Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
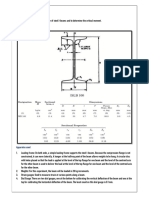
Adv of Venturimeter
Hochgeladen von
sujeet.jha.311Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Adv of Venturimeter
Hochgeladen von
sujeet.jha.311Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Because a venture tube smoothly converges then diverges, it converts potential energy
(pressure) to kinetic energy (velocity and back again with very little agitation or loss of
energy and is useful over a wide range without limiting the process.
An orifice is a sharp edged plate with a (calibrated?) hole in it that causes a pressure drop
with loss of energy (that heats the fluid very slightly by agitation). The orifice plate often
controls the flow as well as register a pressure drop. various size orifice holes can be
substitute as required. The orifice plate is usually contained between (mechanical) flanges
that require gaskets and may leak while venturi tube could be welded into a system
seemlessly. Orifice plates can be removed for inspection and cleaning. Orifice plates may
work best over a rather limited range consistent with their calibration. There are performance
table for orifice plates and when flow is not critical plates may be used without specific
calibration. Orifice plates may be of a different material stainless steel?) than the system
piping (carbon steel) whereas the material of a venturi tube must be consistent with system
piping if welded in (when not flanged). An orifice plate may trap gases or other matter that
likely would sweap on through a venturi tube. Usually the taps for a venturi tube are built into
the unit whereas the differential pressure gage taps for an orifice plate must be a specified
distance upstream and downsteram of the plate requiring additional system penetrations.
Both a venturi tube and an orifice plate may require a certain length of straight pipe upstream
and downstream to avoid flow distortion and the venturi tube may furnish some of the
required length. Performance may also depend upon whether flow is laminar or turbulent. I
would expect most orifice plate applications to be less expensive than a comparable venturi
tube.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Von EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Chilled Water Piping SystemDokument36 SeitenChilled Water Piping Systemchetanvmak100% (2)
- Piping Layout UDLDokument24 SeitenPiping Layout UDLLegend Anbu100% (1)
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers Fin-Fan: by M.M.SorourDokument64 SeitenAir-Cooled Heat Exchangers Fin-Fan: by M.M.SorourNader GaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- City Without A Hero Complete PDFDokument335 SeitenCity Without A Hero Complete PDFsujeet.jha.311100% (1)
- PVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 2Dokument117 SeitenPVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 2Nguyen Quang NghiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Presentation L & TDokument61 SeitenPiping Presentation L & TJitendra SurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Types and SelectionDokument31 SeitenHeat Exchanger Types and Selectionmehul10941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Reference Guide To Piping EngineeringDokument32 SeitenCommon Reference Guide To Piping EngineeringSteve WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reasonable VelocityDokument4 SeitenReasonable VelocityRaithab IlsurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Completion TheoryDokument74 SeitenCompletion TheoryHKHKBOOKSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping and Plumbing Fittings PDFDokument5 SeitenPiping and Plumbing Fittings PDFmichol201450% (4)
- Pipe Schedule: Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel PipeDokument10 SeitenPipe Schedule: Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel PipePrasad BhosaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and CFD Analysis of Orifice Plate at Different Velocity RatiosDokument69 SeitenDesign and CFD Analysis of Orifice Plate at Different Velocity RatiosMohammad Ehraz AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDokument112 SeitenShell and Tube Heat Exchangerramesh pokhrel100% (3)
- Piping FundamentalsDokument12 SeitenPiping FundamentalsKurian JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wellheads Components 1655005135Dokument149 SeitenWellheads Components 1655005135Chandra Setiawan100% (2)
- Ams 4965 HDokument11 SeitenAms 4965 HOTK Micro-FixNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Process Duct WorkDokument17 SeitenFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Process Duct WorkB DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchangers, Strainers and SeperatorsDokument12 SeitenHeat Exchangers, Strainers and SeperatorsJaveed A. Khan100% (1)
- Fin Fan CoolersDokument14 SeitenFin Fan Coolersmohamedyoussef1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping PDFDokument29 SeitenPiping PDFEzekielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversVon EverandSteam Turbines A Book of Instruction for the Adjustment and Operation of the Principal Types of this Class of Prime MoversBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Anchor Bolt For ShearDokument22 SeitenAnchor Bolt For ShearAnonymous P73cUg73LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshVon EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Block Flow DiagramDokument35 SeitenA Block Flow DiagramJerry SimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat ExchangerDokument6 SeitenHeat ExchangeralokbdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inune Exchangers: M I N E Exchanger (After Brown Fintube Koch International)Dokument30 SeitenInune Exchangers: M I N E Exchanger (After Brown Fintube Koch International)Process EngineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Select Shell and Tube HEDokument10 SeitenHow To Select Shell and Tube HEgigihpradana100% (1)
- Design Practices-ReboilerDokument7 SeitenDesign Practices-Reboileragarwalashwin32100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Orifice Metering FMCDokument7 SeitenFundamentals of Orifice Metering FMCapply19842371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shell and Tube Ref - AnandDokument6 SeitenShell and Tube Ref - Anand7761430Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Trend in Heat ExchangerDokument9 SeitenRecent Trend in Heat Exchangersai100% (1)
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Piping DesignDokument24 SeitenHeat Exchanger Piping DesignManan100% (2)
- Presentation For Shell & Tub Heat ExchangerDokument33 SeitenPresentation For Shell & Tub Heat ExchangerHoa Hoang PhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vent Manifold Flare Manifold DesignDokument10 SeitenVent Manifold Flare Manifold Designahsan888Noch keine Bewertungen
- संयुक्त संस्करण सावधान डोगा, कौन PDFDokument128 Seitenसंयुक्त संस्करण सावधान डोगा, कौन PDFsujeet.jha.311100% (1)
- PPXV An Elegant and Fast Method To Predict The Slow Crack Growth Behaviour of High Density Polyethylene Pipe MaterialsDokument7 SeitenPPXV An Elegant and Fast Method To Predict The Slow Crack Growth Behaviour of High Density Polyethylene Pipe MaterialsMehboob ulHaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tube SettlerDokument4 SeitenTube SettlerSIVAPATHASEKARAN100% (4)
- Air Cooled Condenser ACC PDFDokument3 SeitenAir Cooled Condenser ACC PDFHoney TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Construction of Shell & Tube Heat ExchangersDokument12 SeitenBasic Construction of Shell & Tube Heat ExchangerslatshareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1: Schematic of A Shell-and-Tube Heat ExchangerDokument7 SeitenFigure 1: Schematic of A Shell-and-Tube Heat ExchangerSarthak RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger MOCDokument5 SeitenHeat Exchanger MOCanon_268840481Noch keine Bewertungen
- Designing AND Optimization OF A Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDokument8 SeitenDesigning AND Optimization OF A Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerAyush SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- WssDokument13 SeitenWssSushanta SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - PlumbingDokument8 SeitenChapter 3 - PlumbingPrabhakaran DakshinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Lec 3 WcoDokument11 Seiten4th Lec 3 WcoZana M. WasmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coiled Tubing Skid-Mount UnitDokument5 SeitenCoiled Tubing Skid-Mount Unitnoel chris Jindjou100% (1)
- Coiled TubingDokument3 SeitenCoiled TubingMonserrat MontelongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping AuxiliariesDokument12 SeitenPiping AuxiliariesarchitNoch keine Bewertungen
- COIL TubingDokument2 SeitenCOIL TubingHamid RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat ExchangerDokument22 SeitenHeat ExchangerYashwant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offshore Orifice-Plate Impulse Line ArrangementDokument5 SeitenOffshore Orifice-Plate Impulse Line ArrangementTimothy LeonardNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEMA Terminology:: o o o o oDokument5 SeitenTEMA Terminology:: o o o o oNathanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub Surface ToolDokument64 SeitenSub Surface ToolPrithiraj KalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials: ElbowDokument4 SeitenMaterials: ElbowprafullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column PresentationDokument27 SeitenColumn PresentationTaifurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christmas TreeDokument11 SeitenChristmas TreezaideidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoclave Technical InfoDokument16 SeitenAutoclave Technical Info136339Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPE 89600 New Technologies Allow Small Coiled Tubing To Complete The Work Formerly Reserved For Large Coiled Tubing UnitsDokument7 SeitenSPE 89600 New Technologies Allow Small Coiled Tubing To Complete The Work Formerly Reserved For Large Coiled Tubing UnitsClyde San VicenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger Reference TheoryDokument23 SeitenHeat Exchanger Reference TheoryMurugan VeluNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH352 CED Lecture 4Dokument19 SeitenCH352 CED Lecture 4Abhishek UpadhyayulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Plumbing Repairs for the Home and FarmsteadVon EverandSimple Plumbing Repairs for the Home and FarmsteadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Semantic Web (Knowledge Sharing On The Web)Dokument19 SeitenIntroduction To The Semantic Web (Knowledge Sharing On The Web)sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sewa Sambandi Syllabus 2073 PDFDokument1 SeiteSewa Sambandi Syllabus 2073 PDFsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Detail From ClientDokument1 SeiteDetail From Clientsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Title: Your Company Reference 63979dbfdeaeDokument1 SeiteProject Title: Your Company Reference 63979dbfdeaesujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Web Layout MedrasisDokument11 SeitenWeb Layout Medrasissujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expert SystemsDokument10 SeitenExpert Systemssujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation and Integration: (Lectures On Numerical Analysis For Economists II)Dokument50 SeitenDifferentiation and Integration: (Lectures On Numerical Analysis For Economists II)sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- KharejiDokument1 SeiteKharejisujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notice ChinaDokument3 SeitenNotice Chinasujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Language Processing: Aman ShakyaDokument17 SeitenNatural Language Processing: Aman Shakyasujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fitness Aziz AlhaidariDokument2 SeitenFitness Aziz Alhaidariabdulaziz saif ali mansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master's Degree 2: Information and Communication Systems - Hamburg University of Technology - HamburgDokument6 SeitenMaster's Degree 2: Information and Communication Systems - Hamburg University of Technology - Hamburgsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Rs Future Proof Career PDFDokument1 SeiteCcna Rs Future Proof Career PDFsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- The National Broadcasting Regulation, 2052 (1995)Dokument32 SeitenThe National Broadcasting Regulation, 2052 (1995)sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Master Program Academic Adminstration Guidlines 2018 PDFDokument21 SeitenMaster Program Academic Adminstration Guidlines 2018 PDFsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notice Medical EducationDokument1 SeiteNotice Medical Educationsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Insight Into Ielts Workbook Pack With Answers Sample Pages PDFDokument10 SeitenNew Insight Into Ielts Workbook Pack With Answers Sample Pages PDFthao leNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master's Degree 2: Information and Communication Systems - Hamburg University of Technology - HamburgDokument6 SeitenMaster's Degree 2: Information and Communication Systems - Hamburg University of Technology - Hamburgsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Claim Form (English)Dokument1 SeiteMedical Claim Form (English)sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advertisement 2015 CLT Instructor Engineering 20406Dokument1 SeiteAdvertisement 2015 CLT Instructor Engineering 20406sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 7Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 7sujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voucher SampleDokument1 SeiteVoucher Samplesujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Payment DetailDokument1 SeitePayment Detailsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete-Time Random SignalsDokument34 SeitenDiscrete-Time Random SignalsNaeem Ali SajadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 138-Gahri Chal PDFDokument41 Seiten138-Gahri Chal PDFsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- VDokument1 SeiteVsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of PurposeDokument1 SeiteStatement of Purposesujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Link Bank Account Application FormDokument4 SeitenLink Bank Account Application Formsujeet.jha.311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Osborne Reynolds Experiment: CapacuyDokument1 SeiteOsborne Reynolds Experiment: CapacuyDennis Angelo PablicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stainless Steel 321 Technical DataDokument2 SeitenStainless Steel 321 Technical Datasmith willNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear Flow in Open With Variable ThicknessDokument7 SeitenShear Flow in Open With Variable Thicknessashraqat qassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format For Laboratory Reports Lab03Dokument4 SeitenFormat For Laboratory Reports Lab03haloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral BucklingDokument16 SeitenLateral BucklingPrachi ce19b073Noch keine Bewertungen
- Centrifugal Casting Process For Mechanical SealsDokument2 SeitenCentrifugal Casting Process For Mechanical SealsPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrating Wire Strain GaugeDokument2 SeitenVibrating Wire Strain GaugejilofeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold-Formed Steel Structures Around The World: A Review of Recent Advances in Applications, Analysis and DesignDokument9 SeitenCold-Formed Steel Structures Around The World: A Review of Recent Advances in Applications, Analysis and Designshivaji09Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Sager Reciprocal Relations SignificanceDokument7 SeitenOn Sager Reciprocal Relations SignificanceGaurav DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- FHWA Bridge Design Guidance No. 1: Resistance of FastenersDokument10 SeitenFHWA Bridge Design Guidance No. 1: Resistance of FastenersAbdulrahman SaraijiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4404 enDokument5 Seiten1.4404 enyraju88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 6 (Refrigerator) ) 1Dokument10 SeitenExperiment 6 (Refrigerator) ) 1Meor Fitri SE100% (1)
- Electrochemistry (Revision Notes) - RemovedDokument7 SeitenElectrochemistry (Revision Notes) - Removedsaapldesign1 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Single Phase Power Tutorial QuestionsDokument17 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Single Phase Power Tutorial QuestionsFilbert OmbongiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChhaviDokument52 SeitenChhaviavatar rajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statically Indeterminate Structures by The Matrix Force Method-3 PDFDokument14 SeitenStatically Indeterminate Structures by The Matrix Force Method-3 PDFmathewsujith31Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIG444Dokument24 SeitenTIG444Dejan JovanovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Failure Mechanism of CLT Shear Walls Subjected To Seismic ActionDokument2 SeitenDetermination of Failure Mechanism of CLT Shear Walls Subjected To Seismic ActionGuillaumeHNONoch keine Bewertungen
- ENF-VT3 BrochureDokument2 SeitenENF-VT3 BrochurezhangjunpingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical PotentialDokument4 SeitenChemical PotentialVictor BadeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Vapour Deposition: Vijitha I. JRF, Csir-NiistDokument19 SeitenChemical Vapour Deposition: Vijitha I. JRF, Csir-NiistOmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet VDM Alloy 22 PDFDokument13 SeitenData Sheet VDM Alloy 22 PDFAlberto LazzarettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparitive Study of Design of Piping SupportDokument18 SeitenComparitive Study of Design of Piping SupportbkguptazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties and Optimization of Processing Parameters For Epoxy Glass Fiber Reinforced CompositesDokument4 SeitenMechanical Properties and Optimization of Processing Parameters For Epoxy Glass Fiber Reinforced CompositesNavid HoseiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excavation Design in Stratified RockDokument14 SeitenExcavation Design in Stratified RockRobert PrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces at Work in A MoleculeDokument56 SeitenForces at Work in A Moleculekatherine corveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement of Corrosion Resistance of Plasma Nitrided Stainless SteelDokument4 SeitenImprovement of Corrosion Resistance of Plasma Nitrided Stainless SteelpiyupriNoch keine Bewertungen