Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Topic 6 - Imperfect Cause Defect
Hochgeladen von
Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt Spaiee0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten2 SeitenBio question
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBio question
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
65 Ansichten2 SeitenTopic 6 - Imperfect Cause Defect
Hochgeladen von
Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeBio question
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
IMPERFECT CAUSE DEFECT
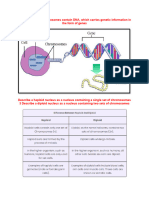
The cells within living organisms have the ability to grow and reproduce through the
production of new cells. In order to ensure that an exact copy of the DNA is assigned to
the new cells, a process called mitosis takes place. Mitosis is a highly dynamic process,
aimed at separating identical copies of genomic material into two daughter cells. When
a new cell is needed, the DNA is copied and allocated equally to new cells; then the cell
splits in half (Hayashi and Karlseder, 2013). When any one of these intricate steps fails,
the results can be adverse for the cell and the whole organism. A failure of the mitotic
process generates cells that carry abnormal chromosome numbers.
Changes in Chromosome Structure
Although relatively rare, damage can occur to chromosomes during mitotic movement.
Sometimes a break occurs in a chromosome and a portion of it is lost, causing a
deletion. If the broken fragment then reattaches upside down, this is called an inversion.
Rarely, such fragments attach to a different chromosome, and lead to a translocation. A
number of human disorders are caused by chromosomal deletions, and, generally, their
phenotypes are more severe than those caused by duplications (Brewer et al., 1998).
Such errors in a growing embryo are primarily lethal, and lead to either miscarriages or
still births. However, some do survive, born with serious birth defects. Chromosome
rearrangements can cause ill health in human population, thus affect the infertility and
mental retardation being the dominant effects (Shakoori et al., 2017).
Changes in Chromosome Number
Nondisjunction is the result of failure of chromosomes to separate during mitosis. This
leads to new cells with either extra or missing chromosomes; a condition called
aneuploidy. These changes can occur during the formation of reproductive cells (eggs
and sperm), in early fetal development, or in any cell after birth. Human embryos with
aneuploidy rarely survive development; with only 0.3% of human aneuploidy
pregnancies producing a live birth. For those children born with aneuploidy, severe
genetic conditions result.
Mitotic Errors and Cancer
Cancer is some form of uncontrolled cell growth. The usual checkpoints of the cell cycle
do not work correctly, and cells progress and repeat mitosis when not needed.
Researchers find many cancer cells with a variety of chromosome irregularities such as
deletions, inversions and translocations.
Case Study Questions:
1. Discuss the failure of mitosis on the chromosome abnormalities.
2. Brief explain 3 common chromosome disorders cause by changes in
chromosome structure.
3. Brief explain 3 common chromosome disorders cause by changes in
chromosome number.
4. Explain how mitosis can cause cancer.
5. Explain the cell division of mitosis for each phases.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chromosomal AbnormalitiesDokument6 SeitenChromosomal AbnormalitiesPrashant MundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 1 - Mitosis and MeiosisDokument22 SeitenGen Bio 1 - Mitosis and MeiosisQuiel Tangonan Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDokument8 SeitenMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomal AbberationsDokument33 SeitenChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE STUDY REPORT GUIDELINE - Doc Final PDFDokument4 SeitenCASE STUDY REPORT GUIDELINE - Doc Final PDFSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Banana Oil via Fischer EsterificationDokument7 SeitenSynthesis of Banana Oil via Fischer EsterificationSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedDokument7 SeitenMitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedJD DX100% (1)
- IAS - Bio - SB1 - Mark Schemes and Assessments PDFDokument74 SeitenIAS - Bio - SB1 - Mark Schemes and Assessments PDFisraa jaaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division PDFDokument11 SeitenCell Division PDFMrinal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3 Writing AnalysisDokument4 SeitenM3 Writing AnalysisGood ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division LessonDokument9 SeitenCell Division LessonGerry100% (1)
- Mitosis Onion Root Tip LabDokument6 SeitenMitosis Onion Root Tip LabNor Ashikin Ismail71% (7)
- Meiosis-Webquest Answer KeyDokument4 SeitenMeiosis-Webquest Answer KeyAshwin Raghuraman0% (1)
- AP Biology Lab ReviewDokument72 SeitenAP Biology Lab ReviewPaweenwat ThongprasopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis & Meiosis NotesDokument6 SeitenMitosis & Meiosis NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- DISORDERS AND DISEASES CELL CYCLE - EllaDokument9 SeitenDISORDERS AND DISEASES CELL CYCLE - EllaKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (1)
- Agro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Dokument260 SeitenAgro-Technology. Thompson, R. Paul. Cambridge, 2011Tiago OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotecnologia de Células AnimaisDokument396 SeitenBiotecnologia de Células AnimaisKayo Paiva100% (1)
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyVon EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Gen. Biology Module 5 (April 12-23)Dokument6 SeitenGen. Biology Module 5 (April 12-23)LouisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology Last Set of ActivitiesDokument2 SeitenGeneral Biology Last Set of ActivitiesAubrey GuilaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Two Faces of Cell Division: Mitosis MeiosisDokument5 SeitenThe Two Faces of Cell Division: Mitosis MeiosisJamie MakrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riview of Lit 2Dokument17 SeitenRiview of Lit 2api-3806162Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Group 7 ReportDokument19 SeitenScience 10 Group 7 ReporthannahkathryllvalenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group3 Errors in Cell CycleDokument26 SeitenGroup3 Errors in Cell CycleRhian CodilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Aberrations: Meiotic NondisjunctionDokument36 SeitenNumerical Aberrations: Meiotic NondisjunctionHemanth_Prasad_2860Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cytogenetics Basics: Chromosomes, Analysis & AbnormalitiesDokument11 SeitenCytogenetics Basics: Chromosomes, Analysis & Abnormalitiesjo_jo_mania100% (1)
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: A Review of Causes and Clinical ConsequencesDokument6 SeitenChromosomal Abnormalities: A Review of Causes and Clinical ConsequencesgeneticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Module 3Dokument5 SeitenBiology - Module 3ASHLEY MONICA PLATANoch keine Bewertungen
- MSU Marawi Cellular Aberration Final Exam AnswersDokument3 SeitenMSU Marawi Cellular Aberration Final Exam AnswersSajeebChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideDokument8 SeitenThis Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideZuzuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Story of Our Cells: Cancer, Growth, Mitosis, Importance in 40 CharactersDokument8 SeitenThe Story of Our Cells: Cancer, Growth, Mitosis, Importance in 40 CharactersDanKimberleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUTATIONDokument30 SeitenMUTATIONbam yeontanieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes and Genetic DisordersDokument4 SeitenChromosomes and Genetic DisordersSakshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1- mitosis and meiosis pre-worksheet key conceptsDokument5 SeitenUnit 1- mitosis and meiosis pre-worksheet key conceptsRoshae SinclairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Learning Journal (Week-6)Dokument3 SeitenBiology Learning Journal (Week-6)IvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes-and-genetic-mutationDokument2 SeitenChromosomes-and-genetic-mutationdeekkrizzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heredity g10Dokument15 SeitenHeredity g10Lucille SagayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karyotyping Virtual Lab PlusDokument3 SeitenKaryotyping Virtual Lab PlusVictoria YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction of CellsDokument1 SeiteReproduction of CellsruivaacobreadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL BIOLOGYDokument5 SeitenGENERAL BIOLOGYFern Nicole TagatacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mutation:: Down's Syndrome, Klinefelter's Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome. Cri-Du-Chat SyndromeDokument7 SeitenMutation:: Down's Syndrome, Klinefelter's Syndrome, Turner's Syndrome. Cri-Du-Chat SyndromeGj Salvador Tuballa IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Cell Bio MitosisDokument4 SeitenLab Report Cell Bio Mitosisain syukriahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting on Mitosis and MeiosisDokument4 SeitenReporting on Mitosis and Meiosisnicole besarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Most Common Cause of Abnormal ChromosomeDokument4 SeitenWhat Is The Most Common Cause of Abnormal ChromosomemaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes: MetacentricDokument12 SeitenChromosomes: MetacentricMuthu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heredity and Variation NotesDokument19 SeitenHeredity and Variation NotesAmelia DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short-And Long-Term Effects of Chromosome Mis-Segregation and AneuploidyDokument37 SeitenShort-And Long-Term Effects of Chromosome Mis-Segregation and AneuploidyMuh. Taqwin 1015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsDokument12 SeitenUnderstanding the Process of Cell Division and GeneticsAnonymous klhru5ENoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Genetic Mutation?: Gene Mutations Can Be Classified in Two Major WaysDokument3 SeitenWhat Is A Genetic Mutation?: Gene Mutations Can Be Classified in Two Major WaysStephanie BulusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis and Meosis Nuclear Division NotesDokument11 SeitenMitosis and Meosis Nuclear Division NotesEshan OmparkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meiosis: Week 4 DiscussionDokument9 SeitenMeiosis: Week 4 DiscussionJacob CarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 4Dokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 4karyo eseymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Division, Cancer Formation and TreatmentDokument4 SeitenCell Division, Cancer Formation and TreatmentArmie Rose FaldasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phases of The Cell CycleDokument9 SeitenPhases of The Cell CycleZia PhotostateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis DefinitionDokument19 SeitenMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders and DiseasesDokument5 SeitenDisorders and DiseasesMhariane MabborangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentDokument8 SeitenSubhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentHero PratikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle LectureDokument3 SeitenCell Cycle LectureR Jay LagdaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell DivisionDokument2 SeitenCell Divisionhm khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosome Abnormalities GuideDokument26 SeitenChromosome Abnormalities GuideJoseph RachealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomal Genetic Disease CitoDokument5 SeitenChromosomal Genetic Disease CitoNatsumiTakamoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDokument12 Seiten1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1Noch keine Bewertungen
- This Might HelpDokument2 SeitenThis Might HelpJoelrey QuilingingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomal Aberration Causes Genetic DisordersDokument4 SeitenChromosomal Aberration Causes Genetic DisordersSyed Shah HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ExamDokument17 SeitenBiology ExamSai Adrienne RealubitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle, Cell Death, and DiseaseDokument14 SeitenCell Cycle, Cell Death, and DiseaseRose Anne ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Examination-BiologyDokument15 SeitenFinal Examination-BiologyAlliah MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 8 Chromosome ActivityDokument7 SeitenSCIENCE 8 Chromosome ActivityAnthony IlustreNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.MS31 NationalconfDokument9 Seiten9.MS31 NationalconfSuriBabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 NotesDokument22 SeitenPart 1 Notesapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4: Determination of The Purity of A Sodium Sulphate Sample by Gravimetric AnalysisDokument2 SeitenExperiment 4: Determination of The Purity of A Sodium Sulphate Sample by Gravimetric AnalysisSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction & Analysis (TLC)Dokument5 SeitenIntroduction & Analysis (TLC)Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA108 ODL Week 9 PDFDokument2 SeitenSTA108 ODL Week 9 PDFSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp6 PDFDokument7 SeitenExp6 PDFCleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA108 ODL Week 8 PDFDokument2 SeitenSTA108 ODL Week 8 PDFSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp6 PDFDokument7 SeitenExp6 PDFCleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLCDokument7 SeitenTLCSnow DropNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Viruses - Summary Notes PDFDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 - Viruses - Summary Notes PDFSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Past Year Questions (Probability & Tree Diagram) : Odl Week 11: 4 - 7 JUNE 2020Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Past Year Questions (Probability & Tree Diagram) : Odl Week 11: 4 - 7 JUNE 2020Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conclusion Bio Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenConclusion Bio Lab ReportSyaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 213 Re Crystallization F 08Dokument2 SeitenChem 213 Re Crystallization F 08Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lab Report 2Dokument1 SeiteBio Lab Report 2Syaza Izzah Athirah Bt SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 C.NDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 C.NSyahmi SpaieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Seri Kembangan Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Science KSSM Form 1Dokument16 SeitenSMK Seri Kembangan Yearly Lesson Plan 2019 Science KSSM Form 1ryeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Ch. 9Dokument53 SeitenBiology Ch. 9Juliet HipolitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology F.SC P-2 Guess Papers by MNA GhummanDokument7 SeitenBiology F.SC P-2 Guess Papers by MNA Ghummanshahid MehboobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 110 Essex Without Recitation Spring 2015Dokument7 SeitenBiol 110 Essex Without Recitation Spring 2015api-281761748Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Lab ReportDokument2 SeitenBiology Lab ReportEmmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition Pierce Test BankDokument24 SeitenGenetics Essentials Concepts and Connections 3rd Edition Pierce Test BankZacharyPrinceyasp100% (34)
- Cells and Organelles Coloring PagesDokument5 SeitenCells and Organelles Coloring Pagescarsontk421Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology I Eoc Review BookDokument22 SeitenBiology I Eoc Review Bookapi-199871042Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slides - Statistical BioinformaticsDokument16 SeitenSlides - Statistical Bioinformaticsst iNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.1 To 11.2 YellowDokument7 Seiten11.1 To 11.2 YellowKay0% (1)
- Soalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4Dokument22 SeitenSoalan Ulangkaji Bab 5 Tingkatan 4Kah WeiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Quantitative Study of Nocodazole's Effect On HeLa Cells'Dokument6 SeitenA Quantitative Study of Nocodazole's Effect On HeLa Cells'Albert FengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheets in General Biology 1 Quarter I, Week 4: MELC: 1Dokument15 SeitenActivity Sheets in General Biology 1 Quarter I, Week 4: MELC: 1Lyka Mae BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SNC 2di W - DR - Biology FallDokument4 SeitenSNC 2di W - DR - Biology Fallapi-234678275Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDokument5 SeitenModule 4-The Cell's Life CycleGoogle BackupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Movie Links Molecular Biology of The CellDokument18 SeitenMovie Links Molecular Biology of The CellmotabsbviniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosome BandingDokument2 SeitenChromosome BandingviktorvishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Ass I QPDokument7 SeitenBio Ass I QPSwayam GosaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactivation of The Cell Cycle in Terminally Differentiated CellsDokument111 SeitenReactivation of The Cell Cycle in Terminally Differentiated CellsSouravChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology and Genetics - Seeley Chapter 3Dokument69 SeitenCell Biology and Genetics - Seeley Chapter 3Juli Damayanty HarahapNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure, Function and Organisation of The Human BodyDokument28 SeitenThe Structure, Function and Organisation of The Human BodyGemma WhitehouseNoch keine Bewertungen