Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Catalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)
Hochgeladen von
Justin Victor AngOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Catalyst Note: (PT, Ni, PD)
Hochgeladen von
Justin Victor AngCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
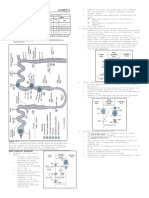
SUBSTRATE REAGENT REACTION MECHANISM MAJOR PRODUCT BYPRODUCT NOTE
catalyst
ALKANES
CH4 Cl2 or Br2 Radical Halogenation SR CH3Cl HCl
ALKENES
CH2=CH2 H2 Catalytic Hydrogenation Cis AE CH3-CH3
(Pt, Ni, Pd) (Reduction)
CH2=CH2 HX Hydrohalogenation Trans or anti AE CH3CH2X X on more substituted
Organic monohalide C; H on less
substituted C
CH2=CH2 X2 Halogenation Trans or anti AE CH2XCH2X
Vicinal dihalide
CH2=CH2 HOH Hydration Trans or anti AE CH3CH2OH
H2SO4 Alcohols
CH2=CH2 Neutral or basic Hydroxylation REDOX (Oxidation) Diols
KMnO4 (aq.)
CH2=CH2 Acidic KMnO4 Oxidative Multiple Bond REDOX (Oxidation) If terminal = CO2 + H2O
Cleavage If internal = RCOOH
CH2=CH2 Peroxyacid Epoxidation REDOX (Oxidation) Epoxide RCOOH
CH2=CH2 X2 , H 2 O Halohydration Trans AE Halohydrins HX
HO-C-C-X
ALKYNES
HCCH H2 Catalytic Hydrogenation Cis AE CH2=CH2
(Lindlar’s Catalyst) (Reduction)
HCCH HOH Hydration Trans or anti AE Enol Markovnikov’s rule
H2SO4, HgSO4 H2=CHOH
Ketone Keto-enol
R2CO Tautomerism
HCCH HX Hydrohalogenation Trans or anti AE CH2=CHX
HCCH X2 Halogenation Trans or anti AE CH2X=CH2X
HCCH Neutral or basic Hydroxylation REDOX (Oxidation) Diols
KMnO4 (aq.)
HCCH Acidic KMnO4 (aq.) Oxidative Multiple Bond REDOX (Oxidation) If terminal = CO2 + H2O
Cleavage If internal = RCOOH
HCCH NaNH2 Acetylide Formation Acid-base reaction (or SN) Acetylide NH3
AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
Benzene X2 Halogenation SE Halobenzene HX
FeX3 or AlX3
Note activators and
Benzene Conc. HNO3 and Nitration SE Nitrobenzene HOH deactivators
Conc. H2SO4
Benzene Fuming H2SO4 Sulfonation SE Benzenesulfonic Acid HOH
(conc. H2SO4 + SO3)
Benzene RCOX (Acid halide) Friedel-Crafts Acylation SE Aromatic ketone HX
AlX3 Cannot undergo
friedel-craft if the ring
contains a deactivator
Benzene RX (Alkyl halide) Friedel-Crafts Alkylation SE Arenes HX
AlX3
Benzene Zn(Hg), conc. HCl Clemmenson Reduction SE Acyl to Alkyl
heat
Ethyl Benzene KMnO4, H2O REDOX (Oxidation) SE If terminal = CO2 + H2O
If internal = RCOOH
(Benzoic Acid)
ALKYL HALIDES
R-X Mgo Synthesis of Grignard AN R-Mg-X Condensation
Reagent Grignard reagent Reaction (ANE)
R-Mg-X H2 O Hydrolysis E R-H Mg(OH)X
Basic magnesium
halide
R-X Strong or weak nucleophile; dependent on SN1 Racemization 3o>2o>1o
substrate; polar protic solvent (enantiomeric
products)
R-X Strong nucleophile; dependent on both substrate SN2 Inversion prod. 1o>2o>3o
and nucleophile; polar aprotic or nonpolar solvent
R-C-X Nu- elimination E1 R=C X-
heat
R-C-X Nu- (basic) elimination E2 R=C X- Major product in more
heat substituted C atom
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
R-OH H-X Hydrohalogenation SN1 R-X H2 O Most reactive with 3o
Hydrogen halide alcohols
ether
R-OH p-TosCl SN1 or SN2 ROTos Pyridine HCl
Toluenesulfonyl
chloride
pyridine
CH3CH2-OH H3O+, THF dehydration E1 CH2=CH2 Less substituted Follows Zaitsev’s rule
More substituted alkene product
alkene product
R-OH KMnO4/CrO3/ REDOX oxidation Aldehydes →
(1o) Na2Cr2O7 Carboxylic acids
(2o) Ketones
R-OH Dess-martin REDOX oxidation RCHO
(1o) periodinane
CH2Cl2
Ar-OH Na2Cr2O7 REDOX Oxidation Benzoquinone
phenol H2 O
Quinone SnCl2 REDOX Reduction Hydroquinone
H2
ETHERS
ROR’ HBr or HI Acidic Cleavage SN2: If 1O or 2O R’Br or R’Cl + ROH Br or I will bond with
SN1: If 3O the less sterically
hindered R between 1o
and 2o
If there is a tertiary R,
Br and I will
automatically bond
with it
EPOXIDES (AKA OXIRANES)
ROH NaO metal or NaH Williamson Ether RONa+ H2 In short:
Synthesis (Alkoxide Ion) ROH+NaH→H2+RON
a
RONa R-X SN2: If 1O or 2O ROR’ NaX RONa+RX→NaX+R
SN1: If 3O OR
EPOXIDE HX, Ether Ring Opening SN2 like: If 1O or 2O Halohydrin X or the halogen will
SN1 like: If 3O is present bond with the 1O
SN2 (accdg to Torres) (between 1O and 2O)
X will bond with 3O if it
is present
EPOXIDE H+, HOH Ring Opening SN2 1,2 diol (glycol)
ALDEHYDES
RCHO KMnO4/CrO3/ REDOX Oxidation RCOOH
Na2Cr2O7
RCHO H2 O Hydration AN Hydrate
(basic OH-) or (acidic (gem diol)
H+)
RCHO HCN Cyanohydrin formation AN nitriles
RCHO NaBH4;ethanol REDOX reduction Primary alcohols
RCHO R-Mg-X Addition of grignard AN Secondary alcohols
reagent
RCHO RNH2 Imine formation ANE RCH-Imine
RCHO R2NH Enamine formation ANE Enamine
RCHO H2NNH2 Wolff-Kishner AN RCH3 N2 + H 2 O
KOH
RCHO ROH Acetal formation ANE Hemiacetal → acetal H2 O
Acid catalyst
KETONES
R2CO H2 O Hydration AN Hydrate
(basic OH-) or (acidic (gem diol)
H+)
R2CO HCN Cyanohydrin formation AN Nitriles
R2CO NaBH4;ethanol REDOX reduction Secondary alcohols
R2CO R-Mg-X Addition of grignard AN Tertiary alcohols
reagent
R2CO RNH2 Imine formation ANE R2C-Imine H2 O
R2CO R2NH2 Enamine formation ANE Enamine H2 O
R2CO H2NNH2 Wolff-Kishner AN R2CH2 N2 + H 2 O
KOH
R2CO ROH Ketal formation ANE Hemiketal → ketal H2 O
Acid catalyst
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
RCOOH SOCl2 SNAcyl RCOCl
RCOOH PBr3, SNAcyl RCOBr
Ether
RCOOH heating Acetic anhydride H2 O Only acetic anhydride
(2 moles acetic is prepared this way
acid)
RCOOH ROH Fischer Esterification SNAcyl Ester H2 O
Acid catalyst (RCOOR’)
RCOOH NH3(alc.) ammonolysis SNAcyl Amide H2 O
DCC (RCONH2)
RCOOH RNH2(alc.) aminolysis SNAcyl Amide H2 O
DCC (RCONHR’)
RCOOH 1. LiAlH4, ether REDOX Reduction Primary alcohol
2. H3O+ (RCH2OH)
ACID HALIDES (CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE)
RCOX H2O Hydrolysis SNAcyl RCOOH HX
RCOX Carboxylate anion SNAcyl Acid Anhydride
(symmetrical or
unsymmetrical)
RCOX ROH Alcoholysis SNAcyl Ester HX
(RCOOR’)
RCOX R’-NH2 (alc) Aminolysis SNAcyl Amides HX Trisubstituted amines
(RCONHR’) can’t be used
RCOX NH3 (alc) Ammonolysis SNAcyl RCONH2 HX
RCOX 1. LiAlH4, ether REDOX (reduction) SNAcyl Primary alcohol HX
2. H3O+ (RCH2OH)
RCOX 2 R-Mg-X Grignard SNAcyl Tertiary alcohols
(Grignard reagent)
RCOX R2CuLi Diorganocopper SNAcyl Ketone R’Cu
Lithium (RCOR’)
diorganocopper
(Gilman) reagent
ACID ANHYDRIDES (CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE)
(RC(O))2O H2O Hydrolysis SNAcyl RCOOH RCOOH
(RC(O))2O ROH Alcoholysis SNAcyl Ester RCOOH
(RCOOR’)
(RC(O))2O R’-NH2 (alc) Aminolysis SNAcyl Amide RCOOH
(RCONHR’)
(RC(O))2O 1. LiAlH4, ether REDOX reduction 2 Primary alcohol
2. H3O+ 2 (RCH2OH)
ESTERS (CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE)
RCOOR’ H2O, NaOH Hydrolysis SNAcyl RCOOH R’OH
H3 O + saponification
RCOOR’ NH3 Aminolysis SNAcyl RCO-NH2 R’OH
ether
RCOOR’ 1. ROH Trans esterification SNAcyl Ester R’OH Double bond O will
2. H3O+ or base (RCOOR’) Primary alcohol become ester
Ester must not have
the same
RCOOR’ 1. LiAlH4, ether REDOX reduction RCOH R’OH
2. H3O+ Primary alcohol Primary alcohol
RCOOR’ R-Mg-X Grignard SNAcyl Tertiary alcohol
(Grignard reagent)
AMIDES (CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVE)
RCONH2 H2O, NaOH Hydrolysis SNAcyl RCOOH NH3
H3 O +
RCONH2 1. LiAlH4, ether REDOX reduction RCH2NH2 H2O
2. H3O+
NITRILES
RC≡N H2 O Hydration AN amide
RCONH2
RC≡N H2O, NaOH Hydrolysis RCOOH NH3
H3 O +
RC≡N LiAlH4, ether REDOX reduction RNH2
Primary amine
RC≡N R-Mg-X (Grignard R2CO NH3
reagent), H2O
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reagent ListDokument9 SeitenReagent ListArka MukhopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDokument78 SeitenFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperDokument23 SeitenISC 2014 Chemistry Theory Paper 1 Solved PaperMd Saif UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 13-Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsDokument5 SeitenUnit 13-Nitrogen Containing Organic CompoundsDeva RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - General Organic ChemistryDokument79 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - General Organic ChemistryTetakali SandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Gaseous State: Chemistry Lecture NotesDokument32 SeitenTopic: Gaseous State: Chemistry Lecture NotesDibya Ranjan BissoyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coordination Compounds 19-06-2020Dokument6 SeitenCoordination Compounds 19-06-2020Vanshaj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Reactive IntermediatesDokument115 Seiten04 Reactive IntermediatesMuhammad ArsalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirDokument10 SeitenChap 05 - Ionic Equilibrium MindNotes by Arnav SirKhushi RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityDokument19 Seiten4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityNimeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Chemistry Question Bank 2023Dokument496 SeitenCBSE Chemistry Question Bank 2023NafeesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo ChemistryDokument13 SeitenThermo ChemistryTushif RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsDokument22 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsLiza DahiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Increasing Decreasing Order - bRHAMASTRA PDFDokument10 SeitenIncreasing Decreasing Order - bRHAMASTRA PDFMohd RameezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL Questions On Synthetic Routes: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingDokument1 SeiteHL Questions On Synthetic Routes: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, InthinkingPranavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - (P-Block) Halogen and Noble Gases - JH Sir PDFDokument33 SeitenAssignment - (P-Block) Halogen and Noble Gases - JH Sir PDFKohli Kiran100% (1)
- 4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDokument36 Seiten4.1.1 Protic Vs Aprotic SolventDawit BirhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee Chemistry DPP by :pjoyDokument3 SeitenIit Jee Chemistry DPP by :pjoyPrakash Joy50% (4)
- VSEPR ShortcutDokument3 SeitenVSEPR ShortcutSubhojyotiDasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument34 SeitenIonic EquilibriumTanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFDokument16 Seiten5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFArinjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name Reactions-II PDFDokument32 SeitenName Reactions-II PDFEstanislao Amadeo Avogadro100% (1)
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Oxidation Reduction Nucleophilic AdditionDokument51 SeitenReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Oxidation Reduction Nucleophilic AdditionmacybnzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI (Pace + Inspire) Chemical Equilibrium Sheet (01.12.2016) Agrawal SirDokument39 SeitenClass XI (Pace + Inspire) Chemical Equilibrium Sheet (01.12.2016) Agrawal Sirdheeraj ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP StereochemistryDokument63 SeitenSP StereochemistryMadhumitha KatreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDokument32 SeitenChemistry Chapter 11 Alcohol, Phenol and EtherVidyakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11Dokument58 SeitenVollhardt 6e Lecture PowerPoints - Chapter 11superfr3shmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Radicals &carbocationsDokument13 SeitenFree Radicals &carbocationsOmkar Kumar JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 14. HydrogenDokument14 SeitenCH 14. HydrogenDipin Preet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Analysis (Theory) - EngDokument28 SeitenSalt Analysis (Theory) - Engjoxis70026100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions NotesDokument141 SeitenChemical Reactions Notesapi-182809945Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Organic Chemistry For IITDokument21 SeitenGeneral Organic Chemistry For IITParas Thakur83% (6)
- Iupac & GocDokument109 SeitenIupac & GocDash PegionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q Data Response - 8Dokument2 SeitenQ Data Response - 8Mayank ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic EquilibriumDokument46 SeitenIonic Equilibriumabhinavsaurabh75% (4)
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDokument23 SeitenSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isomerism - Handwritten NotesDokument7 SeitenIsomerism - Handwritten Notesgovind_galamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amine IIT JEE Organic ChemistryDokument37 SeitenAmine IIT JEE Organic ChemistryThe Rock75% (4)
- Redox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Dokument20 SeitenRedox & Equivalent Concepts (PQRS & J)Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDokument37 SeitenAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsssheeladevi84100% (1)
- PDFDokument155 SeitenPDFHifza shairwani100% (1)
- Solid State Chemistry IPEDokument15 SeitenSolid State Chemistry IPEAdiChemAdi100% (4)
- Equilibrium Multiple ChoiceDokument9 SeitenEquilibrium Multiple ChoicefendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The S-Block ElementsDokument34 SeitenThe S-Block ElementsPrakhar TandonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristicDokument8 SeitenOrganic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristictasneemNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCR Chemistry Exam Question BookletDokument54 SeitenOCR Chemistry Exam Question Bookletkrnc_11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics: SR - 12 Class Chemistry Vol-2Dokument78 SeitenChemical Kinetics: SR - 12 Class Chemistry Vol-2auguste noeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protecting GroupsDokument45 SeitenProtecting GroupsSait MalkonduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classnote 548fee8d37792Dokument46 SeitenClassnote 548fee8d37792vinay guttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Join @iitwale On Telegram: Physical Chemistr y Inorganic Chemistr y Organic Chemistr yDokument51 SeitenJoin @iitwale On Telegram: Physical Chemistr y Inorganic Chemistr y Organic Chemistr yK GhatageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument16 SeitenAtomic StructureKaran100% (3)
- CBSE 2018 12th Chemistry Sample Question PaperDokument8 SeitenCBSE 2018 12th Chemistry Sample Question PapermisostudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- H.D.A. 2021Dokument54 SeitenH.D.A. 2021Every Time Chemistry [ ETC]Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis, Characterization of New Schiff Base and Some Metal Complexes Derived From Glyoxylic Acid and O-PhenylenediamineDokument12 SeitenSynthesis, Characterization of New Schiff Base and Some Metal Complexes Derived From Glyoxylic Acid and O-PhenylenediamineAndzhiita SaampeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisVon EverandThe Determination of Carboxylic Functional Groups: Monographs in Organic Functional Group AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIVon EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Electronic Absorption Spectra and Geometry of Organic Molecules: An Application of Molecular Orbital TheoryVon EverandElectronic Absorption Spectra and Geometry of Organic Molecules: An Application of Molecular Orbital TheoryBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Structure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsVon EverandStructure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Informative Speech On Those ChoicesDokument2 SeitenInformative Speech On Those ChoicesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diuretic Agents: Drug Group Urine Body Nacl Nahco K CL PHDokument4 SeitenDiuretic Agents: Drug Group Urine Body Nacl Nahco K CL PHJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupational Toxicology: Threshold Limit Values (TLVS) Environmental ToxicologyDokument7 SeitenOccupational Toxicology: Threshold Limit Values (TLVS) Environmental ToxicologyJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlcoholsDokument2 SeitenAlcoholsJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org Chem E8 Classification Tests For Organic HalidesDokument4 SeitenOrg Chem E8 Classification Tests For Organic HalidesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cns and AlcoholsDokument6 SeitenCns and AlcoholsJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 SolubilityDokument5 Seiten7 SolubilityJoeco Abay-abayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility Classification Using Water 5Dokument1 SeiteSolubility Classification Using Water 5Justin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Hydrolysates - Paper ChromatographyDokument5 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Hydrolysates - Paper ChromatographyJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminDokument6 SeitenQualitative Color Reactions of AlbuminJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility Classification Using Water 5Dokument1 SeiteSolubility Classification Using Water 5Justin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesDokument7 SeitenExperiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recrystallization: Justin G. Ang and Nadine T. CaragDokument3 SeitenRecrystallization: Justin G. Ang and Nadine T. CaragJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinalysis ReferencesDokument2 SeitenUrinalysis ReferencesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Bianca Andrea C. Acuña, Pamela Tristen G. Agbayani, Gian Searle S. AlkuinoDokument1 SeiteTitle: Bianca Andrea C. Acuña, Pamela Tristen G. Agbayani, Gian Searle S. AlkuinoJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observations:: Lab Report For Experiment #2: Purification of Acetanilide by RecrystallizationDokument2 SeitenObservations:: Lab Report For Experiment #2: Purification of Acetanilide by RecrystallizationJV GamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DsadaDokument2 SeitenDsadaJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Organic HalidesDokument3 SeitenClassification Tests For Organic HalidesRhone Roque100% (6)
- Separation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyDokument4 SeitenSeparation and Identification of Amino Acids by Paper ChromatographyJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 SolubilityDokument5 Seiten7 SolubilityJoeco Abay-abayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesDokument7 SeitenExperiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Bianca Andrea C. Acuña, Pamela Tristen G. Agbayani, Gian Searle S. AlkuinoDokument1 SeiteTitle: Bianca Andrea C. Acuña, Pamela Tristen G. Agbayani, Gian Searle S. AlkuinoJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesDokument7 SeitenExperiment 2: Resultant and Equilibrant ForcesJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9 Chem Formal ReportDokument7 SeitenExperiment 9 Chem Formal ReportJustin Victor AngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zytel 70G50HSLA BK039BDokument17 SeitenZytel 70G50HSLA BK039BCarlos AméricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility of Organic CompoundsDokument3 SeitenSolubility of Organic Compoundspaulocarpio91% (11)
- Dispense BarDokument8 SeitenDispense BarRo NyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Citric Acid: Frank H. Verhoff, Miles Laboratories, Elkhart, Indiana 46515, United StatesDokument6 SeitenCitric Acid: Frank H. Verhoff, Miles Laboratories, Elkhart, Indiana 46515, United StatesHannah MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study On The Indian LiquorDokument7 SeitenA Case Study On The Indian LiquorManish Singh100% (1)
- Differences Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsDokument35 SeitenDifferences Between Organic and Inorganic CompoundsKit GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Lab Manual For RecordDokument19 SeitenSecond Lab Manual For RecordSANDEEP SMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Script of An Initial Brief Alcohol Counseling SessionDokument6 SeitenSample Script of An Initial Brief Alcohol Counseling SessionEmilly CabaneroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Dokument16 SeitenChemistry SPM State Trial Papers-Form5chap2Law Jin YaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safra Function Rooms - PunggolDokument5 SeitenSafra Function Rooms - PunggolPcEngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propofol SynthesisDokument8 SeitenPropofol SynthesisGiorgos Doukas Karanasios0% (1)
- Women and Alcohol: Why Do Women Face Higher Risk?Dokument2 SeitenWomen and Alcohol: Why Do Women Face Higher Risk?Vita RossantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Alcohols Dhwrodleben deDokument5 SeitenFatty Alcohols Dhwrodleben deharshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Exam Reviewer (Mas Malala Talaga Ang Real Exam)Dokument3 SeitenMidterm Exam Reviewer (Mas Malala Talaga Ang Real Exam)Ying YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA2004312C - Production of Allyl Chloride - Google PatentsDokument5 SeitenCA2004312C - Production of Allyl Chloride - Google PatentsTeeTeeXdNoch keine Bewertungen
- En Bigbook ContentsDokument6 SeitenEn Bigbook ContentsLauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tanduay Ice Marketing StudyDokument31 SeitenTanduay Ice Marketing StudyDecieryl MontanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sharm Dreams " All Inclusive " ConceptDokument2 SeitenSharm Dreams " All Inclusive " ConceptFilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 - Health (Dangers of Alcohol)Dokument30 SeitenQ4 - Health (Dangers of Alcohol)Arnulfo AbbangNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHAR3 LAB - Preparation 22-30Dokument2 SeitenPHAR3 LAB - Preparation 22-30Gerard LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OR Sales Monitor by QuantityTue Aug 16 12 - 09 - 22 CST 2022Dokument2 SeitenOR Sales Monitor by QuantityTue Aug 16 12 - 09 - 22 CST 2022armieNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch08 Alcohol, Ether and ThiolDokument65 Seitench08 Alcohol, Ether and ThiolAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar TerminologyDokument11 SeitenBar TerminologyMark Angelo SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlcoholsDokument33 SeitenAlcoholsSakib AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Sch 102 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDokument49 SeitenA-Sch 102 Introduction To Organic ChemistryLes Chikadoras100% (1)
- Sertraline Hydrocloride ProjectDokument10 SeitenSertraline Hydrocloride ProjectkarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlcoholsDokument8 SeitenAlcoholsljbnoibnoibnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deriving The Rate Equations For Product Inhibition Patterns in Bisubstrate Enzyme ReactionsDokument18 SeitenDeriving The Rate Equations For Product Inhibition Patterns in Bisubstrate Enzyme ReactionsvijayalakshmiramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1: Monitoring The Environment: Stage 2 Chemistry Must Know ListDokument40 SeitenTopic 1: Monitoring The Environment: Stage 2 Chemistry Must Know ListThalia MaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methanol Project PDFDokument50 SeitenMethanol Project PDFPaola Nair M ChNoch keine Bewertungen