Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ESS ROC PIL-7 PointLoadTester
Hochgeladen von
Ekky Sang Pangeran KodokCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ESS ROC PIL-7 PointLoadTester
Hochgeladen von
Ekky Sang Pangeran KodokCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
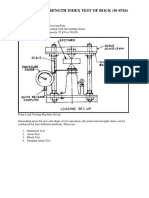
POINT LOAD TESTER
Model PIL-7
APPLICATIONS
The point load tester is used to determine the Point Load
Strength Index (Is(50)). This index provides a method for
establishing rock strength classification.
The index can also be used to determine the rock aniso-
tropy as well as to predict other rock strength properties,
such as uniaxial tensile and compressive strengths.
DESCRIPTION
The PIL-7 point load tester consists of a loading frame,
a mounted hydraulic ram and a pressure gauge for ma-
ximum load indication. An upper conical platen is fixed
on the frame and a lower one on the jack piston. A gra-
duated scale is fixed on the frame and indicates the
specimen diameter.
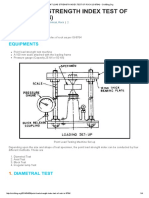
TEST PROCEDURE
Three point load test configurations are used depending
on the available rock specimens:
Diametrical – Axial – Irregular lump
The diametrical and axial tests use core specimens with FEATURES
length/diameter (L/D) ratios greater than 1.0 in the first • Conical platens conform to ISRM
case, and between 0.3 and 1.0 in the second case. Rock suggested method
pieces of suitable irregular shapes are used when cores
are not available. • Direct reading of specimen diameter
The testing steps are the same for all configurations: • Maximum load indicator
1) The specimen is positioned between the • Portable
conical platens. The platens are then closed • Shield protects from chips flying
to make contact. upon failure
2) The distance “De” between the points of contact • Extreme rigidity
is read on the scale.
3) The load is increased such that failure occurs
within 10 to 60 sec. and the failure load “P”
is read and recorded.
INTERPRETATION SPECIFICATIONS
The Point Load Tester allows the user to determine Maximum specimen size 102 mm
an “Uncorrected Point Load Strength Index” (Is). Maximum load 70 kN
This index must be corrected to a standard equivalent Scale minor division 0.5 mm
diameter (De ) of 50 mm. It then becomes a unique Pressure gauge
property of the rock tested (I s(50) ) which is most useful Range 100 000 kPa
in rock strength classification. Accuracy ±0.2% F.S.
Rock anisotropy is quantified by the “Strength Ani- Height 48 cm
sotropy Index” (I a(50) ). This index is the ratio of the Length 27 cm
grea test to least Is(50) index measured respectively Depth 25 cm
perpendicular and parallel to the existing planes of
weakness.
The uniaxial tensile (UTS) and compressive (UCS)
strengths can be approximated from the I s(50) index. ACCESSORIES
The UTS is about 1.25 times Is(50) and the UCS is nor-
• Set of spare conical platens
mally between 20 and 25 times the I s(50) index.
• Spare pressure gauge
I s is obtained from the following equation:
• Spare front protective shield
Is = P / D 2
e
• Spare back protective shield
where: I s: Uncorrected Point Load Strength • Set of optional flat platens
Index, in MPa or psi
• Set of optional spherical seats
P: Failure load, in MN or lbf
(maximum pressure × jack piston area) • Optional low pressure gauge (30 000 kPa)
D e : Equivalent core diameter, in meters or • Carrying case for point load tester
inches (De = D for diametral tests)
The ISRM* “Suggested Method for Determining
Point Load Strength” size correction procedure is
used. I s(50) is obtained either graphically, mathema-
tically or by testing 50 mm (maximum diameter) spe-
cimens.
*ISRM: International Society of Rock Mechanics.
Products and specifications are subject to change without notice. E5048A-050901
© Roctest Limited, 2005.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Point Load Tester - PIL-7Dokument2 SeitenPoint Load Tester - PIL-7Vikash KeshriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Strength - Point Load Test (Civil Eng) - 230619 - 092022Dokument8 SeitenRock Strength - Point Load Test (Civil Eng) - 230619 - 092022Muhammad ZulhilmizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab # 8 Objective:: Mirza Muhammmad Zaid 2009-Min-21Dokument4 SeitenLab # 8 Objective:: Mirza Muhammmad Zaid 2009-Min-21loverbacha100% (2)
- Point Load Strength Index Test of RockDokument5 SeitenPoint Load Strength Index Test of RockRasydanRais50% (4)
- Tests On Rocks: Soil MechanicsDokument5 SeitenTests On Rocks: Soil MechanicsWaqas Sadiq100% (1)
- 5 - MATEPRO - Mechanical Behavior, Testing, and Manufacturing Properties of Materials (09.23.2022)Dokument23 Seiten5 - MATEPRO - Mechanical Behavior, Testing, and Manufacturing Properties of Materials (09.23.2022)Christian TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE242 - Tensile Test - 2023Dokument25 SeitenCE242 - Tensile Test - 2023K K BajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RSI Test (From SI)Dokument4 SeitenRSI Test (From SI)edwinbadajosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile Test LabDokument4 SeitenTensile Test LabputrosigarhidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan 21 Nov 2023Dokument6 SeitenAdobe Scan 21 Nov 2023Shivam VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cope, R.J. & Rao P.V. (1983), Moment Redistribution in Skewed Slab BridgesDokument30 SeitenCope, R.J. & Rao P.V. (1983), Moment Redistribution in Skewed Slab BridgesM KraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Strength and The S-N Diagram Study Notes For Mechanical EngineeringDokument13 SeitenFatigue Strength and The S-N Diagram Study Notes For Mechanical Engineeringaditya.1540011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mos Lab Manual PDFDokument34 SeitenMos Lab Manual PDFs.rihanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Determine The UCS of Samples by Using Point Load Strength IndexDokument5 SeitenTo Determine The UCS of Samples by Using Point Load Strength IndexBoos yousufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Triaxial Rock TestingDokument4 SeitenTriaxial Rock TestingLizardoTalaveranoEstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives:: Lecture No. 7 Strain, Stress-Strain DiagramsDokument29 SeitenObjectives:: Lecture No. 7 Strain, Stress-Strain Diagramsعبدالمحسن العنزيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uji TarikDokument49 SeitenUji Tarikberlian pulungNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Higher Technological Institute (HTI) Department of Biomedical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenThe Higher Technological Institute (HTI) Department of Biomedical EngineeringMahmoud RashwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenMechanics of Solids Lab ManualTacke NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peru NDTDokument50 SeitenPeru NDTGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Load Strength Index Test of Rock (Is-8764)Dokument4 SeitenPoint Load Strength Index Test of Rock (Is-8764)gorkem100% (1)
- Fracture Toughness Testing of MetalsDokument16 SeitenFracture Toughness Testing of MetalsMuhammad AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument138 SeitenUnit 2Abhishek ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Point Load Strength Index of Half-Cut Core SpecimenDokument17 SeitenPoint Load Strength Index of Half-Cut Core SpecimenGbenga AdewumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slender Column Test Reporting and DataDokument6 SeitenSlender Column Test Reporting and DataAsad UzzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fairground Case Study Ethan HolmesDokument14 SeitenFairground Case Study Ethan HolmesethanesholmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- !rangkuman UCS With Strain GaugeDokument8 Seiten!rangkuman UCS With Strain GaugeGumbert Maylda PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory 1 - Tension Test: 1. Objectives The Objectives of This Lab AreDokument3 SeitenLaboratory 1 - Tension Test: 1. Objectives The Objectives of This Lab AreMeirzhan YerzhanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 PDFDokument8 Seiten6 PDFmegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load (N) Length (MM) : SolutionDokument8 SeitenLoad (N) Length (MM) : Solutionاحمد الشوافيNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE-103 Mechanics of Solids - I: Dr. Junaid Ahmad Nice, Scee, NustDokument29 SeitenCE-103 Mechanics of Solids - I: Dr. Junaid Ahmad Nice, Scee, NustArsalan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brazilian TestDokument4 SeitenBrazilian Testmohit kumar [NIT Rourkela]Noch keine Bewertungen
- Point Load TestDokument4 SeitenPoint Load Testkiko auNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension Test ReportDokument7 SeitenTension Test Reportzgts100% (1)
- O o Fig. 4 - Stress-Strain Curves For Steel ReinforcementDokument1 SeiteO o Fig. 4 - Stress-Strain Curves For Steel ReinforcementRonal J Clavijo RNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM D747 Overview PDFDokument41 SeitenASTM D747 Overview PDFtangogll11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2018 - Lab 6 - Force Transducer HWDokument6 SeitenFall 2018 - Lab 6 - Force Transducer HWMuthoka Vincent0% (2)
- Unit - IIIDokument215 SeitenUnit - IIINishigandha Bansode100% (1)
- 1.105 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Fall 2003: Experiment 3 The Tension TestDokument13 Seiten1.105 Solid Mechanics Laboratory Fall 2003: Experiment 3 The Tension TestSuman.SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Metals - Lecture 9, MetE 143Dokument53 SeitenMechanical Properties of Metals - Lecture 9, MetE 143陈小花Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biomaterials II Lec 2Dokument21 SeitenBiomaterials II Lec 2m9trdk92ksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 - CtsDokument56 SeitenChapter 01 - CtssengthaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Parameters ofDokument25 SeitenGeotechnical Parameters ofChelvam sNoch keine Bewertungen
- StressDokument64 SeitenStressHaseena KMNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMT Lab ManualDokument75 SeitenBMT Lab Manualnenu localNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile Test Lab ReportDokument12 SeitenTensile Test Lab ReportXuan Wang100% (1)
- Fatigue TestDokument4 SeitenFatigue TestBaibhav MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME216 MOM - CHPT 3Dokument27 SeitenME216 MOM - CHPT 3Sergio Contreras PancorboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulus of Elasticity For MSDokument6 SeitenModulus of Elasticity For MSafzal taiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 1-ROCK TESTING-Part2Dokument87 SeitenCHP 1-ROCK TESTING-Part2Koh Jia JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis With Strain Gage Measurements: Experiment 1Dokument7 SeitenStructural Analysis With Strain Gage Measurements: Experiment 1Yılmaz GürpınarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Mechanical Properties of Local Concrete by DR Ray Su PDFDokument47 Seiten5 Mechanical Properties of Local Concrete by DR Ray Su PDFNandeesh M PanchapeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Cells Types, How It Works, and ApplicationsDokument21 SeitenLoad Cells Types, How It Works, and ApplicationsEncardio RiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armor Analysis - Laboratorio#1Dokument43 SeitenArmor Analysis - Laboratorio#1rtasulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ductile Fracture SimulationDokument6 SeitenDuctile Fracture SimulationPunit ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM F 382 Experiment - 1 - FoyDokument2 SeitenASTM F 382 Experiment - 1 - FoyLucas MlbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Stress-Strain-Axial (2022)Dokument66 Seiten2 Stress-Strain-Axial (2022)YAŞAR MERT DOĞANAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionVon EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit5 v1.0022101210Dokument52 SeitenUnit5 v1.0022101210Lily KkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal CalculiDokument12 SeitenRenal CalculiArieNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH3161 MATH5165 T1 2023 OutlineDokument10 SeitenMATH3161 MATH5165 T1 2023 OutlineDouglusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level - 1: Expansion of DeterminantsDokument13 SeitenLevel - 1: Expansion of DeterminantsAtomitronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Finance Chapter 4Dokument15 SeitenBusiness Finance Chapter 4chloe frostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesCorey PageNoch keine Bewertungen
- AZ-300 - Azure Solutions Architect TechnologiesDokument3 SeitenAZ-300 - Azure Solutions Architect TechnologiesAmar Singh100% (1)
- Early China 2aDokument4 SeitenEarly China 2aapi-205540374Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monkey Shine - ScriptDokument4 SeitenMonkey Shine - Scriptapi-583045984Noch keine Bewertungen
- Icivics MontesquieuDokument3 SeitenIcivics Montesquieuapi-32806152578% (9)
- Redemption and The Relief Work RevisedDokument234 SeitenRedemption and The Relief Work RevisedYewo Humphrey MhangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Letter of Request To Validate The QuestionnaireDokument2 SeitenSample Letter of Request To Validate The QuestionnaireSamantha AceraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extreme Risk FinanceDokument322 SeitenExtreme Risk FinanceThomas Thomas100% (2)
- Evolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaDokument12 SeitenEvolution of Corporate Social Responsibility in IndiaVinay VinuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convert 2.0 - Frank Kern Official Full Download + FREEDokument127 SeitenConvert 2.0 - Frank Kern Official Full Download + FREETwo Comma Club100% (1)
- 17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFDokument190 Seiten17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFJesus M. RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- (2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiDokument11 Seiten(2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiFajar HatmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-ChinDokument191 SeitenA Phonological Reconstruction of Proto-ChinHming Lem100% (1)
- ATHE Level 3 Diploma in Business (RQF / 60 Credits)Dokument4 SeitenATHE Level 3 Diploma in Business (RQF / 60 Credits)GibsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hayat e Imam Abu Hanifa by Sheikh Muhammad Abu ZohraDokument383 SeitenHayat e Imam Abu Hanifa by Sheikh Muhammad Abu ZohraShahood AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcqmate Com Topic 333 Fundamentals of Ethics Set 1Dokument34 SeitenMcqmate Com Topic 333 Fundamentals of Ethics Set 1Veena DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ruchika Project ReportDokument28 SeitenRuchika Project Reportnavdeep2309Noch keine Bewertungen
- NIA Foundation PLI Proposal Template (Repaired)Dokument23 SeitenNIA Foundation PLI Proposal Template (Repaired)lama dasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description: S&P 500 Dividend AristocratsDokument7 SeitenDescription: S&P 500 Dividend AristocratsCalvin YeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinesDokument8 SeitenLiquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinessaifoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataSheet CertificationPaths InsuranceSuite AnalystsDokument7 SeitenDataSheet CertificationPaths InsuranceSuite Analystsshanmuga89Noch keine Bewertungen
- "The Grace Period Has Ended": An Approach To Operationalize GDPR RequirementsDokument11 Seiten"The Grace Period Has Ended": An Approach To Operationalize GDPR RequirementsDriff SedikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Simple Present Simple For Elementary To Pre-IntermediateDokument2 SeitenQuiz Simple Present Simple For Elementary To Pre-IntermediateLoreinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filters SlideDokument17 SeitenFilters SlideEmmanuel OkoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFP Nms 070708Dokument183 SeitenRFP Nms 070708Md RajaulNoch keine Bewertungen