Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Inclusions Hematology
Hochgeladen von
MurrehCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Inclusions Hematology
Hochgeladen von
MurrehCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
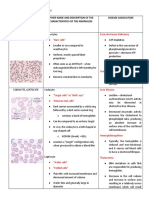
RBC INCLUSIONS
INCLUSIONS APPEARANCE/ DESCRIPTION COMPOSITION CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE PICTURE
Megaloblastic anemia
Coarse densely stained purple granules,
Severe hemolytic process
1. HOWELL-JOLLY BODIES eccentrically located on periphery of Nuclear remnants of DNA; (+) Fuelgen
Thalassemia
membrane
Accelerated erythropoiesis
Lead poisoning
Dark blue granules DISTRIBUTED IN THE
Pyrimidine-5-nucleotidase
CELL; punctuate basophilia
deficiency
Heavy metal poisoning
2. BASOPHILIC STIPPLINGS In lead poisoning – coarse basophilic Precipitation of ribosomes and RNA
Thalassemia
stippling
Pica in children – associated w/ lead
In increased red cell production – fine
poisoning
basophilic stippling
Pica in adult – associated with IDA
Dyserythropoiesis
Remnant of microtubules of mitotic
3. CABOT RINGS Rings, loops, figure of eight, red to purple Megaloblastic anemia
spindle
Severe anemia
Precipitated, denatured hemoglobin due Hereditary defect in Hexose
4. HEINZ BODIES
to oxidative injury. Monophosphate Shunt
(Golf ball – multiple Heinz Deep purple irregularly shaped inclusion
Cannot be seen in Wright’s stain G6PD deficiency
bodies)
Requires supravital stain (crystal violet) Unstable hemoglobins
Tetragonal, Rectangular rod shaped dense
5. HEMOGLOBIN C CRYSTALS hemoglobin C disease
staining crystals (bar of gold, clam shell)
Clarence Witty H. Mendoza, RMT
RBC INCLUSIONS
“Washington monument” shape; finger-
like or quartz like crystal of dense
6. HEMOGLOBIN SC CRYSTALS Hemoglobin SC disease
hemoglobin protruding from the RBC
membrane
Iron overload in mitchondria of
7. RINGED SIDEROBLAST
normoblast.
(Siderocyte – non-nucleated Nucleated RBC that contains non-heme iron Sideroblastic anemia
Due to defective heme synthesis.
cell containing hemosiderin iron particles (hemosiderin) Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
Hemosiderin – Needed for
granules)
identification
Sideroblastic anemia
Basophilic inclusions that aggregate in small Hemoglobinopathies
8. PAPPENHEIMER BODIES clusters NEAR THE PERIPHERY with Unused iron deposits Thalassemia
Wright’s stain. Megaloblastic anemia
MDS
Protozoan transmitted by bite of female
9. MALARIA
Anopheles mosquito
Protozoan inclusion (B. microti), transmitted
10. BABESIA
from deer to humans by tick bite.
MISCELLANEOUS (VARIATIONS IN RED BLOOD CELL PATTERN/DISTRIBUTION)
“Stacking or “coining” pattern of red blood Multiple Myeloma/ Waldenstrom's
A property of plasma, due to abnormal
cells on the blood smear. macroglobulinemia
1. ROULEAUX or increased proteins (plasma globulins);
Blue background on smear microscopically Chronic inflammation (high
Increased ESR
and may look very blue macroscopically. fibrinogen)
Cold autoimmune hemolytic anemias -
2. AUTOAGGLUTINATION Clumping of RBC's with no pattern.
cold-reacting autoantibodies
Clarence Witty H. Mendoza, RMT
RBC INCLUSIONS
PARASITIC INCLUSIONS IN RED BLOOD CELLS
Plasmodium species Size Inclusion Cytoplasm Merozoites
P. vivax Enlarged Schuffner dots Blue discs with red nucleus 12 – 24
Accole forms
Signet-ring forms
P. falciparum Normal Maurer dots Minute rings 6 – 32
Two chromatin dots
Accole forms
Gametes crescent shape
P. malariae Enlarged Ziemman stippling One ring with one dot 6 – 12
P. ovale Normal Schuffner dots One ring form 6 – 14
Additional information:
Normally, there are NO red cell inclusions visible when the smear is stained with Wright's stain;
Any red cell inclusions are pitted out by the spleen as the red cells pass through.
The presence of inclusions decreases red cell deformability and shortens red cell survival.
Structures needing SUPRAVITAL STAIN:
Reticulum of reticulocytes
Heinz bodies
Hemoglobin H
Clarence Witty H. Mendoza, RMT
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fast Facts: Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Determining risk, tailoring therapy, supporting patientsVon EverandFast Facts: Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Determining risk, tailoring therapy, supporting patientsNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCLINICAL CHEMISTRY: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDokument3 SeitenRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HematologyDokument28 SeitenHematologyGNiqM0% (1)
- RBC AnomaliesDokument10 SeitenRBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology Tables Morphology of RBCsDokument5 SeitenHematology Tables Morphology of RBCsGlydenne Glaire Poncardas GayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology 1Dokument5 SeitenHematology 1jaish8904100% (1)
- Mtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineDokument9 SeitenMtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineMoira Pauline LibroraniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BacteriologyDokument1 SeiteBacteriologyCaryn RobertsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingDokument42 SeitenMUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingMerhella Amor Suerte MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology Lecture Notes PDFDokument102 SeitenHematology Lecture Notes PDFMarisa IzzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUST To KNOW in Blood Banking 1Dokument19 SeitenMUST To KNOW in Blood Banking 1Aya Virtucio100% (1)
- Hematology NotesDokument17 SeitenHematology NotesEly Sibayan100% (2)
- Role of Blood Vessels in Hemostasis: Villa, M.D. MLS 4CDokument10 SeitenRole of Blood Vessels in Hemostasis: Villa, M.D. MLS 4CMarianne Dennesse100% (1)
- Study Stack - MLT Table ReviewDokument3 SeitenStudy Stack - MLT Table Review장주연Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology ReviewDokument6 SeitenHematology Reviewsanwel72% (18)
- Hematology ReviewerDokument4 SeitenHematology ReviewerAbigail Puno100% (1)
- Wintrobe Test PDFDokument9 SeitenWintrobe Test PDFMaria Chacón CarbajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Chemistry Board ReviewDokument14 SeitenClinical Chemistry Board ReviewWellaBaylasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeamatologyDokument45 SeitenHeamatologypikachuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLUCOSE, UREA, URIC ACID, CREATININE, CHOLESTEROL, TRIGLYCERIDE, HDL-C, LDL-C, TOTAL PROTEIN, ALBUMIN, BILIRUBIN TEST METHODSDokument4 SeitenGLUCOSE, UREA, URIC ACID, CREATININE, CHOLESTEROL, TRIGLYCERIDE, HDL-C, LDL-C, TOTAL PROTEIN, ALBUMIN, BILIRUBIN TEST METHODSZoe Tagoc100% (3)
- Blood CellsDokument3 SeitenBlood Cellsda1haNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUST To KNOW in HematologyDokument40 SeitenMUST To KNOW in HematologyPatricia Yutuc90% (10)
- Must To Know in Clinical ChemistryDokument56 SeitenMust To Know in Clinical ChemistryJosephine Armanne Aluyen100% (1)
- Hema Notes (Lec)Dokument50 SeitenHema Notes (Lec)Anonymous 0zrCNQNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Chemistry (Lecture) - PrelimsDokument12 SeitenClinical Chemistry (Lecture) - Prelimsisprikitik3100% (1)
- Recall Questions Local Board ExamDokument11 SeitenRecall Questions Local Board ExamLancelot BritaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Specimen Collection and Hematopoiesis ProceduresDokument11 SeitenBlood Specimen Collection and Hematopoiesis ProcedurestkanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteria Biochemical TestsDokument2 SeitenBacteria Biochemical Testsjohnkuys100% (6)
- Clin Path Lab 6 UrinalysisDokument5 SeitenClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysisapi-3743217100% (6)
- Clinical Microscopy ExamDokument3 SeitenClinical Microscopy ExamKarla GiorlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMLS HistopathologyDokument20 SeitenPMLS HistopathologyTrixie Cyrah100% (1)
- MUST To KNOW in HematologyDokument45 SeitenMUST To KNOW in HematologyDen100% (4)
- Blood BankingDokument5 SeitenBlood BankingTel LyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Clinical ChemistryDokument69 SeitenLearning Clinical Chemistryquimico clinico 2798% (46)
- MUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingDokument18 SeitenMUST To KNOW in Immunohematology Blood BankingDanielJeremy DelaCruz Paragas79% (14)
- SerologyDokument84 SeitenSerologyngsusannasuisum100% (2)
- Clinical Chemistry Notes With BlanksDokument34 SeitenClinical Chemistry Notes With Blanksepson printerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Blood SmearDokument59 Seiten1 Blood SmearGabi Tim100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Red Blood CellsDokument37 SeitenChapter 14 Red Blood CellsCatherine LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology EssentialsDokument4 SeitenHematology EssentialsAlfred ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Anemias to Know for BoardsDokument24 SeitenTop 10 Anemias to Know for BoardsSim M ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anion Gap CalculationDokument13 SeitenAnion Gap CalculationDams ZainalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Stacks - Chemistry Table Review PDFDokument14 SeitenStudy Stacks - Chemistry Table Review PDF장주연100% (1)
- Microbio Lab 8Dokument4 SeitenMicrobio Lab 8api-3743217100% (5)
- MUST To KNOW in HematologyDokument38 SeitenMUST To KNOW in HematologyGlanela ManalotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer - Immmunohematology - Part 2Dokument29 SeitenReviewer - Immmunohematology - Part 2Joshua TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLINICAL MICROSCOPY (Urinalysis)Dokument131 SeitenCLINICAL MICROSCOPY (Urinalysis)Roderick95% (19)
- Para Lab 4Dokument3 SeitenPara Lab 4api-3743217Noch keine Bewertungen
- MUST KNOW CLINICAL MICROSCOPY URINALYSISDokument43 SeitenMUST KNOW CLINICAL MICROSCOPY URINALYSISMerhella Amor Suerte MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute and Chronic LeukemiasDokument3 SeitenAcute and Chronic Leukemiaskaku100% (2)
- Clinical Chemistry 1 Notes NPNDokument4 SeitenClinical Chemistry 1 Notes NPNDavid HosamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandSenior Medical Laboratory Technician: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4Von EverandAgglutination, Complement, Neutralization, and Inhibition: Methods in Immunology and Immunochemistry, Vol. 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hematopathology: Morphology, Immunophenotype, Cytogenetics, and Molecular ApproachesVon EverandHematopathology: Morphology, Immunophenotype, Cytogenetics, and Molecular ApproachesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationVon EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Haematology Case Studies with Blood Cell Morphology and PathophysiologyVon EverandHaematology Case Studies with Blood Cell Morphology and PathophysiologyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- La Cabs: Presented By:-Akshita SrivastavaDokument11 SeitenLa Cabs: Presented By:-Akshita SrivastavaPubg GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banquet SopDokument58 SeitenBanquet SopmackybhoyamoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cámara PTZ 4K KYPZ400Dokument4 SeitenCámara PTZ 4K KYPZ400Vanessa Ayala LoaizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warcraft Rules ConversionDokument182 SeitenWarcraft Rules ConversionsaxonD777100% (3)
- Quiz 3 - RizalDokument4 SeitenQuiz 3 - RizalCoco SpencerNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Selected Candidates Against Advertisement No 105 2022Dokument4 SeitenList of Selected Candidates Against Advertisement No 105 2022Awadhesh MalviyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Week MMADokument6 Seiten10 Week MMAFilip VelickovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faq On Ivr 3d SecureDokument2 SeitenFaq On Ivr 3d SecureRio PopoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan HotelDokument36 SeitenBusiness Plan Hoteldammika_077100% (7)
- Bonfire BlanketDokument4 SeitenBonfire BlanketRoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Last ExceptionDokument7 SeitenLast ExceptionAnindhita Mega PNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTC - Autopilot - Method - MAKE - 700$-800$ - PER - WEEK - 2Dokument4 SeitenBTC - Autopilot - Method - MAKE - 700$-800$ - PER - WEEK - 2Aamir RehanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seoul Itinerary XXXDokument4 SeitenSeoul Itinerary XXXJoy JianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vargr Alpha: Leader of the Lycan PackDokument2 SeitenVargr Alpha: Leader of the Lycan PackFarsang PéterNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDB Case Study Adidas ReebokDokument10 SeitenSDB Case Study Adidas ReebokIlori RachaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spanish Nationalism in The Guitar Music of The Early Twentieth CenturyDokument33 SeitenSpanish Nationalism in The Guitar Music of The Early Twentieth CenturyVinny MuscarellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Bar Supplies and Their UsesDokument24 SeitenCommon Bar Supplies and Their UsesNeslie ChoosyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Plays of 1982-1983Dokument584 SeitenBest Plays of 1982-1983chun wu100% (2)
- Design of Steel StructuresDokument4 SeitenDesign of Steel StructuresmysteryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kite FestivalDokument2 SeitenKite FestivalSameer KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Digikam Handbook PDFDokument320 SeitenThe Digikam Handbook PDFFrancisco VieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQ Errata FAQ v1Dokument3 SeitenAQ Errata FAQ v1JorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Camera - Operations - How To Maintain A Camera and Roles of A Camera OperatorDokument22 Seiten1 - Camera - Operations - How To Maintain A Camera and Roles of A Camera Operator18bumby JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Draft: ThesisDokument141 SeitenFinal Draft: ThesisPaolo Mendioro100% (1)
- Ushiro Guide Map: City of KushiroDokument2 SeitenUshiro Guide Map: City of KushiroleithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hungarian CuisineDokument27 SeitenHungarian CuisinemaryadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Bahasa Inggris SDDokument9 SeitenModul Bahasa Inggris SDitsmeupkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Media and Arts in The UKDokument10 SeitenMass Media and Arts in The UKJose RojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walt DisneyDokument2 SeitenWalt DisneyQissy QistinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Odyssey EssayDokument5 SeitenThe Odyssey Essayapi-320308976Noch keine Bewertungen