveolar epithelium.
7.
Which is structure is NOT part of the conducting portion of the
airway?
a. Bronchi
b. Larynx
c. Trachea
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 4 of 6
d. Larynx
e. Respiratory bronchioles
Answer: e
The conducting portion of the airway is where air is moved, warmed
and moistened. The nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx, trachea and
bronchi are all part of the conducting portion of the airway.
The respiratory portion of the airway is where gas exchange occurs.
The respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs and alveoli
are all part of the respiratory portion.
8.
What type of tissue lines the pharynx?
a. Simple squamous epithelium
b. Simple columnar epithelium
c. Stratified squamous epithelium
d. Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells
e. Both c and d
Answer: e
The pharynx is lined by both stratified squamous epithelium and
ciliated pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells. Different regions
are lined by a different type of epithelium. Regions of the pharynx that
are likely to be roughened up by food are lined by stratified squamous
epithelium. Other regions of the pharynx are lined by ciliated
pseudostratified epithelium with goblet cells.
9.
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 5 of 6
What is an olfactory cell?
a. Unipolar neuron
b. Bipolar neuron
c. Multipolar neuron
d. Supporting cell
e. None of the above
Answer: b
An olfactory cell is a bipolar neuron.
10.
Which type of cartilage is found in the larynx?
a. Hyaline cartilage
b. Elastic cartilage
c. Fibrocartilage
d. Both a and b
e. All of the above
Answer: d
The larynx is composed of several cartilages. The thyroid cartilage,
cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, corniculate cartilages and
cuneiform cartilages are all composed of hyaline cartilage. The
epiglottis is elastic cartilage. There is no fibrocartilage in the larynx.
http://www.histology-world.com/testbank/resp2a.htm 19/02/2019, 6?21 PM
Page 6 of 6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MCQ of UpperDokument17 SeitenMCQ of Upperد.مهاجر في أرض اللهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology QuizDokument4 SeitenHistology Quizfacejelly64100% (2)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Ophthalmic and NeuroanatomyVon EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Ophthalmic and NeuroanatomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQS in Blood & Hemopoiesis HistologyDokument7 SeitenMCQS in Blood & Hemopoiesis HistologyGo100% (1)
- Embryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02Dokument120 SeitenEmbryologypracticequestionswithanswers 140707144050 Phpapp02oopie0% (1)
- EmbryologyDokument29 SeitenEmbryologySara Gblabi50% (2)
- Anatomy MCQS: Abdomen: 1 BC 2 D 3 CD 4 B 5 D 6 A 7 C 8 D 9 E 10 BCD 11 CDE 12 BC 13 BCDDokument37 SeitenAnatomy MCQS: Abdomen: 1 BC 2 D 3 CD 4 B 5 D 6 A 7 C 8 D 9 E 10 BCD 11 CDE 12 BC 13 BCDPeter BoatengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teach Yourself HistologyDokument19 SeitenTeach Yourself HistologySambili Tonny100% (1)
- Embryology Mcqs ... Olum-1Dokument47 SeitenEmbryology Mcqs ... Olum-1mujuni emanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology QNSDokument33 SeitenEmbryology QNSElizabeth Gabriel HoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology QuestionsDokument8 SeitenHistology QuestionsRutendo Mutosvori100% (1)
- Teach Yourself EmbryologyDokument15 SeitenTeach Yourself EmbryologySambili Tonny100% (2)
- Histology and HistopathologyDokument42 SeitenHistology and HistopathologyDreyden HaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology MCQsDokument7 SeitenEmbryology MCQsSafiya James100% (1)
- Histology Mock ExamDokument73 SeitenHistology Mock ExamRozen GaiserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology - Nervous System - MCQDokument13 SeitenPhysiology - Nervous System - MCQadham100% (1)
- First Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28Dokument284 SeitenFirst Year Complete Physiology MCQ Bank by Team DR Of2027-28ammejan10100% (1)
- Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio Pineda: Page 1 of 9Dokument9 SeitenLectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio Pineda: Page 1 of 9Famela Anne GOmez Madamba100% (1)
- Histology World MCQDokument43 SeitenHistology World MCQAziz100% (6)
- Test Bank EmbryologyDokument33 SeitenTest Bank EmbryologyLe Shana Valentine100% (1)
- Noninfectious Diseases and Pathology of Reptiles, Color Atlas and Text, 2nd Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Dokument536 SeitenNoninfectious Diseases and Pathology of Reptiles, Color Atlas and Text, 2nd Edition (VetBooks - Ir)Letícia de Oliveira SousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Anatomy Questions PDFDokument63 SeitenAdvanced Anatomy Questions PDFJoanne BlancoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete Histology Mcqs 1st Year Mbbs PDFDokument15 SeitenComplete Histology Mcqs 1st Year Mbbs PDFYasif Abbas100% (2)
- Ganong Physiology Mcqs & SeqsDokument193 SeitenGanong Physiology Mcqs & SeqsRichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Dokument3 SeitenHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Nervous System 1Kat JornadalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology MCQs Part 2Dokument54 SeitenHistology MCQs Part 2RPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit71% (7)
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aDokument5 SeitenHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Skin 1aKat Jornadal100% (1)
- Med 1104 EmbryologyDokument12 SeitenMed 1104 EmbryologyLe Shana ValentineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument10 SeitenRespiratory Systemapi-272862164100% (1)
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleDokument76 SeitenUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervemuscle MCQDokument9 SeitenNervemuscle MCQNishanthy PirabakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Cartilage MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Dokument6 Seiten4-Cartilage MCQ Asnan Ainshams DR - Zahra 2020Shay Os100% (2)
- Embryology MCQDokument10 SeitenEmbryology MCQTofik MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo QuestionsDokument15 SeitenEmbryo QuestionsAnon AnonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesVon EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Anatomy and Neurobiology for UndergraduatesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- MCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisDokument100 SeitenMCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisMatt McCannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Fluids MCQsDokument10 SeitenBody Fluids MCQsAbdulkadir Waliyy Musa50% (2)
- Histology Final ExamDokument8 SeitenHistology Final Examliz gamezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology McqsDokument15 SeitenEmbryology McqsDr-Jahanzaib GondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsDokument8 Seiten200 Level Module 2 Histology QuestionsPrecious Julius100% (1)
- 015 Anatomy MCQ ACEM Primary PDFDokument14 Seiten015 Anatomy MCQ ACEM Primary PDFMoiez Ahmad100% (1)
- PHS MCQ Tutorials 200lDokument4 SeitenPHS MCQ Tutorials 200lcollinsmagNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Anatomy Midyear 2016Dokument78 SeitenMCQ Anatomy Midyear 2016Hager AbosalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryo QuestionsDokument15 SeitenEmbryo QuestionsSalmonella TyphiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Seminar 3 MCQDokument31 SeitenHistology Seminar 3 MCQNeo ShiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsVon EverandAnatomy: 1800 Multiple Choice QuestionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (15)
- Diseases of Periradicular TissuesDokument62 SeitenDiseases of Periradicular Tissuesanubhutigupta1404Noch keine Bewertungen
- HISTOLOGY - CorrectedDokument26 SeitenHISTOLOGY - CorrectedLola KhatimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section-I Mcqs and SeqsDokument3 SeitenSection-I Mcqs and SeqsSadia NasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Questions QuizDokument28 SeitenHistology Questions QuizminervamoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology ExamsDokument2 SeitenHistology Examsqarafi4007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Histology-World! Histology Testbank-Cartilage 2aDokument7 SeitenHistology-World! Histology Testbank-Cartilage 2aAya AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inner Ear AnatomyDokument103 SeitenInner Ear AnatomyGhada WageihNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 Muscle Practice TestDokument31 SeitenCH 7 Muscle Practice TestAia MercNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology MCQDokument13 SeitenHistology MCQHasan Mahmud64% (11)
- CK 7 and CK 20 Positive Tumors Modern Pathol 2000Dokument11 SeitenCK 7 and CK 20 Positive Tumors Modern Pathol 2000api-26176346Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry MCQsDokument19 SeitenBiochemistry MCQsschxzerrydawn100% (1)
- Human Physiology: Exam 2Dokument5 SeitenHuman Physiology: Exam 2Dancebp4100% (5)
- Phys MCQDokument21 SeitenPhys MCQaerowong100% (2)
- 2019PROCEEDINGBOOKBALIDENCE2019Dokument855 Seiten2019PROCEEDINGBOOKBALIDENCE2019Rika LedyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Text - Book of Histology: Descriptive and Practical. For the Use of StudentsVon EverandA Text - Book of Histology: Descriptive and Practical. For the Use of StudentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Tissue EngineeringDokument41 SeitenIntroduction To Tissue EngineeringK CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology 2Dokument1 SeiteHistology 2zaydeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology QuestionsDokument3 SeitenHistology QuestionsAlec Maquiling100% (1)
- Key Histology Exam 2 Fall 2007wDokument18 SeitenKey Histology Exam 2 Fall 2007wlogang48100% (4)
- Embryology+Anatomy Study Questions ONLYDokument10 SeitenEmbryology+Anatomy Study Questions ONLYAnca Badoiu75% (4)
- Embryology BoneDokument6 SeitenEmbryology BoneMarera DomnicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Model ADokument7 SeitenHistology Model AOzgan SüleymanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Dokument19 SeitenNeet - Combined Test - 6 (P, C, B) - 06.08.2017Sankar KumarasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy MataDokument9 SeitenAnatomy MataputriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: B. Cell PhysiologyDokument29 SeitenCells: B. Cell PhysiologyShyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Cornea SuturesDokument14 SeitenRepair Cornea SuturesBima RizkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelium Surface SpecializationsDokument41 SeitenEpithelium Surface SpecializationsMitzel SapaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 3 Monthly-Exam-OctoberDokument3 SeitenScience 3 Monthly-Exam-OctoberJudenable MjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Ts TypesDokument10 SeitenAnimal Ts TypesroshanrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amelogenesis: Prof. Shaleen ChandraDokument16 SeitenAmelogenesis: Prof. Shaleen ChandraAnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeoplasiaDokument21 SeitenNeoplasiaFreakyRustlee LeoragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komunikasi Antar Sel: Irma Yuniar Wardhani, M.PDDokument12 SeitenKomunikasi Antar Sel: Irma Yuniar Wardhani, M.PDIrma YuniarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Short Notes of Anatomy and Physiology by Pooja????????????Dokument174 SeitenSuper Short Notes of Anatomy and Physiology by Pooja????????????shankarmeti2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11th Zoology Chapter 1 Studty MaterialDokument20 Seiten11th Zoology Chapter 1 Studty MaterialPooja sriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Class - Ix (Cbse)Dokument6 SeitenBiology: Class - Ix (Cbse)naman mahawerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology MariebDokument12 Seiten4 Notes Anatomy and Physiology Mariebmine2515Noch keine Bewertungen
- Benign Ovarian TumourDokument45 SeitenBenign Ovarian Tumourahmed shorshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histomorphology of The Pancreas in MynaDokument6 SeitenHistomorphology of The Pancreas in MynaIndian Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences RNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDokument2 Seiten7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histologi Integument - 2022 - Wo Audio-Dikonversi-DikompresiDokument50 SeitenHistologi Integument - 2022 - Wo Audio-Dikonversi-DikompresiMsatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsDokument15 Seiten2009-High Resolution Map of Caenorhabditis Elegans Gap Junction ProteinsyicinenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy - Chapter-4-Skin and MembranesDokument45 SeitenAnaphy - Chapter-4-Skin and MembranesrhmanipolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of The TissuesDokument31 SeitenHistology of The TissuesAbiola NerdNoch keine Bewertungen